Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap 9.5 Hybridization Hybrid Orbitals 9.6 Multiple bonds 9.7 Molecular Orbitals Chapter 9
Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Chapter 9 9.4 Covalent Bonding and Orbital Overlap 9.5 Hybridization & Hybrid Orbitals 9.6 Multiple bonds 9.7 Molecular Orbitals

NaCl Others? Covalent bonds.! alibaba.com.cn
NaCl Others? Covalent Bonds!
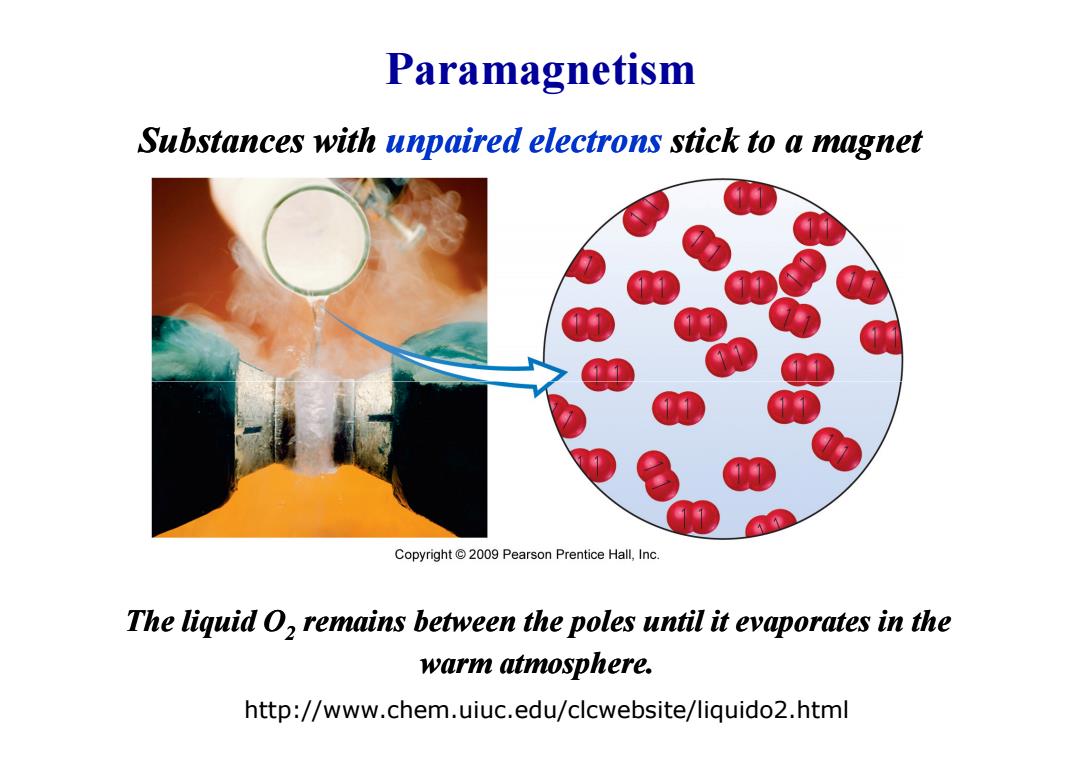
Paramagnetism Substances with unpaired electrons stick to a magnet Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The liquid O,remains between the poles until it evaporates in the warm atmosphere. http://www.chem.uiuc.edu/clcwebsite/liquido2.html
Paramagnetism Substances with unpaired electrons stick to a magnet http://www.chem.uiuc.edu/clcwebsite/liquido2.html The liquid O2 remains between the poles until it evaporates in the warm atmosphere
Molecular Orbital (MO)Theory What's a MO Atomic Orbitals (AO) Wave functions ( Molecular Orbitals(MO) Different‘shapes': -MO:o (sigma)and (pi) -AO:s,p,d,f etc
