
Content I.IP Protection in China 1.Domestic Legal System 2.International Protection II.Enforcement of IP Right (Litigatic China with special reference to measures) 1.Administrative Enforcement 2.Judicial Remedy Cases 同两大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Content I. IP Protection in China 1. Domestic Legal System 2. International Protection II. Enforcement of IP Right (Litigation in China with special reference to remedy measures) 1. Administrative Enforcement 2. Judicial Remedy + Cases

I.The System of IP Protection in China 1.Domestic Legal System (Patent Law as an example) a)Patent Law b)Trademark Law c)Copyright 目 Law and Related Rules Judicial Interpretations: Patent Law,Revised Version 2008 Patent Law Implementing Rules 2002 Judicial Interpretation:abt.division of IP cases in the court. 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
I. The System of IP Protection in China 1. Domestic Legal System (Patent Law as an example) a) Patent Law b) Trademark Law c) Copyright Law and Related Rules & Judicial Interpretations: ¾ Patent Law, Revised Version 2008 ¾ Patent Law Implementing Rules 2002 ¾ Judicial Interpretation: abt. division of IP cases in the court
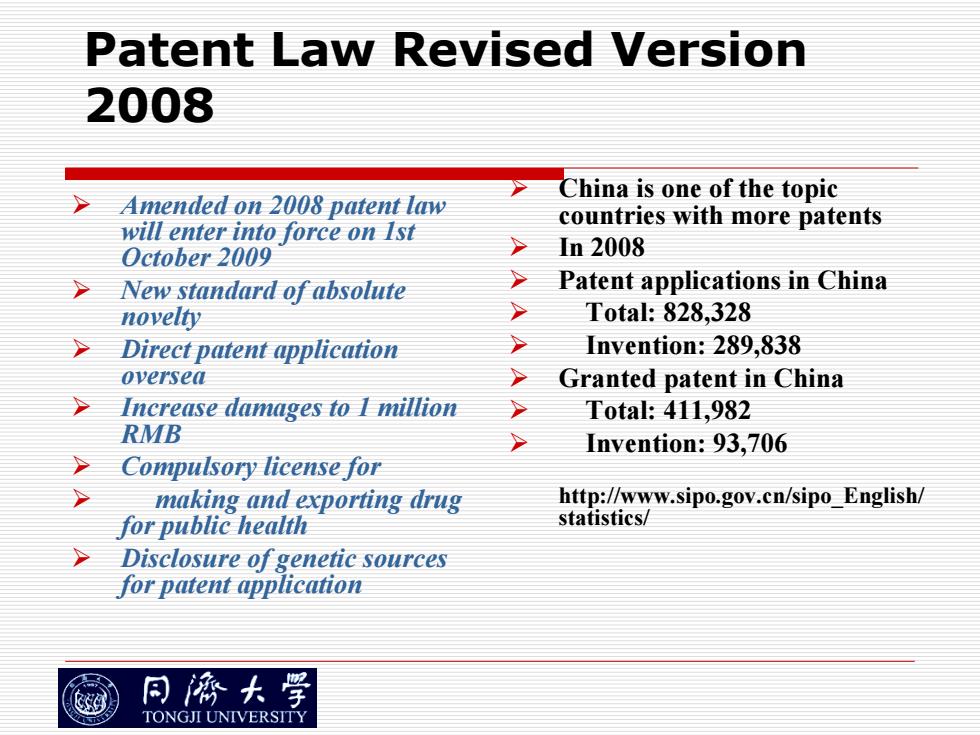
Patent Law Revised Version 2008 China is one of the topic Amended on 2008 patent law will enter into force on Ist countries with more patents October 2009 > In2008 New standard of absolute > Patent applications in China novelty > Tota:828,328 Direct patent application 7 Invention:289,838 oversea > Granted patent in China >Increase damages to I million > Total:411,982 RMB Invention:93,706 Compulsory license for making and exporting drug http://www.sipo.gov.cn/sipo_English/ for public health statistics/ Disclosure of genetic sources for patent application 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Patent Law Revised Version 2008 ¾ Amended on 2008 patent law will enter into force on 1st October 2009 ¾ New standard of absolute novelty ¾ Direct patent application oversea ¾ Increase damages to 1 million RMB ¾ Compulsory license for ¾ making and exporting drug for public health ¾ Disclosure of genetic sources for patent application ¾ China is one of the topic countries with more patents ¾ In 2008 ¾ Patent applications in China ¾ Total: 828,328 ¾ Invention: 289,838 ¾ Granted patent in China ¾ Total: 411,982 ¾ Invention: 93,706 http://www.sipo.gov.cn/sipo_English/ statistics/
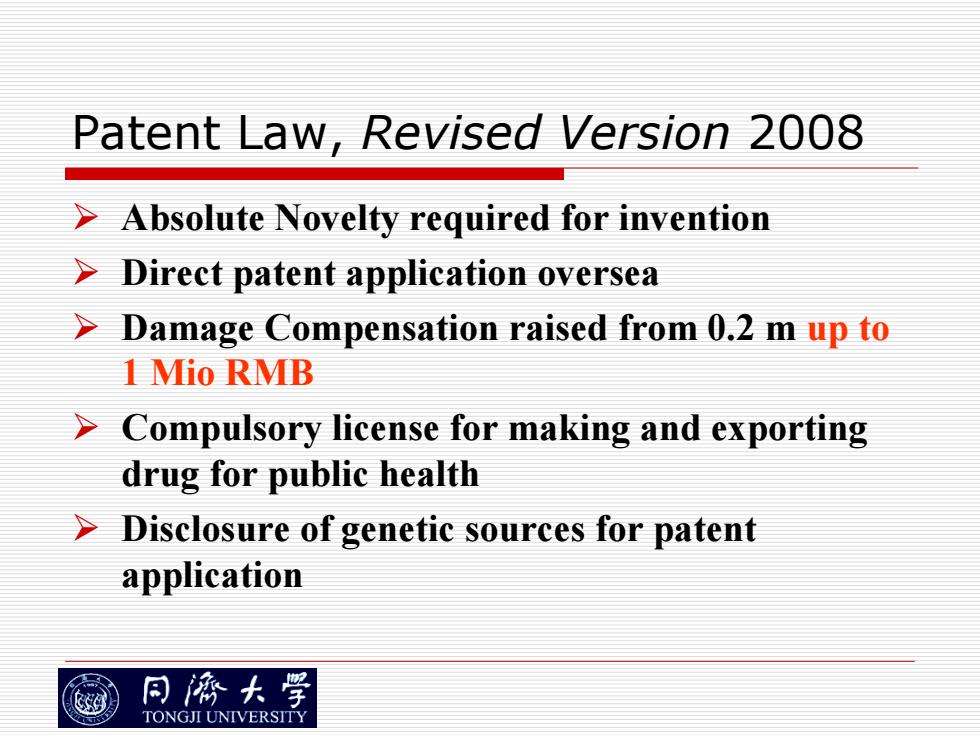
Patent Law,Revised Version 2008 Absolute Novelty required for invention Direct patent application oversea Damage Compensation raised from 0.2 m up to 1 Mio RMB > Compulsory license for making and exporting drug for public health > Disclosure of genetic sources for patent application 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Patent Law, Revised Version 2008 ¾ Absolute Novelty required for invention ¾ Direct patent application oversea ¾ Damage Compensation raised from 0.2 m up to 1 Mio RMB ¾ Compulsory license for making and exporting drug for public health ¾ Disclosure of genetic sources for patent application

