
电子种越女学 University of Electroale Science and Technelery of China 986 Chapter 4 Retiming Dr.Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication
Chapter 4 Retiming Dr. Ling National Key Lab of Science and Technology on Communication
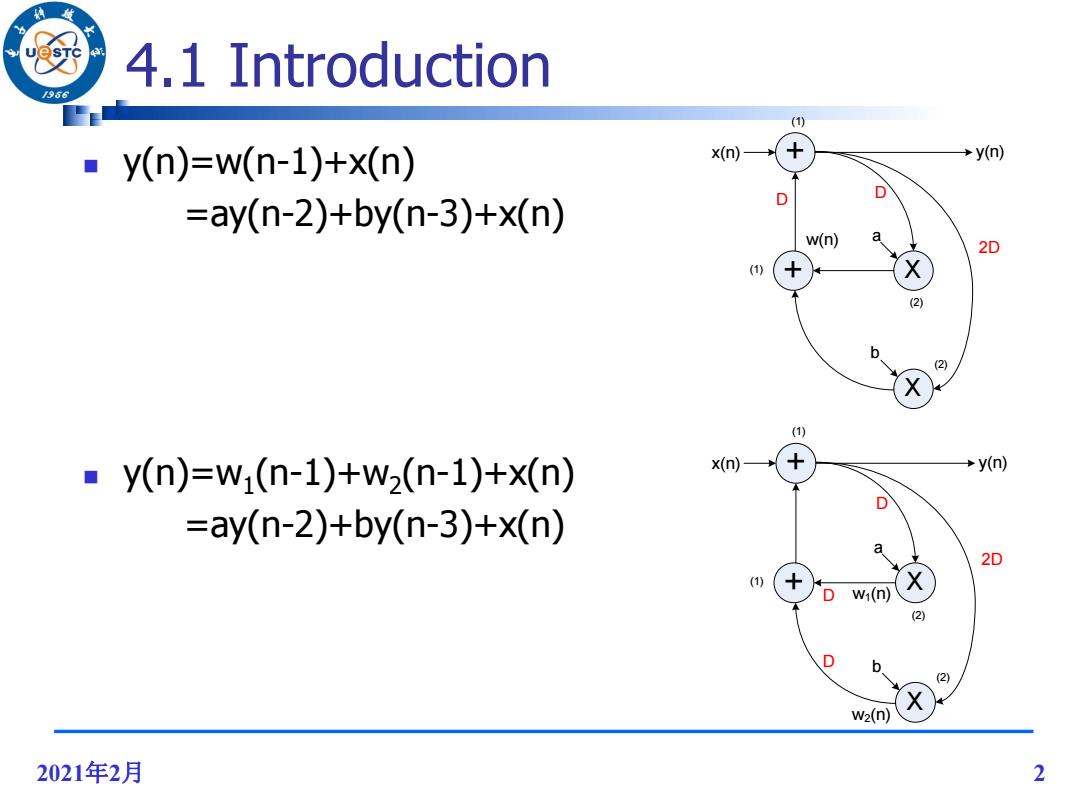
43 4.1 Introduction 96 () y(n)=w(n-1)+x(n) x(n) →yn) D D =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) w(n) a 2D (1) (2) b (2) (1) ay(n)=w(n-1)+w2(n-1)+x(n) x(n) →yn) D =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) a 2D (1) w(n) (2) (2) w2(n) 2021年2月 2
2021年2月 2 4.1 Introduction y(n)=w(n-1)+x(n) =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) y(n)=w1 (n-1)+w2 (n-1)+x(n) =ay(n-2)+by(n-3)+x(n) + X + X D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) x(n) y(n) a b w(n) + X + X D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) x(n) y(n) a b w1(n) D w2(n)
Retiming? /96 Retiming is a transformation technique used to change the locations of delay elements in a circuit without affection the input/output characteristics of the circuit. Retiming has many applications in synchronous circuit design,including reducing the clock period of the circuit, reducing the number of registers in the circuit, -reducing the power consumption of the circuit, logic synthesis. 2021年2月 3
2021年2月 3 Retiming? Retiming is a transformation technique used to change the locations of delay elements in a circuit without affection the input/output characteristics of the circuit. Retiming has many applications in synchronous circuit design, including reducing the clock period of the circuit, reducing the number of registers in the circuit, reducing the power consumption of the circuit, logic synthesis
