
Food Science &Technology 100A Professor S.R.Dungan Final Examination December 9,2003 6 Wellman Name:KEY Last First Signature INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above.Then SIGN the exam copy,signifying that you have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000 WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000 CHECK that there are 70 multiple choice questions.There are a total of 18 pages to the exam. Uea2。 completer There should be plenty of time to take this exam without being rushed.However,you will need to use your time efficiently. Graded exams can be picked up in 110 FSTB during winter quarter. Multiple Choice 180 Short answers 120 Total 200
Food Science & Technology 100A Professor S.R. Dungan Final Examination December 9, 2003 6 Wellman Name:KEY Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above. Then SIGN the exam copy, signifying that you have respected the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000. WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 70 multiple choice questions. There are a total of 18 pages to the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers. You are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of your Scantron. Do not put any marks (other than filling in the answer bubbles) on the left side(s) of the Scantron sheet. There should be plenty of time to take this exam without being rushed. However, you will need to use your time efficiently. Graded exams can be picked up in 110 FSTB during winter quarter. Multiple Choice /180 Short answers / 20 Total 200

FST 100A Final Exam,September 29,2004 Page 1 1.Limonene is a phospholipid monene I of the above The following 2 questions refer to the fatty acid group below. 2.This group is an -3 fatty acid@ 30 a short chair atty acid group e. of the above 3.The name of this group is id c stearic acid d.hexadecanoic acid e.hexadecenoic acid 4.Which of the following is true of most plant oils? a groups d.They fatty .None of acid 5.Which of the following would have the strongest flavor(detectable at the lowest threshold .gy acide concentration)? A 8-0 fatty acid An 18:0 fatty acid d.An18:1△9 fatty acid e.Triglycerides in olive oil
FST 100A Final Exam, September 29, 2004 Page 1 1. Limonene is a a. lipid b. terpene c. phospholipid d. answer a and b @ e. Limonene is all of the above The following 2 questions refer to the fatty acid group below: 2. This group is a. an ω-3 fatty acid @ b. a saturated group c. a short chain fatty acid group d. answer a and c e. This group is all of the above 3. The name of this group is a. linolenic acid @ b. oleic acid c. stearic acid d. hexadecanoic acid e. hexadecenoic acid 4. Which of the following is true of most plant oils? a. They do not contain any saturated fatty acid groups b. They contain many short chain fatty acid groups c. Their sn-2 position is primarily saturated d. They contain only one type of fatty acid group e. None of the above characterize plant oils @ 5. Which of the following would have the strongest flavor (detectable at the lowest threshold concentration)? a. A 4:0 fatty acid @ b. A 8:0 fatty acid c. An 18:0 fatty acid d. An 18:1∆9 fatty acid e. Triglycerides in olive oil O O

