
Food chemistry final exam (A)-Key 一、选择题(每小题1.5分,共22.5分) 1.In general,which of the following is NOT expected to increase as water activity increases? a)lipolysis reaction rates b)Carbohydrate hydrolys sis reaction rates Micro ganism growt d)All of the above would be expected to increasea 2.Why are Maillard reactions slower at high water activities? a)Because Maillard reactions are hydrolysis reactions b)Because polyphenol oxidase is inactive at high water activities )Because all the brov ments dissolv way at high water activities d Because water is an initial product of Maillard browning@ e)Because reducing sugars become non-reducing at high water activities 3.When a food of low water activity is sealed in the same package as a food of high water activity what will occur over time? a)Moisture will migrate from the low water activity food to the high water activity food b)Moisture will not migrate in either direction c)The high water activity food will increase in moisture content d)Answer a and c will occur e)Moisture will migrate from the high water activity food to the low water activity food@ Sucrose would participate in which of the following reactions a)An oxidation test b)Maillard browning c)Caramelization a d)Enzymatic b ownin Sucrose would participate inall of the above 5.Which of the following is a good strategy for preventing Maillard browning? a)Removing reducing sugars@ b)Adding PPO c)Adding alcohol d )Answer a and b e)Answer a,b and c 6.Which of the following sugars is the least sweet at room temperature? a)Fructose b)Lactose@ Sucros d)Glucose e)D-Fructopyranose
Food chemistry final exam (A) Key 一、选择题(每小题 1.5 分,共 22.5 分) 1. In general, which of the following is NOT expected to increase as water activity increases? a) Lipolysis reaction rates b) Carbohydrate hydrolysis reaction rates c) Microorganism growth d) All of the above would be expected to increase@ 2. Why are Maillard reactions slower at high water activities? a) Because Maillard reactions are hydrolysis reactions b) Because polyphenol oxidase is inactive at high water activities c) Because all the brown pigments dissolve away at high water activities d) Because water is an initial product of Maillard browning @ e) Because reducing sugars become nonreducing at high water activities 3. When a food of low water activity is sealed in the same package as a food of high water activity what will occur over time? a) Moisture will migrate from the low water activity food to the high water activity food b) Moisture will not migrate in either direction c) The high water activity food will increase in moisture content d) Answer a and c will occur e) Moisture will migrate from the high water activity food to the low water activity food @ 4. Sucrose would participate in which of the following reactions? a) An oxidation test b) Maillard browning c) Caramelization @ d) Enzymatic browning e) Sucrose would participate in all of the above 5. Which of the following is a good strategy for preventing Maillard browning? a) Removing reducing sugars @ b) Adding PPO c) Adding alcohol d) Answer a and b e) Answer a, b and c 6. Which of the following sugars is the least sweet at room temperature? a) Fructose b) Lactose @ c) Sucrose d) Glucose e) DFructopyranose

