
电子料做女学 University of Electroe Scioncad TechofChina /986 Chapter 1 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Systems Dr.Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication
Chapter 1 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Systems Dr. Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication

Digital signal vs.Analog signal /96 ■Noise Noise can not be accumulated and propagated in digital signal process. DSP is insensitive to environment. ■ In analog signal process,noise is treated same as the signals. Environment affect the analog signal process significantly. ■ Store and recovery of signals Flexible and easy for digital signal storage. It is hard for analog signal storage,especially in high accuracy requirement. Always be true? 2021年2月 2
2021年2月 2 Digital signal vs. Analog signal Noise Noise can not be accumulated and propagated in digital signal process. DSP is insensitive to environment. In analog signal process, noise is treated same as the signals. Environment affect the analog signal process significantly. Store and recovery of signals Flexible and easy for digital signal storage. It is hard for analog signal storage, especially in high accuracy requirement. Always be true?

Digital signal vs.Analog signal 96 ■Signal process ■Linear transform ■Nonlinear transform ■Convert Adaptive process The current applications of analog Radio modules in communication and radar ■Power devices Industrial auto-control systems 2021年2月 3
2021年2月 3 Digital signal vs. Analog signal Signal process Linear transform Nonlinear transform Convert Adaptive process The current applications of analog Radio modules in communication and radar Power devices Industrial auto-control systems
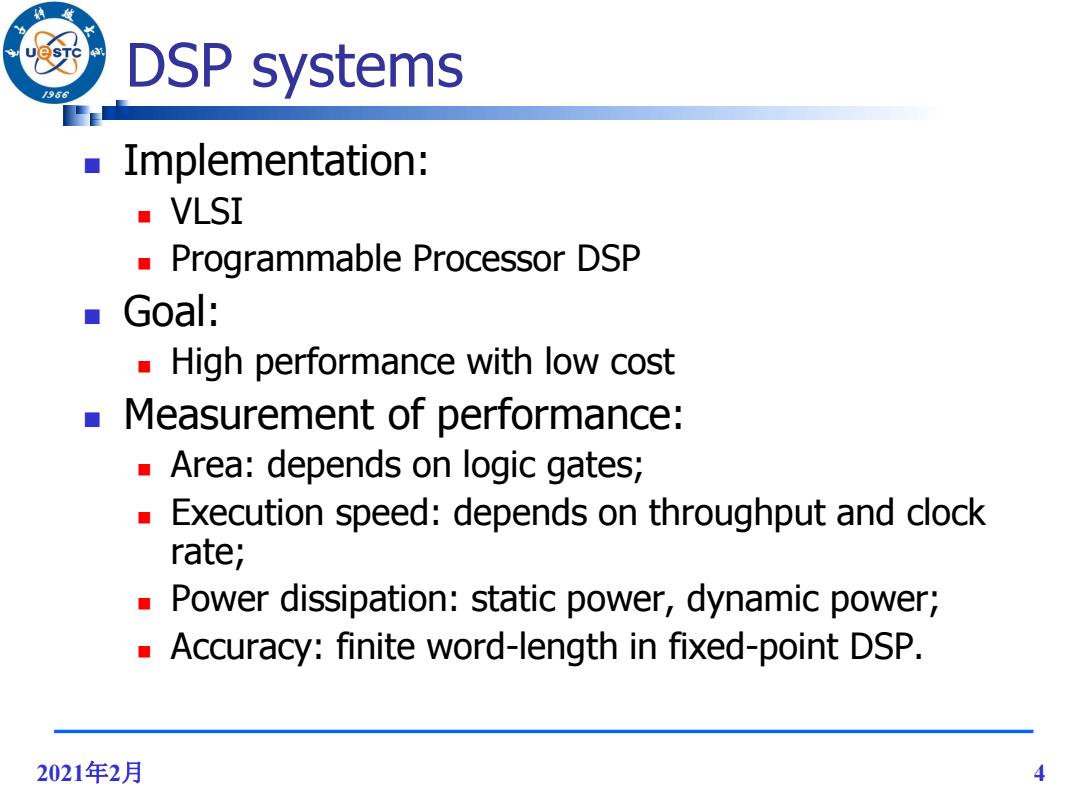
DSP systems 956 Implementation: ■VLSI Programmable Processor DSP ■Goal: High performance with low cost Measurement of performance: Area:depends on logic gates; Execution speed:depends on throughput and clock rate; Power dissipation:static power,dynamic power; Accuracy:finite word-length in fixed-point DSP. 2021年2月 4
2021年2月 4 DSP systems Implementation: VLSI Programmable Processor DSP Goal: High performance with low cost Measurement of performance: Area: depends on logic gates; Execution speed: depends on throughput and clock rate; Power dissipation: static power, dynamic power; Accuracy: finite word-length in fixed-point DSP
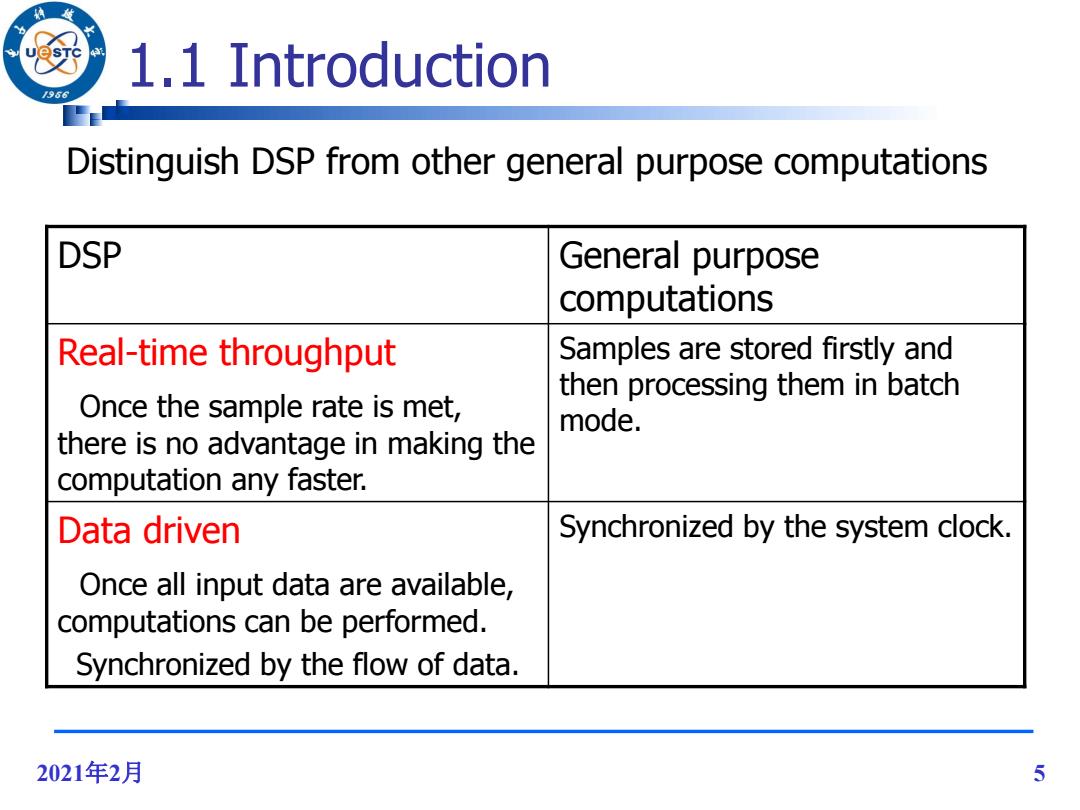
1.1 Introduction /96 Distinguish DSP from other general purpose computations DSP General purpose computations Real-time throughput Samples are stored firstly and then processing them in batch Once the sample rate is met, mode. there is no advantage in making the computation any faster. Data driven Synchronized by the system clock. Once all input data are available, computations can be performed. Synchronized by the flow of data. 2021年2月 5