EST 100A Final:December 9.2003 Page2 6.Transesterification reactions will a.increase the degree of saturation b.produce free fatty acids as the final product c.create a different distribution of fatty acid groups on the triglycerides@ d.create aldehydes and rancid odors e.break fatty acid groups into short chains 7.Which of the following is NOT true of diglycerides? a.They contain two hydroxyl(OH)groups@ b.They have two fatty acid chains They are produced by hydrolysis of triglycerides e.They are lipids 8. The process of hydrogenation Proace produces cis fatty acids a decreases the melting point of the lipid e. Aseraana2digdgaion The following 2 questions refer to the structure below: BH H CH2 CC=C cHCH一CH H DH H 9.Which labeled hydrogen in this structure is most likely to be abstracted during lipid oxidation? A E@ C.C d.D e.They are all equally likely to be abstracted 10.What is best explanation of why this hydrogen is abstracted to form a free radical? a.Because C-H bonds are always very weak b.Because it is pulled off by a stro ong acid Because the ult is a adical st cture stabilized by Ie sonance@ esult i is a structure with conj gated double bonds Because hydrocarbons are very strong acids
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 2 6. Transesterification reactions will a. increase the degree of saturation b. produce free fatty acids as the final product c. create a different distribution of fatty acid groups on the triglycerides @ d. create aldehydes and rancid odors e. break fatty acid groups into short chains 7. Which of the following is NOT true of diglycerides? a. They contain two hydroxyl (OH) groups @ b. They have two fatty acid chains c. They are produced by hydrolysis of triglycerides d. They are amphiphilic e. They are lipids 8. The process of hydrogenation a. saturates double bonds @ b. produces cis fatty acids c. decreases the melting point of the lipid d. occurs naturally during digestion e. Answer a and c The following 2 questions refer to the structure below: 9. Which labeled hydrogen in this structure is most likely to be abstracted during lipid oxidation? a. A b. B @ c. C d. D e. They are all equally likely to be abstracted 10. What is best explanation of why this hydrogen is abstracted to form a free radical? a. Because C-H bonds are always very weak b. Because it is pulled off by a strong acid c. Because the result is a free radical structure stabilized by resonance @ d. Because the result is a structure with conjugated double bonds e. Because hydrocarbons are very strong acids C C H H H H H H C C A B C D CH2 CH2 CH2 C CH2 H H

FST 100A Final;December 9,2003 Page3 11.Which of the following is most vulnerable to lipid oxidation reactions? a.Peanut Butter b.Lard C.Fish oils d.Milk fat e.Cocoa butter 12.Which of the following polysaccharides is digested(absorbed)to produce calories? a.Pectin b.Cellulose Carrageenan ectin@ e.All of the above would be digested 13.At higher water activities water is more available for microorganism growth@ s more we s h e.answer a and b 14.Which of the following describes the composition of honey? B.puresucrose solution A solution with roughly equal glucose and fructose,but slightly higher in fructose@ a A solution with roughly equal glucose and fructose,but slightly higher in glucose An approximately 30%overall sugar solution,with a wide variety of sugar types e. Honey's composition is very similar to molasses 15.When foods are in the glassy state,they .rate due to degrdaion reactions are cr n no water 】分 e. 16.Glass formation will be promoted a.at temperatures above the glass transition temperature b.by the addition of hydrophilic polysaccharides@ c.at temperatures above the gelatinization temperature d.at low concentrations of hydrophilic solutes e.by the addition of glassifying enzymes