Structure of Chinese Patent Law Basics of Chinese Patent Law Type of Patent Invention:product invention,process invention Utility Model Industrial Design 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Structure of Chinese Patent Law Basics of Chinese Patent Law Type of Patent ¾ Invention: product invention, process invention ¾ Utility Model ¾ Industrial Design

Structure of Chinese Patent Law (1)What can be granted? Patents are granted for any inventions which are new, involve an inventive step, are suspectible of industrial application. 同诱大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Structure of Chinese Patent Law (1) What can be granted ? Patents are granted for any inventions which ¾ are new, ¾ involve an inventive step, ¾ are suspectible of industrial application

Structure of Chinese Patent Law (2)Unpatentable are 1).General Prohibition:Art.5 Patent Law, Differs from country to country 2).List of Prohibition (in line with TRIPs) surgical,therapeutic and diagnostic methods >scientific discoveries,aesthetic creations, mathematical methods computer programs as such but:computer implemented inventions are patentable Invention created by using heritage resource 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Structure of Chinese Patent Law (2) Unpatentable are 1). General Prohibition: Art. 5 Patent Law, Differs from country to country 2). List of Prohibition (in line with TRIPs) ¾ surgical, therapeutic and diagnostic methods ¾ scientific discoveries, aesthetic creations, mathematical methods ¾ computer programs as such but: computer implemented inventions are patentable ¾ Invention created by using heritage resource

Structure of Chinese Patent Law Who can be the right holder (1)In general,nationals and foreigners (national treatment under Conventions and Treaties like TRIPs) Private Autonomy Service Invention (Art.6,Para.1) Joint Invention (Art.8) 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Structure of Chinese Patent Law Who can be the right holder (1) In general, nationals and foreigners (national treatment under Conventions and Treaties like TRIPs) ¾ Private Autonomy ¾ Service Invention (Art. 6, Para. 1) ¾ Joint Invention (Art. 8)

Structure of Chinese Patent Law (2)For foreigner:Paris Convention and TRIPs National Treatment Art.18:Article 18.[Practice of international treaty or by the principle of reciprocity for foreign applicant]Where any foreigner,foreign enterprise or other foreign organization having no habitual residence or business office in China files an application for a patent in China,the application shall be treated under this Law in accordance with any agreement concluded between the country to which the applicant belongs and China,or in accordance with any international treaty to which both countries are party,or on the basis of the principle of reciprocity. Link:Art.29 同濟大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Structure of Chinese Patent Law (2) For foreigner: Paris Convention and TRIPs – National Treatment Art. 18:Article 18. [Practice of international treaty or by the principle of reciprocity for foreign applicant] Where any foreigner, foreign enterprise or other foreign organization having no habitual residence or business office in China files an application for a patent in China, the application shall be treated under this Law in accordance with any agreement concluded between the country to which the applicant belongs and China, or in accordance with any international treaty to which both countries are party, or on the basis of the principle of reciprocity. Link: Art. 29

Conditions for Granting Patent ▣(1)Novelty New Definition in 2008 Patent Law adopted the definition of EPC (European Patent Convention): Absolute Novelty The invention or utility model is absolutely new compared with "the technology existing before the date of filing the invention"(home and abroad) 同源大学 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Conditions for Granting Patent (1 )Novelty New Definition in 2008 Patent Law adopted the definition of EPC (European Patent Convention): Absolute Novelty :The invention or utility model is absolutely new compared with “the technology existing before the date of filing the invention ” (home and abroad)