
Food Science Technology 100A Professor S.R.Dungan Second Midterm Examination November 22,2004 Version A Name:KEY Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above.Then SIGN the exam copy. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000. WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron00. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 36 multiple choice questions.There are a total of 11 pages to the exam. your Scantron Please respect the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. There should be plenty of time to take this exam without being rushed.However,you will need to use your time efficiently. Graded exams can be picked up in 110 FSTB. Multiple Choice /90 /10 answers Total 100
Food Science & Technology 100A Professor S.R. Dungan Second Midterm Examination November 22, 2004 Version A Name:KEY Last First Signature: INSTRUCTIONS PRINT your last and first names above. Then SIGN the exam copy. PRINT your name on the front of your Scantron #2000. WRITE the test version that appears at the top of this page on your Scantron #2000. WRITE your student identification number in the appropriate area of your Scantron #2000 on Part 1 and follow the instructions to CODE your ID number in the bubbles. CHECK that there are 36 multiple choice questions. There are a total of 11 pages to the exam. Use a #2 pencil to mark your Scantron answers. You are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of your Scantron. Do not put any marks (other than filling in the answer bubbles) on the left side(s) of the Scantron sheet. Please respect the UC Davis Honor Code in the taking of this exam. There should be plenty of time to take this exam without being rushed. However, you will need to use your time efficiently. Graded exams can be picked up in 110 FSTB. Multiple Choice /90 Short answers / 10 Total 100

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page2 1.Triacylglycerols a.do not contain any chiral centers b.have only one acyl chain c.are molecules with a strong flavor d.contain three fatty acid groups attached to glycerol@ e.contain only single bonds 2.Cholesterol a.is a lipid b.has different molecular structures depending on whether it is"good"or"bad" cholesterol 且in e.answer a and b 3.In general,fatty acid groups on triglycerides found naturally in foods &.aenaomsmmoeahnioiceatbobieRond c are branched e None ration 4.Which of the following are NOT true of low density lipoprotein(LDL)particles? inids in the blood LDL choleste ol levels are associated with risk of heart disease d.LDL cholesterol levels are influenced by the ty e.All of the above answers are true of LDL particles 5.The major portion of food lipids are made up of z acids c.phenolic compounds d.monoglycerides e.None of the above
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 2 1. Triacylglycerols a. do not contain any chiral centers b. have only one acyl chain c. are molecules with a strong flavor d. contain three fatty acid groups attached to glycerol @ e. contain only single bonds 2. Cholesterol a. is a lipid b. has different molecular structures depending on whether it is "good" or "bad" cholesterol c. contains a fused ring structure d. answer a and c @ e. answer a and b 3. In general, fatty acid groups on triglycerides found naturally in foods a. contain an even number of carbons @ b. never contain more than one double bond c. are branched d. contain double bonds primarily in the trans configuration e. None of