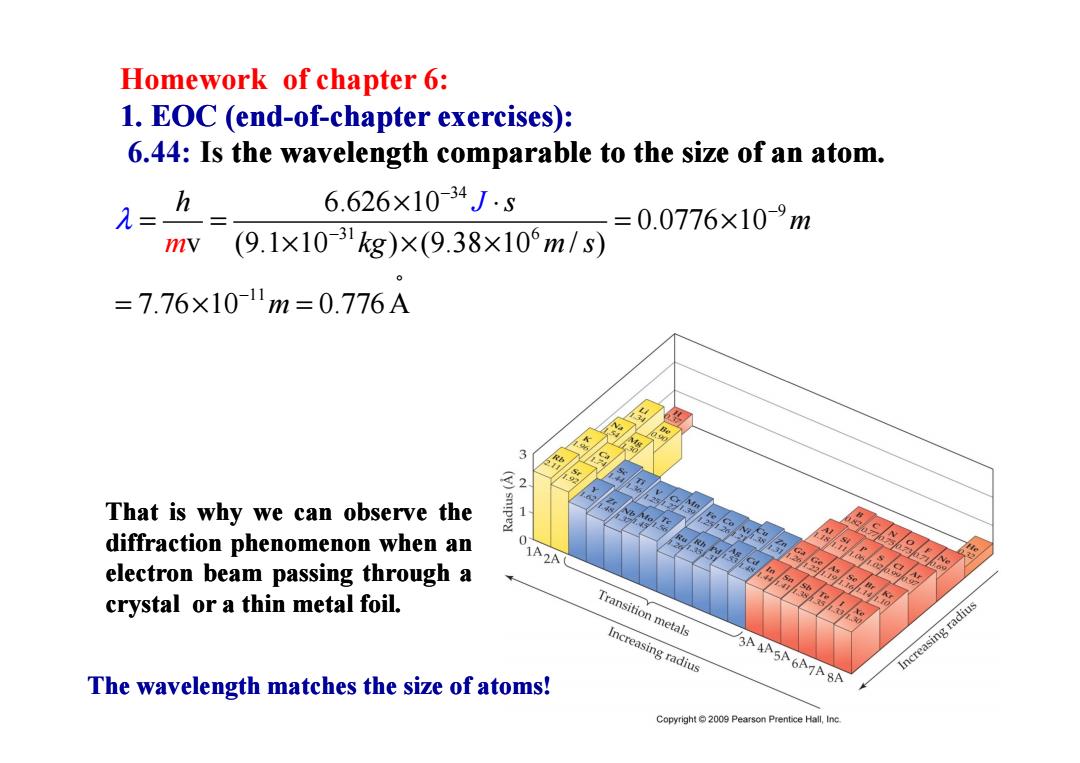
Homework of chapter 6: 1.EOC (end-of-chapter exercises): 6.44:Is the wavelength comparable to the size of an atom. h 6.626×10-34J.s = 0.0776×10-9m mv (9.1×10-31kg)×(9.38×10m/s) =7.76×10-1m=0.776A 32 That is why we can observe the diffraction phenomenon when an 0 bessasshee ® electron beam passing through a C8 crystal or a thin metal foil. Transition metals Increasing radius A AASA6A7A8A Increasing radius The wavelength matches the size of atoms! Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Homework of chapter 6: 1. EOC (end 1. EOC (end-of-chapter exercises): chapter exercises): 6.44: Is the wavelength comparable to the size of an atom. the wavelength comparable to the size of an atom. 34 9 31 6 11 6.626 10 0.0776 10 v (9.1 10 ) (9.38 10 / ) 7.76 10 0.776 A m h s m kg m s m J λ − − − ° − × ⋅ = = = × × × × = × = That is why we can observe observe the diffraction diffraction phenomenon phenomenon when an electron electron beam passing passing through through a crystal crystal or a thin metal foil. The wavelength matches the size of atoms!