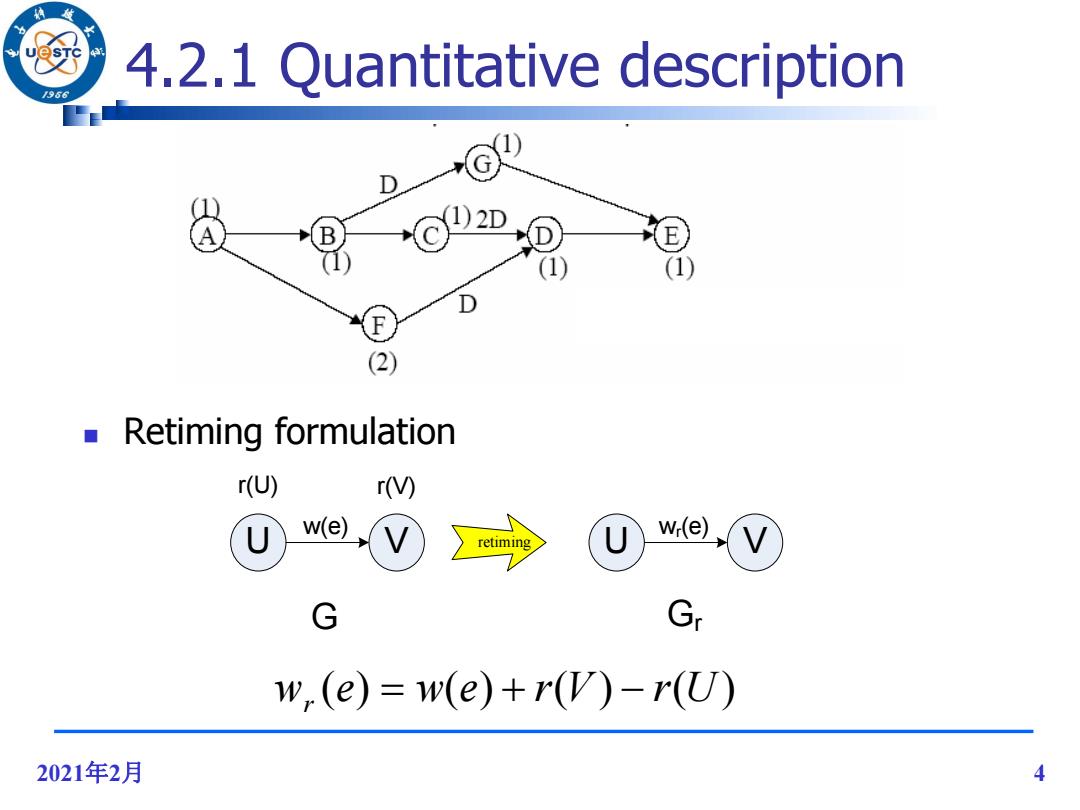
4.2.1 Quantitative description 966 1)2D 1) (1) D (2) Retiming formulation r(U) r U w(e) V U w(e) retiming V G Gr w,(e)=w(e)+r(V)-r(U) 2021年2月 4
2021年2月 4 4.2.1 Quantitative description Retiming formulation w (e) w(e) r(V) r(U) r U V w(e) r(U) r(V) retiming U V wr(e) G Gr

(1) /96 ■Letr(1)=0,r(2)=1,r(3)=0,r(4)=0 D (1) (2) 2D w,(3→2)=1w(3→2)+r(2)-r(3)=0+1-0=1 2 3 w,(4→2)=w(4→2)+r(2)-r(4)=0+1-0=1 w,(2→1)=w(2→1)+r(1)-r(2)=1+0-1=0 (2) (1) A retiming solution is feasible only if w-(e)>0 holds for all edges. (1) (2) 2D How to determine the retiming value,r(V),will be 2 3 discussed in section 4.4.2.And the method of solving systems of inequalities is used,which will be given in section 4.3. D (2) 2021年2月 5
2021年2月 5 Let r(1)=0, r(2)=1, r(3)=0, r(4)=0 A retiming solution is feasible only if wr (e)≥0 holds for all edges. How to determine the retiming value, r(V), will be discussed in section 4.4.2. And the method of solving systems of inequalities is used, which will be given in section 4.3. 1 4 2 3 D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) D w (3 2) w(3 2) r(2) r(3) 0 1 0 1 r wr (4 2) w(4 2) r(2) r(4) 0 1 0 1 1 4 2 3 D D 2D (1) (1) (2) (2) wr (2 1) w(2 1) r(1) r(2) 1 0 1 0
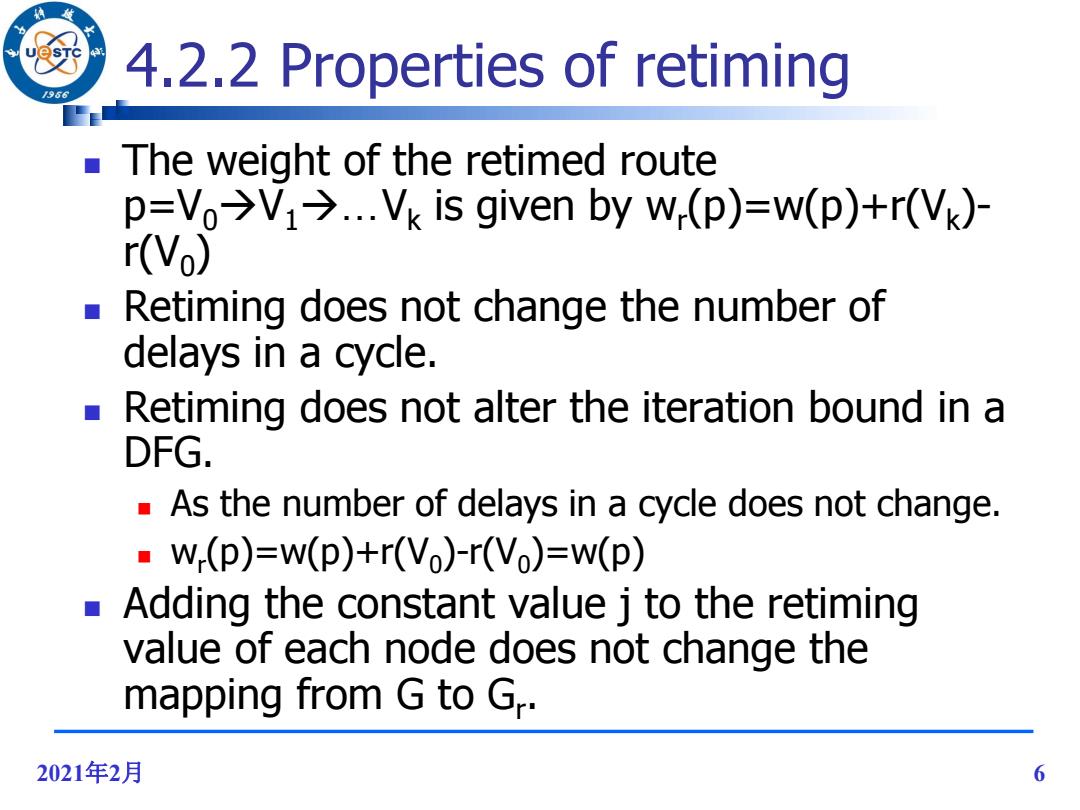
4.2.2 Properties of retiming /96 The weight of the retimed route p=Vo>V1>...Vk is given by w(p)=w(p)+r(Vk)- r(Vo) Retiming does not change the number of delays in a cycle. ■ Retiming does not alter the iteration bound in a DFG. As the number of delays in a cycle does not change. -W-(p)=w(p)+r(Vo)-r(Vo)=w(p) Adding the constant value j to the retiming value of each node does not change the mapping from G to G.. 2021年2月 6