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Atomic Orbitals ( ) Wave functions ( ) Molecular Orbitals ( ) A MO O ψ Different ‘shapes’: – MO: σ (sigma) and π (pi) – AO: s, p, d, f, etc
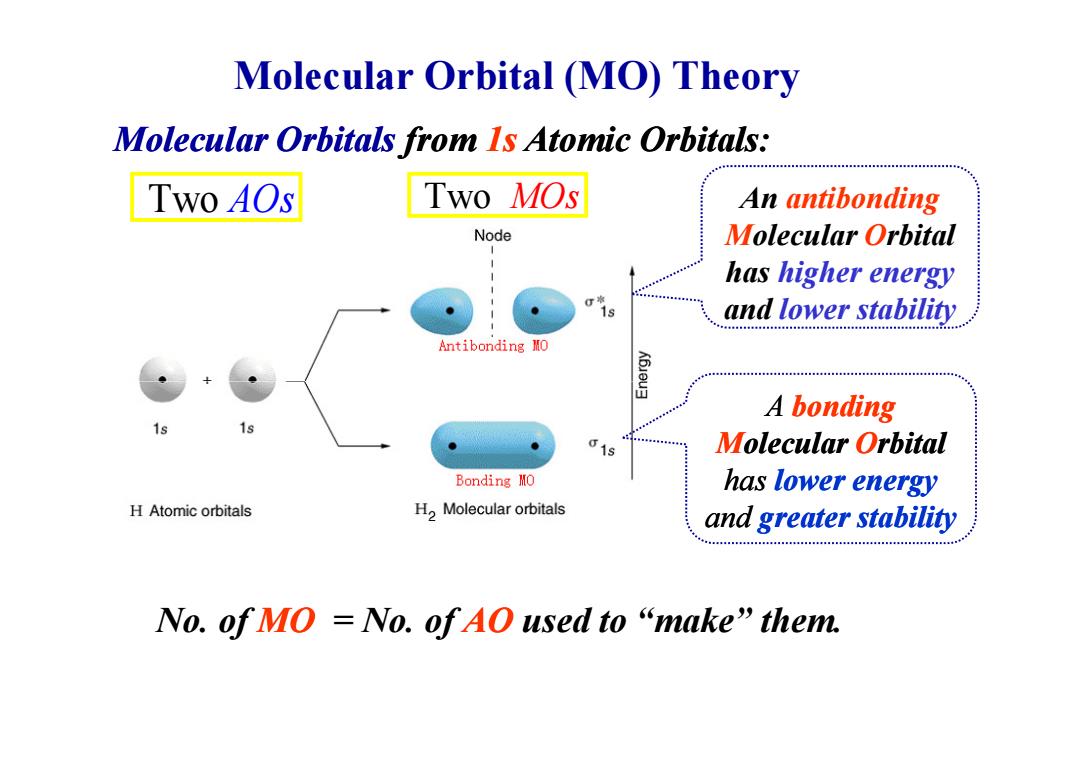
Molecular Orbital (MO)Theory Molecular Orbitals from Is Atomic Orbitals: Two A0s Two MOs An antibonding Node Molecular Orbital has higher energy s and lower stability Antibonding MO A bonding 61 Molecular Orbital Bonding MO has lower energy H Atomic orbitals H2 Molecular orbitals and greater stability No.ofMO=No.ofAO used to“make”them
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Two AOs Two MOs An antibonding Molecular Orbital has higher energy and lower stability Molecular Orbitals from 1s Atomic Orbitals: No. of MO = No. of AO used to “make” them. A bonding Molecular Orbital has lower energy and greater stability
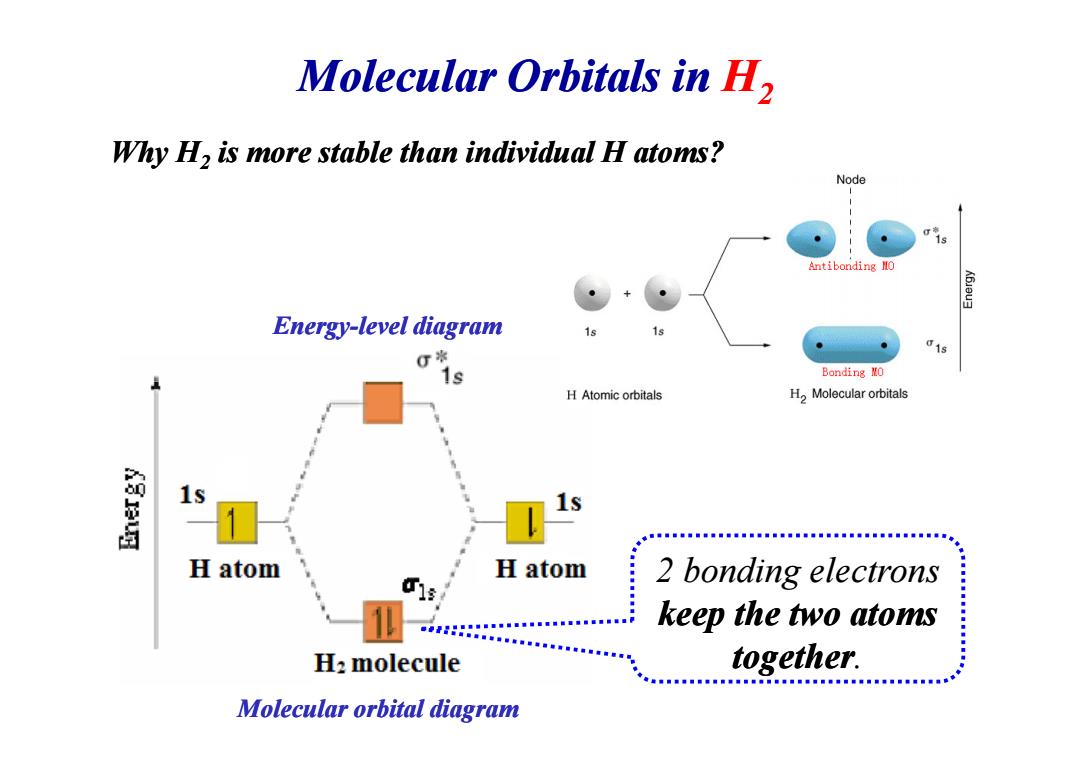
