Retinal Disease Jingfa Zhang,Ph.D. Tongji Eye Institute,Tongji University School of Medicine
Retinal Disease Jingfa Zhang, Ph.D. Tongji Eye Institute, Tongji University School of Medicine

Outline Anatomy of the eye and the retina ● Retinal diagnostic test Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
• Anatomy of the eye and the retina • Retinal diagnostic test • Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) • Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Outline
Outline Anatomy of the eye and the retina ● Retinal diagnostic test Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
• Anatomy of the eye and the retina • Retinal diagnostic test • Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) • Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Outline
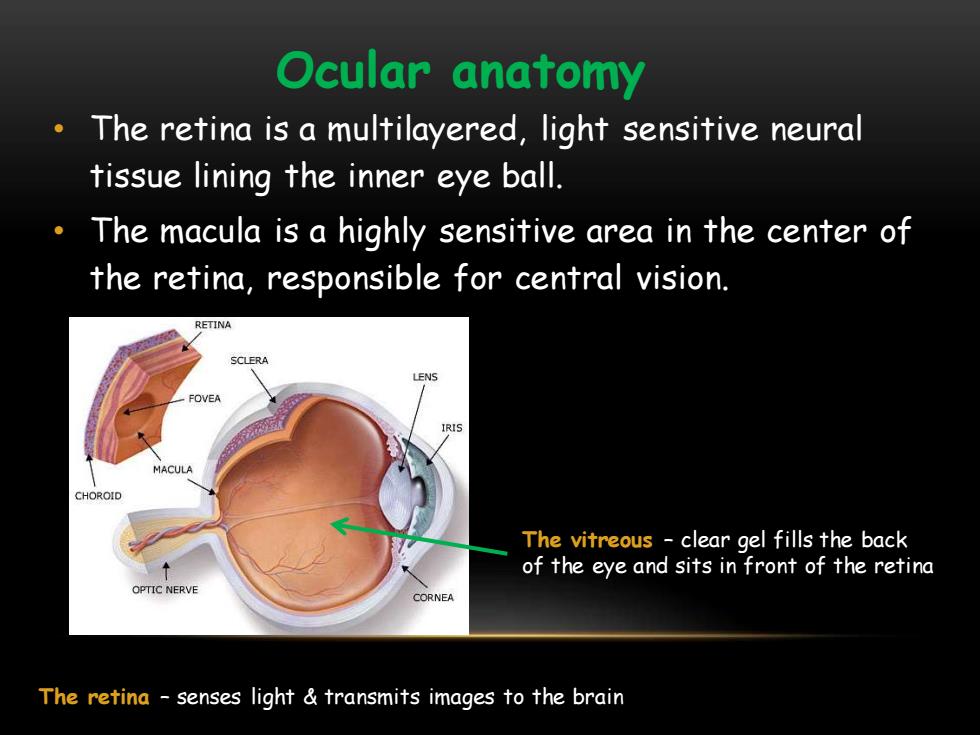
Ocular anatomy The retina is a multilayered,light sensitive neural tissue lining the inner eye ball. The macula is a highly sensitive area in the center of the retina,responsible for central vision. RETINA SCLERA NS -OVEA IRIS MACULA CHOROID The vitreous -clear gel fills the back of the eye and sits in front of the retina OPTIC NERVE CORNEA The retina -senses light transmits images to the brain
