
Name:KEY Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above.Then SIGN the exam copy,indicating that you have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in taking this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000 WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000 WRITE your student identification number in the ap iate area of your Scantron 2000nPartand follow the instructionsOPE your I number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 35 multiple choice questions.There are a total of 10 pages to this part of the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers.You are responsible for the accuracy s of your Scantron.Do not put any ma rks(other than filling in the answer pubbles)on the left side(s)of the Scantron sheet. There should be plenty of tim owever,you will to take this exam o use your time efficiently Multiple Choice 63 Short answers 7 Total 70
Food Science & Technology 100A Professor S.R. Dungan Midterm Examination #2 November 19, 2003 Name:KEY Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above. Then SIGN the exam copy, indicating that you have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in taking this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000. WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 35 multiple choice questions. There are a total of 10 pages to this part of the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers. You are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of your Scantron. Do not put any marks (other than filling in the answer bubbles) on the left side(s) of the Scantron sheet. This exam is closed book, closed notes. There should be plenty of time to take this exam without being rushed. However, you will need to use your time efficiently. Multiple Choice 63 Short answers 7 Total 70

Midterm #2,Fall 2003 FST 100A 1.Which of the following is an amphiphile? eride fatty acid salts e. above are amphiphiles@ 2.Saponification involves stabilization of a free radical formati fatty acid groups answer a anc 3.Waxes are NOT esters of long chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols triterpenes very hvdr 4.Which of the following is true of nucleation? 合2eao t occu s spontaneously usua lroug d.It e.Iisa chemical reaction repons or rennr only at ten well above the melting ter 5. Polymorphism is used to describe the second step in lipid oxidation in butter texture due to changes in crystal form d.all of the above e.none of the above 6.Which of the following is true of fish oils? they contair they oxidize very easily@ d.they are Page 1
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 1 1. Which of the following is an amphiphile? a. phosphatidylcholine b. monoglyceride c. fatty acid salts d. diacylglycerol e. all of the above are amphiphiles @ 2. Saponification involves a. removing double bonds from fatty acid chains b. triglyceride hydrolysis catalyzed by a base @ c. stabilization of a free radical d. formation of trans fatty acid groups e. answer a and d 3. Waxes are NOT a. esters of long chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols b. lipid molecules c. triterpenes @ d. very water impermeable e. very hydrophobic 4. Which of the following is true of nucleation? a. It is driven by the favorable free energy change of fusion @ b. It occurs spontaneously, regardless of the size of the nucleus formed c. It usually occurs through a homogeneous mechanism, where nuclei form throughout the bulk of the liquid d. It occurs only at temperatures well above the melting temperature e. It is a chemical reaction responsible for creating antioxidants 5. Polymorphism is used to describe a. the second step in lipid oxidation b. soap formation c. changes in butter texture due to changes in crystal form @ d. all of the above e. none of the above 6. Which of the following is true of fish oils? a. they contain primarily trans fatty acids b. they contain primarily short chain fatty acids c. they oxidize very easily @ d. they are primarily saturated e. none of the above

