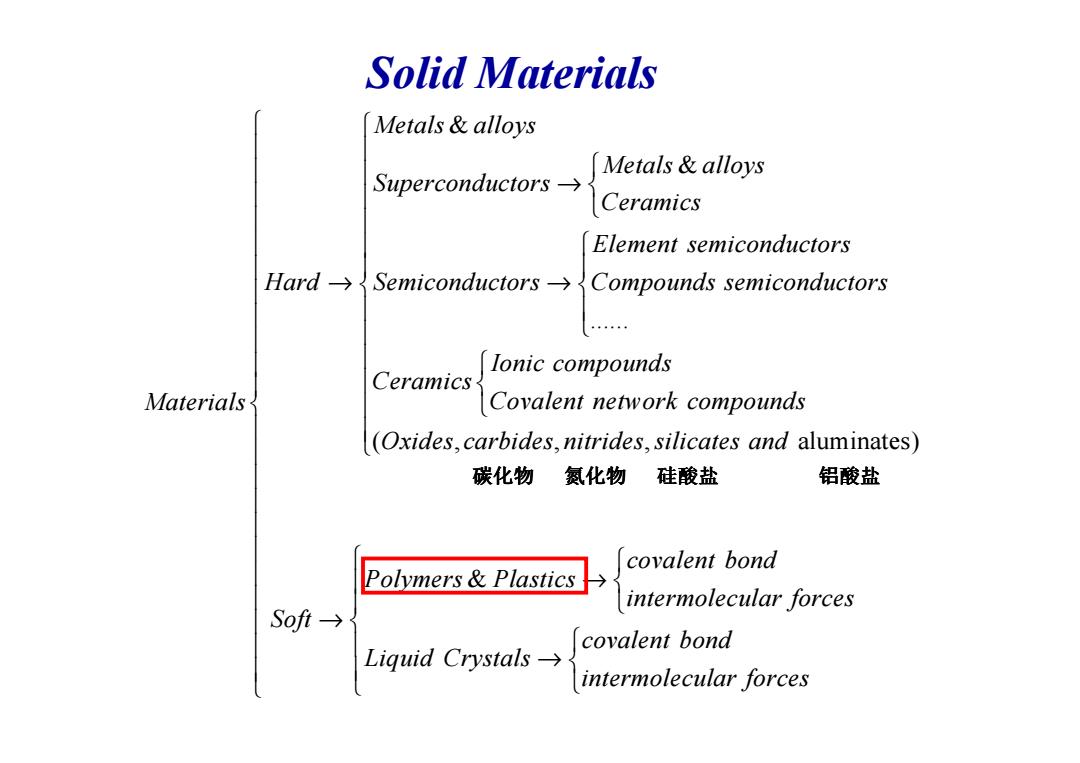
Solid Materials Metals alloys Metals alloys Superconductors→ Ceramics Element semiconductors Hard->Semiconductors->Compounds semiconductors lonic compounds Ceramics Materials Covalent network compounds (Oxides,carbides,nitrides,silicates and aluminates) 碳化物 氮化物 硅酸盐 铝酸盐 covalent bond Polymers&Plastics→ intermolecular forces Sofi→ covalent bond Liquid Crystals-→ intermolecular forces
Solid Materials & & ...... Metals alloys Metals alloys Superconductors Ceramics Element semiconductors Hard Semiconductors Compounds semiconductors Ionic compounds Ceramics → → → ( , Ceramics Materials Covalent network compounds Oxides c , , aluminates) & arbides nitrides silicates and covalent bond Polymers Plastics intermolecular forces Soft covalent bond Liquid Crystals intermolecular forces → → → 碳化物 氮化物 硅酸盐 铝酸盐
