
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.I Chemical Bonds 8.2 Ionic bond, 8.3 Covalent Bonding 8.4 Bond polarity electronegativ ty 8.5 Lewis Structure
Chapter 8 Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds 8.2 Ionic bond, 8.3 Covalent Bonding 8.4 Bond polarity & 8.4 Bond polarity & electronegativity electronegativity 8.5 Lewis Structure

Hard-soft:hardness; Electron conductor-semiconductor-Physical insulator:conductivity; properties Solid liquidgas:phase or states; Chemical Poisonous-safe:chemical reactivity. alibaba.com.cn crscientito.com
Hard—soft: hardness; Electron conductor—semiconductor— insulator: conductivity; Physical properties Chemical insulator: conductivity; Solid—liquid—gas: phase or states; Poisonous—safe: chemical reactivity. properties Chemical
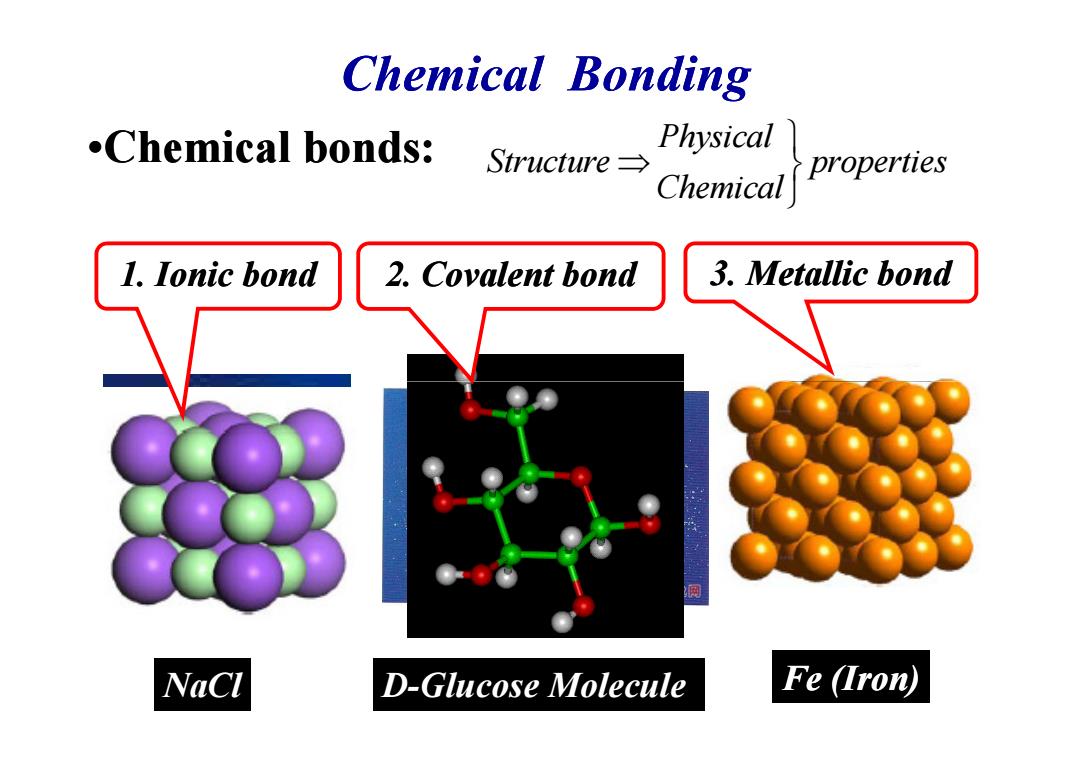
Chemical bonding .Chemical bonds: Physical Structure→ Chemical properties 1.Ionic bond 2.Covalent bond 3.Metallic bond NaCl D-Glucose Molecule Fe (Iron)
Chemical Bonding •Chemical bonds: 1. Ionic bond 2. Covalent bond 3. Metallic bond Physical Structure properties Chemical ⇒ NaCl D-Glucose Molecule Fe (Iron)
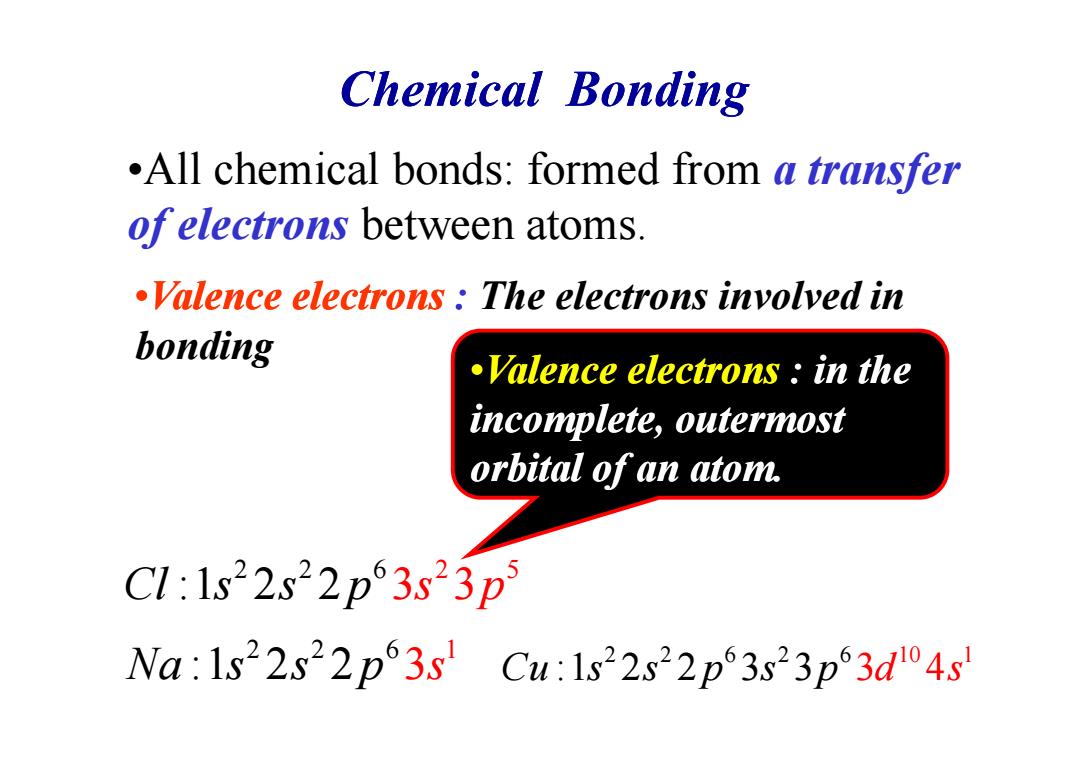
Chemical bonding .All chemical bonds:formed from a transfer ofelectrons between atoms. Valence electrons The electrons involyed in bonding Valence electrons in the incomplete,outermost orbital of an atom. C1:1s22s22p63s23p Na:1s22s22p3s Cu:1s22s22p63s23p3d4s