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 3 11. Which of the following is most vulnerable to lipid oxidation reactions? a. Peanut Butter b. Lard c. Fish oils @ d. Milk fat e. Cocoa butter 12. Which of the following polysaccharides is digested (absorbed) to produce calories? a. Pectin b. Cellulose c. Carrageenan d. Amylopectin @ e. All of the above would be digested 13. At higher water activities a. water is more available for microorganism growth @ b. water is more difficult to freeze c. hydrolysis reactions are slower d. sugars become less soluble e. answer a and b 14. Which of the following describes the composition of honey? a. A pure sucrose solution b. A solution with roughly equal glucose and fructose, but slightly higher in fructose @ c. A solution with roughly equal glucose and fructose, but slightly higher in glucose d. An approximately 30% overall sugar solution, with a wide variety of sugar types e. Honey's composition is very similar to molasses 15. When foods are in the glassy state, they a. rapidly deteriorate due to degradation reactions b. are crystalline c. contain no water d. are solid yet disordered @ e. are always at equilibrium 16. Glass formation will be promoted a. at temperatures above the glass transition temperature b. by the addition of hydrophilic polysaccharides @ c. at temperatures above the gelatinization temperature d. at low concentrations of hydrophilic solutes e. by the addition of glassifying enzymes
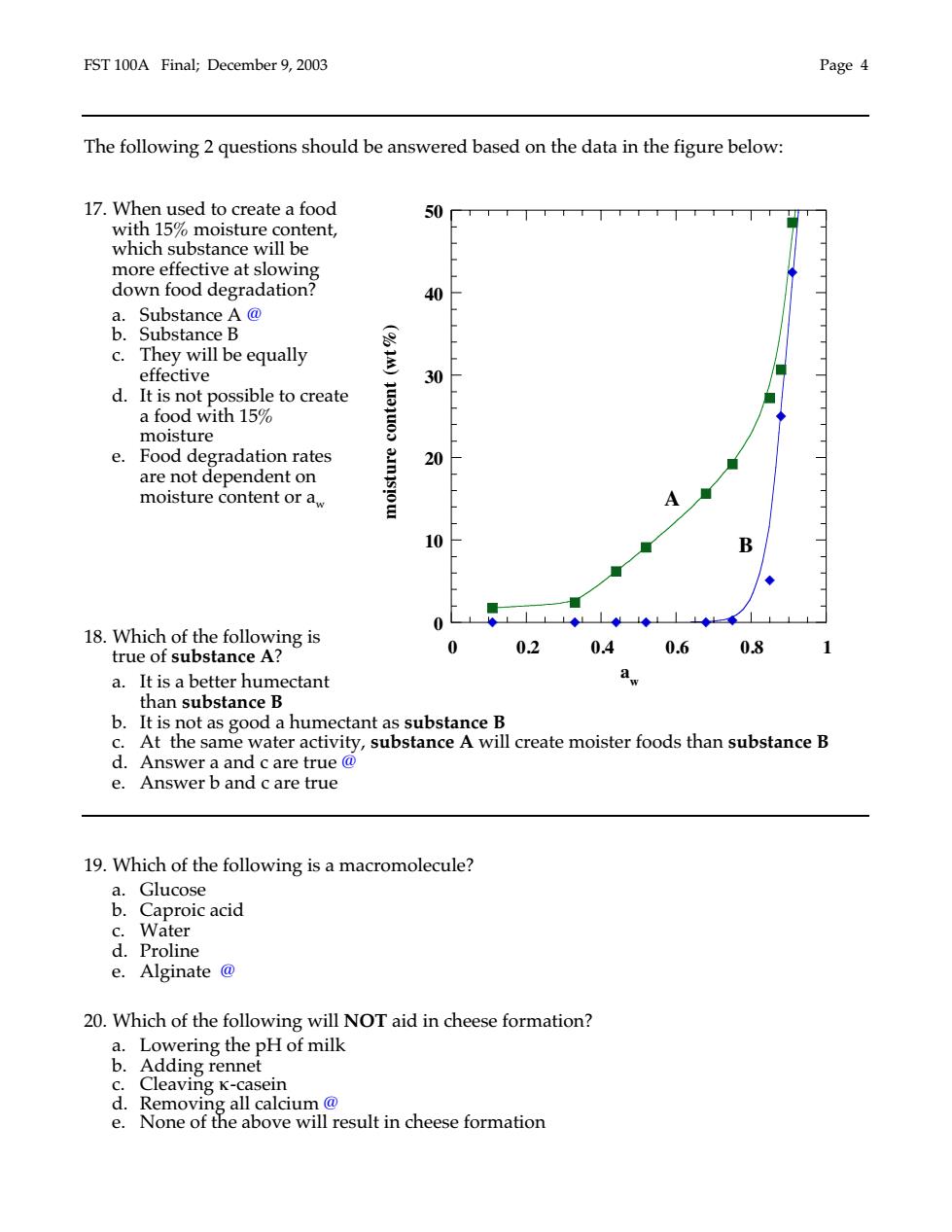
EST 100A Final:December 9.2003 Page 4 The following 2 questions should be answered based on the data in the figure below: 17.When used to create a food with 15%moisture content, which substance will be more effective at slowing down food degradation? 40 &Substance合@ c.They will be equally effective 30 d.It is not possible to create a food with 15 moisture e.Food degradation rates 20 are not dependent on moisture content or a, 0 18.te 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 a.It is a better humectant b.It is not as good a humectant as substance B c.At the same water activity,substance A will create moister foods than substance B d.Answer a and c are true@ e.Answer b and c are true 19.Which of the following is a macromolecule? .Cproie acid c Water d.Proline e.Alginate@ 20.Which of the following will NOT aid in cheese formation? a.Lowering the pH of milk Adding rennet Cleaving K- seir calcium ove wI esult in cheese formation
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 4 The following 2 questions should be answered based on the data in the figure below: 17. When used to create a food with 15% moisture content, which substance will be more effective at slowing down food degradation? a. Substance A @ b. Substance B c. They will be equally effective d. It is not possible to create a food with 15% moisture e. Food degradation rates are not dependent on moisture content or aw 18. Which of the following is true of substance A? a. It is a better humectant than substance B b. It is not as good a humectant as substance B c. At the same water activity, substance A will create moister foods than substance B d. Answer a and c are true @ e. Answer b and c are true 19. Which of the following is a macromolecule? a. Glucose b. Caproic acid c. Water d. Proline e. Alginate @ 20. Which of the following will NOT aid in cheese formation? a. Lowering the pH of milk b. Adding rennet c. Cleaving κ-casein d. Removing all calcium @ e. None of the above will result in cheese formation 0 10 20 30 40 50 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 aw moisture content (wt%) A B