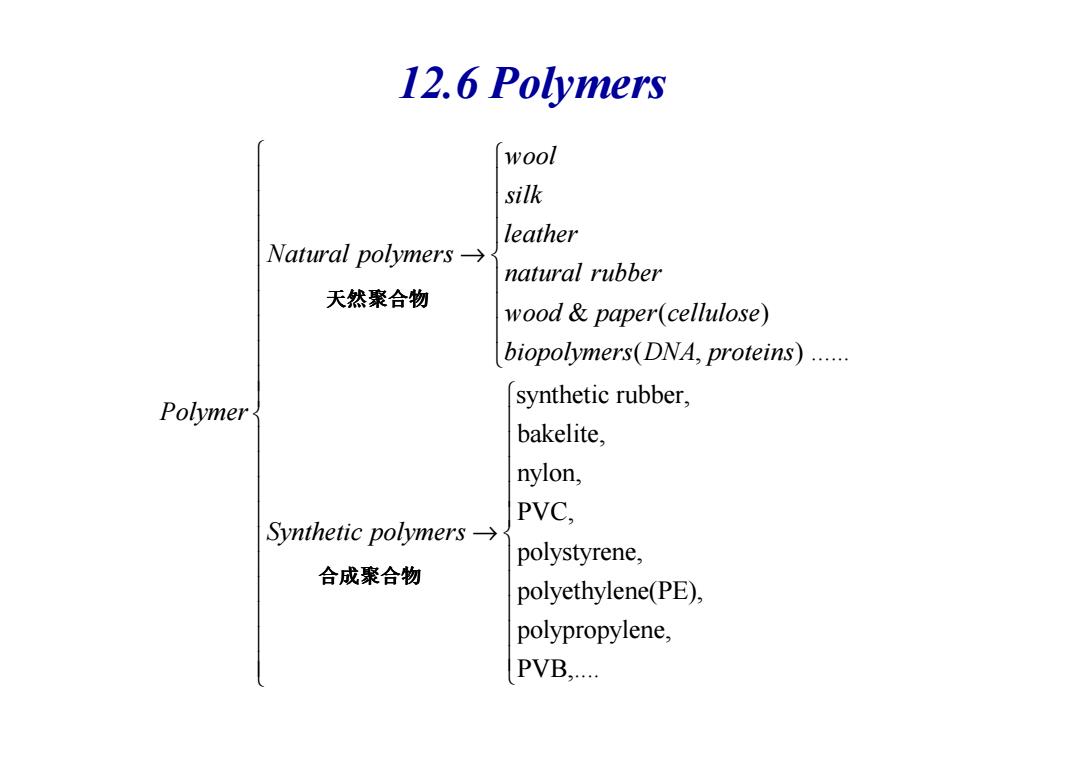
12.6 Polymers 1w00l silk leather Natural polymers→ natural rubber 天然聚合物 wood paper(cellulose) biopolymers(DNA,proteins)...... Polymer synthetic rubber, bakelite, nylon, PVC, Synthetic polymers-→ polystyrene, 合成聚合物 polyethylene(PE), polypropylene, PVB
12.6 Polymers & ( ) ( , ) ...... synthetic rubber, wool silk leather Natural polymers natural rubber wood paper cellulose biopolymers DNA proteins → 天然聚合物 synthetic rubber, bakelite, nylon, PVC, polystyrene, polyethylene(PE Polymer Synthetic polymers → ), polypropylene, PVB,.... 合成聚合物
Soft materials:Polymers and Plastics Polymers are substances containing a large number of structural units joined by the same type of linkage. These substances often form into a chain-like structure Polymers already