7.Pectin is a polysaccharide of galacturonic acid and galcturonic acid derivative b)a polysaccharide of glucose subunits c)a protein rich in proline and proline derivatives d)a supplement for building up pectoral muscles e)all ofthe above 8. Gelatin is obtained from a)seaweed b)fruit c)derivatized cellulose d)collagen from animals@ 9. Above the gelatinizatio n ten perature a)collagen turns to gelatin b)starch granules lose their crystallinaty@ c)pectin forms a gel d)amylopectin becomes insoluble in water and precipitates e)none of the above 10. During lipid digestion,fatty acids are most what positions? a)sn-1 and sn-3@ b)sn-1 and sn-2 c)sn-2 and sn-3 d)sn-2only 11.Which ofthe following is a major difference between lard and cocoa butter a)Cocoa butter melts at a much lower temperature than does lard b)Cocoa butter is much higher in fat than lard c)Cocoa butter has a much narrower melting range than does lard@ d)Cocoa butte r ha s very different types of fatty acid groups than does lard None ofthe above 12.Why would soybean oil be hydrogenated? a)To increase its melting point b)To make it more solid at room temperature c)Toprotect it from oxidation d) Answer a and b onl e) Answer a,b and c@ 13.Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the lowest temperature? a)Triglycerides containing arachidic acid (20:0)groups only b)Triglycerides containing palmitic acid(16:0)groups only ce s contain ng cis oleic acid (18:1 groups only d)Triglycerides containing transoleic acid(18:1)groups only e)Triglycerides containing stearic acid(18:0)groups only 14.Hydrolysis of proteins leads to a)an increase in the hydrophobic character of amino acids
7. Pectin is a) a polysaccharide of galacturonic acid and galcturonic acid derivatives subunits @ b) a polysaccharide of glucose subunits c) a protein rich in proline and proline derivatives d) a supplement for building up pectoral muscles e) all of the above 8. Gelatin is obtained from a) seaweed b) fruit c) derivatized cellulose d) collagen from animals @ 9. Above the gelatinization temperature a) collagen turns to gelatin b) starch granules lose their crystallinaty @ c) pectin forms a gel d) amylopectin becomes insoluble in water and precipitates e) none of the above 10. During lipid digestion, fatty acids are most likely cleaved from what positions? a) sn1 and sn3 @ b) sn1 and sn2 c) sn2 and sn3 d) sn2 only e) sn4 11. Which of the following is a major difference between lard and cocoa butter? a) Cocoa butter melts at a much lower temperature than does lard b) Cocoa butter is much higher in fat than lard c) Cocoa butter has a much narrower melting range than does lard @ d) Cocoa butter has very different types of fatty acid groups than does lard e) None of the above 12. Why would soybean oil be hydrogenated? a) To increase its melting point b) To make it more solid at room temperature c) To protect it from oxidation d) Answer a and b only e) Answer a, b and c @ 13. Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the lowest temperature? a) Triglycerides containing arachidic acid (20:0) groups only b) Triglycerides containing palmitic acid (16:0) groups only c) Triglycerides containing cis oleic acid (18:1) groups only @ d) Triglycerides containing trans oleic acid (18:1) groups only e) Triglycerides containing stearic acid (18:0) groups only 14. Hydrolysis of proteins leads to a) an increase in the hydrophobic character of amino acids

b)oxidation of peptides c)cleavage of peptide bonds@ answer a and none of the above 15.Which of the following is an emulsion? a)a dispersion of sugar in water b)a dispersion ofoil in watera as lution of protein in wate d)a dispersion of solid peanuts in peanut oil? e)all of the above are examples ofemulsions 二、判断题(每小题1.5分,共7.5分) 1 Lysozyme is one of the major proteins ofegg yolk.(x) 23 Phosvitin isa kind of protein egg yolk. Soy protein has four kinds of globular protein,2S.7S.I1S,15. (√) 4. Peanut protein is short of two amino acids(Met and Trp)() 5.Benzoic acid exhibits optimum activity in the pH above 7.