• The retina is a multilayered, light sensitive neural tissue lining the inner eye ball. • The macula is a highly sensitive area in the center of the retina, responsible for central vision. Ocular anatomy The vitreous – clear gel fills the back of the eye and sits in front of the retina The retina – senses light & transmits images to the brain
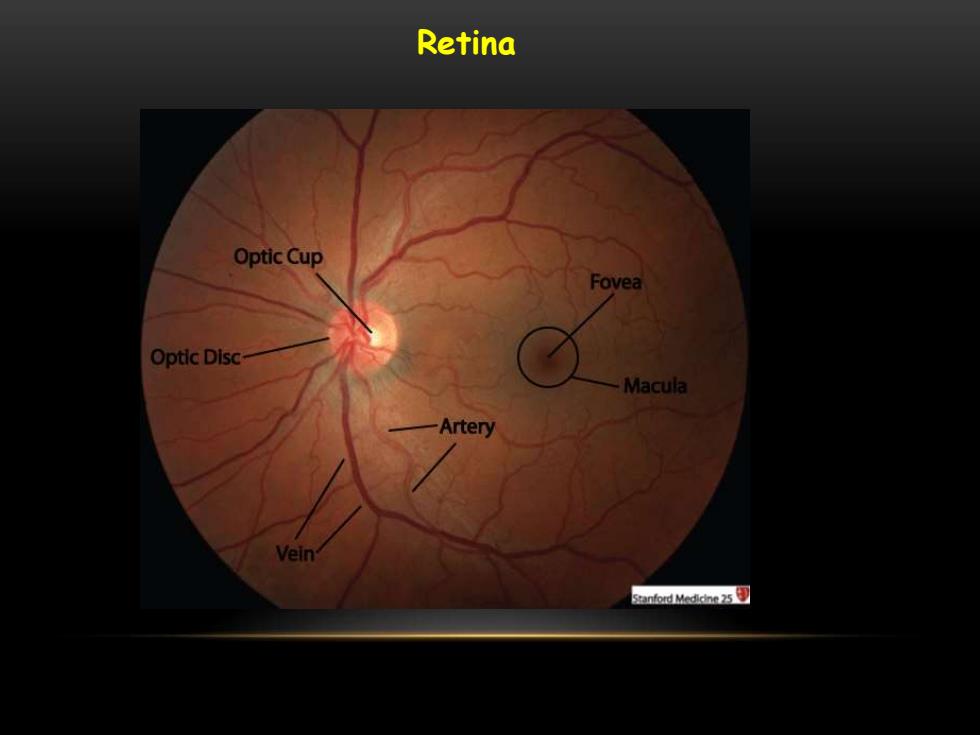
Retina Optic Cup Fovea Optic Disc Macula Artery Vein Stanford Medidine 5
Retina
Retinal histology ·Ten layers ·Four cell types: ·Wacula/.Fovea ·Optic nerve head
Retinal histology • Ten layers • Four cell types: • Macula/Fovea • Optic nerve head
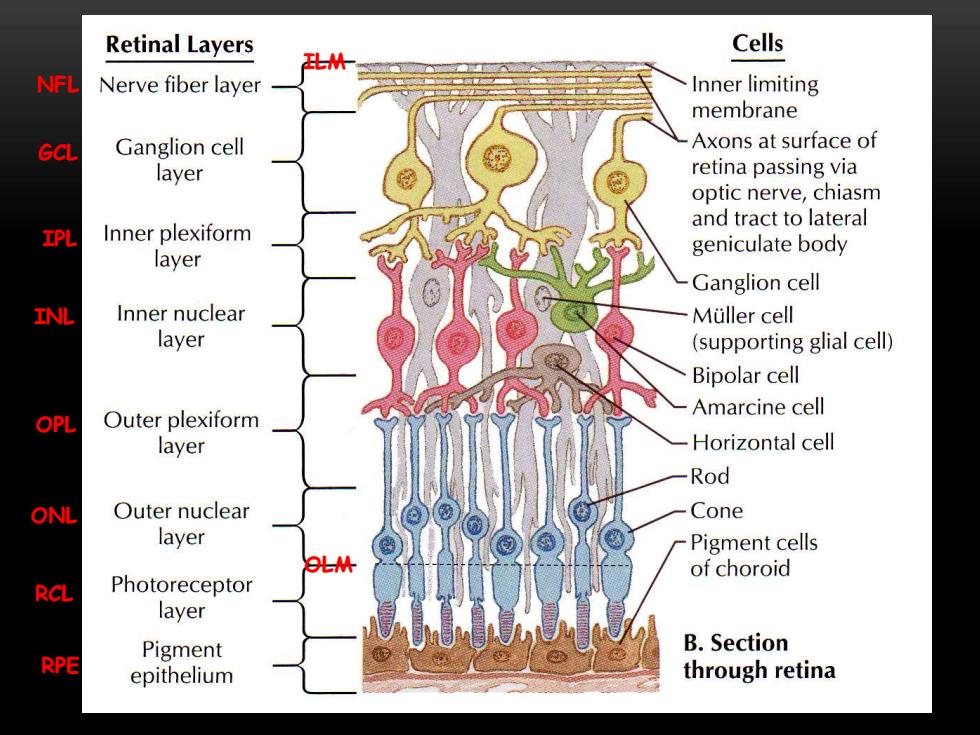
Retinal Layers Cells NFL Nerve fiber layer Inner limiting membrane GCL Ganglion cell Axons at surface of layer retina passing via optic nerve,chiasm and tract to lateral IPL Inner plexiform geniculate body layer Ganglion cell INL Inner nuclear Muller cell layer (supporting glial cell) Bipolar cell OPL Outer plexiform Amarcine cell layer Horizontal cell Rod ONL Outer nuclear Cone layer Pigment cells OLM of choroid RCL Photoreceptor layer Pigment B.Section RPE epithelium through retina
ILM NFL GCL IPL INL OPL ONL OLM RCL RPE