have a range of applications that far exceeds that of any other class of material available to human being. tp://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/polymers/ware.html
Soft materials: Polymers and Plastics Polymers are substances containing a large number of structural units joined by the same type of linkage. These substances often form into a chain-like structure. Polymers already have a range of applications that far exceeds that of any other class of material available to human being. http://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/polymers/ware.html
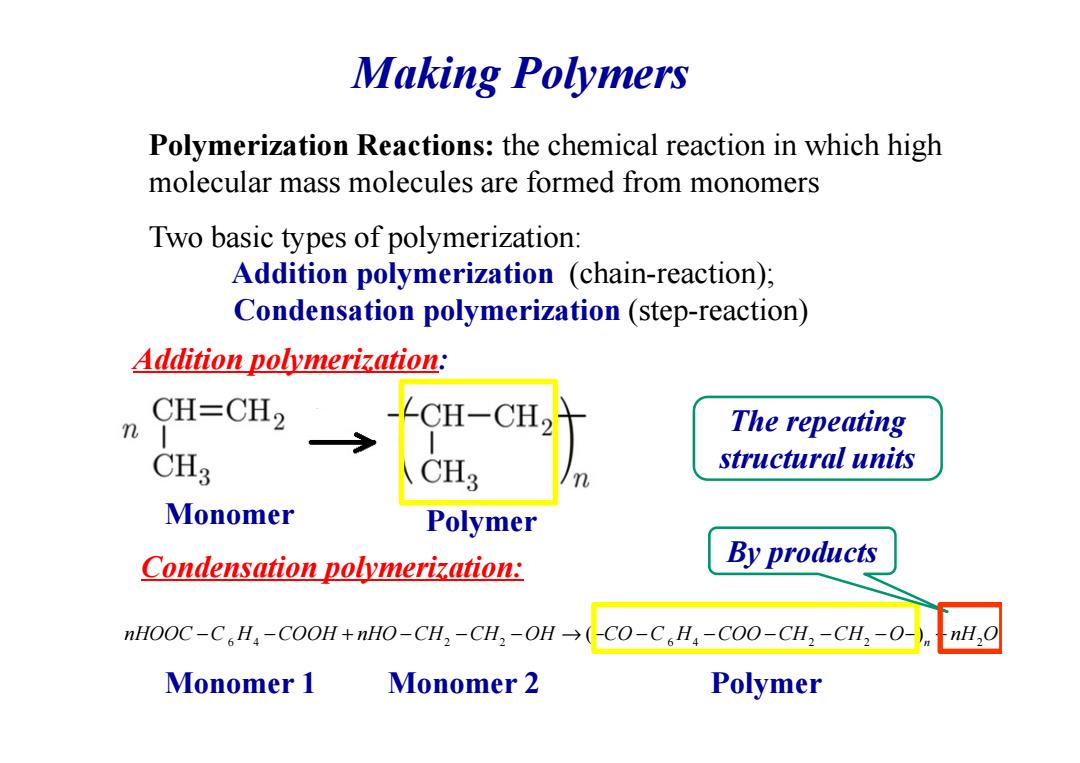
Making Polymers Polymerization Reactions:the chemical reaction in which high molecular mass molecules are formed from monomers Two basic types of polymerization: Addition polymerization (chain-reaction); Condensation polymerization (step-reaction) Addition polymerization: CH=CH2 CH-CH2 The repeating CH3 CH3 structural units Monomer Polymer Condensation polymerization: By products nHOOC-C H:-COOH+nHO-CH,-CH,-OH(-CO-C.H,-C00-CH,-CH:-0-) nH,O Monomer 1 Monomer 2 Polymer
Making Polymers Polymerization Reactions: the chemical reaction in which high molecular mass molecules are formed from monomers Addition polymerization : Two basic types of polymerization: Addition polymerization (chain-reaction); Condensation polymerization (step-reaction) 6 4 2 2 6 4 2 2 2 ( ) n nHOOC C H COOH nHO CH CH OH CO C H COO CH CH O nH O − − + − − − → − − − − − − − + The repeating structural units Condensation polymerization: Monomer Polymer Monomer 1 Monomer 2 Polymer By products
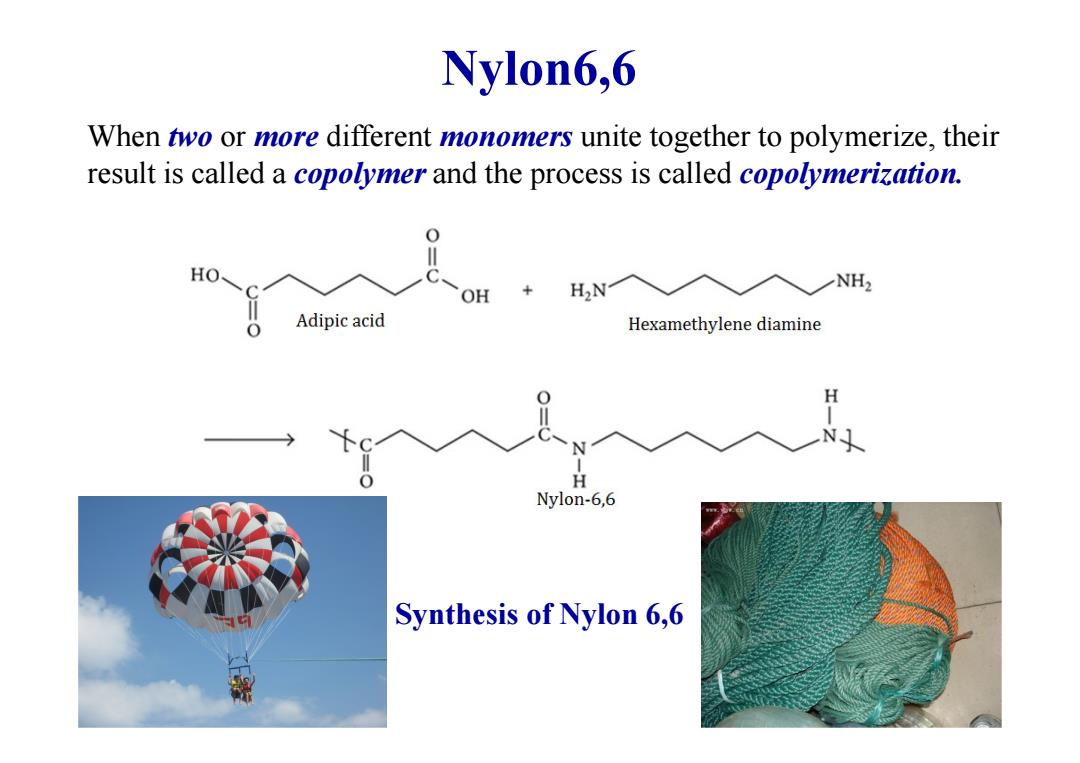