the above answers are generally true for natural fatty acid groups 4. Which of the following are NOT true of low density lipoprotein (LDL) particles? a. They contain cholesterol b. They transport lipids in the blood c. Higher LDL cholesterol levels are associated with risk of heart disease d. LDL cholesterol levels are influenced by the type of triglycerides you eat e. All of the above answers are true of LDL particles @ 5. The major portion of food lipids are made up of a. free fatty acids b. triglycerides @ c. phenolic compounds d. monoglycerides e. None of the above

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 3 The following 3 questions refer to the structure below. 0 A H2C-0- 9 H2C-0 6.This molecule contains an 18:1 fatty acid group at the &ma。 c.sn-3 position d.sn-1 and sn-3 position e.none of the above 7.Fatty acid group A is palmitic acid 8.This molecule is structurally similar to~80%of the triglycerides in a.lard b.olive oil c.tallow d.cocoa butter@ e.all of the above 9.Which of the following is true of photooxidation? en into the singlet state e.All of the above are true of photooxidation@
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 3 The following 3 questions refer to the structure below. 6. This molecule contains an 18:1 fatty acid group at the a. sn-1 position b. sn-2 position @ c. sn-3 position d. sn-1 and sn-3 position e. none of the above 7. Fatty acid group A is a. caprylic acid b. palmitic acid @ c. oleic acid d. linoleic acid e. erucic acid 8. This molecule is structurally similar to ~80% of the triglycerides in a. lard b. olive oil c. tallow d. cocoa butter @ e. all of the above 9. Which of the following is true of photooxidation? a. It is a mechanism for initiating lipid oxidation b. It involves capture of light energy by sensitizers c. It involves excitation of oxygen into the singlet state d. It is delayed by storing lipids in the dark e. All of the above are true of photooxidation @ C C H2C O C HC O H2C O O O O A

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 4 The following 3 questions refer to the graph below: 60 50 40 30 osn-1 asn-2 30 sn-3 10 0 C16:0C18:0C18:1C18:2 Fatty Acid Group 10.Based on this graph,the fatty acid groups overall could best be characterized as primarily shorhn primarily unsaturated e. 11.Unsaturated fatty acid groups in this lipid are primarily found at a.sn-1 position b.sn-2 position@ c.sn-3 position e. none of the 12.It is most likely that this graph characterizes the triglycerides in c.Milk fat d.Cocoa butter e.All of the above are equally likely
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 4 The following 3 questions refer to the graph below: 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 C16:0 C18:0 C18:1 C18:2 Fatty Acid Group sn-1 sn-2 sn-3 all 10. Based on this graph, the fatty acid groups overall could best be characterized as a. primarily saturated b. primarily short-chain c. primarily unsaturated @ d. primarily polyunsaturated e. answer a and b 11. Unsaturated fatty acid groups in this lipid are primarily found at a. sn-1 position b. sn-2 position @ c. sn-3 position d. sn-1 and sn-3 position e. none of the above 12. It is most likely that this graph characterizes the triglycerides in a. Peanut oil @ b. Lard c. Milk fat d. Cocoa butter e. All of the above are equally likely