2021年2月 6 4.2.2 Properties of retiming The weight of the retimed route p=V0V1…Vk is given by wr (p)=w(p)+r(Vk )- r(V0 ) Retiming does not change the number of delays in a cycle. Retiming does not alter the iteration bound in a DFG. As the number of delays in a cycle does not change. wr (p)=w(p)+r(V0 )-r(V0 )=w(p) Adding the constant value j to the retiming value of each node does not change the mapping from G to Gr

4.3 Solving systems inequalities Given a set of M inequalities,where each inequality has the form r-rsk for integer values of k. Draw a constrain graph. Draw the node i for N variables ri,i=1,..N; ■Draw the node N+l; For each inequality ri-ri with length k; ■For each node i,.draw edge N+l→i with length0. ■ Solve using a shortest path algorithm. Bellman-Ford algorithm(single-point shortest path algorithm) Floyd-Warshall algorithm(all-point shortest path algorithm) ■ If a solution exists(if no negative cycle in constraint graph), the retiming value r is obtained (r is the minimum-length from node N+1 to node i). 2021年2月 7
2021年2月 7 4.3 Solving systems inequalities Given a set of M inequalities, where each inequality has the form ri -rj≤k for integer values of k. Draw a constrain graph. Draw the node i for N variables ri , i=1,..N; Draw the node N+1; For each inequality ri -rj≤k, draw edge ji with length k; For each node i, draw edge N+1i with length 0. Solve