Nylon6,6 When two or more different monomers unite together to polymerize,their result is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerization. 0 HO、 NH2 OH ,+H2N Adipic acid Hexamethylene diamine H N H Nylon-6,6 Synthesis of Nylon 6,6
Nylon6,6 When two or more different monomers unite together to polymerize, their result is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerization. Synthesis of Nylon 6,6
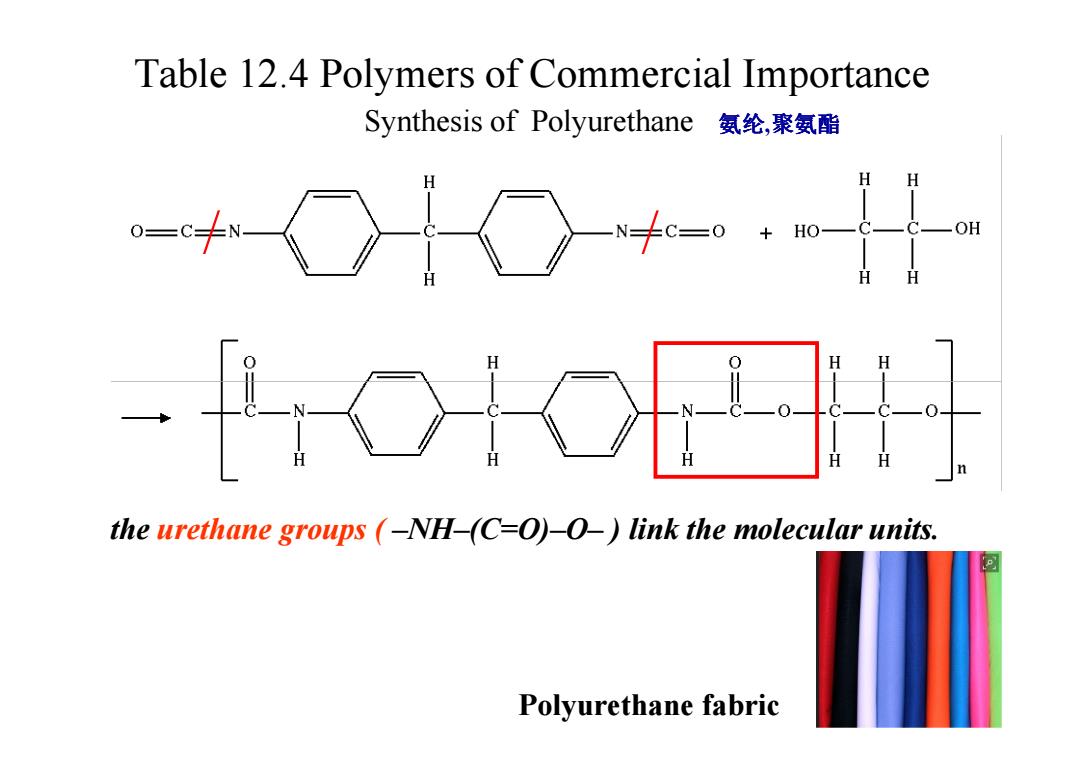
Table 12.4 Polymers of Commercial Importance Synthesis of Polyurethane氨纶,聚氨酯 H H N十c=0+o- OH H the urethane groups (-NH-(C-O)-O-)link the molecular units. Polyurethane fabric
Table 12.4 Polymers of Commercial Importance / / Synthesis of Polyurethane 氨纶,聚氨酯 the urethane groups ( –NH–(C=O)–O– ) link the molecular units. Polyurethane fabric