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 5 The following 2 questions refer to the free fatty acids below. A HO B HO HO HO 13.Which of these fatty acids would have the strongest flavor? a.Molecule A b.Molecule B c.Molecule C@ d.Molecule D e.All of these molecules would have equal flavor 14.Which of the following melting point (M.P.)relations are true for these molecules? a.M.P.(A)=M.P.(D) M.P.(A)<M.P.(B) M.P.(D)<M.P.(A 15.Lipid molecules are defined as amines lar,poc
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 5 The following 2 questions refer to the free fatty acids below. 13. Which of these fatty acids would have the strongest flavor? a. Molecule A b. Molecule B c. Molecule C @ d. Molecule D e. All of these molecules would have equal flavor 14. Which of the following melting point (M.P.) relations are true for these molecules? a. M.P.(A) = M.P.(D) b. M.P.(A) < M.P.(B) c. M.P.(D) < M.P.(A) d. M.P.(C) < M.P.(D) @ e. M.P.(A) = M.P.(B) 15. Lipid molecules are defined as a. polyhydroxy compounds b. cyclic compounds c. amines d. molecules with polar and charged characteristics e. nonpolar, poorly water-soluble molecules @ C O HO C O HO C O HO C O HO A B C D

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 6 The following 3 questions refer to the digestion and absorption of the triglyceride below in the human gastrointestinal tract. H2C-0-C 0 入人B HC一O一0 0 HC-O 入入入入 6 g choices is most likely to be sent directly into the ssembly into chylo a.Free fatty acid A@ b.Free fatty acid B c.Free fatty acid C d.A monoglyceride containing fatty acid B e Ans wer a and care equally likely 17.The fatty acid groups that are likely to be cleaved first during digestion are a.groups Aand C@ b.groups A and B c.group B only d.groups B and C e.groups A,B and C equally a.group A 6 group B@ group C equally likely Positions of fatty acid groups are never conserved after e gro
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 6 The following 3 questions refer to the digestion and absorption of the triglyceride below in the human gastrointestinal tract. 16. After hydrolysis, which of the following choices is most likely to be sent directly into the blood stream, without assembly into chylomicrons? a. Free fatty acid A @ b. Free fatty acid B c. Free fatty acid C d. A monoglyceride containing fatty acid B e. Answer a and c are equally likely 17. The fatty acid groups that are likely to be cleaved first during digestion are a. groups A and C @ b. groups A and B c. group B only d. groups B and C e. groups A, B and C equally 18. Which fatty acid group is most likely to be found in the same triglyceride position before absorption, and after reassembly into triglycerides carried in chylomicrons? a. group A b. group B @ c. group C d. groups A and C are equally likely e. Positions of fatty acid groups are never conserved after absorption O O O H2C O HC O H2C O C C C A B C

EST 100A Midterm 2:November 22 2004 Page 7 19.Which of the following does NOT catalyze lipid hydrolysis? a.Lipases b.Base ll of th 20.A fat mimetic is (at) c.alipid molecule like Olestra d.an antioxidant e.none of the above@ 21.When compared to a B'or a crystal,a B crystal form ordered ost e ng point d.a e.answers a,b and c 22.Which of the following would NOT contribute calories? Olestra@ d.Hydrogenated fats and oils e.Answer c and d would not contribute calories 23.Conjugated double bonds hl on polym d.are found on saturated fatty acid chains e.are formed as part of lipid hydrolysis reactions 24.Why are hydrogenation reactions used? a.To make triglycerides more digestible 6 To rem double bonds To remove chol esterol e.To make oils more stable to oxidation