Chemical Bonding •All chemical bonds: formed from a transfer of electrons between atoms. •Valence electrons : The electrons involved in bonding •Valence electrons : in the 2 2 6 1 Na s s :1 2 2 p 3 s 2 6 2 2 5 C s s p l :1 2 2 3 3 s p 2 2 6 2 6 10 1 C s s p s p u :1 2 2 3 3 3 4 d s •Valence electrons : in the incomplete, outermost orbital of an atom
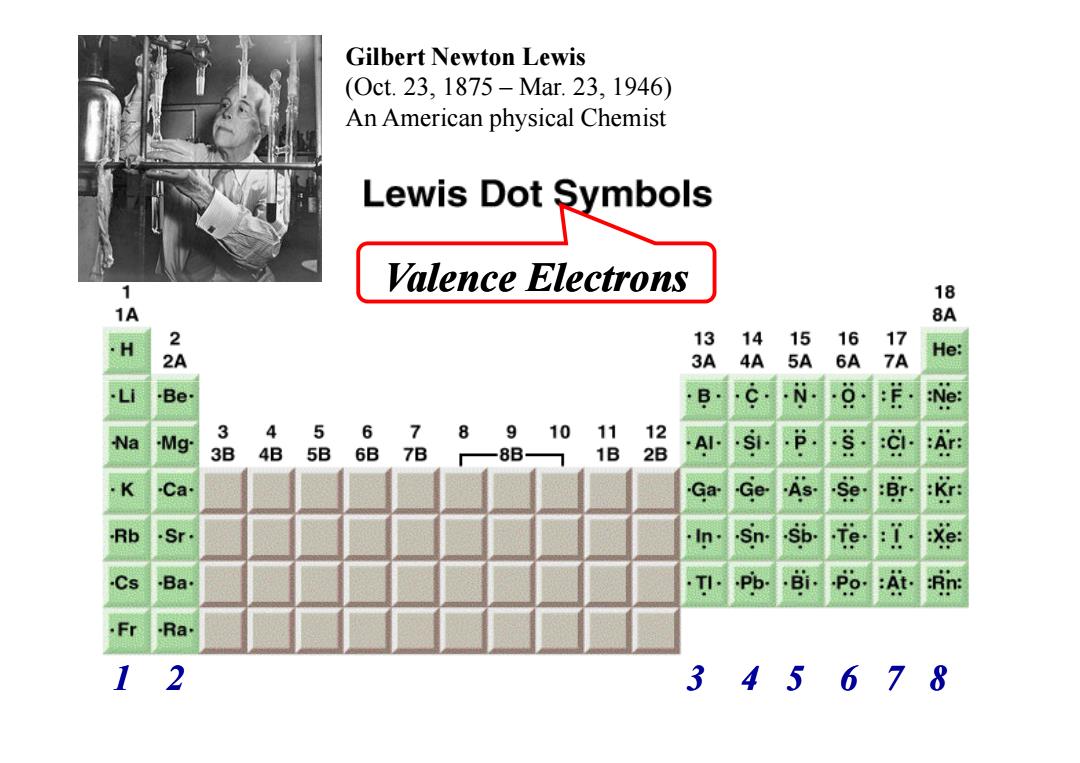
Gilbert Newton Lewis (0ct.23,1875-Mar.23,1946) An American physical Chemist Lewis Dot Symbols Valence electrons 18 1A 8A 2 13 14 15 16 17 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A He: Be B -N- 0 :Ne: 4 5 6 7 8 Na -Mg 3 91011 12 .P 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B —8B 1B 2B -AI-.SI- A K Ca Ga Ge.As.se.:Br. K Rb Sr .In..sn.sb.fe.:1. :Xe: Cs .Ba. TI..Pb..Bi.Po.At. :Rn: Fr Ra 2 345678