Ten layers nerve fiber layer Internal limiting membrane inner plexiform layer ganglion cell inner nuclear layer outer plexiform layer 8吧 outer nuclear layer external limiting membrane rods and cones pigmented epithelium choroid lamina vitrea sclera
Ten layers Internal limiting membrane
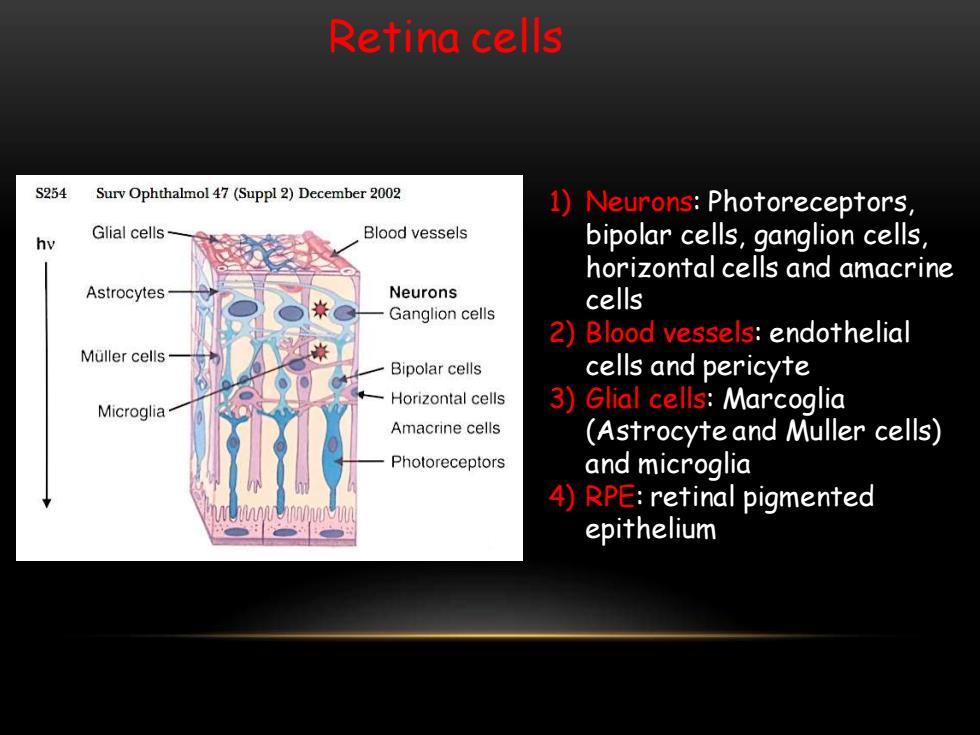
Retina cells S254 Surv Ophthalmol 47(Suppl 2)December 2002 1)Neurons:Photoreceptors, Glial cells Blood vessels hv bipolar cells,ganglion cells, horizontal cells and amacrine Astrocytes Neurons cells Ganglion cells 2)Blood vessels:endothelial Muller cells Bipolar cells cells and pericyte Horizontal cells Microglia 3)Glial cells:Marcoglia Amacrine cells (Astrocyte and Muller cells) Photoreceptors and microglia 4)RPE:retinal pigmented epithelium
Retina cells 1) Neurons: Photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells and amacrine cells 2) Blood vessels: endothelial cells and pericyte 3) Glial cells: Marcoglia (Astrocyte and Muller cells) and microglia 4) RPE: retinal pigmented epithelium
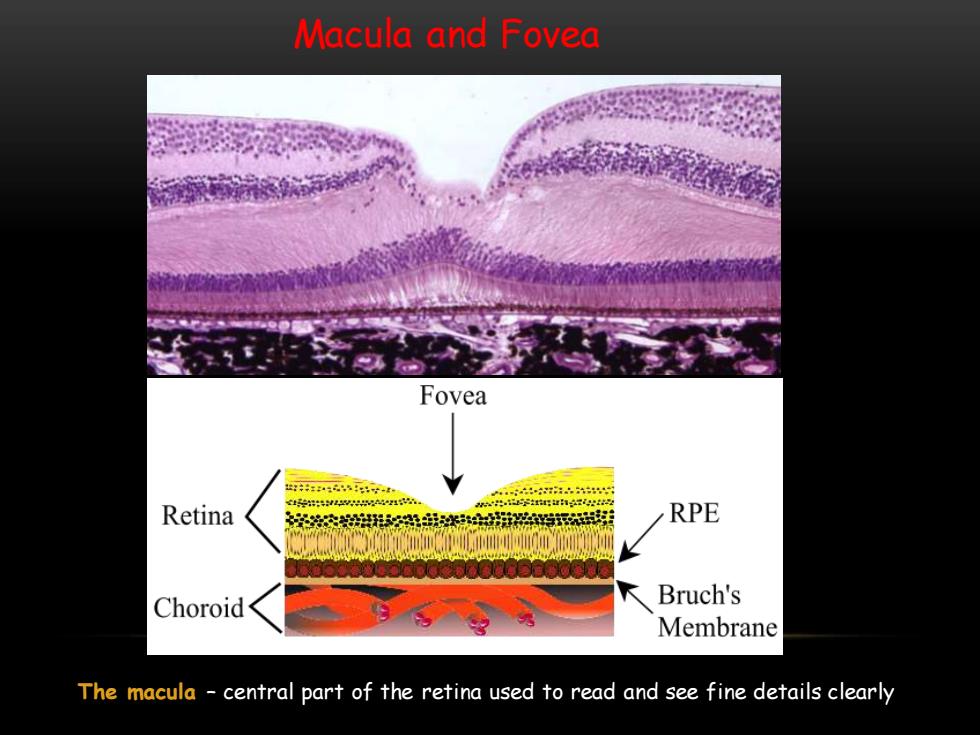
Macula and Fovea Fovea 4- Retina RPE Choroid Bruch's Membrane The macula central part of the retina used to read and see fine details clearly
Macula and Fovea The macula – central part of the retina used to read and see fine details clearly