
生物化学 Biochemistry 李 伟 大连水产学院食品工程系 aisingioro@dlfu.edu.cn 84763553 2007
生物化学 Biochemistry 李 伟 大连水产学院食品工程系 aisingioro@dlfu.edu.cn 84763553 2007
What Is Biochemistry? • Biochemistry studies living systems to discover and understand their chemical composition and how organisms carry out life processes. 生命的化学,是在分子水平上研究生物体化学本 质及其生命活动过程中化学变化规律的科学。 • Combines biology and organic, inorganic or physical chemistry to study life processes. •Overview of Biochemistry
What Is Biochemistry? • Biochemistry studies living systems to discover and understand their chemical composition and how organisms carry out life processes. 生命的化学,是在分子水平上研究生物体化学本 质及其生命活动过程中化学变化规律的科学。 • Combines biology and organic, inorganic or physical chemistry to study life processes. •Overview of Biochemistry

Brief history of Biochemistry 现代生物化学起源于18世纪晚期, 发展于19世纪,在20世纪初期始成为 一门独立科学。它是在化学及生理学 发展的影响下产生的,故最初称为生 理化学,到1903年起称为生物化学
Brief history of Biochemistry 现代生物化学起源于18世纪晚期, 发展于19世纪,在20世纪初期始成为 一门独立科学。它是在化学及生理学 发展的影响下产生的,故最初称为生 理化学,到1903年起称为生物化学
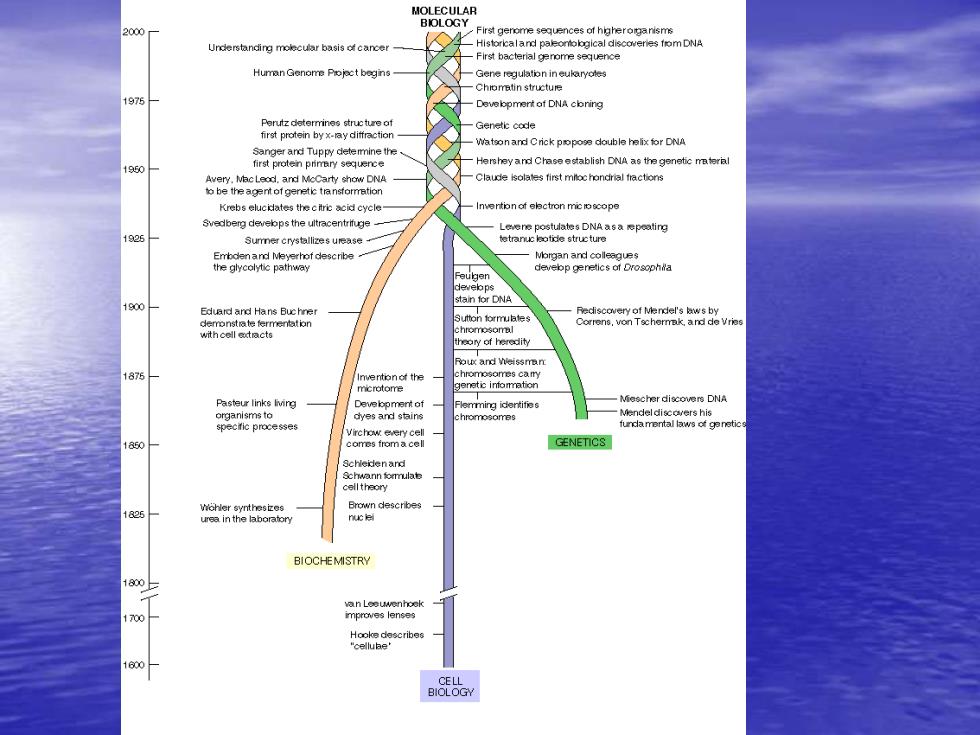
2000 First gerome sequences of higheroganisms Jnderstanding basis of cancer Historkcaland paleonolgical discoveries fom DNA First bacteral genome sequence Human Genome begins stetue 1975 Devebpment of DNA cbning Genetic code first protein byx-ay diffractior Watsonand Crick popose double helix for DNA Sanger and Tuppy detemmine the Hersheyand Chaseestablish DNA as the genetic mterial 1950 first proten prmary sequence Avery MacLeod.and McCarty show DNA Claude isolates first mloc handrial fractions to be the agent of genetic transforrretion Krebs elucidates the citric acid cycle Svedberg develops the uitracentrifuge Surmner crystallizes urease Morgan and colleagues devebop genetics of Drosopha stain for DNA 1900 Eduard and Hans Buc hner