(X) 三、填空题(每空格1分,共12分) 1. Important factors governing the stability of foods during handling,processing. and storage are time,temperature,pH,water activity,components, and so on. 2.Starch granules are composed of a mixture of two polymers:an essentially linear polysaccharide called amylose,and a highly branched polysaccharide called 3. Flavor consists of five dimensions,which are aroma,taste,mouth feeling. appearance and color,sound. 四、问答题(共42分) Ouestion 1(9 points) (a)Describe the Maillard reaction in detail,which includes3 steps.(3points) Each step Ipt A:Carbonyl group undergoes nucleophilic attack by amine Amadori rearrangment Deamination (loss of amine)and further isomerization leads to several dicarbonyl compounds (b)Give three examples of where this reaction occurs in foods,and whether they are favourable or unfavourable.(6 points) Each example 2pts
b) oxidation of peptides c) cleavage of peptide bonds @ d) answer a and c e) none of the above 15. Which of the following is an emulsion? a) a dispersion of sugar in water b) a dispersion of oil in water @ c) a solution of protein in water d) a dispersion of solid peanuts in peanut oil? e) all of the above are examples of emulsions 二、判断题(每小题 1.5 分,共 7.5 分) 1. Lysozyme is one of the major proteins of egg yolk.(×) 2. Phosvitin is a kind of protein from egg yolk.(√) 3. Soy protein has four kinds of globular protein, 2S, 7S, 11S, 15S. (√) 4. Peanut protein is short of two amino acids (Met and Trp) (√) 5. Benzoic acid exhibits optimum activity in the pH above 7.(×) 三、填空题(每空格1分,共12分) 1. Important factors governing the stability of foods during handling, processing, and storage are time, temperature, pH, water activity, components, .and so on. 2. Starch granules are composed of a mixture of two polymers: an essentially linear polysaccharide called amylose, and a highly branched polysaccharide called amylopectin. 3. Flavor consists of five dimensions, which are aroma, taste, mouth feeling, appearance and color, sound. 四、问答题(共 42 分) Question 1 (9 points) (a) Describe the Maillard reaction in detail, which includes 3 steps. (3 points) Each step 1pt. A: Carbonyl group undergoes nucleophilic attack by amine Amadori rearrangment Deamination (loss of amine) and further isomerization leads to several dicarbonyl compounds (b) Give three examples of where this reaction occurs in foods, and whether they are favourable or unfavourable. (6 points) Each example 2pts

A:Favourable:Bread,Soy sauce,Milk,chocolate Roasted,grilled meats,Coffee Unfavourable:Dehydrated potatoes,Egg powder Corn starch,Dried foods(milk Fruits)Roasted.grilled meats and so on. Ouestion 2(8 points) Describe protein gelation by discussing the following (a)What is a protein gel?(full description required)(points) A:Protein gel is thought to be intermediate between solutions (eg.water)and proteins.Protein partially aggregates to form cross-links. (b)The two-step process involved the formation of protein gels,(2 points) A:Heat gellation a two step process which begins by protei denaturation and is followed by aggregation of the proteins to form a crossed linked matrix. (c)The 4 factors that affect protein gelation.(4 points) each factor Ip A:Temperature protein concentration/pH/salt concentration/calcium concentration/free sulfhydryl concentration. Question3(11 points) Autoxidation of Lipids-discuss the following as (a)The three steps involved in the autoxidation of lipids?(3points) each step Ipt Al:Initiation,Propagation,Termination A2: RH>R.+H. R。+ 02 ROO. 之RO0: +RH→ROOH+R ROO. +ROO.>stable products (b)List four ways to reduce the extent of lipid oxidation.and briefly describe why each ofthem works.(8 points) Each way I pt,the reason of each way Ipt. A:Delaying photooxidation -Store oils in dark -blanching Chelating agents(EDTA,citric acid) Antioxidants(Vitamin E,C,polyphenol.) Substances which slow oxidation