2021年2月 5 1.1 Introduction Distinguish DSP from other general purpose computations DSP General purpose computations Real-time throughput Once the sample rate is met, there is no advantage in making the computation any faster. Samples are stored firstly and then processing them in batch mode. Data driven Once all input data are available, computations can be performed. Synchronized by the flow of data. Synchronized by the system clock
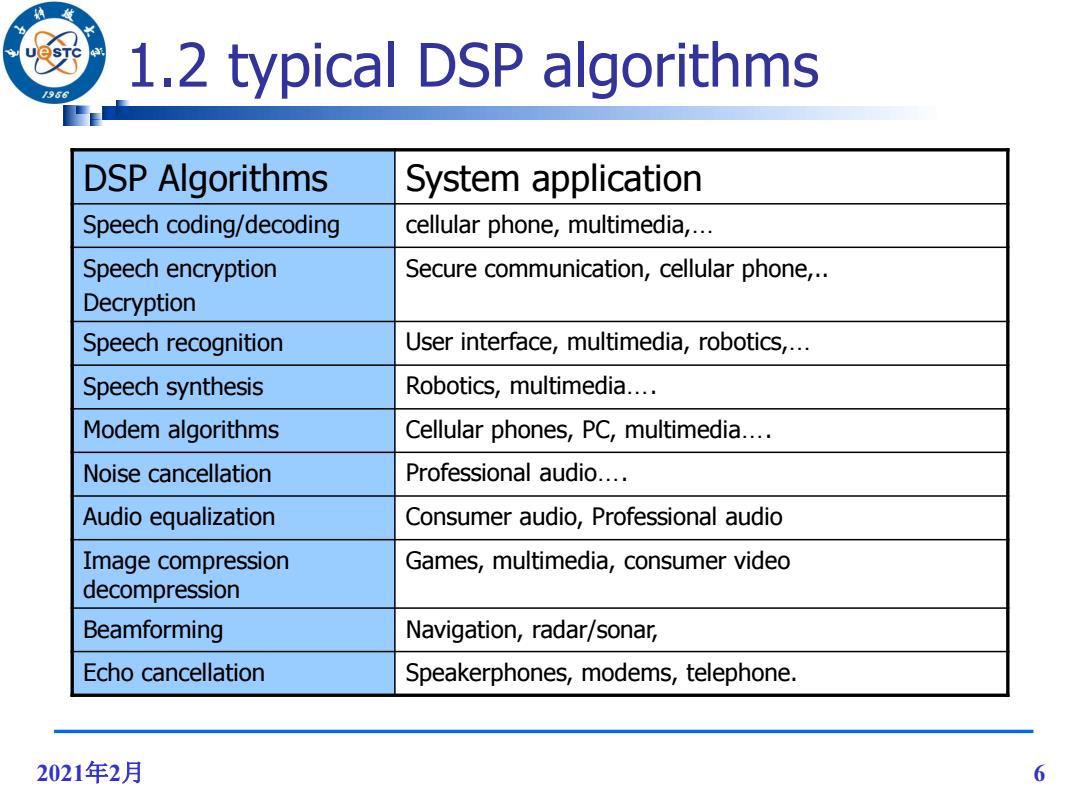
1.2 typical DSP algorithms /966 DSP Algorithms System application Speech coding/decoding cellular phone,multimedia,... Speech encryption Secure communication,cellular phone,.. Decryption Speech recognition User interface,multimedia,robotics,... Speech synthesis Robotics,multimedia.... Modem algorithms Cellular phones,PC,multimedia.... Noise cancellation Professional audio.... Audio equalization Consumer audio,Professional audio Image compression Games,multimedia,consumer video decompression Beamforming Navigation,radar/sonar, Echo cancellation Speakerphones,modems,telephone. 2021年2月 6