FST 100A Final;December 9,2003 Page 5 The following 4 questions refer to the molecule at the right: 21.This molecule is A-HC-O a.D-galactose@ HC-OH b.D-galacturonic acid c.D-glucitol HO-C-H d.D-glucose CHO-C-H e.D-fructose 22.This molecule can participate as a reactant in .yryodic inkage a 23.This sugar is a"D"sugar because of its conformation about &Caoo吧 bon Eon e.carbon C only 24.Which of the marked carbons are chiral centers? only e. There are no chiral centers in this molecule 25.Protein denaturation is NOT promoted &时mr ence of many disulfide bonds@ c.by the addition of a salting-out salt d.by extremes in pH e.All of the above promote denaturation 26.What is a suspension? a.A dispersion of solid in liquid@ b.A solution containing dissolved sugars or salts c.A single-phase,amorphous solid d.A clear,single -phase rystal e.A mixture of liquid oil and water
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 5 The following 4 questions refer to the molecule at the right: 21. This molecule is a. D-galactose @ b. D-galacturonic acid c. D-glucitol d. D-glucose e. D-fructose 22. This molecule can participate as a reactant in a. oxidation of a sugar b. hydrolysis of a glycosidic linkage c. enzymatic browning d. Maillard browning e. answer a and d @ 23. This sugar is a "D" sugar because of its conformation about a. carbon A only b. carbon B or C only c. carbon D only @ d. carbon E only e. carbon C only 24. Which of the marked carbons are chiral centers? a. Carbon A only b. Carbons B, C, and D only @ c. Carbons B and D only d. Carbons B, C, D, and E only e. There are no chiral centers in this molecule 25. Protein denaturation is NOT promoted a. at high temperatures b. by the presence of many disulfide bonds @ c. by the addition of a salting-out salt d. by extremes in pH e. All of the above promote denaturation 26. What is a suspension? a. A dispersion of solid in liquid @ b. A solution containing dissolved sugars or salts c. A single-phase, amorphous solid d. A clear, single-phase crystal e. A mixture of liquid oil and water E D C B A C C C C HC OH H OH HO H H HO H CH2OH O

FST 100A Final;December 9,2003 Page 6 .ho blw Of the mnoderno A B CH:-CH-CH2- OH-CH2- CH ○》-cH,- &Rdue com邮 c.Residues B and C only dteA带nae 28.Why do food scientists modify cellulose by attaching carboxymethyl groups? ater solubility c.To increase r d.Answer b and c pulsion between solutes e.All of the above are correct reasons 29.Which of the following are common features of amylose and cellulose? They both are glucans (chains of glucose subunits) y hoth are easily dig sted c.They both form helical structures d.They are both highly water soluble e.All of the above are common features 30.Starch in potatoes,corn or wheat a.is dissolved in aqueous solution b.is found in solid,semicrystalline granules@ c.contains only amylose d.contains a mixture of amylopectin and cellulose e.forms long,strong linear fibers which give structure to the plant 31.Which of the following(a-d)is NOT true of an enediol?(Choose"e"if all are true) a.It can be created during isomerization reactions b. It is produced b y adding a proton to the enolate ion It is an intermec iate in the isomerization of glucose to fructose