Valence Electrons Gilbert Newton Lewis (Oct. 23, 1875 – Mar. 23, 1946) An American physical Chemist 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
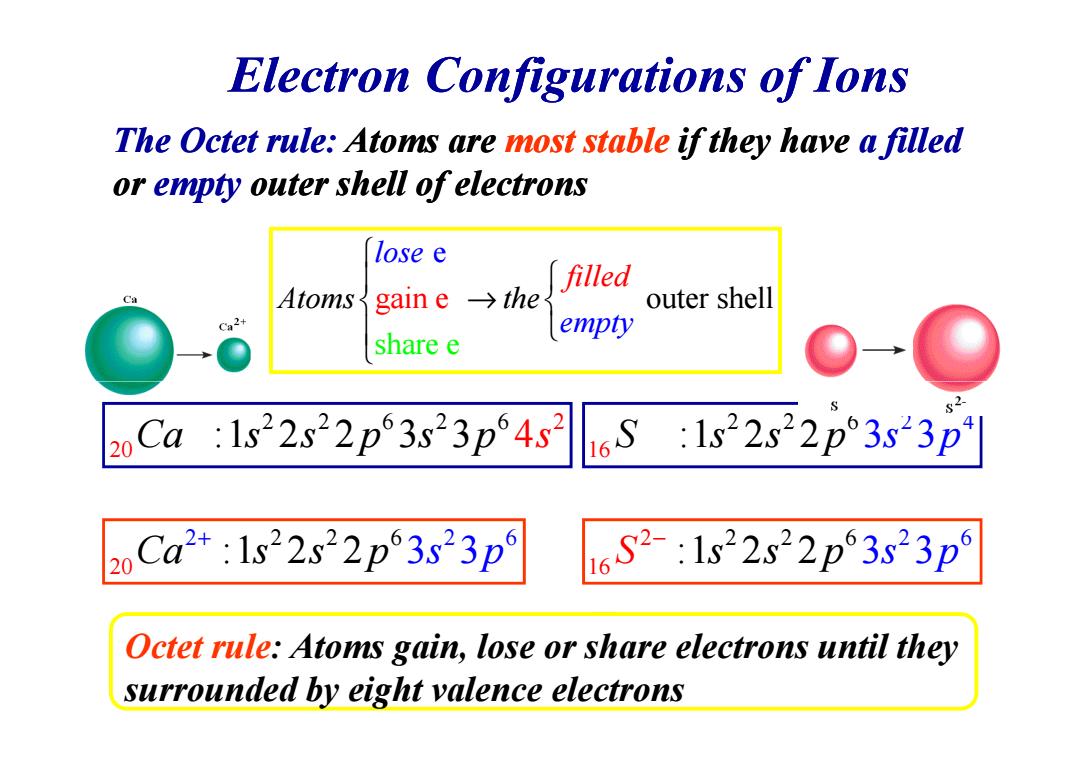
Electron Configurations of Ions The Octet rule:Atoms are most stable if they have a filled or empty outer shell of electrons lose e filled Ca Atoms gain e→the outer shell empty share e 20 Ca 1s22s22p3s23p4s2 16S:1s22s22p3s23p Ca2+:1s22s22p3s23p 16S2-:1s22s22p3s23p Octet rule:Atoms gain,lose or share electrons until they surrounded by eight valence electrons
Electron Configurations of Ions The Octet rule: Atoms are most stable if they have a filled or empty outer shell of electrons outer s shel hare gain e e e A l lose empty fille toms the d → Octet rule: Atoms gain, lose or share electrons until they surrounded