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 7 19. Which of the following does NOT catalyze lipid hydrolysis? a. Lipases b. Base c. Acid d. All of the above catalyze lipid hydrolysis @ e. None of the above catalyze lipid hydrolysis 20. A fat mimetic is a. based on lipid (fat) b. an oxidized lipid c. a lipid molecule like Olestra d. an antioxidant e. none of the above @ 21. When compared to a β' or α crystal, a β crystal form a. is the most ordered @ b. has the lowest melting point c. most easily nucleates d. answer a and b e. answers a, b and c 22. Which of the following would NOT contribute calories? a. Triglycerides b. Free fatty acids c. Olestra @ d. Hydrogenated fats and oils e. Answer c and d would not contribute calories 23. Conjugated double bonds a. occur only when monounsaturated fatty acid chains are oxidized b. consist of two double bonds separated by a methylene (CH2) group c. help to stabilize lipid free radicals on polyunsaturated fatty acids @ d. are found on saturated fatty acid chains e. are formed as part of lipid hydrolysis reactions 24. Why are hydrogenation reactions used? a. To make triglycerides more digestible b. To remove trans double bonds c. To create Olestra d. To remove cholesterol e. To make oils more stable to oxidation @

EST 100A Midterm 2:November 22.2004 Page 8 25.Lipid oxidation can be catalyzed by a.Singlet oxygen b.Metal ions c.Polyphenoloxidase d.Answer a and b only@ e.All of answers a,b and c help catalyze oxidation 26.Why are phenolic compounds good antioxidants? a.Because they are very hydrophilic b.Because they exhibit a high degree of steric hindrance Because they form resonance structures with an unpaired electron@ ave an antioxidant factor that is less than one(AF <1) e. Answer a and b 27.The difference in texture between cocoa butter and lard is due primarily to a.a more homogeneous distribution of triglyceride structures in cocoa butter compared to lard@ b.the much larger quantities of unsaturated fatty acid gro oups in cocoa butter c.the fact tha ard has a sharp melting point that is much lower than cocoa butter's d melting point larger qua ntities of short chain fatty acid groups in lard e 28.The first step in saponification is ceophif free radic cal tt he triglyceride by abase a prot ff of the nydrocarbon chair 29.Transformation of a lipid crystal from an a form to a B form is a process called .o & sm e conjugat 30.Why are fish oils susceptible to oxidation? They are rich in short-chain saturated fatty acid groups interrupted double bonds rh and c@ zed by resonance e.Answe r a and c
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 8 25. Lipid oxidation can be catalyzed by a. Singlet oxygen b. Metal ions c. Polyphenoloxidase d. Answer a and b only @ e. All of answers a, b and c help catalyze oxidation 26. Why are phenolic compounds good antioxidants? a. Because they are very hydrophilic b. Because they exhibit a high degree of steric hindrance c. Because they form resonance structures with an unpaired electron @ d. Because they have an antioxidant factor that is less than one (AF < 1) e. Answer a and b 27. The difference in texture between cocoa butter and lard is due primarily to a. a more homogeneous distribution of triglyceride structures in cocoa butter compared to lard @ b. the much larger quantities of unsaturated fatty acid groups in cocoa butter c. the fact that lard has a sharp melting point that is much