Molecular Orbitals in H2 Why H2 is more stable than individual H atoms? Node Antibonding MO K6ieu3 Energy-level diagram 015 1s Bonding MO H Atomic orbitals H2 Molecular orbitals 1s 1s H atom H atom 2 bonding electrons keep the two atoms H:molecule together. Molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbitals in H2 Why H2 is more stable than individual H atoms? Energy-level diagram level diagram 2 bonding electrons keep the two atoms together. Molecular orbital diagram

9.7 Molecular Orbital (MO)Theory Electron configuration of quantized MO: Lowest energy rule ---Lowest energy level fills first Pauli's Exclusion Principle ---2e maximum per orbital Hund's rule --For degenerate orbitals 1 electron in each orbital before double-up!
9.7 Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Lowest energy rule --- Lowest energy level fills Lowest energy level fills first Electron configuration of quantized MO : Pauli’s Exclusion Principle --- 2e maximum per 2e maximum per orbital Hund’s rule --- For degenerate orbitals : 1 electron in each orbital before double electron in each orbital before double-up!
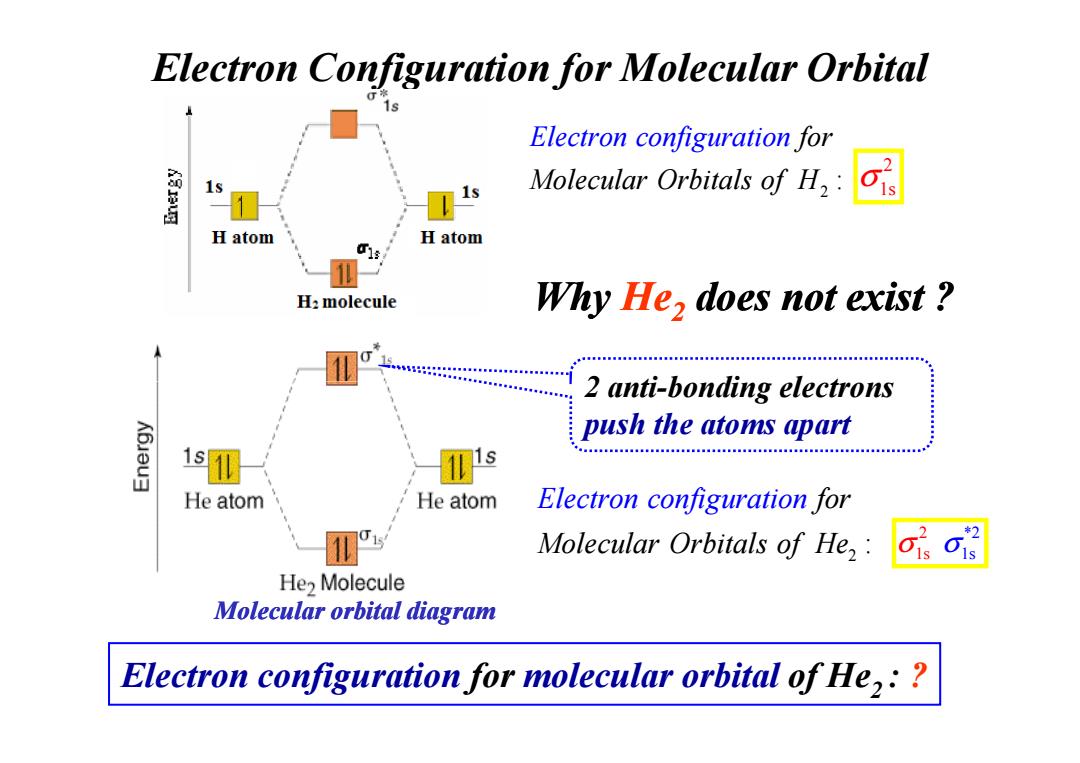
Electron Configuration for Molecular Orbital Electron configuration for Molecular Orbitals of H, H atom H atom H:molecule Why He,does not exist 2 anti-bonding electrons K6Jau push the atoms apart 1 He atom He atom Electron configuration for Molecular Orbitals of He,: He2 Molecule Molecular orbital diagram Electron configuration for molecular orbital of He,:
Why He2 does not exist ? Electron Configuration for Molecular Orbital 2 anti-bonding electrons 2 : for Molecular Elec Orb tron conf ital ig s of u atio H r n 2 σ1s 2 anti-bonding electrons push the atoms apart 2 : for Molecular Elec Orbi tron c tals onfigurati f o He n o Molecular orbital diagram Electron configuration for molecular orbital of He2 : ? 2 * 1s 2 σ σ1s
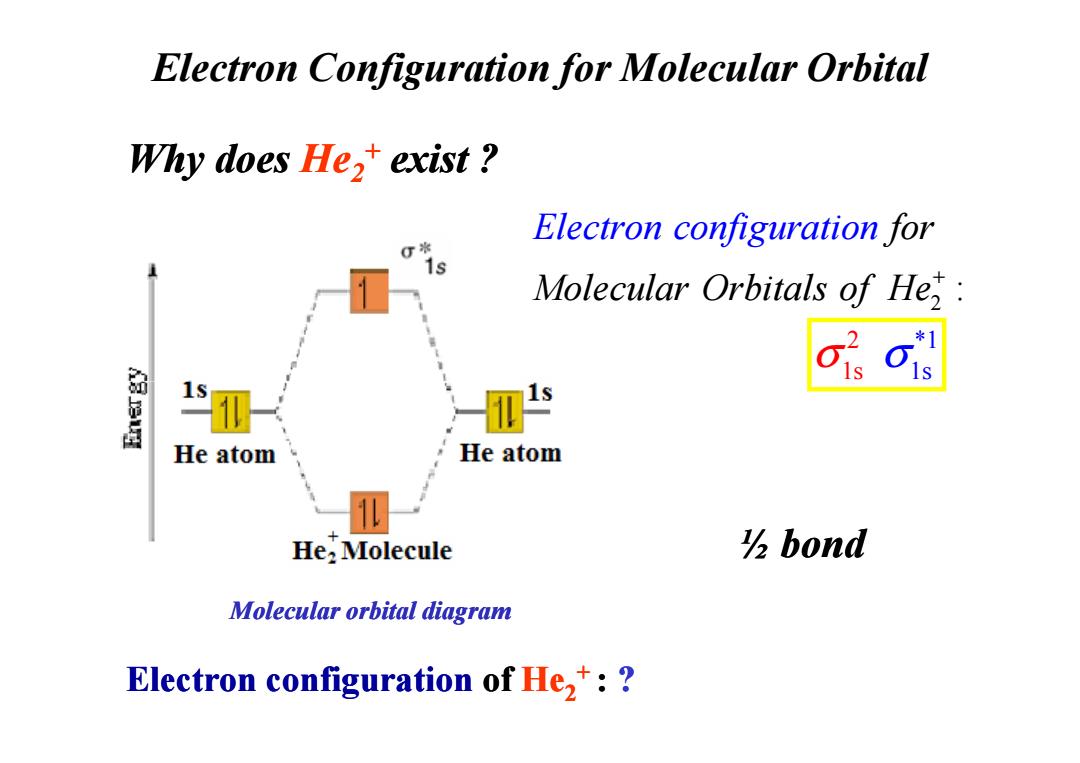