A: Favourable: Bread, Soy sauce, Milk, chocolate Roasted, grilled meats, Coffee Caramel and so on. Unfavourable: Dehydrated potatoes, Egg powder, Corn starch, Dried foods(milk, Fruits) Roasted, grilled meats and so on. Question 2 (8 points) Describe protein gelation by discussing the following: (a) What is a protein gel? (full description required); (2 points) A: Protein gel is thought to be intermediate between solutions (eg. water) and proteins. Protein partially aggregates to form crosslinks. (b) The twostep process involved the formation of protein gels; (2 points) A: Heat induced gellation is a two step process which begins by protein denaturation and is followed by aggregation of the proteins to form a crossed linked matrix. (c) The 4 factors that affect protein gelation. (4 points) each factor 1pt A: Temperature/ protein concentration/ pH/ salt concentration/ calcium concentration/ free sulfhydryl concentration. Question3 (11 points) Autoxidation of Lipids discuss the following aspects: (a) The three steps involved in the autoxidation of lipids? (3 points) each step 1pt A1: Initiation,Propagation,Termination A2: RH R• + H• R• + O2 ROO• ROO• + R H ROOH + R• ROO• + ROO• stable products (b) List four ways to reduce the extent of lipid oxidation, and briefly describe why each of them works. (8 points) Each way 1 pt, the reason of each way 1pt. A: Delaying photooxidation –Store oils in dark –Opaque containers Deactivate lipoxygenase enzymes –blanching Chelating agents (EDTA, citric acid) Antioxidants (Vitamin E, C, polyphenol.) Substances which slow oxidation
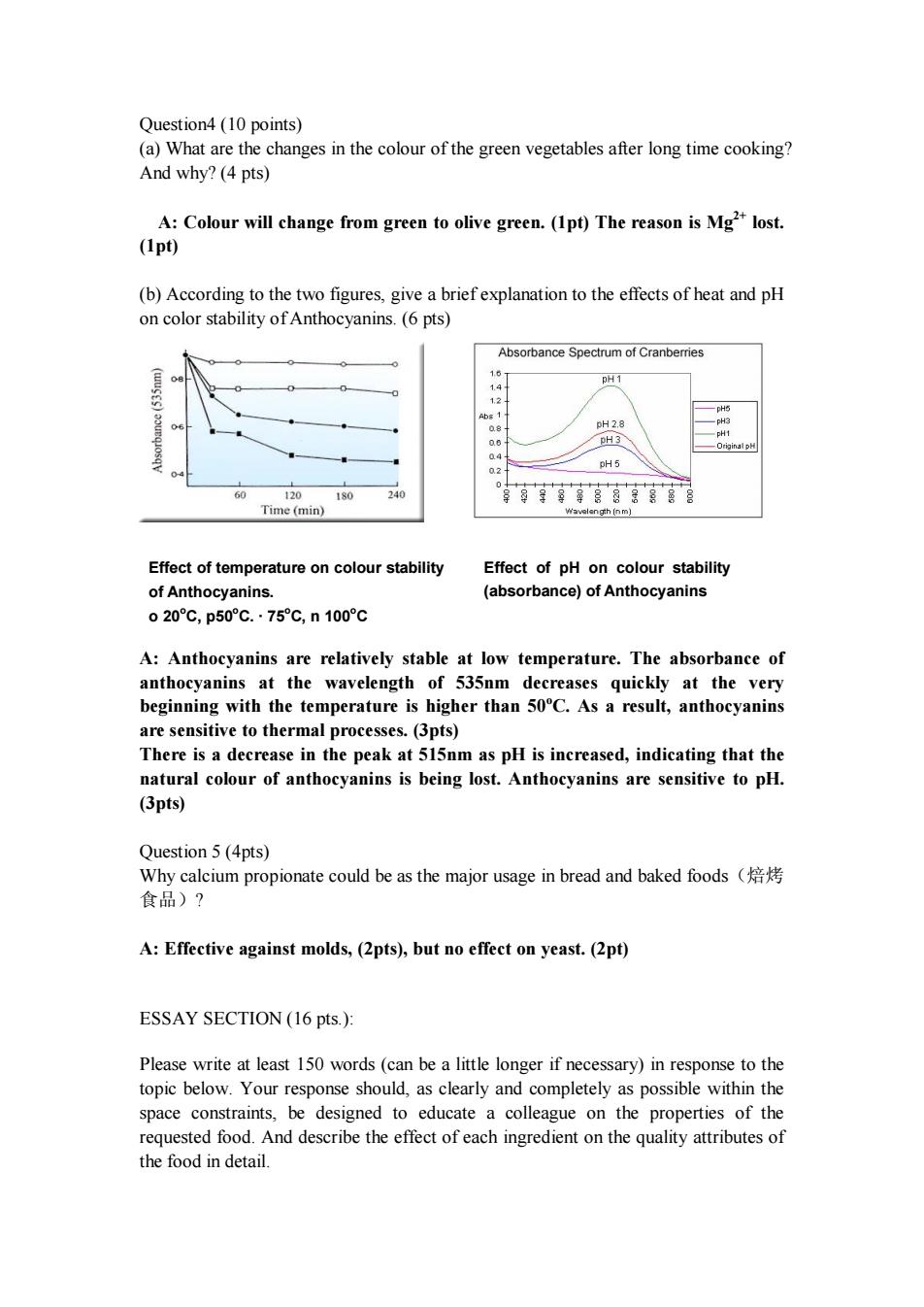
Question4(10 points) (a)What are the changes in the colour of the green vegetables after long time cooking? And why?(4 pts) A:Colour will change from green to olive green.(Ipt)The reason is Mg lost. (Ipt) (b)According to the two figures,give a briefexplanation to the effects of heat and pH on color stability ofAnthocyanins.(6 pts) pH 1 6H2 pH5 Time(min) Effect of temperature on colour stability Effect of pH on colour stability of Anthocyanins. (absorbance)of Anthocyanins 020℃,p50C.·75C,n100°c A:Anthocyanins are relatively stable at low temperature.The absorbance of anthocyanin at the wavelength at the v beginning with the tempcrature is hisher than 5ocases quckly C.As a result,anthocyanins are sensitive to thermal processes.(3pts) There is a decrease in the peak at 515nm as pH is increased,indicating that the natural colour of anthocvanins is being lost.Anthocyanins are sensitive to pH. (3pts) Question 5(4pts) Why calcium propionate could be as the major usage in bread and baked foods 食品)? A:Effective against molds,(2pts),but no effect on yeast.(2pt) ESSAY SECTION (16 pts.) Please write at least 150 words(can be a little longer if necessary)in response to the topic below.Your response should,as clearly and completely as possible within the space constraints,be designed to educate a colleague on the properties of the And describe the effect of each ingredient on the quality attributes of the food in detail