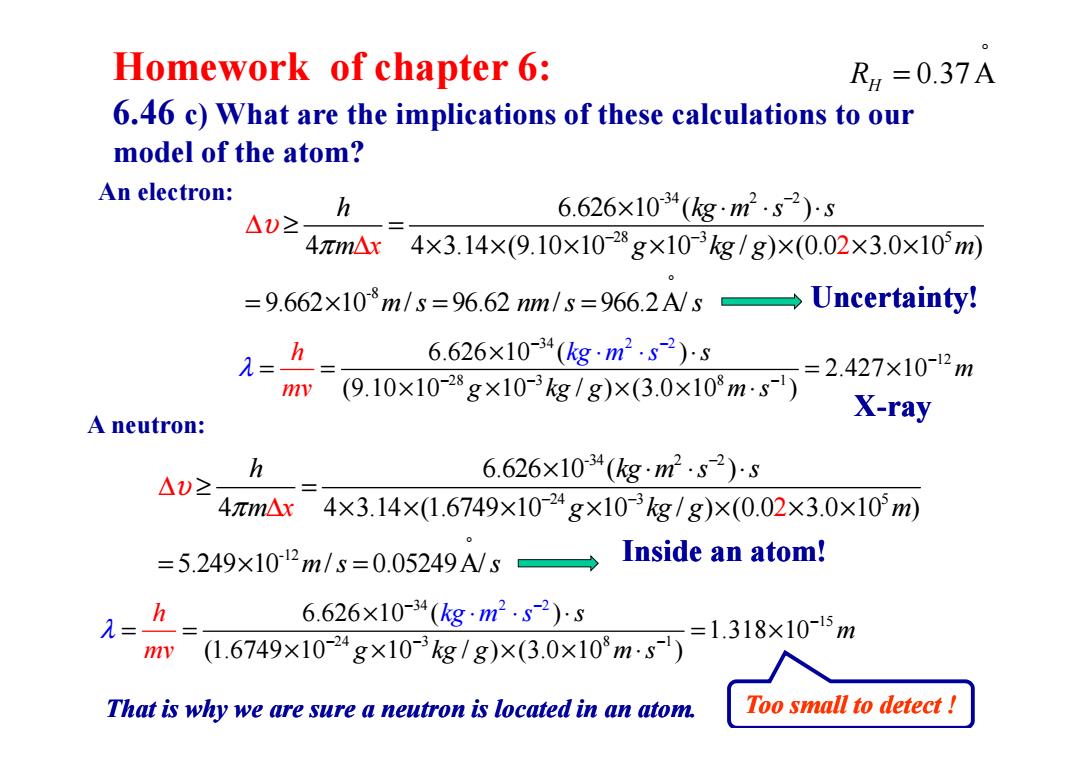
Homework of chapter 6: RH=0.37A 6.46 c)What are the implications of these calculations to our model of the atom? An electron: h 6.626×1034(gm2.s2)s △)2 4元m△x 4×3.14×(9.10×10-28g×103g/g)×(0.02×3.0×10m) =9.662x10m/s=96.62 nm/s=966.2A/sUncertainty! =- h 6.626×10-34(kgm2.s-2)s =2.427×10-12m mv (9.10×10-28g×10-3kg/g)×(3.0×10m·s) X-ray A neutron: h 6.626×1034(gm2.s2)s △U2 4元m△x 4×3.14×1.6749×10-24g×103kg/g)×(0.02×3.0×10m) =5.249×102m/s=0.05249A/5→ Inside an atom! 6.626×10-34(kg·m2.s-2)5 =1.318×10-15m (1.6749×10-24g×10-3kg/g)×(3.0×103m-s) That is why we are sure a neutron is located in an atom. Too small to detect!