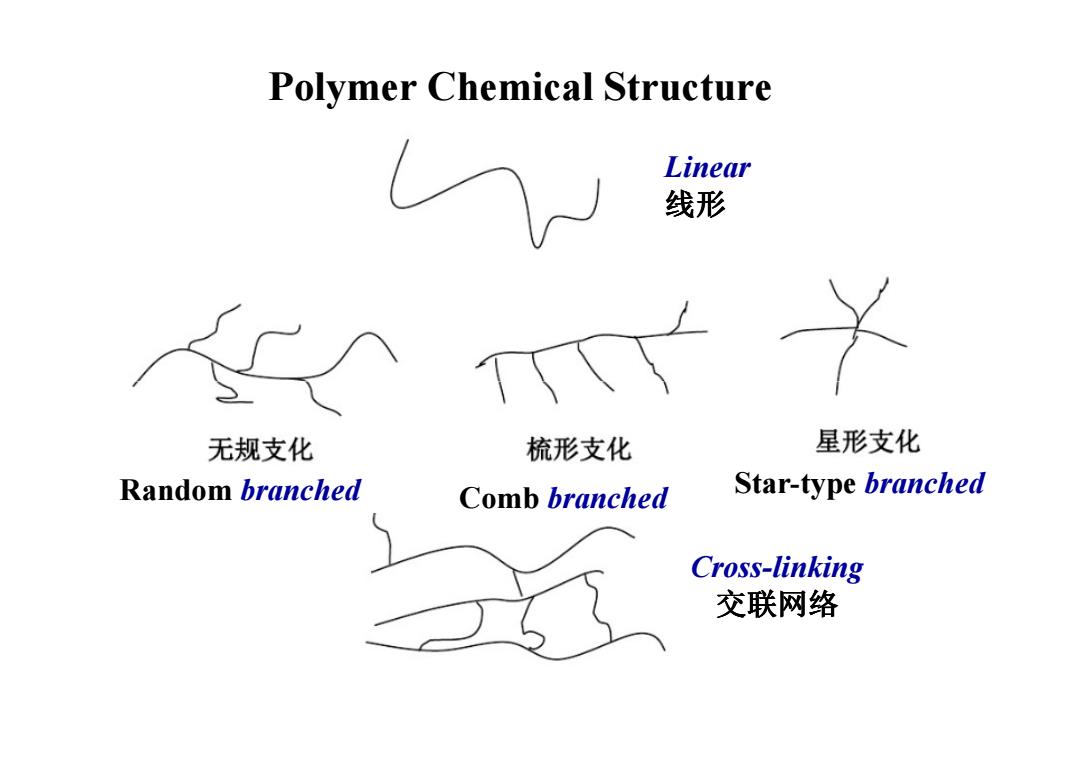
Polymer Chemical Structure Linear 线形 无规支化 梳形支化 星形支化 Random branched Comb branched Star-type branched Cross-linking 交联网络
Polymer Chemical Structure Linear 线形 Cross-linking 交联网络 Star-type branched Random Comb branched branched

Properties of Polymers Are they made from Polyethylene? 聚乙烯 HDPE LOPE-LOW DENSITY POLYETHYLENE E栏别OM IOKTHUSAC1 MAPPUCAT2N性 LDPE
Properties of Polymers 聚乙烯
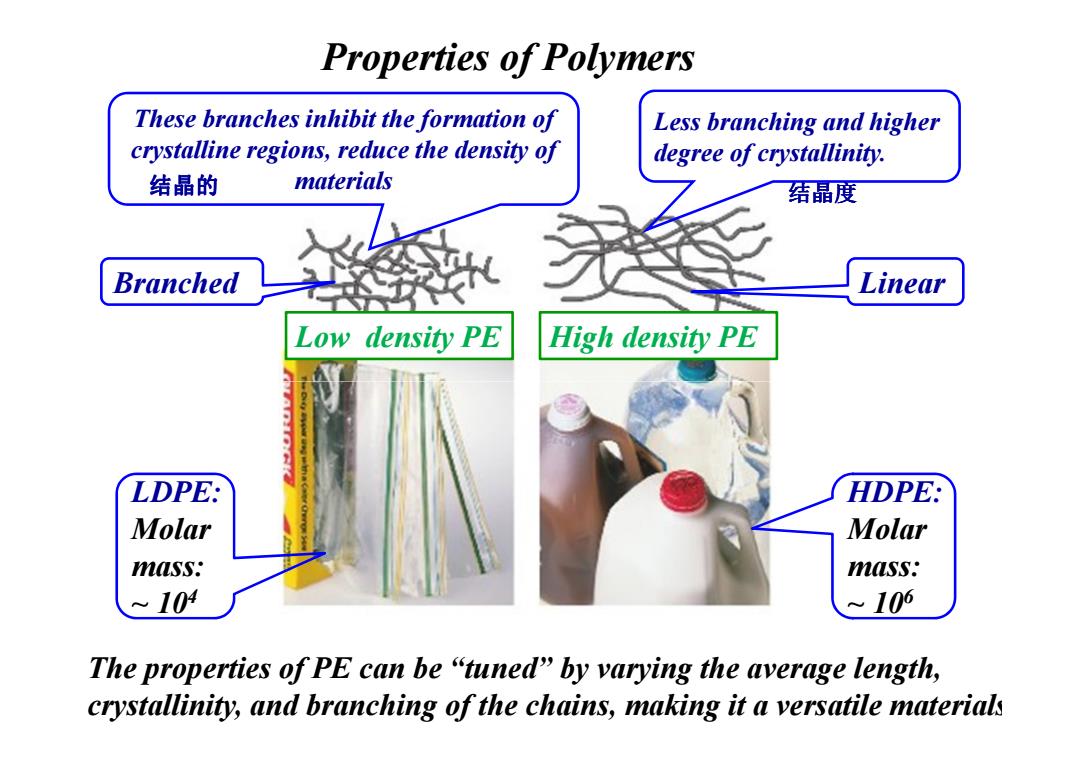
Properties of Polymers These branches inhibit the formation of Less branching and higher crystalline regions,reduce the density of degree of crystallinity. 结晶的 materials 结晶度 Branched Linear Low density PE High density PE LDPE: HDPE: Molar Molar mass: mass: 104 ~106 The properties of PE can be "tuned"by varying the average length, crystallinity,and branching of the chains,making it a versatile material
