
Ocular trauma Xiaogiang Liu MD PhD Department of Ophthalmology,Shanghai Tenth People's Hospital Tongji University School of Medicine
Ocular trauma Xiaoqiang Liu MD PhD Department of Ophthalmology, Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital Tongji University School of Medicine

Epidemiology 40%of monocular blindness is related to trauma The leading cause of monocular blindness 70-80%injured are male Age range is 0-100 yrs but most are young average age 30yr Incidence of penetrating eye injuries:3.6/100000 。 Incidence of Eye injuries requiring hospitalisation: 15.2/100000
Epidemiology • 40% of monocular blindness is related to trauma – The leading cause of monocular blindness • 70-80% injured are male • Age range is 0-100 yrs but most are young – average age 30yr • Incidence of penetrating eye injuries: 3.6/100000 • Incidence of Eye injuries requiring hospitalisation: 15.2 /100000

Sources of Injury Blunt objects-30-40% rocks,fists,branches,champagne corks Motor Vehicle Injuries-9% ·Play or sports-l/3 -golf/squash balls,shoulder/elbow,bats/racquets,horse ·Falls-4% ·Sharp objects-l8% Globe involvement in 22%of cases
Sources of Injury • Blunt objects - 30-40% – rocks, fists, branches, champagne corks • Motor Vehicle Injuries - 9% • Play or sports - 1/3 – golf/squash balls, shoulder/elbow, bats/racquets, horse • Falls - 4% • Sharp objects - 18% • Globe involvement in 22% of cases

Classification Causative factors of injury -Mechanical ocular trauma -Non-mechanical ocular trauma 。Degree of injury -Microtrauma Moderate injury -Macrotrauma
Classification • Causative factors of injury – Mechanical ocular trauma – Non-mechanical ocular trauma • Degree of injury – Microtrauma – Moderate injury – Macrotrauma
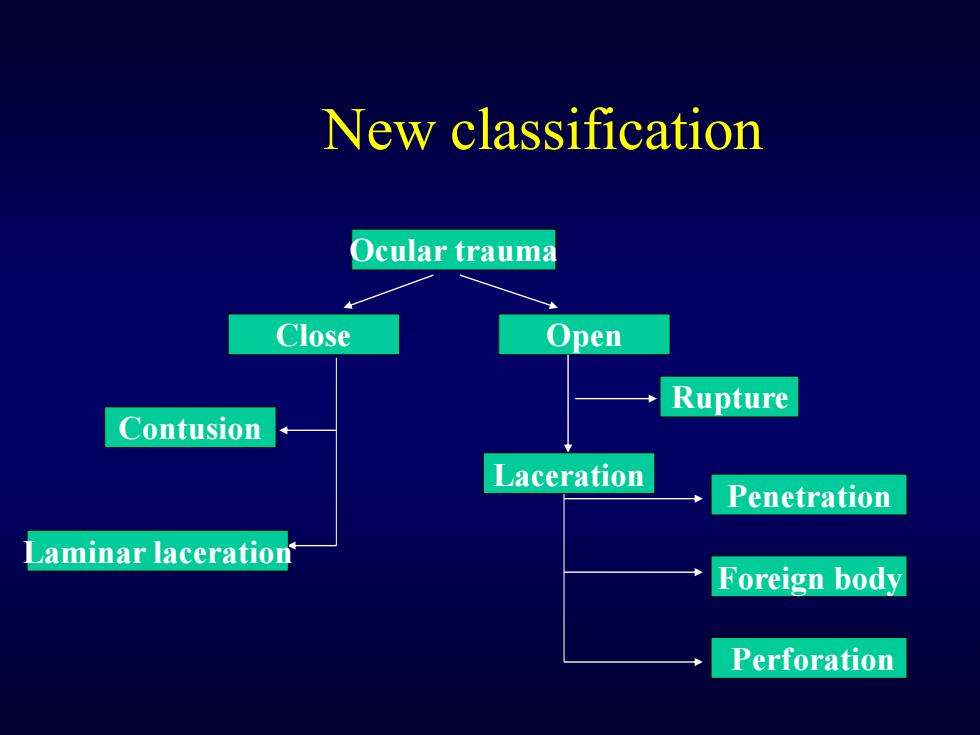
New classification Ocular trauma Close Open Rupture Contusion Laceration Penetration Laminar laceration Foreign body Perforation
New classification Ocular trauma Close Open Contusion Laminar laceration Rupture Penetration Foreign body Perforation Laceration

Common types of eye injury ●Corneal abrasions ● ● Foreign bodies ● Radiation damage Chemical damage ● Blunt injuries with hyphaema ● Penetrating injuries
Common types of eye injury • ● Corneal abrasions • ● Foreign bodies • ● Radiation damage • ● Chemical damage • ● Blunt injuries with hyphaema • ● Penetrating injuries

Assessment ■History ■Forces involved Blunt,FB?,Penetrating ■Chemical ■Acid? ■Alkali?? ■Contact allergy?
Assessment ◼History ◼Forces involved ◼Blunt, FB?, Penetrating ◼Chemical ◼Acid? ◼Alkali? ◼Contact allergy?