34 12 28 2 3 8 2 1 6.626 10 ( ) 2.427 10 (9.10 10 10 / ) (3.0 10 ) s m g kg g m h kg m mv s s λ − − − − − − × ⋅ = = = × × × × × ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ Homework of chapter 6: 6.46 c) What are the implications of these calculations to our model of the atom? -34 2 2 28 3 5 -8 6.626 10 ( ) 4 4 3.14 (9.10 10 10 / ) (0.0 3.0 10 ) 9.662 10 / 96.62 / 966.2A 2 / h kg m s s m g kg g m m s nm s s x υ π − − − ° × ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ≥ = × × × ∆ ∆ × × × × = × = = An electron: Uncertainty! ° RH = 0.37 A 28 3 8 1 2.427 10 (9.10 10 10 / ) (3.0 10 ) m mv g kg g m s λ − − − = = = × × × × × ⋅ 34 15 24 3 8 1 2 2 6.626 10 ( ) 1.318 10 (1.6749 10 10 / ) (3.0 10 ) s m g kg g m h g m s s mv k λ − − − − − − × ⋅ = = = × ⋅ × × × × ⋅ ⋅ That is why we are sure a neutron is located in an atom. A neutron: -34 2 2 24 3 5 -12 6.626 10 ( ) 4 4 3.14 (1.6749 10 10 / ) (0.0 3.0 10 ) 5.249 10 / 0.05249A/ 2 h kg m s s m g kg g m