Properties of Polymers These branches inhibit the formation of crystalline regions, reduce the density of materials Less branching and higher degree of crystallinity. Branched Linear Low density PE High density PE 结晶的 结晶度 LDPE: Molar mass: ~ 10 4 HDPE: Molar mass: ~ 10 6 The properties of PE can be “tuned” by varying the average length, crystallinity, and branching of the chains, making it a versatile materials
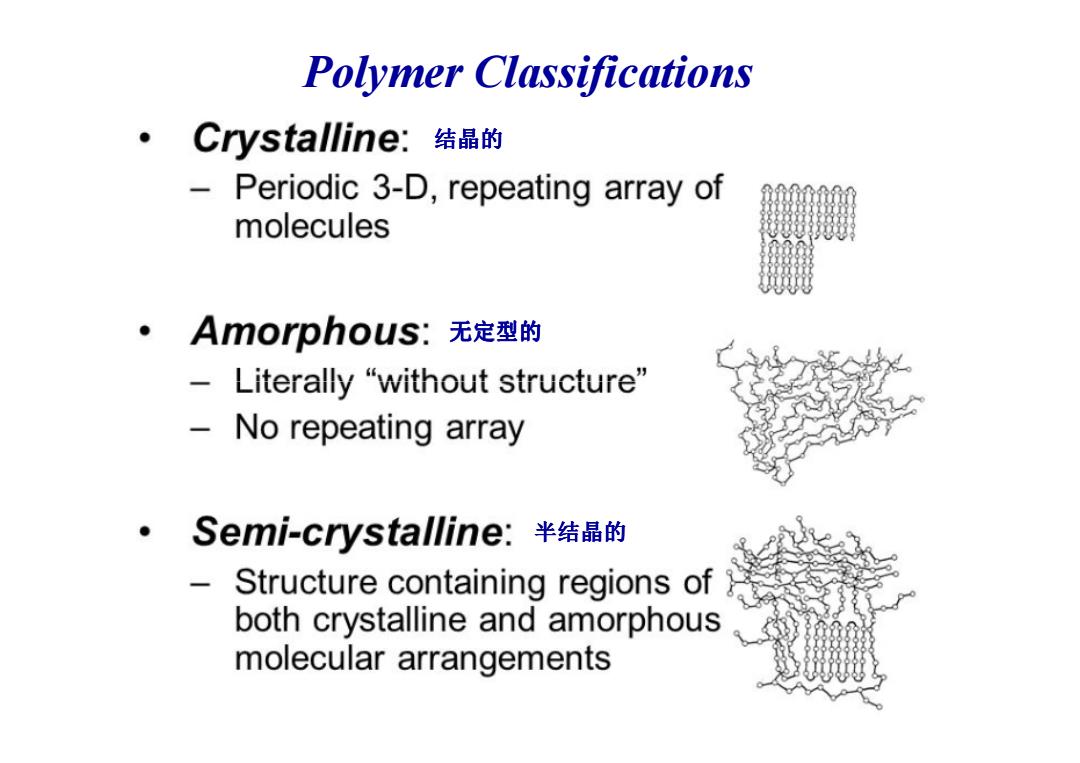
Polymer Classifications ·Crystalline:结晶的 - Periodic 3-D,repeating array of molecules 。Amorphous:无定型的 -Literally“without structure” No repeating array 。·Semi-crystalline:半结晶的 Structure containing regions of both crystalline and amorphous molecular arrangements
Polymer Classifications Thermoplastics 结晶的 无定型的 Thermosets 半结晶的