2021年2月 6 1.2 typical DSP algorithms DSP Algorithms System application Speech coding/decoding cellular phone, multimedia,… Speech encryption Decryption Secure communication, cellular phone,.. Speech recognition User interface, multimedia, robotics,… Speech synthesis Robotics, multimedia…. Modem algorithms Cellular phones, PC, multimedia…. Noise cancellation Professional audio…. Audio equalization Consumer audio, Professional audio Image compression decompression Games, multimedia, consumer video Beamforming Navigation, radar/sonar, Echo cancellation Speakerphones, modems, telephone
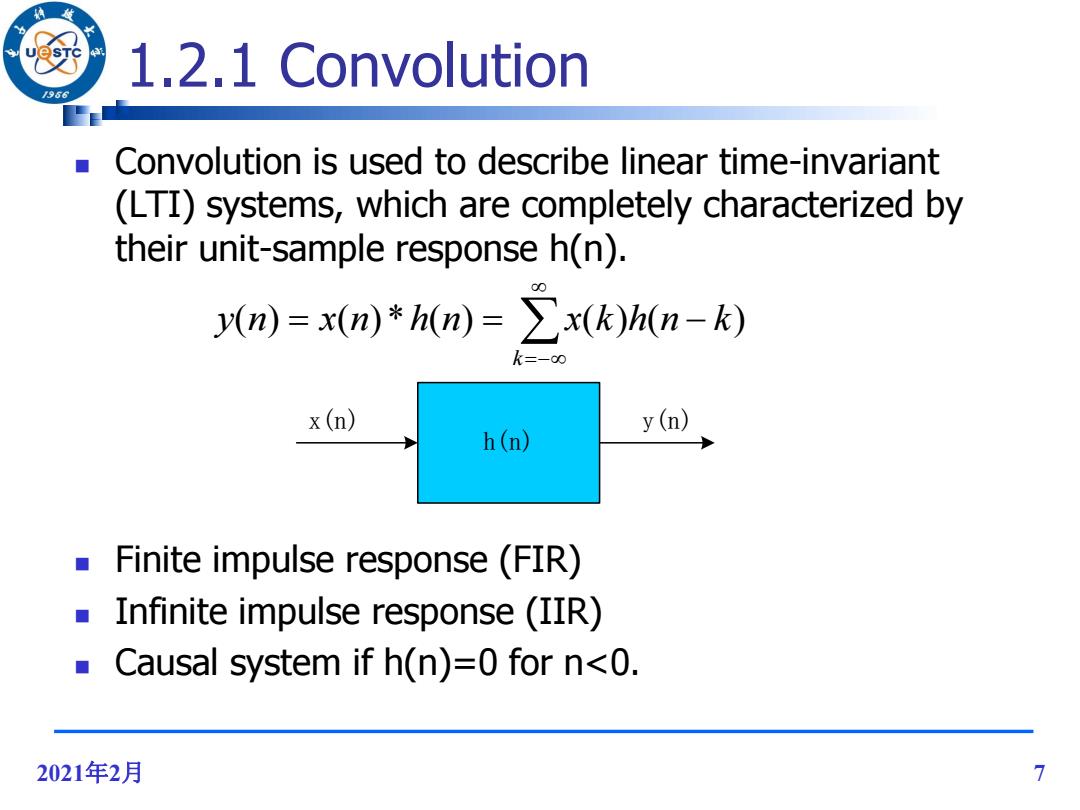
1.2.1 Convolution /96 Convolution is used to describe linear time-invariant (LTI)systems,which are completely characterized by their unit-sample response h(n). y(n)=x(n)h(n)=>x(k)h(n-k) k=-0 x (n) y(n) h(n) Finite impulse response(FIR) Infinite impulse response (IIR) Causal system if h(n)=0 for n<0. 2021年2月 7
2021年2月 7 1.2.1 Convolution Convolution is used to describe linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, which are completely characterized by their unit-sample response h(n). Finite impulse response (FIR) Infinite impulse response (IIR) Causal system if h(n)=0 for n<0. k y(n) x(n)*h(n) x(k)h(n k) h(n) x(n) y(n)

1.2.2 Correlation /96 Correlation is widely used in communication and random signal processing y(n)=a(k)x(n+k)=a(-n)*a(n) 2021年2月 8
