
CHAPTER 16 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM JIANG,WENXIA Department of Pathology Tongji University School of Medicine
CHAPTER 16 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM JIANG, WENXIA Department of Pathology Tongji University School of Medicine

厂 Disorders of the Nervous Systems *General disorders 。Infections 。Neoplasms 。Vascular diseases 。Trauma Congenital malformations 。Metabolic disorders Specific disorders 。Diseases of myelin Degenerative diseases
Disorders of the Nervous Systems General disorders Infections Neoplasms Vascular diseases Trauma Congenital malformations Metabolic disorders Specific disorders Diseases of myelin Degenerative diseases

The General Characteristics of the Nervous System Disorders 1 Location of lesions is closely relation to dysfunction 2 The same disorders in the different regions will lead to different syndromes and effects 3 Cells of the nervous systems react straitlaced to different pathogenic factors->the same lesions will be present in different disorders
The General Characteristics of the Nervous System Disorders ① Location of lesions is closely relation to dysfunction ② The same disorders in the different regions will lead to different syndromes and effects ③ Cells of the nervous systems react straitlaced to different pathogenic factors → the same lesions will be present in different disorders

4 The effects of some certain anatomic features are two sides of coin e.g.,skull (the rigid confines): protects the brain from trauma and noxious elements in the external environment >renders the brain vulnerable to expansile intracranial lesions,raise intracranial pressure-compromise the function of the organ,cerebral hernia
④ The effects of some certain anatomic features are two sides of coin e.g., skull (the rigid confines): protects the brain from trauma and noxious elements in the external environment renders the brain vulnerable to expansile intracranial lesions, raise intracranial pressure → compromise the function of the organ, cerebral hernia

5 Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier and Virchow-Robin space not only act as a natural line of defense,but also prevent the inflammation to penetrate to the parenchyma 6 There is no resident lymphoid tissues,the lymphocytes are all conveyed by the blood circulation
⑤ Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier and Virchow-Robin space not only act as a natural line of defense, but also prevent the inflammation to penetrate to the parenchyma ⑥ There is no resident lymphoid tissues, the lymphocytes are all conveyed by the blood circulation

Section I The Cells and It's Basic Changes of Nervous System I.Neuron The neuron is a pyramidal cell with a rounded nucleus and prominent nucleolus. The granularity of the cytoplasm is imparted by rough endoplasmic reticulum(Nissl substance)
Section I The Cells and It’s Basic Changes of Nervous System I. Neuron The neuron is a pyramidal cell with a rounded nucleus and prominent nucleolus. The granularity of the cytoplasm is imparted by rough endoplasmic reticulum (Nissl substance)

Basic Changes of Neuron: (I)Acute injury Neuron necrosis (red neuron,ghost cell) Neuronophagia (Il )Simple neuronal atrophy e.g.Neuronal transsynaptic degeneration (Ill)Central chromatolysis(Disapearance of central Nissl body )and Waller degeneration (IV)Forming of inclusions e.g.Negri body (V)Abnormalities of the structural proteins e.g.neurofibrillary tangle-Alzheimer disease Lewy body formation-Parkinson disease
Basic Changes of Neuron: ( I ) Acute injury Neuron necrosis (red neuron, ghost cell) Neuronophagia ( II ) Simple neuronal atrophy e.g.Neuronal transsynaptic degeneration (III) Central chromatolysis (Disapearance of central Nissl body ) and Waller degeneration (IV) Forming of inclusions e.g. Negri body (V) Abnormalities of the structural proteins e.g. neurofibrillary tangle — Alzheimer disease Lewy body formation — Parkinson disease