ST10 Fall203 Midte The following 3 questions refer to the graph below: 100 80 osn-1 sn-2 ■Sn-3 20 all ■ C16:0C18:0C18:1C18:2 Fatty Acid Group 7.The triglycerides represented in this graph have primarily rated 二 sat short ch ain fa e. none of 8.The saturated fatty acid groups in this lipid a. are primarily located at the sn-2 positions b.are primaril located at the sn- and sn-3 positions e randomly positioned at all three trigly aoe not contal 8eop。 contalns only satura ratty acia group 9.Of the choices below,this graph most likely describes which of the following food lipids? ater d. Page 2
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 2 The following 3 questions refer to the graph below: 0 20 40 60 80 100 C16:0 C18:0 C18:1 C18:2 Fatty Acid Group sn-1 sn-2 sn-3 all 7. The triglycerides represented in this graph have primarily a. saturated fatty acid groups b. monounsaturated fatty acid groups @ c. polyunsaturated fatty acid groups d. short chain fatty acid groups e. none of the above 8. The saturated fatty acid groups in this lipid a. are primarily located at the sn-2 positions b. are primarily located at the sn-1 and sn-3 positions @ c. are randomly positioned at all three triglyceride positions d. This lipid does not contain any saturated fatty acid groups e. This lipid contains only saturated fatty acid groups 9. Of the choices below, this graph most likely describes which of the following food lipids? a. Milkfat b. Cocoa Butter c. Lard d. Olive oil @ e. Fish Oil
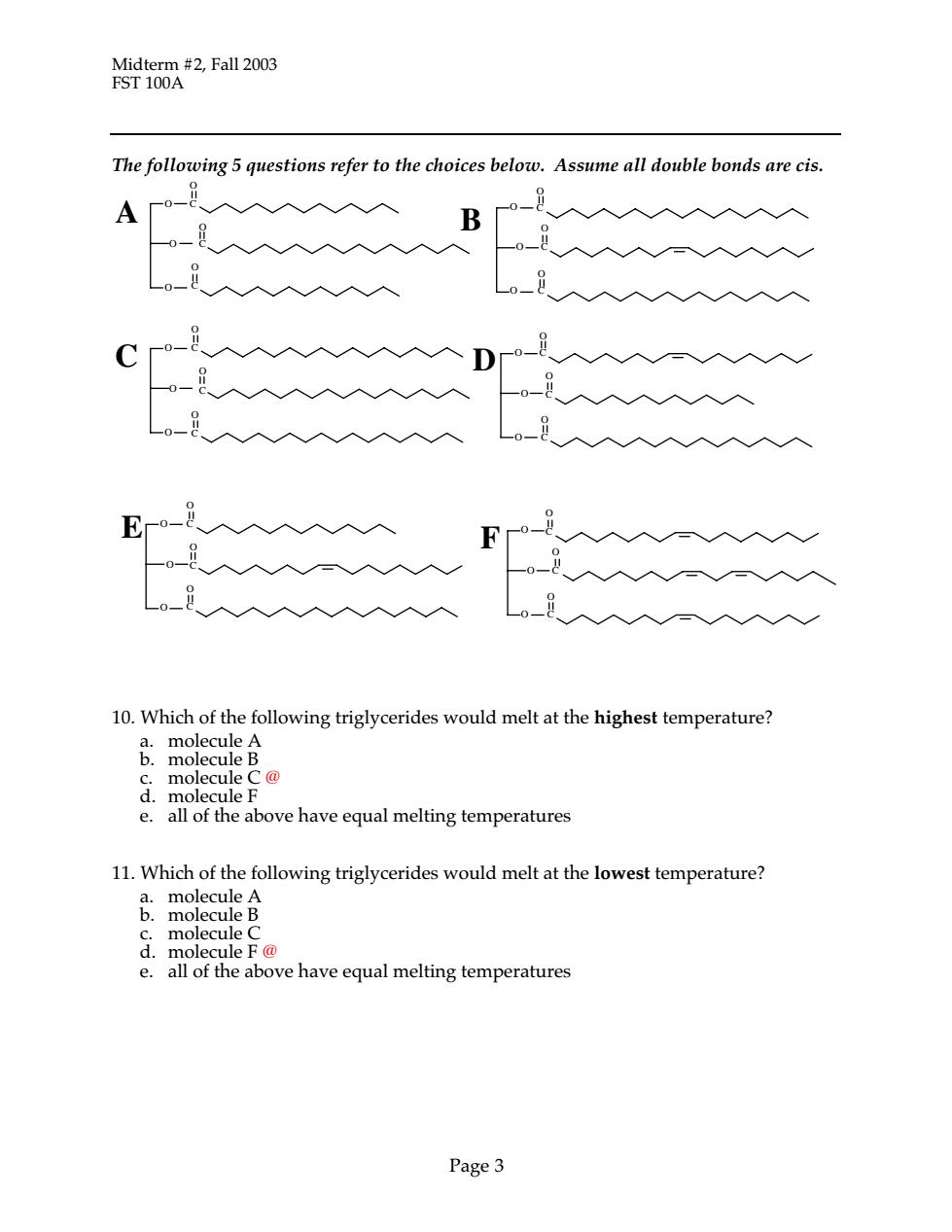
Midterm #2,Fall 2003 FST 100A The following 5 questions refer to the choices below.Assume all double bonds are cis. B 一入入入 Fo 10.Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the highest temperature? d.molecule F e.all of the above have equal melting temperatures 11.Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the lowest temperature? c.molecule C d.molecule F@ e.all of the above have equal melting temperatures Page3
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 3 The following 5 questions refer to the choices below. Assume all double bonds are cis. 10. Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the highest temperature? a. molecule A b. molecule B c. molecule C @ d. molecule F e. all of the above have equal melting temperatures 11. Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the lowest temperature? a. molecule A b. molecule B c. molecule C d. molecule F @ e. all of the above have equal melting temperatures C C O O O O C O C O C O C O D C O O O O C O C O E C O O O O C O O O O C O B C O C A O C O O O O C O C O O O O C F O C O

02,a208 Reminder:The questions in this page refer to molecules shown on p.3 12.Which of the following would have the narrowest melting range? a mixture or d F a mixture of molecules B and E d.a mixture of molecules A and B e.all of the above mixtures have the same melting range 13.Which of the following triglycerides would be most easily oxidized? c.molecule C d.molecule B e.None of these molecules can oxidize 14.During digestion,which of the following triglycerides would most likely produce an unsaturated monoglyceride? &moleue合 Fwould both likely produce an unsaturated 15.Which of the following is a difference between short and long chain fatty acids? .rurowhle onhain atty acids are reesterified &all of the boveern8ha盈 16.Hydrogenation reactions me6tcoap double bonds d decrea h e.Hydrogenation reactions do none of the above@ Page 4
