
4907 悠© WATH IS PATHOLOGY? HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?
+ WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? + DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY + WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?

WATH IS PATHOLOGY? Pathology is the study(logos)of disease(pathos) PATHOLOGY is from GREEK “Patho”-Suffering Every body has “Loges”--Study a secret. + How the organs and tissues of a ILO VENTIMIGLIA healthy body PATHOLOGY (the basis of normal anatomy and physiology) C R E A T O ---change to those of a sick person IN THEATRES APRIL 18TH Pathology is the study of suffering?
WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos) + PATHOLOGY is from GREEK “Patho” --- Suffering “Loges” --- Study + How the organs and tissues of a healthy body (the basis of normal anatomy and physiology) ---change to those of a sick person Pathology is the study of suffering?

Pathology is the study ) (logos)of disease (pathos) To study the structural,biochemical and functional changes in cells,tissues and organs that underlie disease To use molecular,microbiologic, immunologic and morphologic techniques To explain the clinical manifestations of PATHOLOGY the disease +1 To provide basis for clinical care and therapy Is the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine Scientific foundation for all of medicine
Pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos) + To study the structural, biochemical and functional changes in cells, tissues and organs that underlie disease + To use molecular, microbiologic, immunologic and morphologic techniques + To explain the clinical manifestations of the disease + To provide basis for clinical care and therapy Is the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine Scientific foundation for all of medicine

Branches of pathology Pathology---Human pathology General pathology--- Anatomic pathology Systemic pathology--- Clinical pathology Experimental pathology Veterinary pathology---concerned with animal disease Phytopathology---the study of plant disease
+ Pathology---Human pathology Anatomic pathology Clinical pathology Experimental pathology + Veterinary pathology---concerned with animal disease + Phytopathology---the study of plant disease + General pathology--- + Systemic pathology--- Branches of pathology

4907 © NGJI v WATH IS PATHOLOGY? HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?
+ WATH IS PATHOLOGY? + HOW TO STUDY PATHOLOGY? + DIAGNOSTIC AND RESEARCH TECHNIQUES IN PATHOLOGY + WHAT DO PATHOLOGISTS DO?

How to study Pathology? The four aspects of a disease process that form the core of pathology--- The cause---Etiology The mechanisms of its development---Pathogenesis The structural alterations induced in the cells and organs of the body---Morphologic changes The functional consequences of the morphologic changes ---Clinical significance
How to study Pathology? The four aspects of a disease process that form the core of pathology--- + The cause --- Etiology + The mechanisms of its development --- Pathogenesis + The structural alterations induced in the cells and organs of the body --- Morphologic changes + The functional consequences of the morphologic changes --- Clinical significance