Red Neuron
red neuron Red Neuron
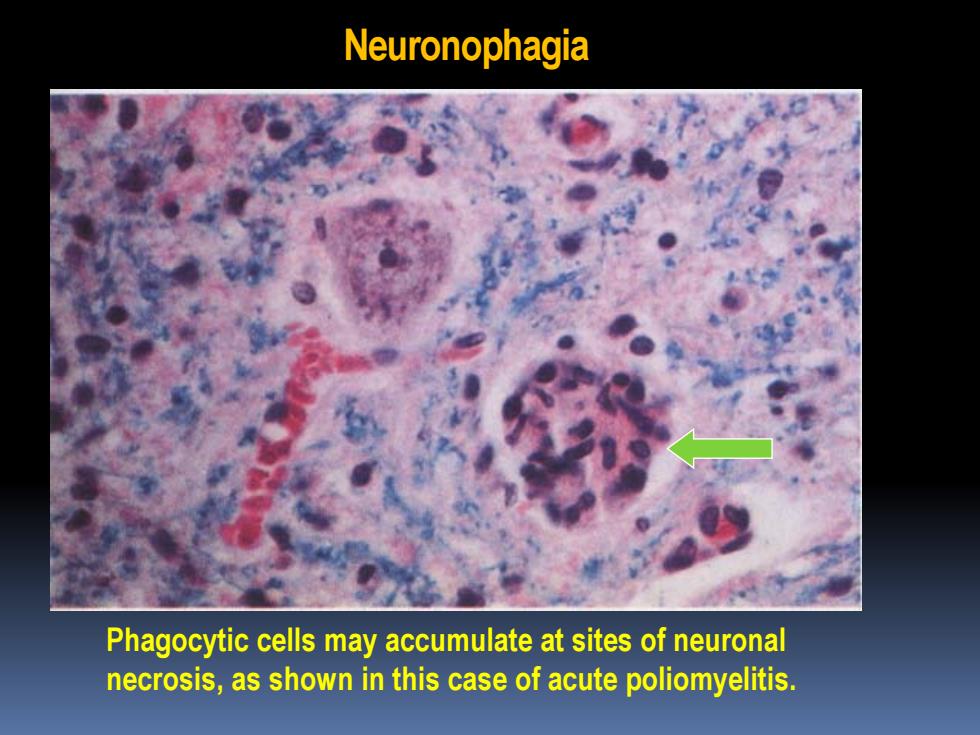
Neuronophagia Phagocytic cells may accumulate at sites of neuronal necrosis,as shown in this case of acute poliomyelitis
Neuronophagia Phagocytic cells may accumulate at sites of neuronal necrosis, as shown in this case of acute poliomyelitis
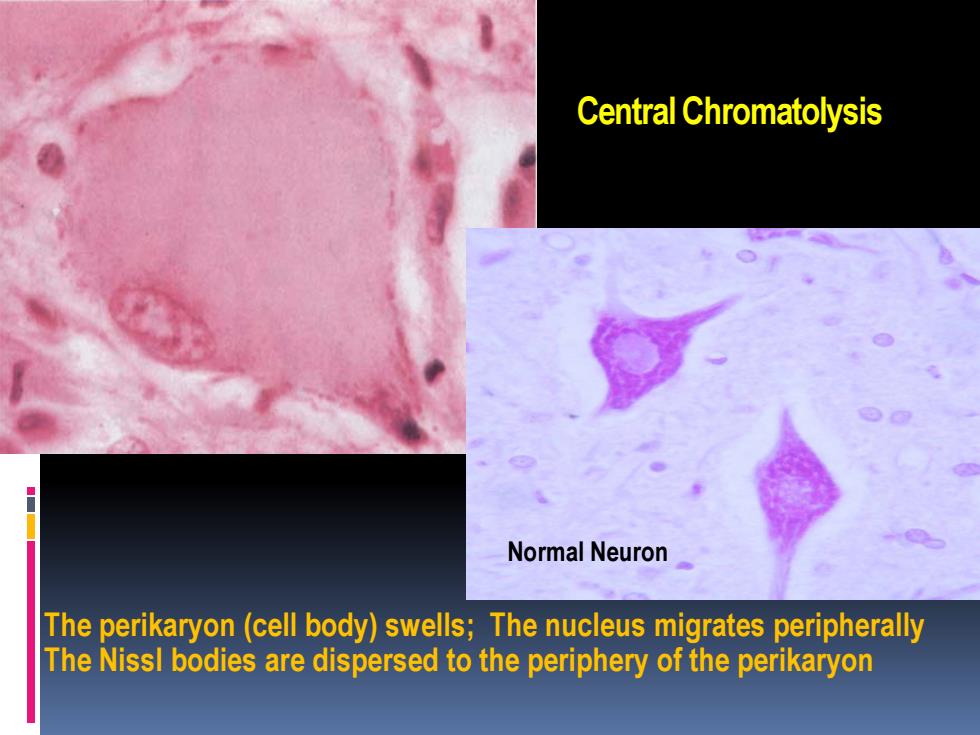
Central Chromatolysis Normal Neuron The perikaryon(cell body)swells;The nucleus migrates peripherally The Nissl bodies are dispersed to the periphery of the perikaryon
Central Chromatolysis The perikaryon (cell body) swells; The nucleus migrates peripherally The Nissl bodies are dispersed to the periphery of the perikaryon Normal Neuron