Question4 (10 points) (a) What are the changes in the colour of the green vegetables after long time cooking? And why? (4 pts) A: Colour will change from green to olive green. (1pt) The reason is Mg 2+ lost. (1pt) (b) According to the two figures, give a brief explanation to the effects of heat and pH on color stability of Anthocyanins. (6 pts) A: Anthocyanins are relatively stable at low temperature. The absorbance of anthocyanins at the wavelength of 535nm decreases quickly at the very beginning with the temperature is higher than 50 oC. As a result, anthocyanins are sensitive to thermal processes. (3pts) There is a decrease in the peak at 515nm as pH is increased, indicating that the natural colour of anthocyanins is being lost. Anthocyanins are sensitive to pH. (3pts) Question 5 (4pts) Why calcium propionate could be as the major usage in bread and baked foods(焙烤 食品)? A: Effective against molds, (2pts), but no effect on yeast. (2pt) ESSAY SECTION (16 pts.): Please write at least 150 words (can be a little longer if necessary) in response to the topic below. Your response should, as clearly and completely as possible within the space constraints, be designed to educate a colleague on the properties of the requested food. And describe the effect of each ingredient on the quality attributes of the food in detail. Effect of temperature on colour stability of Anthocyanins. o 20 oC, p50 oC. ∙ 75 oC, n 100 oC Effect of pH on colour stability (absorbance) of Anthocyanins

The following is the list of ingredients in FUMA soft sandwich cake Fresh egc refined four suc wder,sorbitol (山梨糖醇),maltitol(麦芽糖醇) refined vegetableoil mulsifying alcohol,.raising agent(膨松剂)thickening agent,.edible sal orange essence flavoring agent,B-carotene,.sodium dehydroacetate,natamycin(那他霉素),colorant Grading 1.Properties and fuanctions of the major mgredicnt refined flour,sugar,vegetable shortening oil and total is 5pts). 2.Other ingredients(0.5 pt for each,total is 6 pts) 3.Reaction involved in the process including the maillard reaction, caramelization and lipid oxidation and so on (3 pts). 4.Words expression(2pts) Fresh egg:protein,protein functionalities,lecithin(emulsifier),texture refined flour:starch,gluten,texture sugar:sweeter.browning reaction vegetable shortening oil:oil,lipid oxidation,texture whole milk powder,protein,browning reaction sorbitol:sweeter,humectant maltitol:sweeter,humectant refined vegetable oil:oil,flavor emulsifving agent:emulsifier edible alcohol:flavo raising agent:texture thickening agent:texture edible salt,orange essence,flavoring agent:flavor B-carotene,colorant:color sodium dehydroac etate natamycin:antimicrobial agent
The following is the list of ingredients in FUMA soft sandwich cake Fresh egg, refined flour, sugar, vegetable shortening oil, whole milk powder, sorbitol (山梨糖醇), maltitol(麦芽糖醇), refined vegetable oil, emulsifying agent, edible alcohol, raising agent(膨松剂 )thickening agent, edible salt, orange essence, flavoring agent, bcarotene, sodium dehydroacetate, natamycin(那他霉素), colorant Grading 1. Properties and functions of the major ingredients, including the fresh egg, refined flour, sugar, vegetable shortening oil and whole milk (1pt for each, total is 5pts). 2. Other ingredients (0.5 pt for each, total is 6 pts) 3. Reaction involved in the process including the maillard reaction, caramelization and lipid oxidation and so on (3 pts). 4. Words expression (2pts) A: Fresh egg: protein, protein functionalities, lecithin(emulsifier), texture refined flour: starch, gluten, texture sugar: sweeter, browning reaction vegetable shortening oil: oil, lipid oxidation, texture whole milk powder, protein, browning reaction sorbitol: sweeter, humectant maltitol: sweeter, humectant refined vegetable oil: oil, flavor emulsifying agent: emulsifier edible alcohol: flavor raising agent: texture thickening agent: texture edible salt, orange essence, flavoring agent: flavor bcarotene, colorant: color sodium dehydroacetate, natamycin: antimicrobial agent