Etiology (or cause) Carl Posner Rudolf Virchow Two major classes of etiologic factors--- Acquired Infection,Nutritional, Chemical,and physical Genetic Genetic mutation All forms of organ injury start with molecular or 1821-1902 structural alteration in cells, "All disease is disease of a concept first put forth cells";"All cells come from during the 19th century by pre-existing cells". Dr.Rudolf Virchow. ----Cell Pathology
Etiology (or cause) Two major classes of etiologic factors--- Acquired Infection, Nutritional, Chemical, and physical & Genetic Genetic mutation All forms of organ injury start with molecular or structural alteration in cells, a concept first put forth during the 19th century by Dr. Rudolf Virchow. 1821-1902 “All disease is disease of cells”; “All cells come from pre-existing cells”. ----Cell Pathology
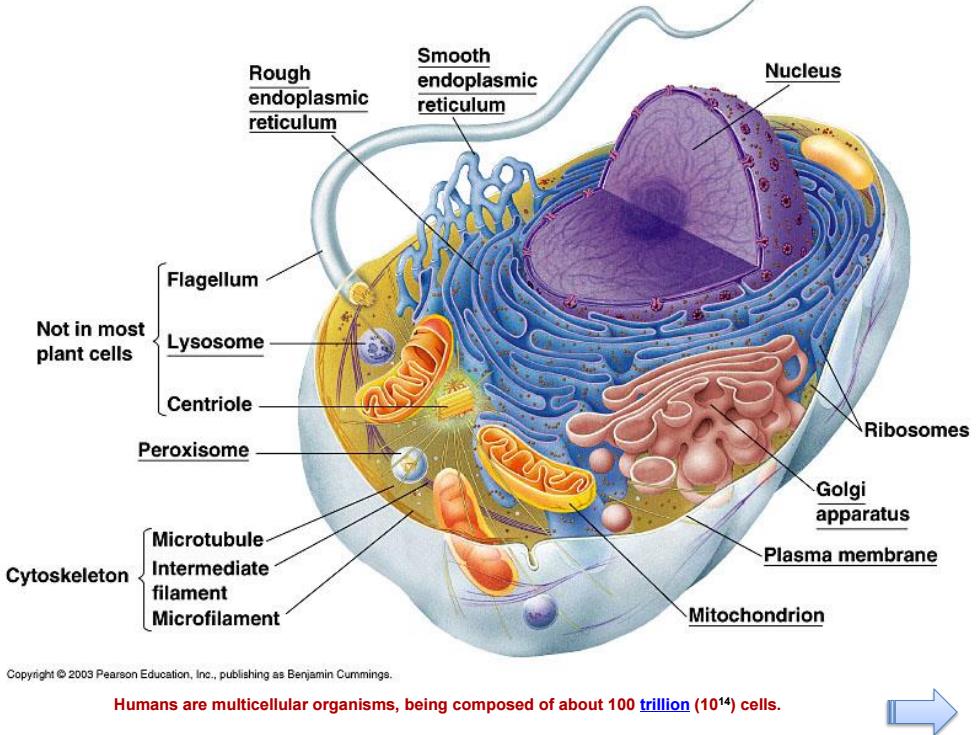
Smooth Rough endoplasmic Nucleus endoplasmic reticulum reticulum Flagellum Not in most plant cells Lysosome Centriole Ribosomes Peroxisome Golgi apparatus Microtubule Plasma membrane Cytoskeleton Intermediate filament Microfilament Mitochondrion Copyright2003 Pearson Education,Ine..publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Humans are multicellular organisms,being composed of about 100 trillion(1014)cells
Humans are multicellular organisms, being composed of about 100 trillion (1014) cells