by eight valence electrons 2 2 2 2 6 0 6 2 Ca s s p s p :1 2 2 3 3 4 s 2 2 2 6 0 2 6 2 Ca s s :1 2 2 p 3 3 s p + 2 2 6 2 4 16 S s s :1 2 2 p 3 3 s p 2 6 2 2 2 6 1 6 S :1 2 2 s s p 3 s 3 p −
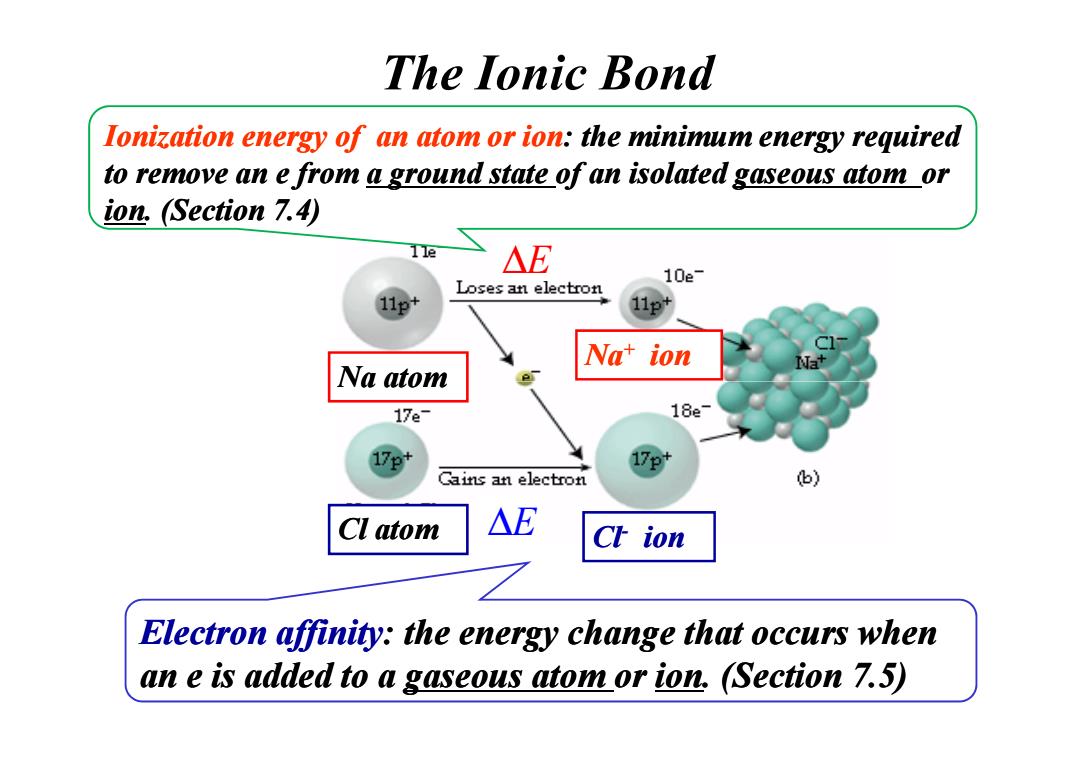
The lonic bond lonization energy of an atom or ion:the minimum energy required to remove an e from a ground state of an isolated gaseous atom or ion.(Section 7.4) 11e △E 10e- Loses an electron 11p+ Nat ion Na atom 17e- 18e 17e* Cains an electron 6) Cl atom △E Ch ion Electron affinity:the energy change that occurs when an e is added to a gaseous atom or ion,(Section 7.5)
Na atom Na+ ion Ionization energy of an atom or ion: the minimum energy required to remove an e from to remove an e from a ground state a ground state of an isolated