m s s x υ π − − − ° × ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ ∆ ≥ = ∆ × × × × × × × = × = X-ray Inside an atom! Too small to detect !

Homework of chapter 6: 6.46 c)What are the implications of these calculations to our model of the atom? Nucleus ~10-4 <—1-5A
Homework of chapter 6: 6.46 c) What are the implications of these calculations to our model of the atom? Nucleus
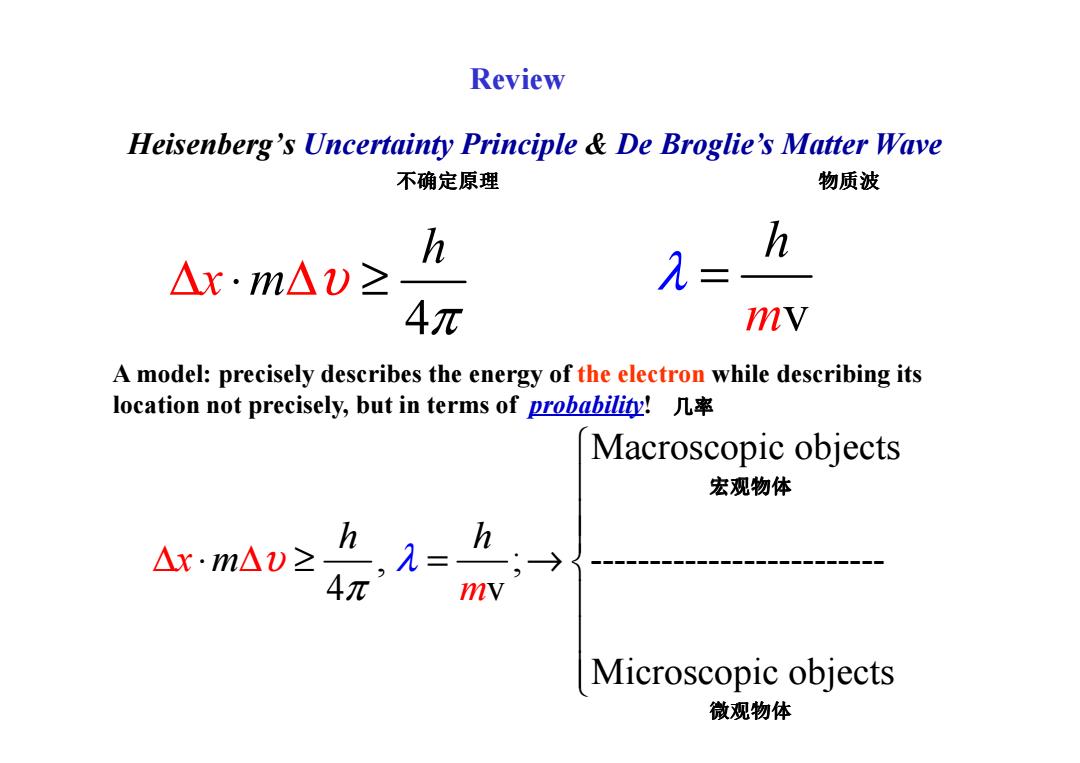
Review Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle De Broglie's Matter Wave 不确定原理 物质波 h h △x·m△)≥ = 4元 mV A model:precisely describes the energy of the electron while describing its location not precisely,but in terms of probability! Macroscopic objects 宏观物体 h △x·m△v≥ h,= mv Microscopic objects 微观物体
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle & De Broglie’s Matter Wave 4 h x m υ π ∆ ⋅ ∆ ≥ mv h λ = A model: precisely describes the energy of the electron while describing its 不确定原理 物质波 Review Macroscopic objects , ; ------------------------- 4 v Microscopic objects x h m h m υ π λ ∆ ∆ ⋅ ≥ = → A model: precisely describes the energy of the electron while describing its location not precisely, but in terms of probability! 几率 宏观物体 微观物体
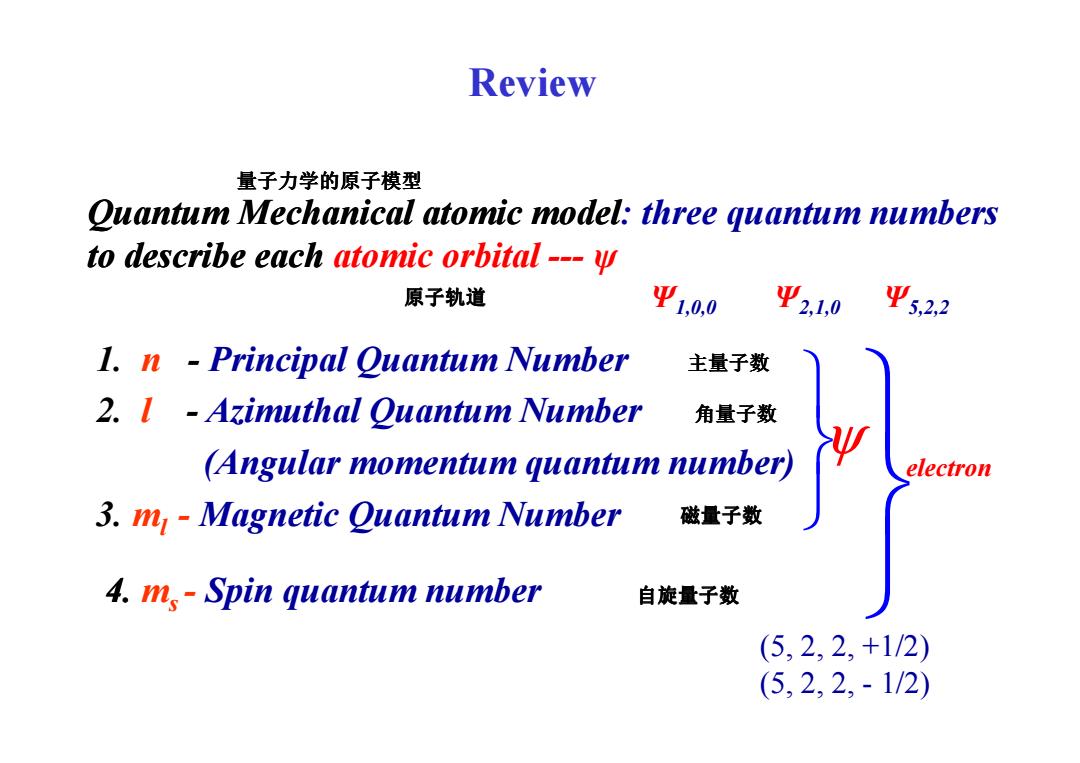
Review 量子力学的原子模型 Quantum Mechanical atomic model:three quantum numbers to describe each atomic orbital---y 原子轨道 Ψ1,0,0 Ψ21,0 Ψ52,2 1.n -Principal Quantum Number 主量子数 2.I Azimuthal Quantum Number 角量子数 (Angular momentum quantum number) electron 3.m Magnetic Quantum Number 磁量子数 4.m,-Spin quantum number 自旋量子数 (5,2,2,+1/2) (5,2,2,-1/2)
Quantum Mechanical atomic model: three quantum numbers to describe each atomic orbital --- ψ 1. n - Principal Quantum Number Review 主量子数 量子力学的原子模型 原子轨道 Ψ1,0,0 Ψ2,1,0 Ψ5,2,2 2. l - Azimuthal Quantum Number (Angular momentum quantum number) 3. ml - Magnetic Quantum Number 4. m s - Spin quantum number ψ 角量子数 磁量子数 自旋量子数 electron (5, 2, 2, +1/2) (5, 2, 2, - 1/2)