lower than cocoa butter's melting point d. the much larger quantities of short chain fatty acid groups in lard e. the large amounts of trans fats found naturally in cocoa butter 28. The first step in saponification is a. formation of a free radical b. nucleophilic attack of the triglyceride by a base @ c. loss of a proton off of the hydrocarbon chain d. formation of a carbocation e. all of the above 29. Transformation of a lipid crystal from an α form to a β form is a process called a. oxidation b. nucleation c. polymorphism @ d. hydrogenation e. conjugation 30. Why are fish oils susceptible to oxidation? a. They are rich in short-chain saturated fatty acid groups b. Their triglycerides contain multiple, methylene interrupted double bonds c. They form lipid free radicals that are stabilized by resonance d. Answer b and c @ e. Answer a and c

FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 9 31.For triglycerides with all three fatty acid groups identical,which of the crystal structures below is most likely =毛E车 &83aletuciucl c.Crystal structure III d.Crystal structure IV@ e.Triglycerides do not form crystals 32.Which of the following raises the melting point of triglycerides? a.high temperatures b.steric interactions between bulky groups c.increased effects of entropy d.strong Van der Waals attraction between lipids@ e.the presence of rigid double bonds
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 9 31. For triglycerides with all three fatty acid groups identical, which of the crystal structures below is most likely? a. Crystal structure I b. Crystal structure II c. Crystal structure III d. Crystal structure IV @ e. Triglycerides do not form crystals 32. Which of the following raises the melting point of triglycerides? a. high temperatures b. steric interactions between bulky groups c. increased effects of entropy d. strong Van der Waals attraction between lipids @ e. the presence of rigid double bonds I III IV II
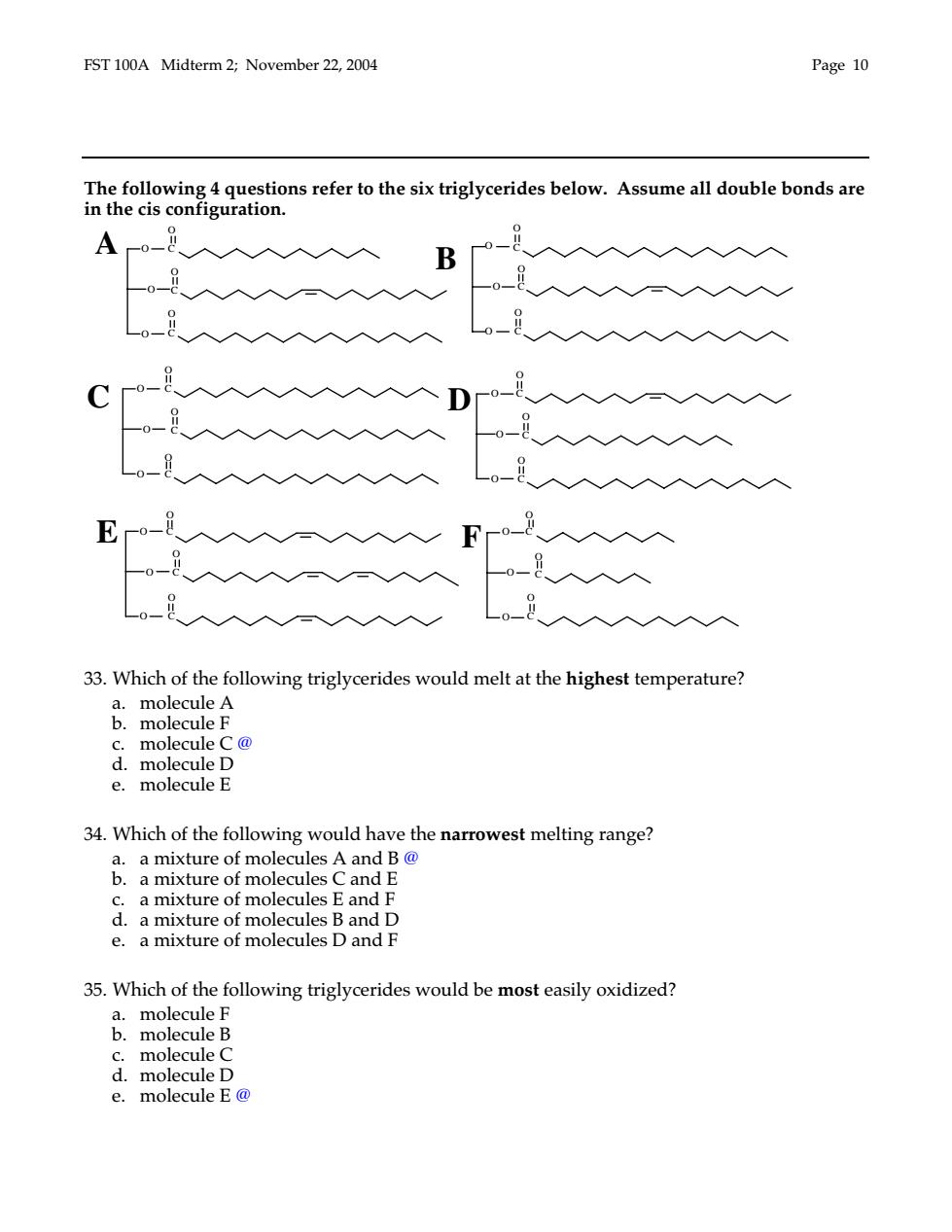
FST 100A Midterm 2;November 22,2004 Page 10 The following 4 questions refer to the six triglycerides below.Assume all double bonds are in the cis configuration. B ro- F-o -8 33.Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the highest temperature? c.molecule C@ d.molecule D e.molecule E 34.Which of the following would have the narrowest melting range? a.a mixture of molecules A and B@ b.a mixture of molecules Cand E c.a mixture of molecules E and F d.a mixture of molecules B and D e.a mixture of molecules D and F 35.Which of the following triglycerides would be most easily oxidized? a.molecule F b.molecule B c.molecule C d.molecule D e.molecule E@
FST 100A Midterm 2; November 22, 2004 Page 10 The following 4 questions refer to the six triglycerides below. Assume all double bonds are in the cis configuration. 33. Which of the following triglycerides would melt at the highest temperature? a. molecule A b. molecule F c. molecule C @ d. molecule D e. molecule E 34. Which of the following would have the narrowest melting range? a. a mixture of molecules A and B @ b. a mixture of molecules C and E c. a mixture of molecules E and F d. a mixture of molecules B and D e. a mixture of molecules D and F 35. Which of the following triglycerides would be most easily oxidized? a. molecule F b. molecule B c. molecule C d. molecule D e. molecule E @ C O F C O O O O C O C O O O O C O B C O C O C O D C O O O O C C O O O O C O C O C O C O E C O O O O C O A C O O O O C O