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 6 27. Three amino acid R groups are shown below. Of the amino acids bearing these groups, which is hydrophobic? a. Residue B only b. Residue C only c. Residues B and C only d. Residues A and B only @ e. Residues A, B and C 28. Why do food scientists modify cellulose by attaching carboxymethyl groups? a. To make it sweeter b. To enhance its water solubility c. To increase repulsion between solutes d. Answer b and c @ e. All of the above are correct reasons 29. Which of the following are common features of amylose and cellulose? a. They both are glucans (chains of glucose subunits) @ b. They both are easily digested c. They both form helical structures d. They are both highly water soluble e. All of the above are common features 30. Starch in potatoes, corn or wheat a. is dissolved in aqueous solution b. is found in solid, semicrystalline granules @ c. contains only amylose d. contains a mixture of amylopectin and cellulose e. forms long, strong linear fibers which give structure to the plant 31. Which of the following (a-d) is NOT true of an enediol? (Choose "e" if all are true) a. It can be created during isomerization reactions b. It is produced by adding a proton to the enolate ion c. It is an intermediate in the isomerization of glucose to fructose d. It contains a carbon-carbon double bond e. All of the above are true of an enediol @ C OH CH2 B CH2 A CH3 CH CH2 CH3

FST 100A Final;December 9,2003 Page 7 The following 3 questions apply to the list of polysaccharides below: amvlose Ⅱcellulose III amylopectin IV pectin 32.Which of the above molecules contain a[1,4]glycosidic linkages? a.Molecules I and IV only b.Molecule II only c.Molecules I,II and III only d.Molecules I,III and IV only@ e.Molecule I only 33.Which of the above molecules is digested by humans? Mokule e.Molecules II,II and IV 34.Which of the above molecules is most insoluble in water? a.Molecule I h molecule ni@ c.Molecule I d.Molecule IV All of these molecules are very water soluble 35.Which of the following will increase the energy of an emulsion of lipid droplets in water, all other things being equal? Adding surfactan D of oil (decreasing the volume fraction) d. the size of the d lets 36.Gelatin is obtained from b. seaweed c.derivatized cellulose d.collag
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 7 The following 3 questions apply to the list of polysaccharides below: I amylose II cellulose III amylopectin IV pectin 32. Which of the above molecules contain α[1,4] glycosidic linkages? a. Molecules I and IV only b. Molecule II only c. Molecules I, II and III only d. Molecules I, III and IV only @ e. Molecule I only 33. Which of the above molecules is digested by humans? a. Molecules I and III only @ b. Molecule I only c. Molecule II only d. Molecules III and IV only e. Molecules I, II, III and IV 34. Which of the above molecules is most insoluble in water? a. Molecule I b. Molecule II @ c. Molecule III d. Molecule IV e. All of these molecules are very water soluble 35. Which of the following will increase the energy of an emulsion of lipid droplets in water, all other things being equal? a. Adding surfactant b. Decreasing the concentration of oil (decreasing the volume fraction) c. Increasing the size of the emulsion droplets d. Decreasing the size of the emulsion droplets @ e. Allowing the emulsion to sit for a long time 36. Gelatin is obtained from a. seaweed b. fruit c. derivatized cellulose d. collagen from animals @ e. jello trees

EST 100A Final:December 9.2003 Page 8 37.What is responsible for the tenderness of pot roast meat? The formation of getimdesen d.Low oHto the iseeri pontduring coon e.Choosing cuts of meat with very little connective tissue 38.The relative sweetness of lactose is 7 c13 d.0.3@ e.0.9 39.In which of the following foods would we expect to find lactose? .Comsyp c.Ice Cream@ d.Broccoli e.None of the above 40.Starch granules .r waer are pure cellulose d.rgeling nin m and jellie e.are dietary fibe 41.Why is the solubility of B-lactoglobulin lowest around pH 5.2-5.4? The proiePH c.Disulfide bonds break at this pH d.The protein forms extended fibers at this pH e.Protein-protein repulsion is weakest at this pH@ 42.By definition,above the gelatinization temperature 6.rotur starch granules lose crystallinity@ e.saturated lipids oxidize