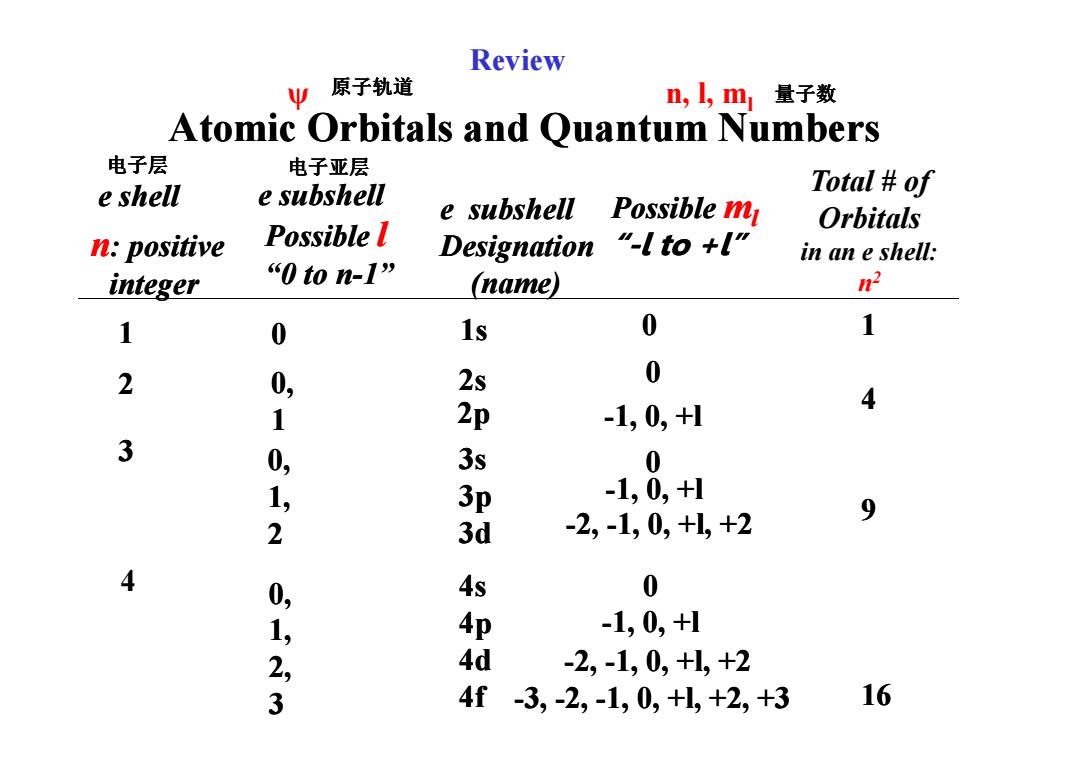
Review Ψ 原子轨道 n,,m量子数 Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers 电子层 电子亚层 e shell e subshell Total of e subshell Possible m Orbitals n:positive Possible l Designation "-l to +l" in an e shell: integer “0ton-l” (name) n2 1 0 1s 0 1 2 0, 2s 0 2p 4 1 -1,0,+1 3 0, 3s 0 1, 3p -1,0,+1 -2,-1,0,+l,+2 9 2 3d 4 0, 4s 0 1, 4p -1,0,+1 2, 4d -2,-1,0,+1,+2 3 4f -3,-2,-1,0,+1,+2,+3 16
Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers e shell 12 Possible l “0 to n “0 to n-1” 0 0, n: positive integer 1s 2s Possible ml “-l to +l” l to +l” 00 Total # of Orbitals in an e shell: n 2 14 ψ n, l, ml Review e subshell subshell e subshell subshell Designation (name) 原子轨道 量子数 电子层 电子亚层 23 4 0, 1 0, 1, 2 0, 1, 2, 3 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f 0 -1, 0, +l 1, 0, +l 0 -1, 0, +l 1, 0, +l -2, -1, 0, +l, +2 1, 0, +l, +2 0 -1, 0, +l 1, 0, +l -2, -1, 0, +l, +2 1, 0, +l, +2 -3, -2, -1, 0, +l, +2, +3 1, 0, +l, +2, +3 49 16