demronstrate fermentation Sutton formulates Rediscovery of Mendel's bws by Correns,von Tschermak,and de Vries withcell extracts chromesoml theary of heredity Roux and Weissman 1875 genetic intomation Pasteur links living Mescher discovere DNA Devebpment ot Flemrming identifies dyes and stains chromosomes Mendeldiscovers his funcamental laws of genetic 1850 comes fromacell GENETICS Schleidenand Schwann formulate celltheory 1825 Wohler synthesizes urea in the labaratory BIOCHEMISTRY 1800- 700 Hooke describes cellube' 1600
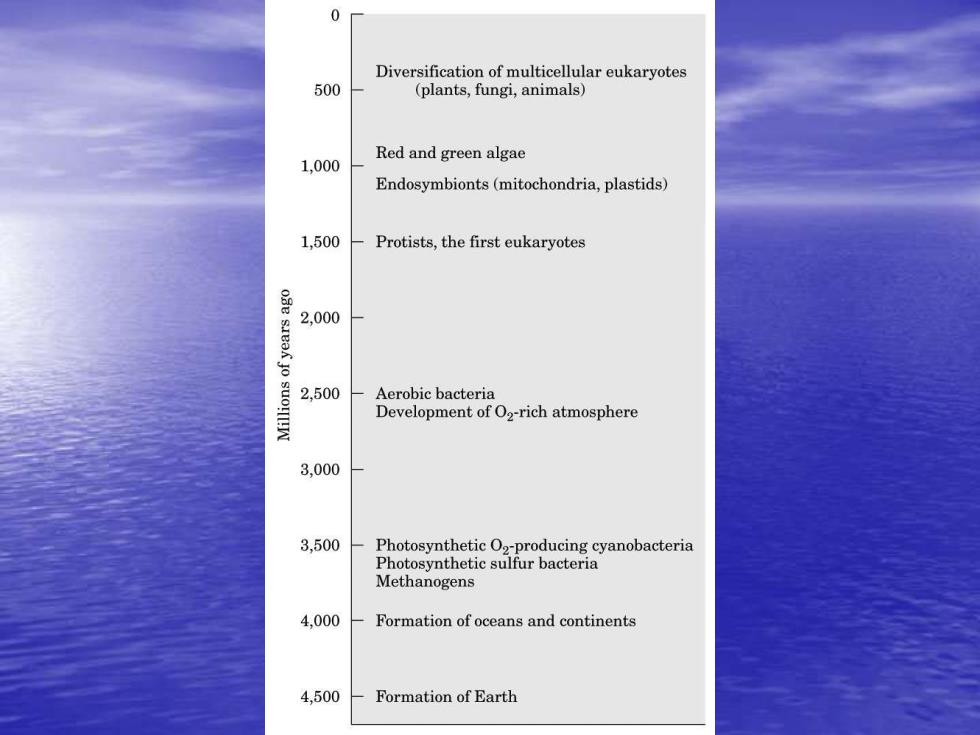
0 Diversification of multicellular eukaryotes 500 (plants,fungi,animals) Red and green algae 1,000 Endosymbionts(mitochondria,plastids) 1,500 Protists,the first eukaryotes 2,000 2,500 Aerobic bacteria Development of O2-rich atmosphere 3,000 3,500 Photosynthetic O2-producing cyanobacteria Photosynthetic sulfur bacteria Methanogens 4,000 Formation of oceans and continents 4,500 Formation of earth