Electron Configuration for Molecular Orbital Why does He,+exist? Electron configuration for Molecular Orbitals of He, He atom He atom He:Molecule bond Molecular orbital diagram Electron configuration of He,:
Why does He2+ exist ? Electron Configuration for Molecular Orbital 2 : for Molecul Electr ar Orbital on conf s of iguratio He n + 2 * 1s 1 σ σ1s Electron configuration of He2+ : ? Molecular orbital diagram 1s 1s ½ bond
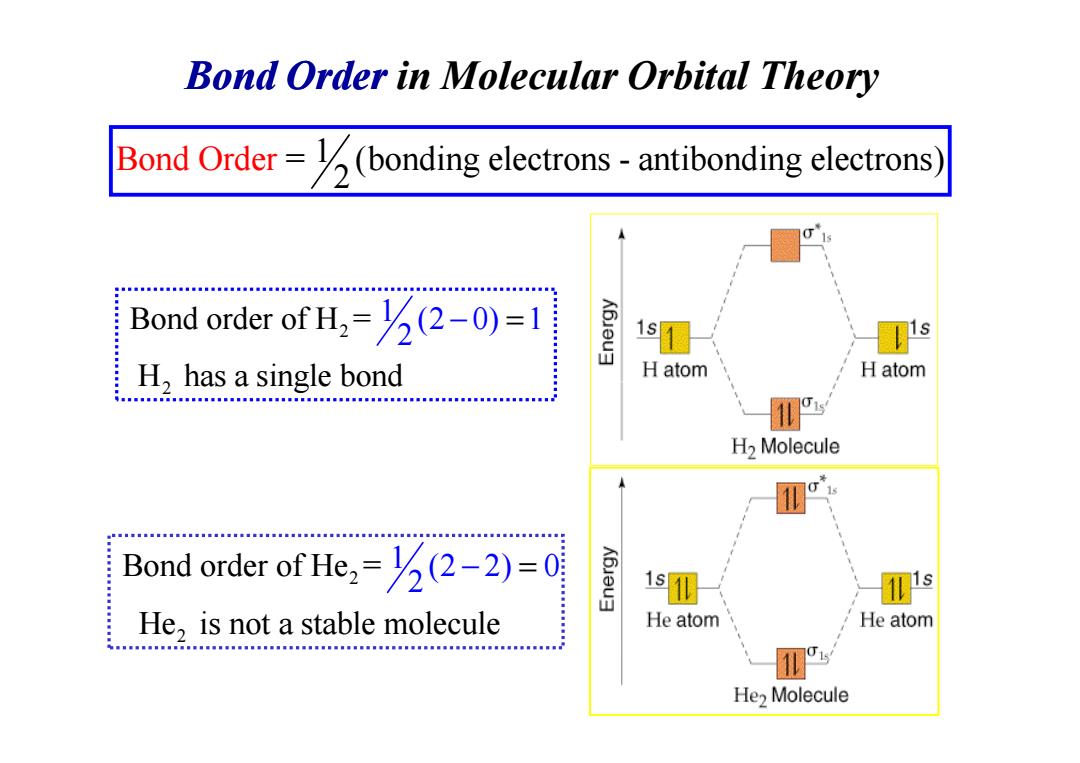
Bond Order in Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Order=(bonding electrons-antibonding electrons Bond order of H=(-0)=1 1s H,has a single bond H atom H atom CHHH.HEHBH....MNNAM.MNN.MM3n...l... H2 Molecule Bond order of He=(2-2)=0 He,is not a stable molecule He atom He atom He>Molecule
Bond Order in Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Ord = (bonding electrons - antibonding 1 electr 2 er ons) 2 2 1 Bond order of H = (2 0) 1 H has a singl 2 e bond − = 2 H has a singl 2 2 Bond order of He = He is not a stable 1 (2 m 2) 0 2 olecule − =