of an isolated gaseous atom gaseous atom or ion. (Section 7.4) The Ionic Bond ∆E Na atom Cl- Cl atom ion Electron affinity: the energy change that occurs when an e is added to a an e is added to a gaseous atom gaseous atom or ion. (Section 7.5) ∆E
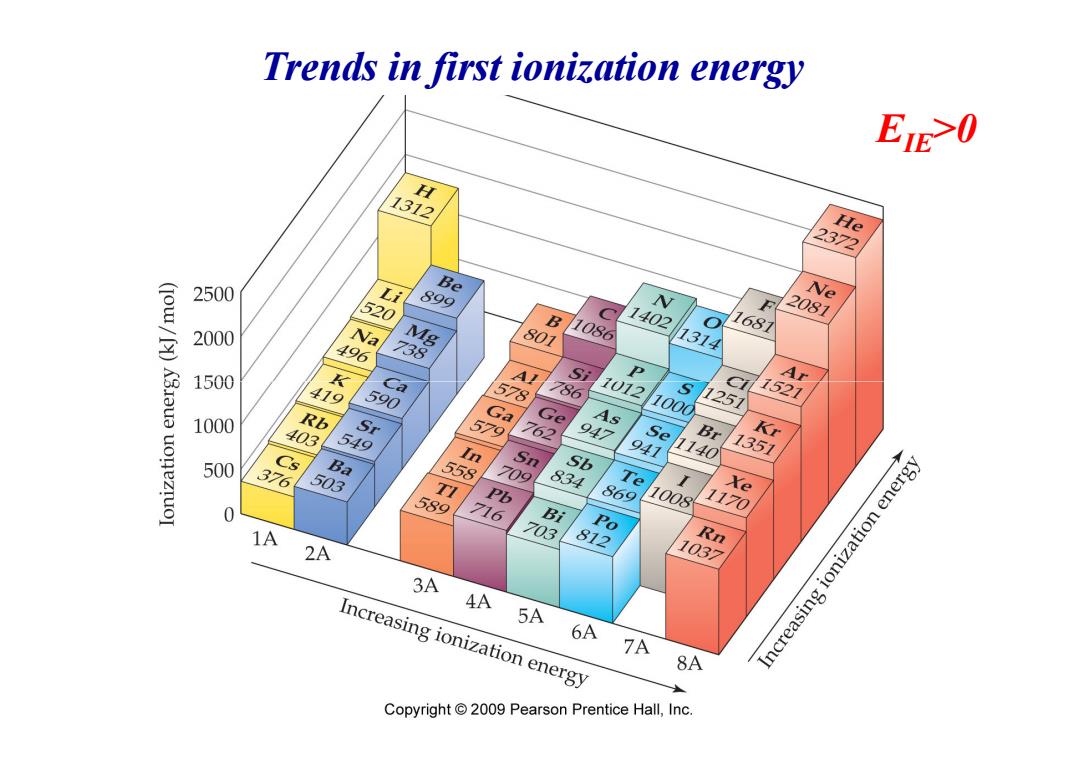
Trends in first ionization energy EIE0 H 1312 He 2372 2500 Li Be 520 899 V Ne F 2081 2000 Na 496 Mg B 801 1086 1402 1314 1681 738 K3Iaua 1500 Ca A! S Ar 419 590 578 786 1012 Ci 1000 1251 1521 1000 Rb Ga 579 Ge 762 As 403 9 Se Br Kr uonezro 549 n 1351 500 Cs 3 Ba 5 Sn 709 Sb 9 1140 503 TI 834 Te 589 Pb 86 Xe 716 1008 Bi 1170 o 1A 7 Rn 2A 81 1037 3A 4A Increasing ionization energy 5A 6A 7A Increasing ionization energy 8A Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Trends in first ionization energy EIE>0
