
Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue
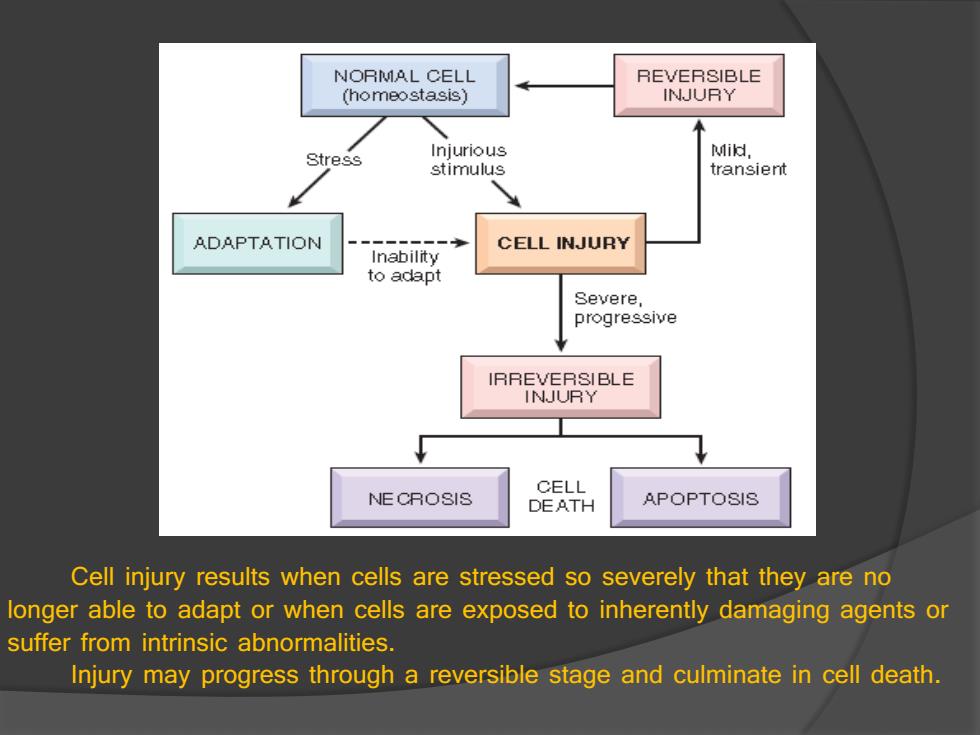
NORMAL CELL REVERSIBLE (homeostasis) INJURY Stress Injurious Mi以, stimulus transient ADAPTATION CELL INJURY Inability to adapt Severe, progressive IRREVERSIBLE INJURY CELL NE CROSIS DEATH APOPTOSIS Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death
Cell injury results when cells are stressed so severely that they are no longer able to adapt or when cells are exposed to inherently damaging agents or suffer from intrinsic abnormalities. Injury may progress through a reversible stage and culminate in cell death

CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) o Chemical Agents o Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors oNutritional Imbalances o Physical Agents o Aging
CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Oxygen Deprivation (Hypoxia) Chemical Agents Infectious Agents Immunologic Reactions Genetic Factors Nutritional Imbalances Physical Agents Aging

THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY E.g. myocardial cells Reversible i Irreversible cell injury cell injury Ultrastructural Light changes microscopic √noncontractile changes Cell Cell death after 1 to 2 function minutes of ischemia \Grass morphologic dead after 2 to changes 3 hours by electron microscopy by light DURATION OF INJURY microscopy for 6 to 12 hours The relationship among cellular function,cell death,and the morphologic changes of cell injury
THE MORPHOLOGY OF CELL AND TISSUE INJURY The relationship among cellular function, cell death, and the morphologic changes of cell injury. E.g. myocardial cells noncontractile after 1 to 2 minutes of ischemia dead after 2 to 3 hours by electron microscopy by light microscopy for 6 to 12 hours

>Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments
►Reversible Injury of Cell and Tissue Hydropic degeneration Fatty change Hyaline degeneration Myxoid degeneration Deposition of amyloid Intracellular accumulation of glycogen Deposition of pathological pigments