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 4 Reminder: The questions in this page refer to molecules shown on p. 3 12. Which of the following would have the narrowest melting range? a. a mixture of molecules C and F b. a mixture of molecules A, D and F c. a mixture of molecules B and E @ d. a mixture of molecules A and B e. all of the above mixtures have the same melting range 13. Which of the following triglycerides would be most easily oxidized? a. molecule A b. molecule F @ c. molecule C d. molecule B e. None of these molecules can oxidize 14. During digestion, which of the following triglycerides would most likely produce an unsaturated monoglyceride? a. molecule A b. molecule B c. molecule D d. molecule F e. molecules B and F would both likely produce an unsaturated monoglyceride @ 15. Which of the following is a difference between short and long chain fatty acids? a. short chain fatty acids have stronger flavor b. short chain fatty acids are absorbed directly during digestion, while long chain fatty acids are reesterified c. short chain fatty acids melt at a higher temperature than long-chain fatty acids d. all of the above are differences between short and long chain fatty acids e. only answers a and b are differences @ 16. Hydrogenation reactions a. decrease the melting point of food lipids b. increase the number of double bonds in food lipids c. decrease the amount of trans fatty acids in food lipids d. remove hydrogen from fatty acid double bonds e. Hydrogenation reactions do none of the above @

Midterm #2,Fall 2003 FST 100A 17.Which of the following is a good strategy for delaying the onset of lipid oxidation? de to form free fatty acids d.Store in La li ht,well-ventilated area e.All of the above are good strategies 18.Which of the following is NOT expected to increase as water activity increases? B.lipolysis reaction ra d.my catalyed action nisn wth e.All of the above would be expected to increase@ The following 2 questions refer to the reaction below: CEE'E-BEEE -S -P -0 -0 .D -0 -S S:Stearic acid(18:0);P:Palmitic acid(16:0):O:Oleic acid(18:1) 19.Which of the following best describes the reaction above? nation oxidation 20.As a result of this reaction ng range of mixture is broader e.trans fatty acids are produced Page5
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 5 17. Which of the following is a good strategy for delaying the onset of lipid oxidation? a. Add chelating agents @ b. Hydrolyze triglycerides to form free fatty acids c. Inactivate lipase d. Store in a light, well-ventilated area e. All of the above are good strategies 18. Which of the following is NOT expected to increase as water activity increases? a. lipolysis reaction rates b. vapor pressure of water c. microorganism growth d. enzymatic catalyzed reaction rates e. All of the above would be expected to increase @ The following 2 questions refer to the reaction below: S: Stearic acid (18:0); P: Palmitic acid (16:0); O: Oleic acid (18:1) 19. Which of the following best describes the reaction above? a. hydrogenation b. caramelization c. oxidation d. saponification e. transesterification @ 20. As a result of this reaction a. the lipid product is more saturated b. the melting range of the lipid mixture is broader c. the melting range of the lipid mixture is narrower @ d. rancid odors are produced e. trans fatty acids are produced S + ++ S P P P S O O O O O P + ++ S O P P O S P O P O O S