using a shortest path algorithm. Bellman-Ford algorithm (single-point shortest path algorithm) Floyd-Warshall algorithm (all-point shortest path algorithm) If a solution exists (if no negative cycle in constraint graph), the retiming value r is obtained (ri is the minimum-length from node N+1 to node i). J i w

966 Example 4.3.1 r1-r2≤0 0 0 5 r3-r15 ● 0 r4r1≤4 5 0 r4r3≤-1 4 r3-r2≤2 ■ Shortest path r(4)=(0,0,0,-1) ■Thus,retiming value r1=0、r2=0、r3=0、r4=-1. 2021年2月 8
2021年2月 8 Example 4.3.1 r1 -r2≤0 r3 -r1≤5 r4 -r1≤4 r4 -r3≤-1 r3 -r2≤2 Shortest path r(4)=(0,0,0,-1) Thus, retiming value r1=0、 r2=0、 r3=0、 r4=-1. 2 1 4 3 0 5 4 -1 5 0 2 0 0 0

4.4 Retiming techniques 96 Two special cases of retiming Cutset retiming ·pipelining ■Two algorithms To minimize the clock period To minimize the number of registers 2021年2月 9
2021年2月 9 4.4 Retiming techniques Two special cases of retiming Cutset retiming pipelining Two algorithms To minimize the clock period To minimize the number of registers

4.4.1 Cutset retiming and pipelining Cutset retiming only affects the weights of the edges in the cutset. If the two disconnected subgraphs are labeled G1 and G2,then cutset retiming consists of adding k delays to each edge from Gi to G2, then removing k delays from each edge from G2 to G1. 2021年2月 10
2021年2月 10 4.4.1 Cutset retiming and pipelining Cutset retiming only affects the weights of the edges in the cutset. If the two disconnected subgraphs are labeled G1 and G2 , then cutset retiming consists of adding k delays to each edge from G1 to G2 , then removing k delays from each edge from G2 to G1