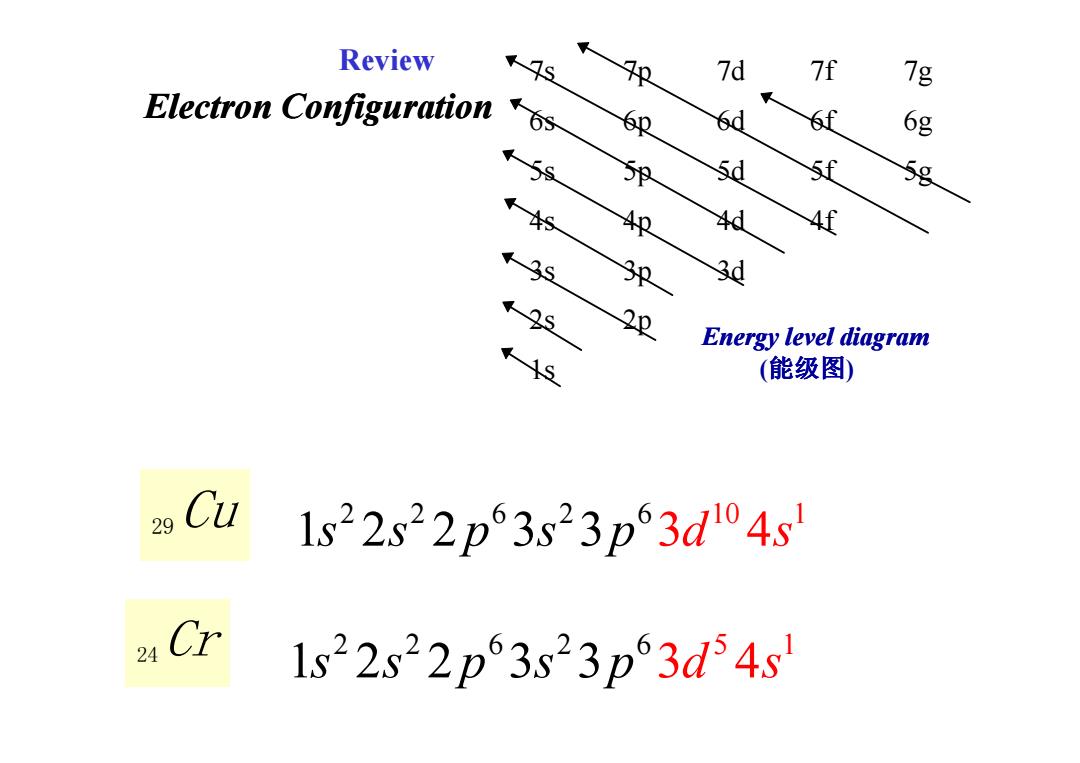
Review 9s 7d 7f 7g Electron Configuration 6p 6g 59 5d 58 4牧 4d 4f 3d Energy level diagram (能级图) 29 Cu 1s22s22p63,s23p63dl04s Cr 1s22s22p63s23p3d4s
Electron Configuration 7s 7p 7d 7f 7g 6s 6p 6d 6f 6g 5s 5p 5d 5f 5g 4s 4p 4d 4f 3s 3p 3d 2s 2p 1s Energy level diagram (能级图 ) Review 29Cu 24 Cr 2 2 6 2 6 10 1 1s s p s p 2 2 3 3 3d s 4 2 2 6 2 6 5 1 1 2 2 3 3 s s p s p 3 4 d s 1s ( )
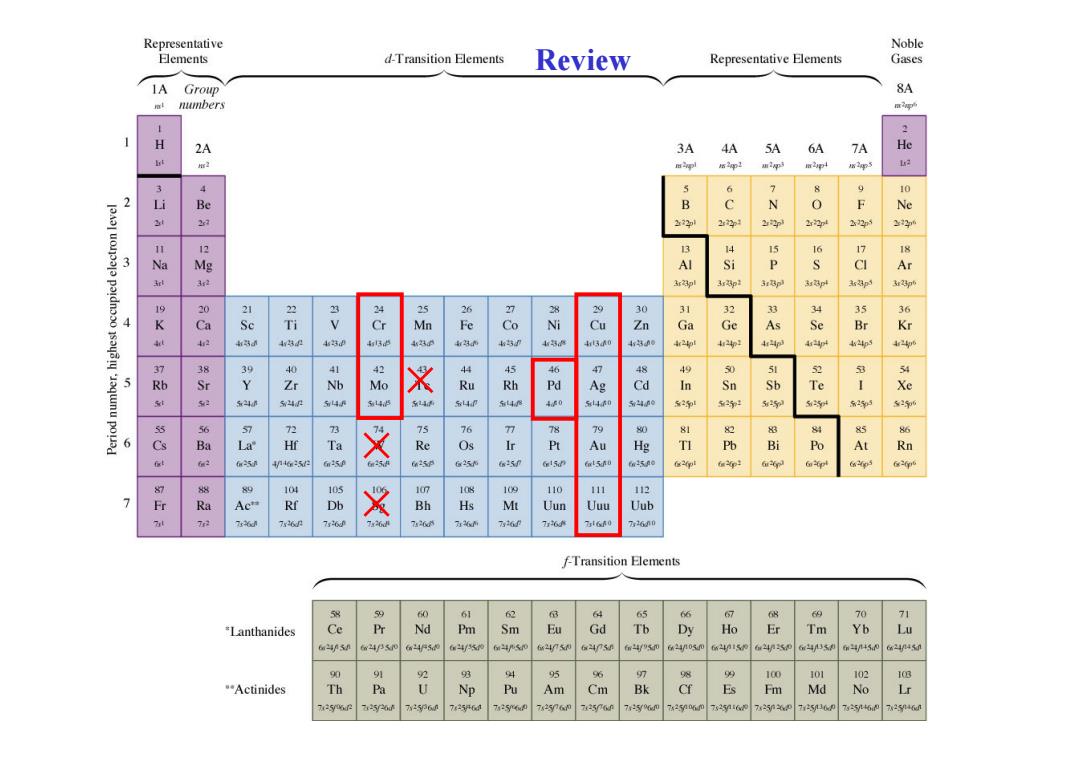
Representative Noble Elements d-Transition曰ements Review Representative Elements Gases IA Group 8A numbers 1 2 H 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A He s2gp1 通2p m2p 3 4 6 2 Be N 0 F Ne 2学1 22p 22p 22 12 13 3 Si P A 3rBpl 23 26 7 0 A 9K8 R 83 Ti & Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As 4特8 450 44p 新 5 8分 Y m 品 4 t48 314 6 84 A知 品 B Po m 625 625 105 110 111 112 7 行 A Bh Uun Uuu Uub 7 76 7r60 2 7426 76 76 t60 26n0 F-Transition Elements 58 1 6 65 69 70 71 *Lanthanides r Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 6m5n 2450 24n050 62415 6J5 6m/45M 6a2445n 90 2 男 94 95 96 98 100 101 1(B Actinides Th Pa Am Cm Bk Es Fm Md No Lr 5 7256n 7e256d 7a250 72n 75y0 7250 7206 7252 75y60 7a246n
× Review × ×
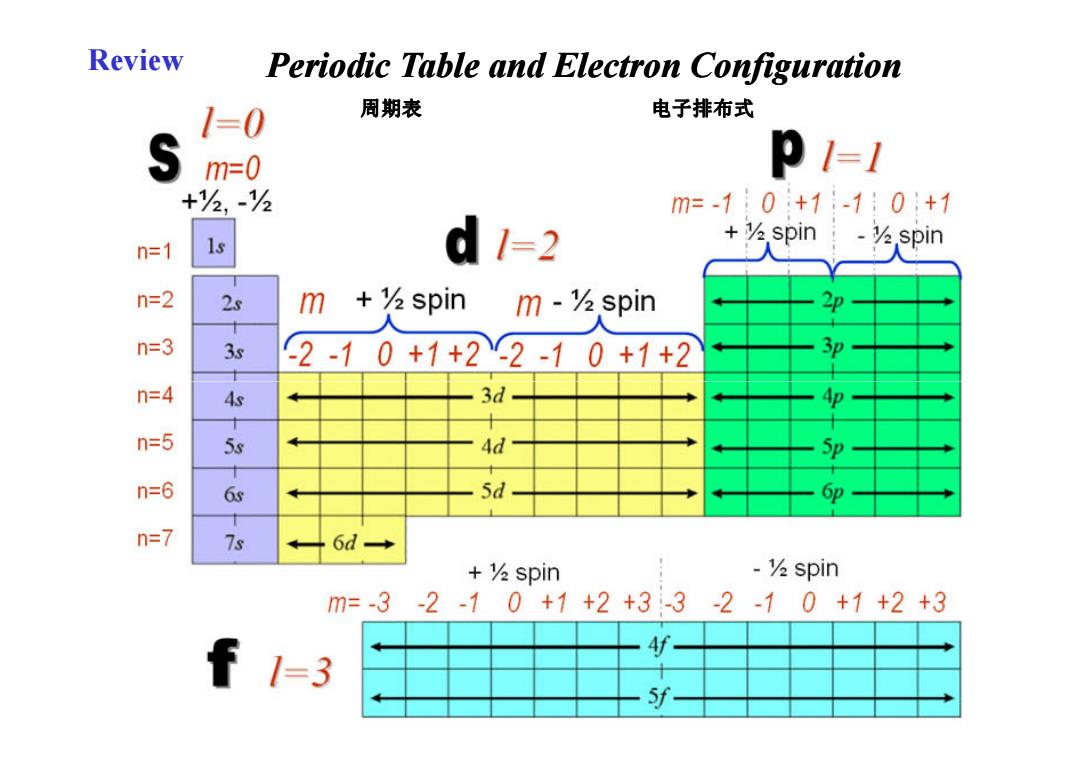
Review Periodic Table and Electron Configuration 1=0 周期表 电子排布式 m=0 p1=1 +么,-h m=-10+1-10+1 +spin V.spin n=1 1s d1=2 n=2 25 m +spin m-么spin n=3 3s 2-10+1+22-10+1+2 3P n=4 As 3d 十 n=5 5s Ad 5p n=6 Gs 5d 6p 十 n=7 7s 6d→ +%spin -V spin m=-3-2-10+1+2+3-3-2-10+1+2+3 f 1=3 斯 十 5f-
Review 周期表 Periodic Table and Electron Configuration 电子排布式

Review The size ofAtoms,ions and Molecules Trends in atomic radii. A Na (10-10m) 3 2 Nb Mo Co Ru .15 1A2A Rh G1.3 31 5 h.48 9 Transition metals Increasing radius 3AAAGA6A7A8A Increasing radius Li+ Li Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. 0.90 1.34
Trends in atomic radii. The size of Atoms, ions and Molecules Review Å (10-10 m)