Midte m#2,Fal2003 FST 100A 21.Lipid hydrolysis can be catalyzed by &9 ip) 怎none r the6ods Dase and c@ 22.What are sensitizers? es that make hydrolysisproducts smelstonge down tion by quenc let oxygen e.Answers a and d 23.Which of the following are fat substitutes? tra n d.Medium-chain triglycerides e.All of the above 24.The propagation stage of lipid oxidation is NOT B.slowed by many antioxidants a reaction involving formation of peroxy free radicals d.the sloy e. ottheare ue otthe o e 25.Compared to oxidation rates of saturated fatty acid groups at room temperature, monounsaturated groups oxidize approximately .1more a 10 times faster 100 mes 26.Why do phenolic compounds work well as antioxidants? a.they are metal ions b.they form very reactive free radicals they form free rad ss bilize by resonance a e. al form hexanal Page 6
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 6 21. Lipid hydrolysis can be catalyzed by a. acid b. hydrolases (lipases) c. base d. answers a, b and c @ e. none of the above 22. What are sensitizers? a. Molecules that make hydrolysis products smell stronger b. Molecules that slow down oxidation by quenching singlet oxygen c. Molecules that capture light energy and promote formation of singlet oxygen @ d. Molecules used to catalyze hydrogenation e. Answers a and d 23. Which of the following are fat substitutes? a. Salatrim b. Olestra c. Caprenin d. Medium-chain triglycerides e. All of the above @ 24. The propagation stage of lipid oxidation is NOT a. slowed by many antioxidants b. a chain reaction c. a reaction involving formation of peroxy free radicals d. the slowest stage in the oxidation reaction @ e. All of the above are true of the propagation stage 25. Compared to oxidation rates of saturated fatty acid groups at room temperature, monounsaturated groups oxidize approximately a. at the same rate b. 10 times slower c. 10 times faster d. 100 times faster @ e. 100 times slower 26. Why do phenolic compounds work well as antioxidants? a. they are metal ions b. they form very reactive free radicals c. they form free radicals stabilized by resonance @ d. they break down to form hexanal e. all of the above

Midterm #2,Fall 2003 FST 100A 27.Plant oils y po ed f ate acid e.all of the above e. answer a and c@ 29.Which of the following foods has a water content that is much less than 80%? milkges e. above contain more than 80%water 30.The type of fatty acid group at the sn-2 position a.will be lar gely conserved during digestion will af ucture of lipid crystal formed 31.The crystal structure depicted at right is most likely to form if a.the fatty acid groups at the sn-2 position are very different from those at the sn-1 and sn-3 b. positons are very s e. Page7
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 7 27. Plant oils a. never contain saturated fatty acid groups b. contain mainly polyunsaturated fatty acids c. have mainly unsaturated fatty acid groups at the sn-2 position @ d. naturally have large quantities of trans fatty acids e. all of the above 28. Which of the following contributes to the strong smells caused by oxidation reactions? a. shorter chain molecules created by hydroperoxide decomposition b. limonene c. aldehydes d. cholesterol e. answer a and c @ 29. Which of the following foods has a water content that is much less than 80%? a. oranges b. milk c. carrots d. margarine @ e. all of the above contain more than 80% water 30. The