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 8 37. What is responsible for the tenderness of pot roast meat? a. The formation of gelatin from collagen @ b. The formation of pectin salt bridges c. The action of lipase d. Lowering of the pH to the isoelectric point during cooking e. Choosing cuts of meat with very little connective tissue 38. The relative sweetness of lactose is a. 1.7 b. 1 c. 1.3 d. 0.3 @ e. 0.9 39. In which of the following foods would we expect to find lactose? a. Tomatoes b. Corn syrup c. Ice Cream @ d. Broccoli e. None of the above 40. Starch granules a. dissolve quickly in cold water b. are birefringent @ c. are pure cellulose d. are the primary gelling agent in jams and jellies e. are dietary fiber 41. Why is the solubility of β-lactoglobulin lowest around pH 5.2-5.4? a. The protein net charge is quite high at this pH b. The protein's native structure is unstable at this pH c. Disulfide bonds break at this pH d. The protein forms extended fibers at this pH e. Protein-protein repulsion is weakest at this pH @ 42. By definition, above the gelatinization temperature a. glasses melt b. proteins denature c. starch granules lose crystallinity @ d. sucrose is hydrolyzed e. saturated lipids oxidize

FST 100A Final;December 9,2003 Page9 43.Blanching times c.will become longer at higher temperatures d.are determined by the time needed for starch hydrolysis e.are determined by the time needed to melt any solids in the food 44.The hydrophobic group of most lipid and synthetic food emulsifiers a.is a phenolic group b.is a carboxymethyl group c.is a glycose unit d.is a fatty acid group@ e.is a cellulose chain 45.Which of the following are NOT emulsifiers? a.Monoglycerides b.a-Lactalbumin c.Phospholipids d.Tweens e.Amylopectin@ 46.What enzyme hydrolyzes amylose to produce a viscous solution with almost no sweetness? a.a-Amylase@ b.B-Amylase c.Glucoamylase d.Lipoxygenase e.Answer a,b and c 47.The Maillard reaction can involve .miremods c.Amadori compounds d.all of the above e.answer a and c 48.Antioxidants .heoduring odto capture energy from light and transfer it to singlet oxygen e.catalyze the oxidation of galactose
FST 100A Final; December 9, 2003 Page 9 43. Blanching times a. are determined by the time needed to hydrolyze proteins b. are determined by the time needed to denature enzymes at a given temperature @ c. will become longer at higher temperatures d. are determined by the time needed for starch hydrolysis e. are determined by the time needed to melt any solids in the food 44. The hydrophobic group of most lipid and synthetic food emulsifiers a. is a phenolic group b. is a carboxymethyl group c. is a glycose unit d. is a fatty acid group @ e. is a cellulose chain 45. Which of the following are NOT emulsifiers? a. Monoglycerides b. α-Lactalbumin c. Phospholipids d. Tweens e. Amylopectin @ 46. What enzyme hydrolyzes amylose to produce a viscous solution with almost no sweetness? a. α-Amylase @ b. β-Amylase c. Glucoamylase d. Lipoxygenase e. Answer a, b and c 47. The Maillard reaction can involve a. reducing sugars b. amine compounds c. Amadori compounds d. all of the above @ e. answer a and c 48. Antioxidants a. bind metal ions b. slow the propagation rate during oxidation @ c. capture energy from light and transfer it to singlet oxygen d. denature polyphenol oxidase e. catalyze the oxidation of galactose