Examination ■Pt review are there life threatening injuries which need to be treated first? ■?brain injury,fracture ☐Facial Exam lacerations/bruising,numbness,weakness ■Ocular exam VA,lids and lacrimal system,orbital rim/orbital bones, ocular motility,globe,optic nerve
Examination ◼ Pt review ◼ are there life threatening injuries which need to be treated first? ◼?brain injury , fracture ◼ Facial Exam ◼ lacerations/bruising, numbness, weakness ◼ Ocular exam ◼ VA, lids and lacrimal system, orbital rim/orbital bones, ocular motility, globe, optic nerve

Examination ■Visual Acuity ■Skin/lids Evidence of severity of injury ■Evert lids ■?Subtarsal FB Look for fine scratches on upper cornea ■Conjunctiva ■Laceration Look carefully for scleral injury beneath ■Sub conj hemorrhage
Examination ◼ Visual Acuity ◼ Skin/lids ◼ Evidence of severity of injury ◼ Evert lids ◼ ? Subtarsal FB ◼ Look for fine scratches on upper cornea ◼ Conjunctiva ◼ Laceration ◼ Look carefully for scleral injury beneath ◼ Sub conj hemorrhage
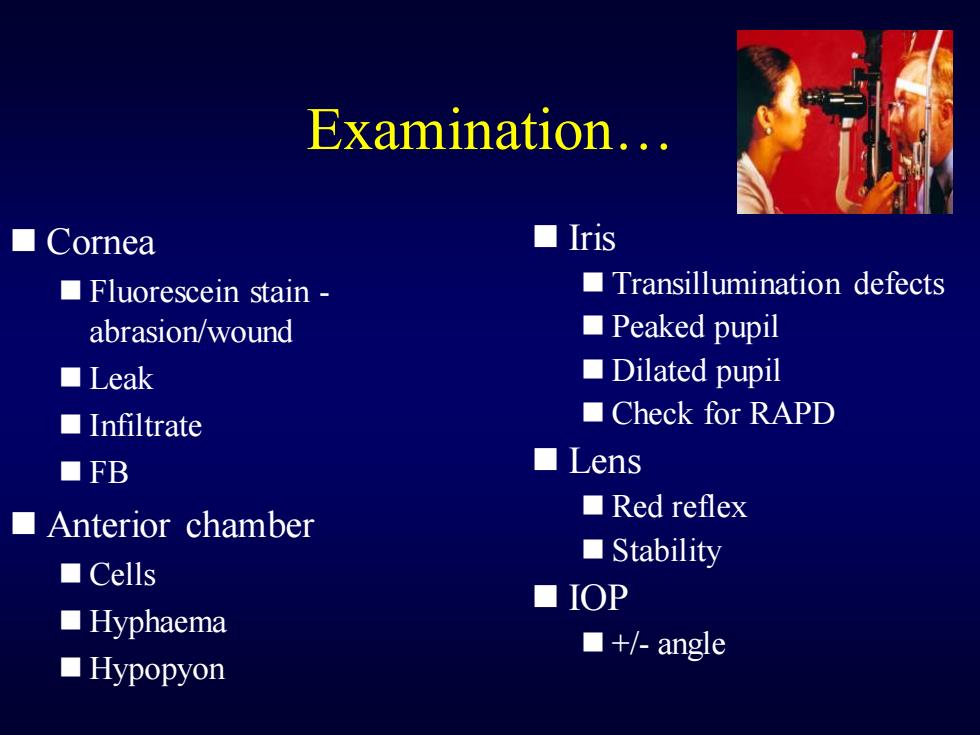
Examination... ■Cornea ■ris ■Fluorescein stain- Transillumination defects abrasion/wound ■Peaked pupil ■Leak ■Dilated pupil ■Infiltrate ■Check for RAPD ■FB ■Lens ■Anterior chamber ■Red reflex ■Stability ■Cells ■IOP ■Hyphaema ■+/-angle ■Hypopyon
Examination… ◼ Cornea ◼ Fluorescein stain - abrasion/wound ◼ Leak ◼ Infiltrate ◼ FB ◼ Anterior chamber ◼ Cells ◼ Hyphaema ◼ Hypopyon ◼ Iris ◼ Transillumination defects ◼ Peaked pupil ◼ Dilated pupil ◼ Check for RAPD ◼ Lens ◼ Red reflex ◼ Stability ◼ IOP ◼ +/- angle