type of fatty acid group at the sn-2 position a. will be largely conserved during digestion b. will affect the melting temperature c. will affect the rate of oxidation d. will affect the structure of lipid crystal formed e. all of the above @ 31. The crystal structure depicted at right is most likely to form if a. the fatty acid groups at the sn-2 position are very different from those at the sn-1 and sn-3 positions @ b. the fatty acid groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions are very similar c. the fatty acid groups at the sn-1 and sn-3 positions are very different d. all of the fatty acid groups are very similar e. all of the fatty acid groups are saturated

02,a28 32.Water activity will be effectively lowered by adding &ag贺mecan d allof the above e.answers b and c 33.Water activity will be effectively lowered by &es。 ting lipid crystallization d.adding phobic solutes e.answers b and c 34.Freezing food &.fgatesx&cencewiteaiguidaohatamgnoegyithtnmwihpureioe@ structure d.increases the water activity e.decreases the temperature of the food,but does not change its physical state 35.Hydrolysis of lipids .reaction c.involves preakdown otan oo bond so that H.Ois a product .rbymucleopo of base d.proceeds by free radic Page 8
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 8 32. Water activity will be effectively lowered by adding a. triglycerides b. a good humectant @ c. waxes d. all of the above e. answers b and c 33. Water activity will be effectively lowered by a. heating the food b. preventing lipid crystallization c. dehydration @ d. adding hydrophobic solutes e. answers b and c 34. Freezing food a. creates a concentrated liquid solution in equilibrium with pure ice @ b. is an excellent way to avoid damaging food structure c. increases the amount of available water d. increases the water activity e. decreases the temperature of the food, but does not change its physical state 35. Hydrolysis of lipids a. is an isomerization reaction b. creates a water leaving group, so that H2O is a product c. involves breakdown of an O-O bond d. proceeds by free radical formation e. proceeds by nucleophilic addition of base @
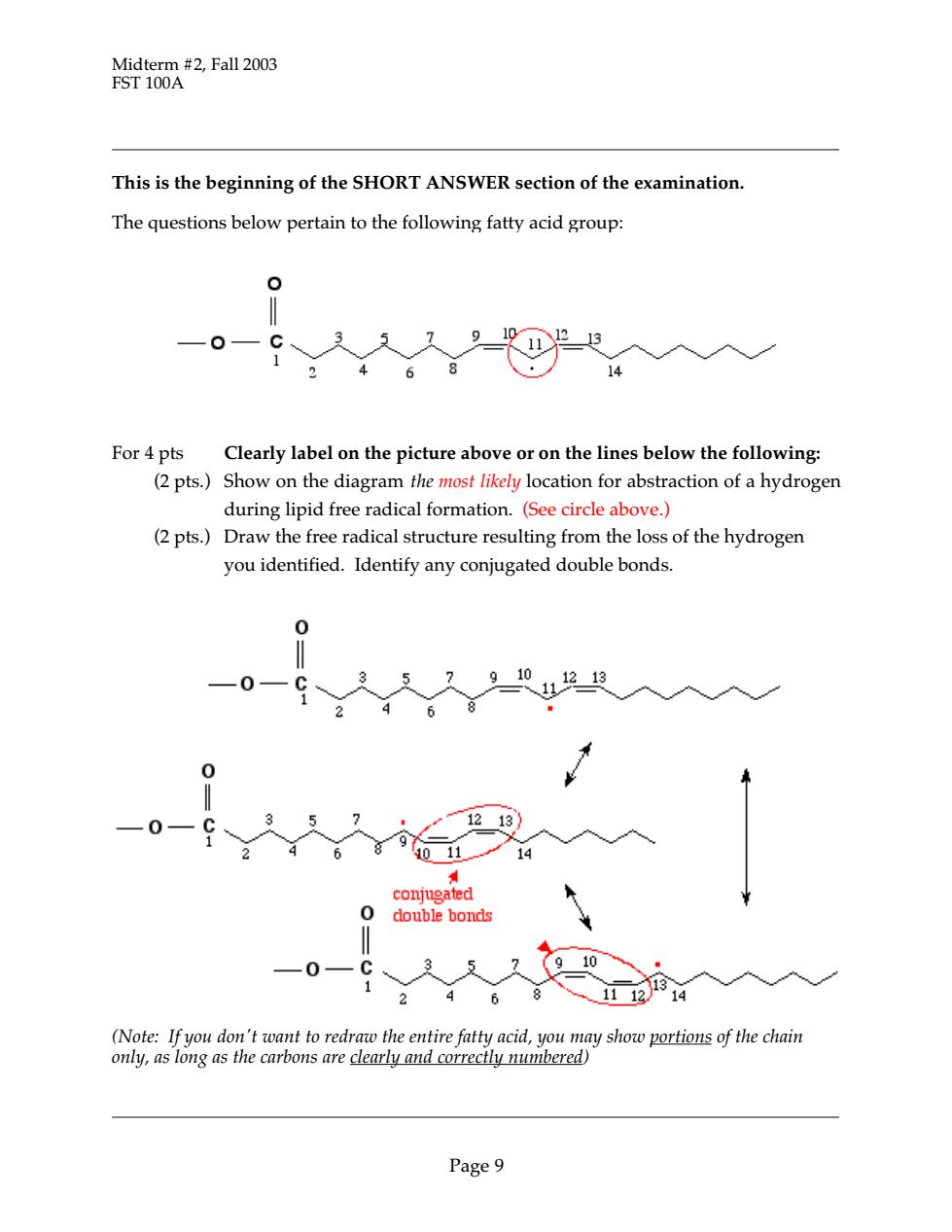
Midterm #2,Fall 2003 FST 100A This is the beginning of the SHORT ANSWER section of the examination The questions below pertain to the following fatty acid group: 0 一0 68 For 4 pts Clearly label on the picture above or on the lines below the following: (2 pts.)Show on the diagram the most likely location for abstraction of a hydrogen during lipid free radical formation.(See circle above.) (2 pts.)Draw the free radical structure resulting from the loss of the hydrogen you identified.Identify any conjugated double bonds. 0 910 121 0 0— (Note:If you don't want to redraw the entire fatty acid,you may show portions of the chain only,as long as the carbons are clearly and correctly numbered) Page9
Midterm #2, Fall 2003 FST 100A Page 9 This is the beginning of the SHORT ANSWER section of the examination. The questions below pertain to the following fatty acid group: For 4 pts Clearly label on the picture above or on the lines below the following: (2 pts.) Show on the diagram the most likely location for abstraction of a hydrogen during lipid free radical formation. (See circle above.) (2 pts.) Draw the free radical structure resulting from the loss of the hydrogen you identified. Identify any conjugated double bonds. (Note: If you don't want to redraw the entire fatty acid, you may show portions of the chain only, as long as the carbons are clearly and correctly numbered)