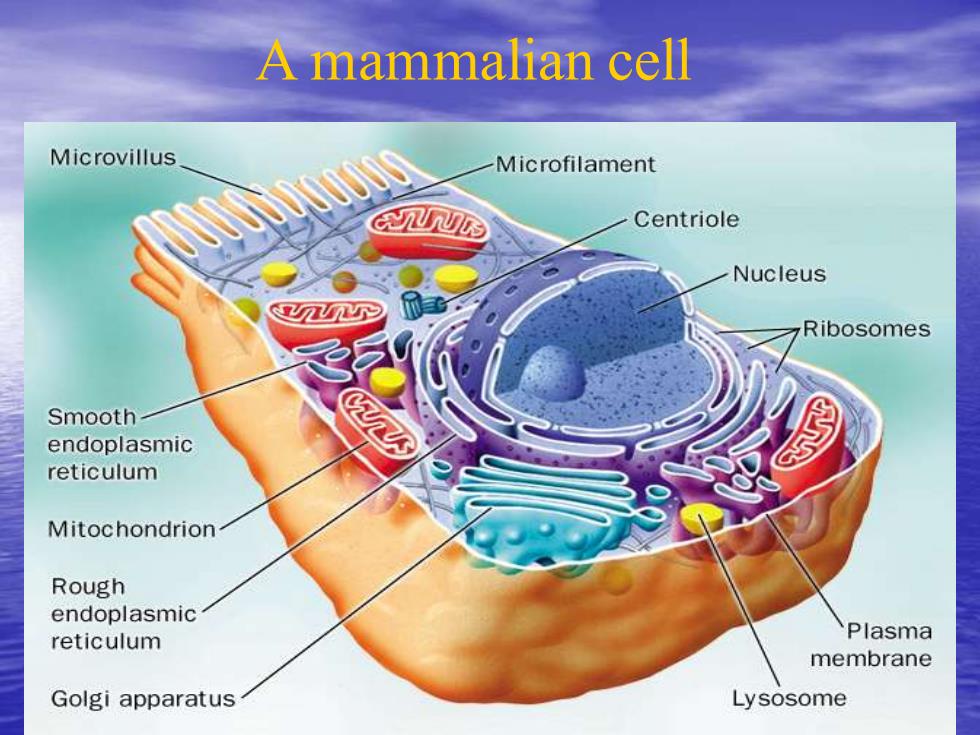
A mammalian cell
A mammalian cell
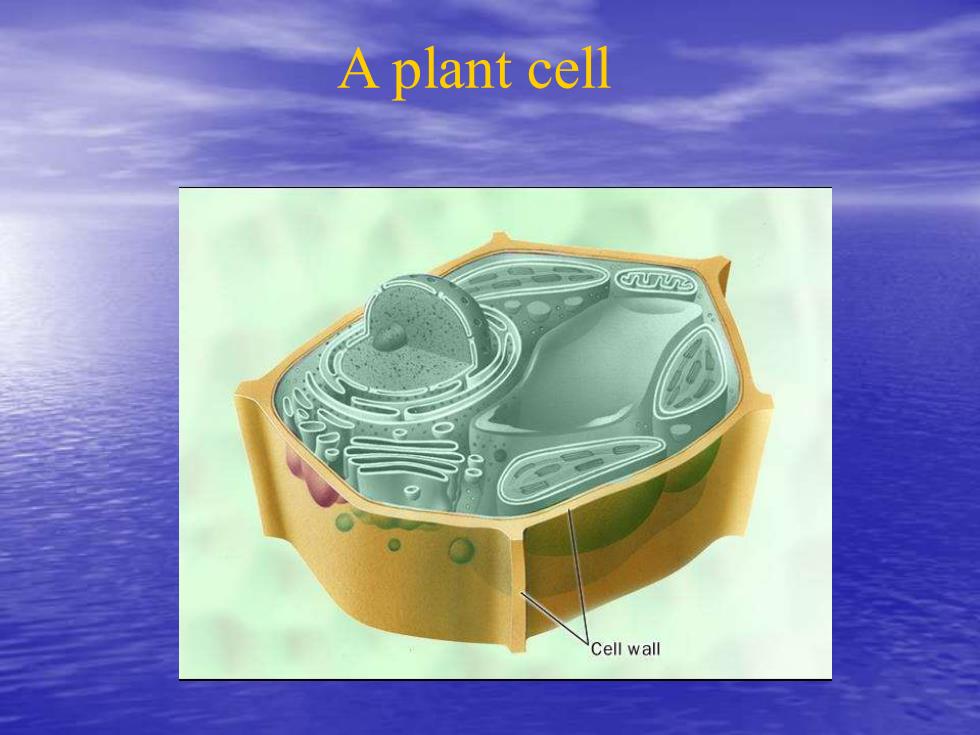
A plant cell
A plant cell
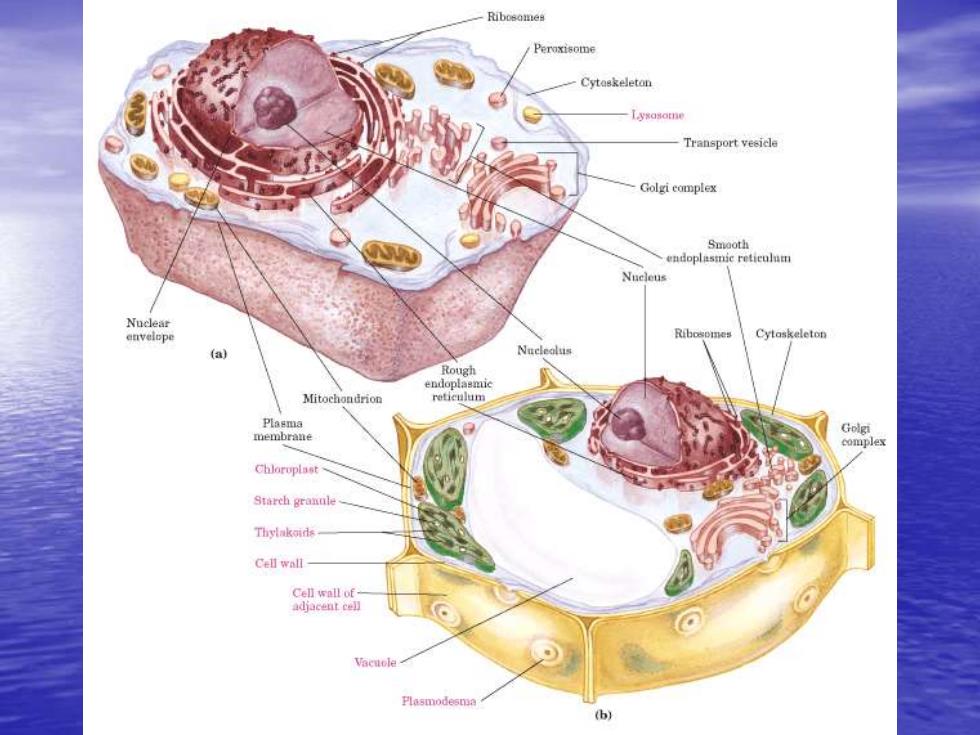
Peroxisome Cytaskeleton -Lyxasomne Transport vesicle Golgi eomplex Smooth Nuclear envelope Cytaskeleton (a) Rough endopl Mitochondrion re里am Plasma membrane Golgi complex Chloruplast Starch granule Thylakoids. Cell wall Cell wall of adjacent cell Plasmodesma
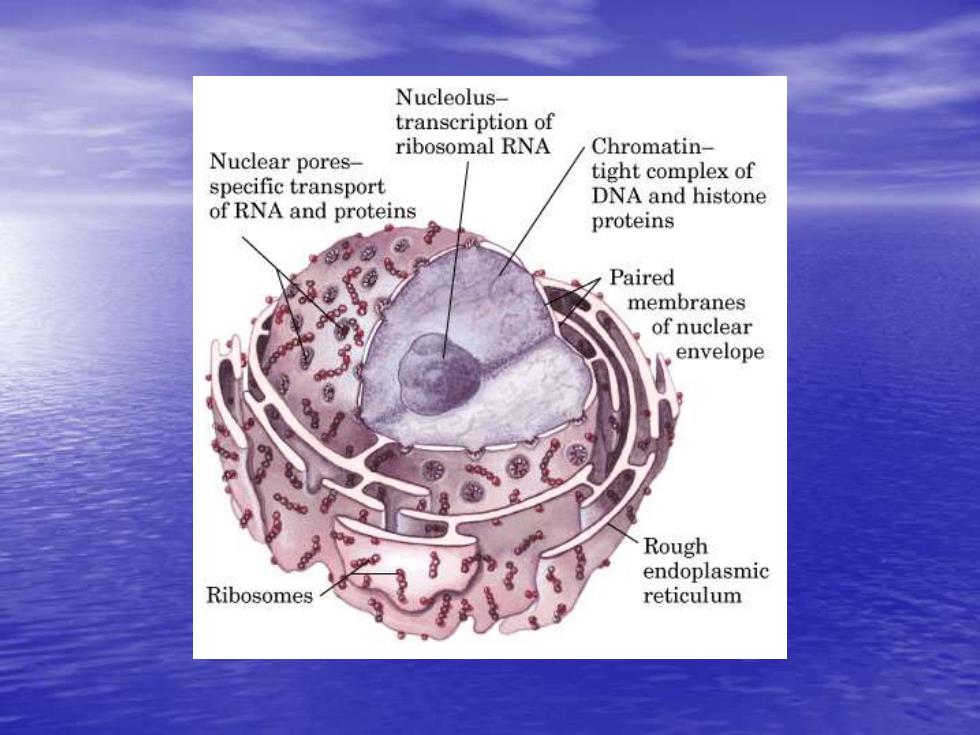
Nucleolus- transcription of ribosomal RNA Chromatin- Nuclear pores- tight complex of specific transport DNA and histone of RNA and proteins proteins Paired membranes of nuclear envelope Rough endoplasmic Ribosomes reticulum

Electron micrograph of the nucleus of the alga chlamydomonas
Electron micrograph of the nucleus of the alga chlamydomonas