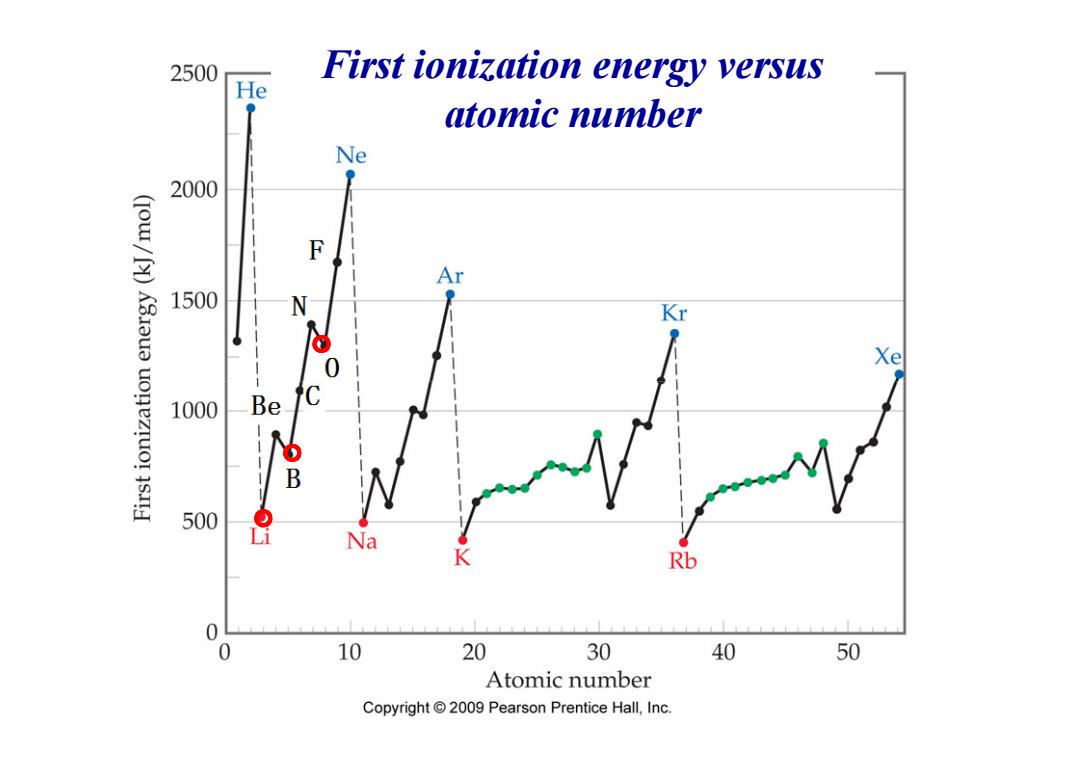
2500 First ionization energy versus He atomic number Ne 2000 F (Iow/[)K3Iua uonezruo!sI Ar 1500 Kr Xe 1000 Be C bB 500 Na K Rb 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 Atomic number Copyright2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
First ionization energy versus atomic number 。 。
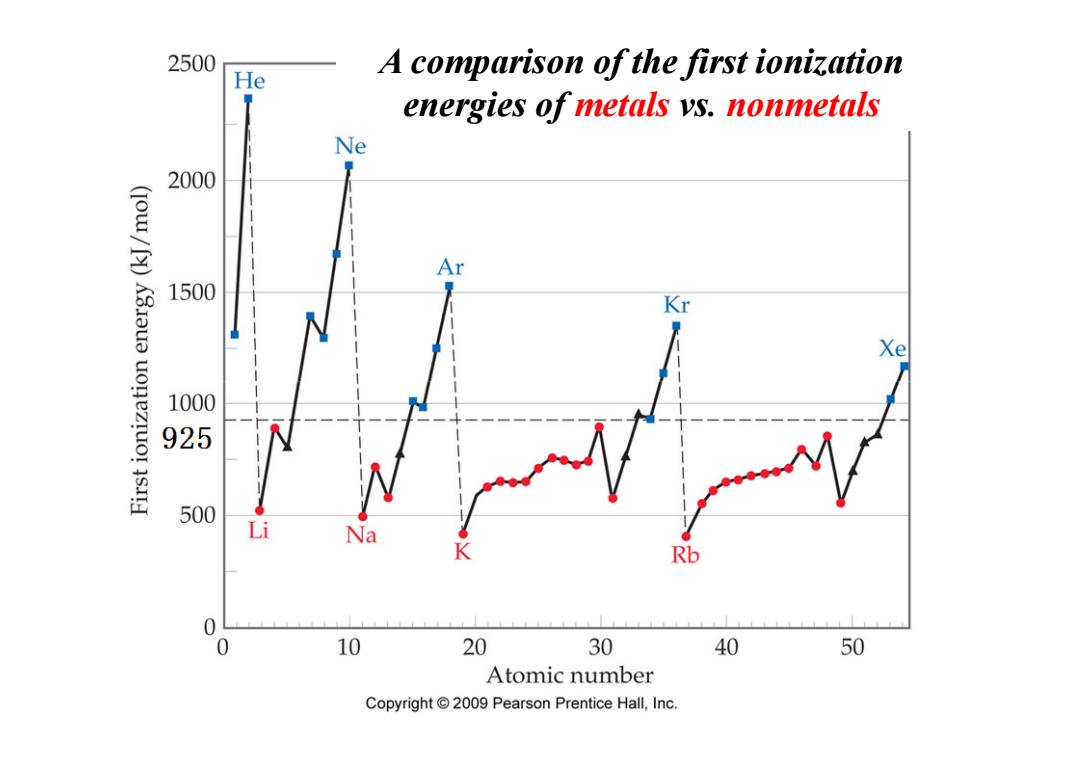
2500 He A comparison of the first ionization energies of metals ys.nonmetals Ne 2000 (IOw/[)K3aua uonezruo!s.I Ar 1500 Kr Xe 100 925 500 Li Na K Rb 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 Atomic number Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
A comparison of the first ionization energies of metals vs. nonmetals