Cellular swelling O Gross:when it affects many cells,it causes pallor,increase in size and weight of the affected organ,and loss of normal glistening translucence -“boiled meat”appearance O Microscope:The parenchyma cells are enlarged in various degrees and crowded together,and the cytoplasm is translucent and stains more lightly
Cellular swelling Gross: when it affects many cells, it causes pallor, increase in size and weight of the affected organ, and loss of normal glistening translucence – “boiled meat” appearance Microscope: The parenchyma cells are enlarged in various degrees and crowded together, and the cytoplasm is translucent and stains more lightly

Ballooning change (hydropic degeneration) in hepatocytes
Ballooning change (hydropic degeneration) in hepatocytes
w√Fatty change Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells o In hypoxic injury and in various forms of toxic or metabolic injury Manifested by the appearance of small or large lipid vacuoles in the cytoplasm
Fatty change Abnormal accumulation of triglycerides within parenchymal cells In hypoxic injury and in various forms of toxic or metabolic injury Manifested by the appearance of small or large lipid vacuoles in the cytoplasm

1.Fatty liver --Causes of fatty liver Accumulation of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of liver cells occurs in the following conditions: (1)When there is increased mobilization of adipose tissue; (2)When the rate of conversion of fatty acids to triglycerides is increased; (3)When oxidation of triglycerides to acetyl-CoA and ketone bodies is decreased; (4)When synthesis of lipid acceptor proteins is deficient
1. Fatty liver --- Causes of fatty liver Accumulation of triglycerides in the cytoplasm of liver cells occurs in the following conditions: (1) When there is increased mobilization of adipose tissue; (2) When the rate of conversion of fatty acids to triglycerides is increased; (3) When oxidation of triglycerides to acetyl-CoA and ketone bodies is decreased; (4) When synthesis of lipid acceptor proteins is deficient
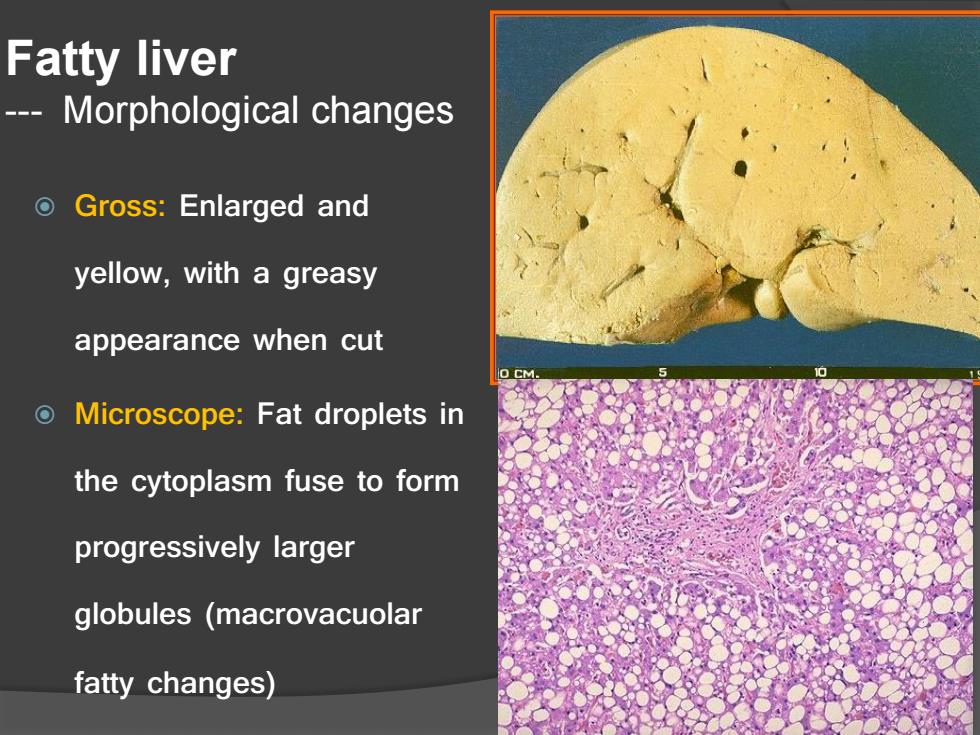
Fatty liver Morphological changes Gross:Enlarged and yellow,with a greasy appearance when cut Microscope:Fat droplets in the cytoplasm fuse to form progressively larger globules (macrovacuolar fatty changes)
Fatty liver --- Morphological changes Gross: Enlarged and yellow, with a greasy appearance when cut Microscope: Fat droplets in the cytoplasm fuse to form progressively larger globules (macrovacuolar fatty changes)