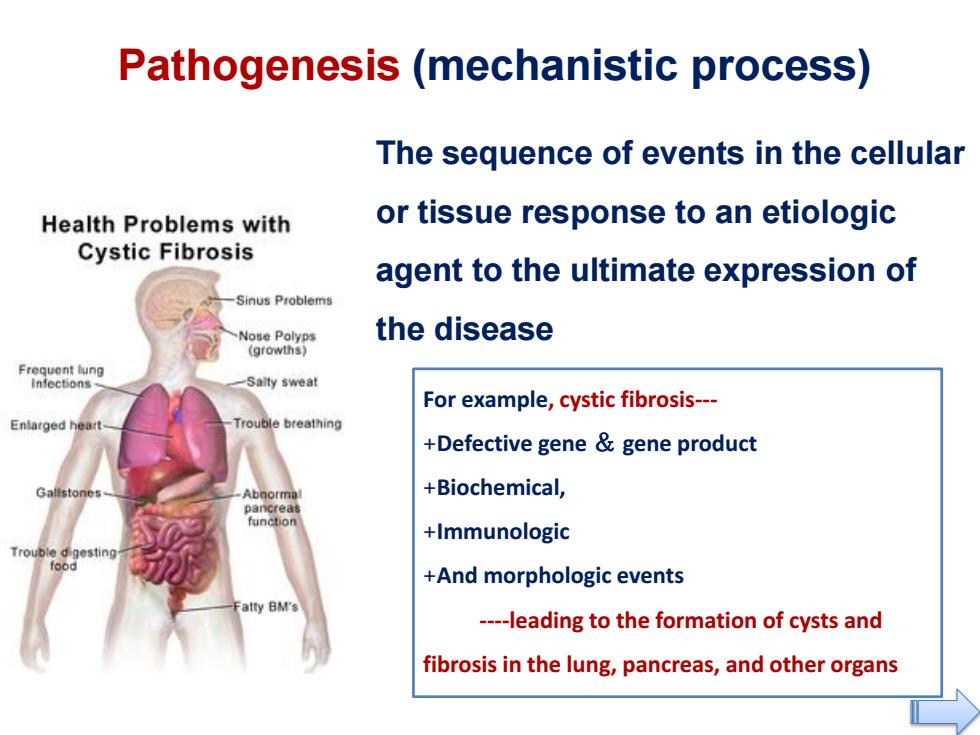
Pathogenesis (mechanistic process) The sequence of events in the cellular Health Problems with or tissue response to an etiologic Cystic Fibrosis agent to the ultimate expression of Sinus Problems Nose Polyps the disease (growths) Infections Salty sweat For example,cystic fibrosis--- Enlarged heart Trouble breathing +Defective gene gene product +Biochemical, pancreas functio +Immunologic Trouble dgesting +And morphologic events atty BM's ----leading to the formation of cysts and fibrosis in the lung,pancreas,and other organs
Pathogenesis (mechanistic process) The sequence of events in the cellular or tissue response to an etiologic agent to the ultimate expression of the disease For example, cystic fibrosis--- +Defective gene & gene product +Biochemical, +Immunologic +And morphologic events ----leading to the formation of cysts and fibrosis in the lung, pancreas, and other organs
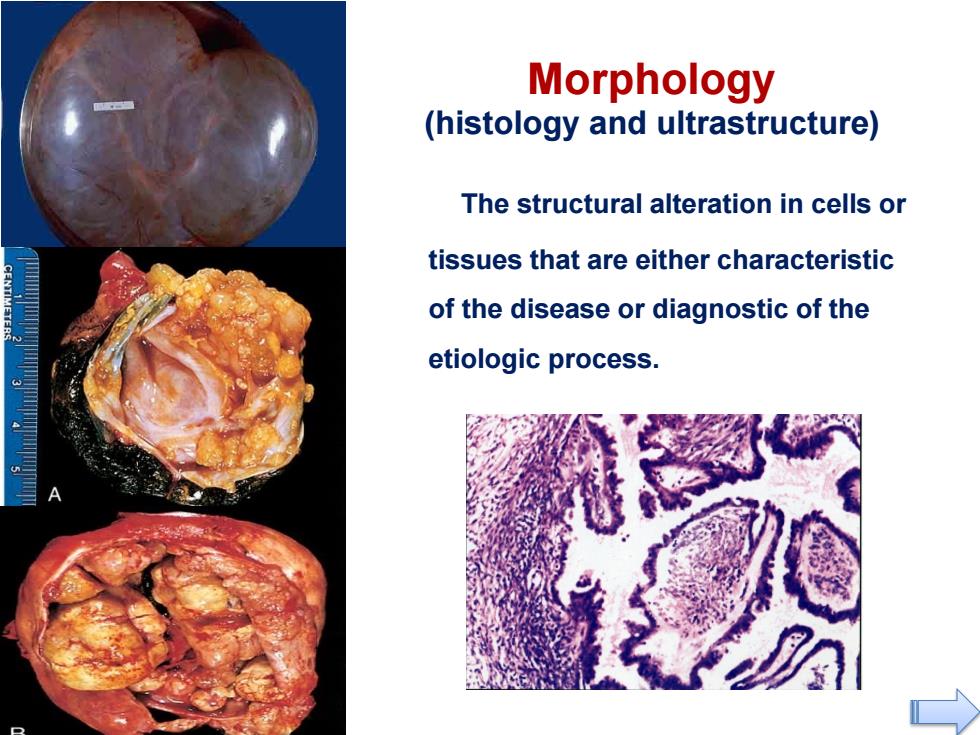
Morphology (histology and ultrastructure) The structural alteration in cells or tissues that are either characteristic of the disease or diagnostic of the etiologic process
Morphology (histology and ultrastructure) The structural alteration in cells or tissues that are either characteristic of the disease or diagnostic of the etiologic process