
Test two I、填空题 1.对真实气体压缩因子Z的定义是: 2.有1molH,O(①,在373K、100kPa下,向真空蒸发为同温、同压下的水蒸汽, 则此过程:△H零:△S(系统)零:△G零。(填:大于、小于 或等于) 3.在298K和100kPa下,反应3C(s)+O2(g+3H2(g)→CH3C00CH3(①等压热Qp 与等容热Qy之差为 4.某温度下真实气体化学势的表示式: 5.均相多组分系统中,组分B的偏摩尔体积V= 6.反应C(s+HO(g)=C0(g)+H(g),在400℃时达到平衡,△ Hme=133.5kJ/mol,为使反应物转化率增加,可采取的措施有(1) (2) ;(3) (4) (5) 7.二元恒压气-液相图如右图,系统点位于 图中M点处时,系统中的气相和液相的 质量比w气/W液= Ⅱ.选择题(请将答案填在下列答案表中) 0.310.540.72 题号 1 2 答案 1.关于临界状态的描述正确的是: A.在临界状态气体和液体的摩尔体积相同 B.临界点就是三相点 C.符合理想气体状态方程 D.低于临界温度气体不能被液化 1 PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ww,fineprint.com.cn
1 Test two I、填空题 1. 对真实气体压缩因子 Z 的定义是: 。 2. 有 1mol H2O(l),在 373K、100kPa 下,向真空蒸发为同温、同压下的水蒸汽, 则此过程:ΔH 零;ΔS(系统) 零;ΔG 零。(填:大于、小于 或等于) 3. 在 298K 和 100kPa 下,反应 3C(s)+O2(g)+3H2(g)→CH3COOCH3(l)等压热 Qp 与等容热 QV之差为 。 4. 某温度下真实气体化学势的表示式: 。 5. 均相多组分系统中,组分 B 的偏摩尔体积 VB= 。 6. 反 应 C(s)+H2O(g) = CO(g) + H2(g), 在 400 ℃ 时 达 到 平 衡 , Δ rHm y=133.5kJ/mol,为使反应物转化率增加,可采取的措施有(1) ; (2) ;(3) ;(4) ; (5) 。 7. 二元恒压气-液相图如右图,系统点位于 图中 M 点处时,系统中的气相和液相的 质量比w气 / w液 =____________. II. 选择题(请将答案填在下列答案表中) 题号 1 2 3 4 5 答案 1. 关于临界状态的描述正确的是: A.在临界状态气体和液体的摩尔体积相同 B.临界点就是三相点 C.符合理想气体状态方程 D.低于临界温度气体不能被液化 T PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn

2.理想气体经节流膨胀过程: A.AT>0 AU>0 B.△T-0AU>0 C.AT0 D.△T=0AU=0 3.水的凝固点降低常数为1.86 K.mor.kg,在水中溶解少量的非挥发性溶质B 形成理想稀溶液,测得溶液凝固点为-0.50℃,该溶液B的质量摩尔浓度为 A.0.1 mol-kg B.0.27 mol-kg C.0.37 mol-kg D.0.93 mol-kg" 4.PCl的分解反应PC5(g)=PCl(g)+Ch(g)在473K达到平衡时PCls(g)有 48.5%分解,在573K达到平衡时,有97%分解,则此反应是: A.吸热反应 B.放热反应 C.反应的标准摩尔焓变为零的反应 D.在这两个温度下标准平衡常数相等的反应 5.己知水的摩尔蒸发焓为40668J小mo',50℃时水的饱和蒸汽压为: A.101.325kP B.5.308kPa C.771kPa D.13.308kPa III.(1)A sample consisting of 1.0 mol of a monatomic perfect gas is changed irreversibly and adiabatically to 273K and 100kPa.Given that A S=20.9JK. mor,W=1255J,and the molar entropy of the final state of its gas Sm=188.3J mol.Kl.Calculate△U,△H,△G (2)Derive the relation: (aH =-T +v ar IV.A and B are two partially miscible liquids at 25C.The binary system consists of two phases(I and l2)in equilibrium with each other.The compositions of the two phases (I and l2)in equilibrium are XB.1=0.98 and XB.2=0.01,respectively 2 PDF文件使用“pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ww,fineprint.con,cn
2 2. 理想气体经节流膨胀过程: A.ΔT>0 DU >0 B.ΔT=0 DU>0 C.ΔT0 D.ΔT=0 DU =0 3. 水的凝固点降低常数为 1.86K×mol-1 ×kg,在水中溶解少量的非挥发性溶质 B 形成理想稀溶液,测得溶液凝固点为-0.50℃, 该溶液 B 的质量摩尔浓度为: A. 0.1 mol×kg-1 B. 0.27 mol×kg-1 C. 0.37 mol×kg-1 D. 0.93 mol×kg-1 4. PCl5 的分解反应 PCl5(g)= PCl3 (g) + Cl2(g) 在 473K 达到平衡时 PCl5(g)有 48.5%分解,在 573K 达到平衡时,有 97%分解,则此反应是: A. 吸热反应 B. 放热反应 C. 反应的标准摩尔焓变为零的反应 D. 在这两个温度下标准平衡常数相等的反应 5. 已知水的摩尔蒸发焓为 40668 J•mol-1,50℃时水的饱和蒸汽压为: A. 101.325 kPa B. 5.308 kPa C. 771kPa D. 13.308 kPa III.