2021年2月 8 1.2.2 Correlation Correlation is widely used in communication and random signal processing. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )* ( ) k y n a k x n k a n a n
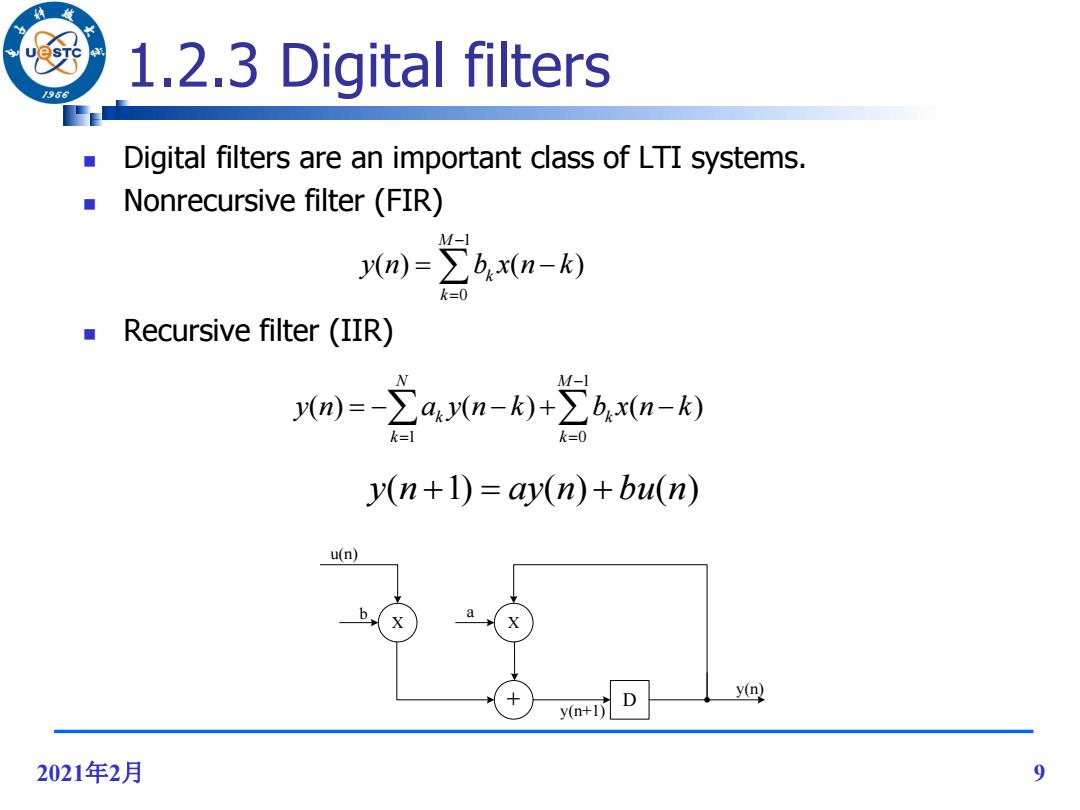
1.2.3 Digital filters /966 Digital filters are an important class of LTI systems. Nonrecursive filter(FIR) M-1 y(m)=∑bx(n-k) k=0 Recursive filter(IIR) M-l 0m)=-2a0n-k)+2b,an-k) k=0 y(n+1)=ay(n)+bu(n) u(n) a y(n) y(n+) D 2021年2月 9
2021年2月 9 1.2.3 Digital filters Digital filters are an important class of LTI systems. Nonrecursive filter (FIR) Recursive filter (IIR) 1 1 0 ( ) ( ) ( ) N M k k k k y n a y n k b x n k 1 0 ( ) ( ) M k k y n b x n k y(n 1) ay(n) bu(n) X + D X y(n) u(n) b a y(n+1)
1.2.4 Adaptive filters /96 ■ Adaptive filter predict one random process y(n)}from observations of another random process {x(n)}using linear models. The coefficients in adaptive digital filters are updated at each iteration. Adaptive filters usually consist of a general filter block and coefficient update block. 2021年2月 10
2021年2月 10 1.2.4 Adaptive filters Adaptive filter predict one random process {y(n)} from observations of another random process {x(n)} using linear models. The coefficients in adaptive digital filters are updated at each iteration. Adaptive filters usually consist of a general filter block and coefficient update block