(1)A sample consisting of 1.0 mol of a monatomic perfect gas is changed irreversibly and adiabatically to 273K and 100kPa. Given thatΔS=20.9J•K -1• mol-1 , W=1255J,and the molar entropy of the final state of its gas Sm=188.3J• mol-1•K -1 . CalculateΔU,ΔH,ΔG. (2)Derive the relation: V T V T p H T p ÷ + ø ö ç è æ ¶ ¶ = - ÷ ÷ ø ö ç ç è æ ¶ ¶ IV. A and B are two partially miscible liquids at 25℃. The binary system consists of two phases (l1 and l2) in equilibrium with each other. The compositions of the two phases (l1 and l2) in equilibrium are XB,1=0.98 and XB,2=0.01, respectively. PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn
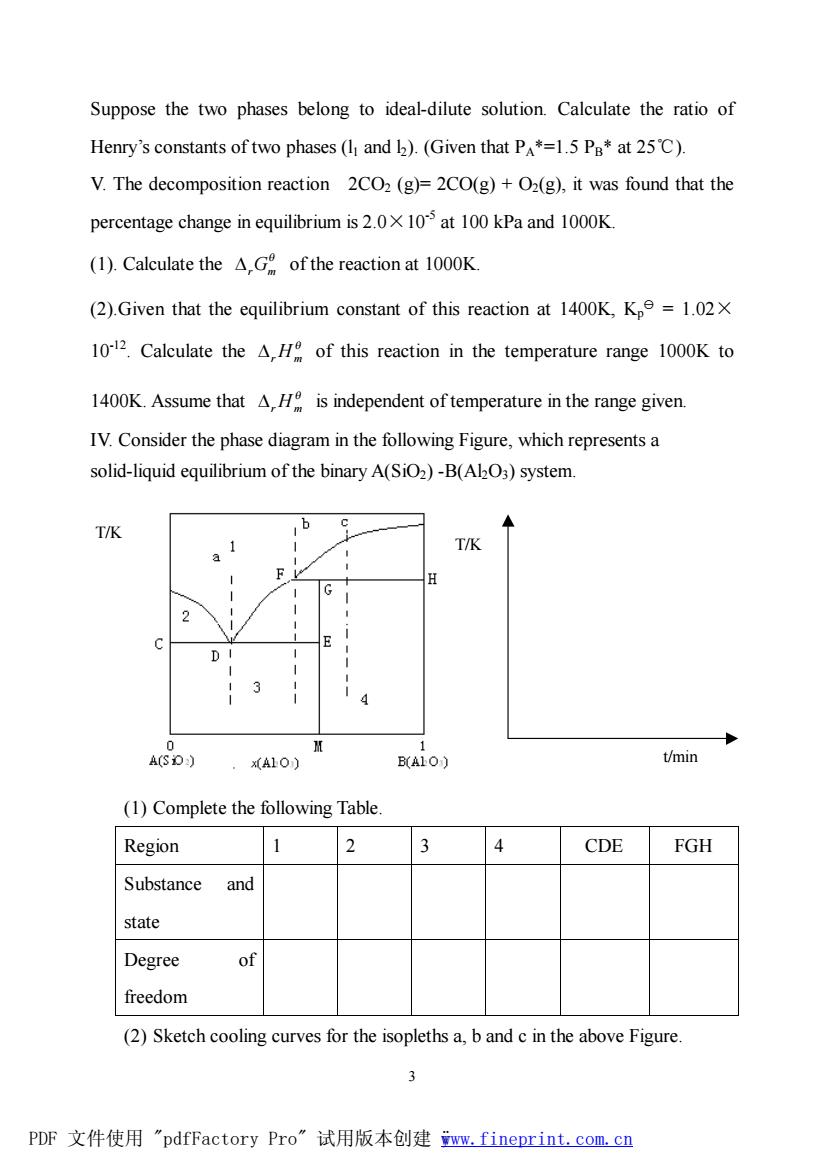
Suppose the two phases belong to ideal-dilute solution.Calculate the ratio of Henry's constants of two phases (I and )(Given that P*=1.5 Pa*at 25C). V.The decomposition reaction 2CO2(g)=2CO(g)+O2(g),it was found that the percentage change in equilibrium is 2.010 at 100 kPa and 1000K. (1).Calculate the AG of the reaction at 1000K (2).Given that the equilibrium constant of this reaction at 1400K,Kp=1.02X 1012.Calculate the H of this reaction in the temperature range 1000K to 1400K.Assume that AH is independent of temperature in the range given IV.Consider the phase diagram in the following Figure,which represents a solid-liquid equilibrium of the binary A(SiO2)-B(AkO3)system T/K T/K D A10) B(ALO) t/min (1)Complete the following Table Region 2 4 CDE FGH Substance and state Degree of freedom (2)Sketch cooling curves for the isopleths a,b and c in the above Figure. 3 PDF文件使用"pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建ww,fineprint.com,cn
3 Suppose the two phases belong to ideal-dilute solution. Calculate the ratio of Henry’s constants of two phases (l1 and l2). (Given that PA*=1.5 PB* at 25℃). V. The decomposition reaction 2CO2 (g)= 2CO(g) + O2(g), it was found that the percentage change in equilibrium is 2.0×10-5 at 100 kPa and 1000K. (1). Calculate the q DrGm of the reaction at 1000K. (2).Given that the equilibrium constant of this reaction at 1400K, Kp y = 1.02× 10-12 . Calculate the q DrHm of this reaction in the temperature range 1000K to 1400K. Assume that q DrHm is independent of temperature in the range given. IV. Consider the phase diagram in the following Figure, which represents a solid-liquid equilibrium of the binary A(SiO2) -B(Al2O3) system. (1) Complete the following Table. Region 1 2 3 4 CDE FGH Substance and state Degree of freedom (2) Sketch cooling curves for the isopleths a, b and c in the above Figure. t/min T/K T/K PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 ÿwww.fineprint.com.cn

4 PDF文件使用”pdfFactory Pro”试用版本创建,fineprint.com.cn
4 PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn