
Review Predicting Molecular Geometries: 分子构型 Total Electron- Electron Pair Bonding Nonbonding Molecular Pairs Geometry Pairs Pairs Geometry Example 4 pairs 4 0 Tetrahedral Tetrahedral四面体 正四面体 3 1 Trigonal pyramid 三角锥 2 2 B Bent折线形
Predicting Molecular Geometries: Review 分子构型 四面体 三角锥 折线形 正四面体

Review Central atoms with Expanded Valence Shells: 分子构型 Number of Electron- Electron Pair Bonding Nonbonding Molecular Pairs Geometry Pairs Pairs Geometry Example B 5 pairs 5 0 Trigonal 三角双锥 Trigonal 三角双锥 bipyramidal ipyramidal Axial 4 1 B B 跷跷板 Seesaw Equatorial 90° 3 2 T-型 T-shaped 120 2 3 直线型 Linear
Central atoms with Expanded Valence Shells: 分子构型 三角双锥 三角双锥 Review 跷跷板 T-型 直线型
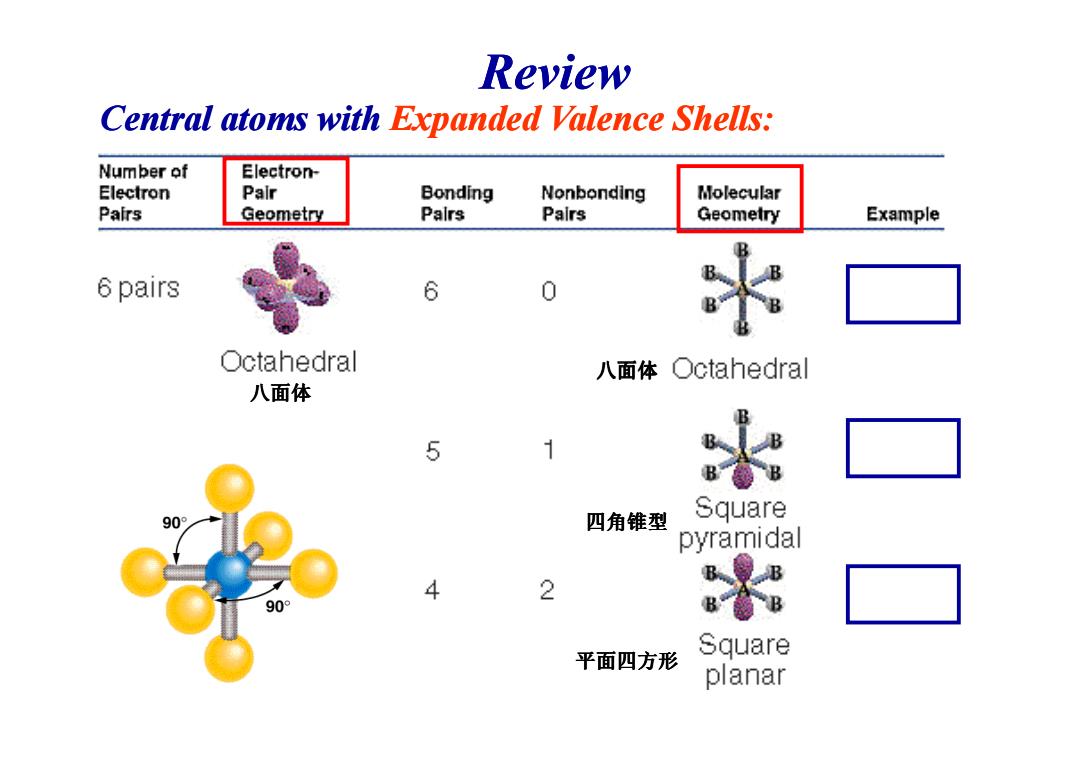
Review Central atoms with Expanded Valence Shells: Number of Electron- Electron Pair Bonding Nonbonding Molecular Pairs Geometry Palrs Palrs Geometry Example 6 pairs 6 0 Octahedral 八面体○ctahedral 八面体 5 1 B B 90° 四角锥型 Square pyramidal B 4 2 90° B Square 平面四方形 planar
Central atoms with Expanded Valence Shells: 八面体 Review 八面体 四角锥型 平面四方形
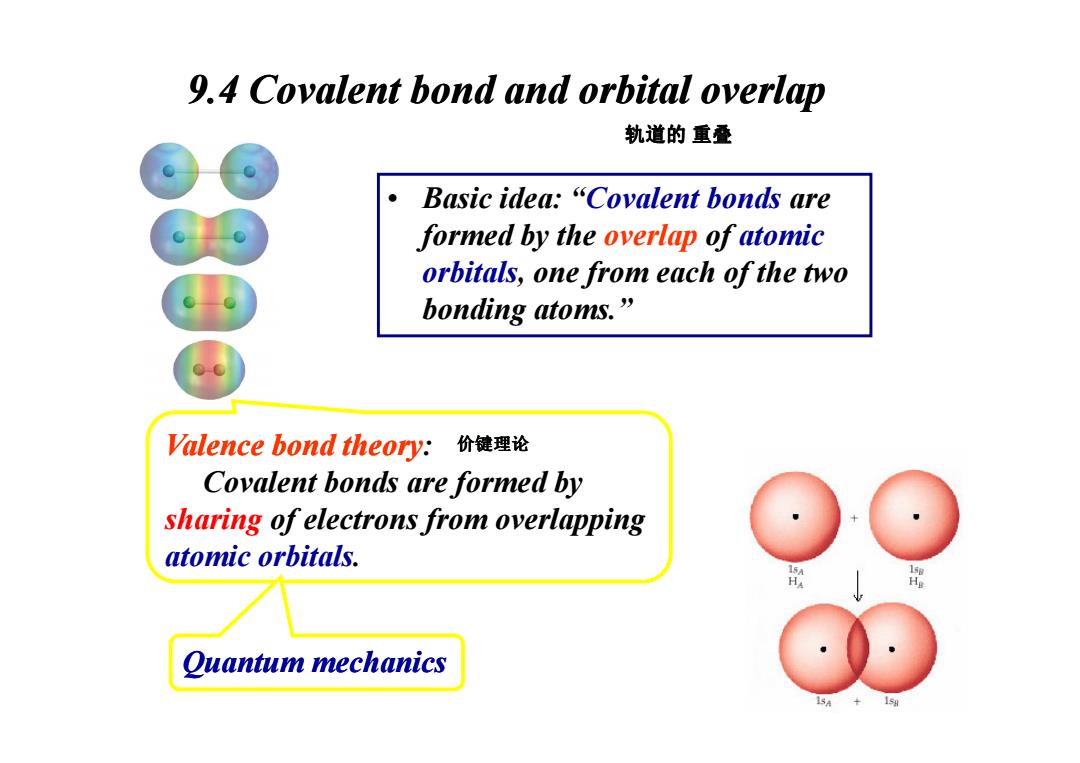
9.4 Covalent bond and orbital overlap 轨道的重叠 Basic idea:"Covalent bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals,one from each of the two bonding atoms.” Valence bond theory:t 价键理论 Covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons from overlapping atomic orbitals. Quantum mechanics
9.4 Covalent bond and orbital overlap • Basic idea: “Covalent bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals, one from each of the two bonding atoms.” 轨道的 重叠 Valence bond theory: Covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons from overlapping atomic orbitals. Quantum mechanics 价键理论

Valence Bond Theory (VBT) 价键理论 H-CI:H=1s1 Cl=1s22s22p63s23p5 1s 3Px Is 3p The overlap of the Is orbital of H and the 3p orbital in CL
Cl = 1s22s22p6 3s2 H = 1s1 3p5 Valence Bond Theory (VBT) H-Cl: 价键理论 The overlap of the 1s orbital of H and the 3p orbital in Cl. 1s 3p
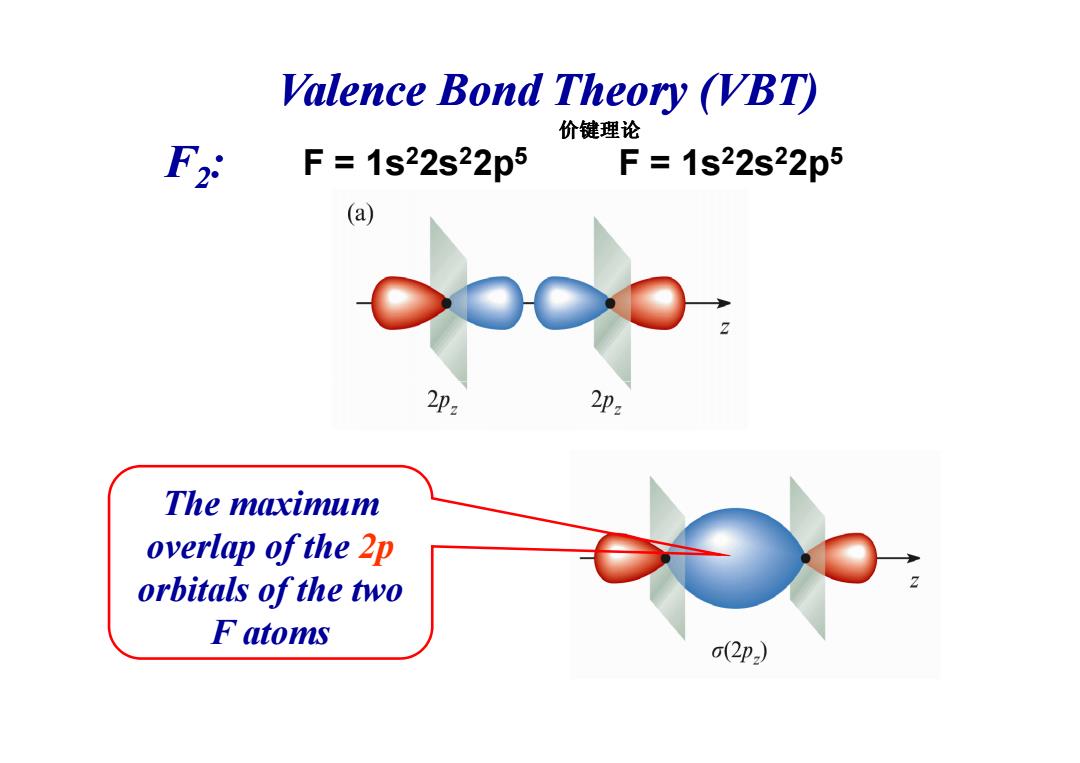
Valence Bond Theory (VBT) 价键理论 F2 F=1s22s22p5F=1s22s22p5 (a) 2p2 2p2 The maximum overlap of the 2p orbitals of the two F atoms (2p)
F = 1s22s22p5 Valence Bond Theory (VBT) F2: F = 1s22s22p5 价键理论 The maximum overlap of the 2p orbitals of the two F atoms
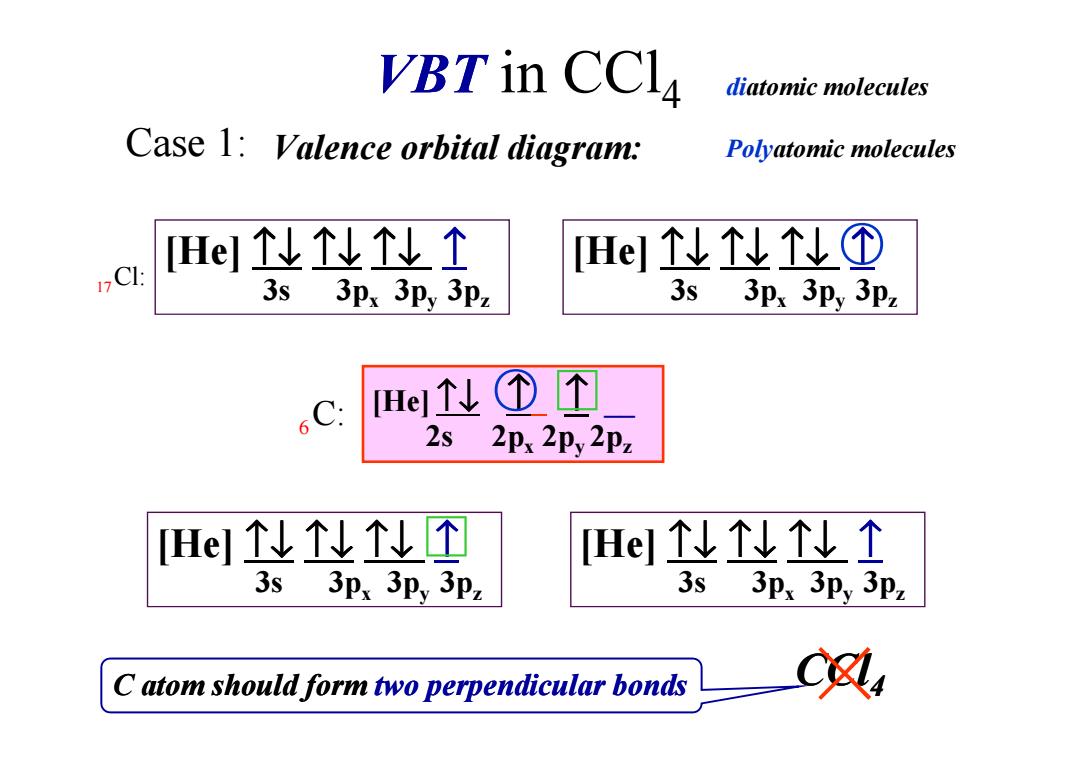
VBT in CCla diatomic molecules Case 1:Valence orbital diagram: Polyatomic molecules [HelN个↑ [Hey!L① 12C: 3s 3px 3py 3pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 6C. HeL①个 2s 2Px 2Py 2pz HeNN个个 HeNN个N个 3s 3px 3py 3pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz C atom should form two perpendicular bonds
VBT in CCl4 Valence orbital diagram: [He] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 3s 3px 3py 3pz Case 1: 17Cl: ↑↓ ↑ ↑ [He] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 3s 3px 3py 3pz ○ ○ □ diatomic molecules Polyatomic molecules C atom should form two perpendicular bonds CCl ×4 6C: [He] ↑↓ ↑ ↑ __ 2s 2px 2py 2pz ○ [He] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 3s 3px 3py 3pz □ □ [He] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ 3s 3px 3py 3pz

9.5 Orbital Hybridization 轨道杂化 CCL Lewis VSEPR Molecular Structure Theory: geometry Linus Carl Pauling 109.5 VBT introduced the idea of orbital hybridization
9.5 Orbital Hybridization VSEPR Theory: 109.5° Lewis Structure 轨道杂化 Linus Carl Pauling Molecular geometry CCl4 VBT introduced the idea of orbital hybridization

spi Hybrid Orbitals CCL 杂化轨道 C:1s22s22p 2p 2p 2s 2s 11 11 Ground State Promoted State 4 sp'hybrid orbitals 基态 激发态 2P Hybridization 杂化 2P 2P, 4 sp hybrid orbitals 杂化轨道
sp3 Hybrid Orbitals 2 6 2 2 C : 1s 2s p 2 CCl4 杂化轨道 基态 激发态 杂化 杂化轨道
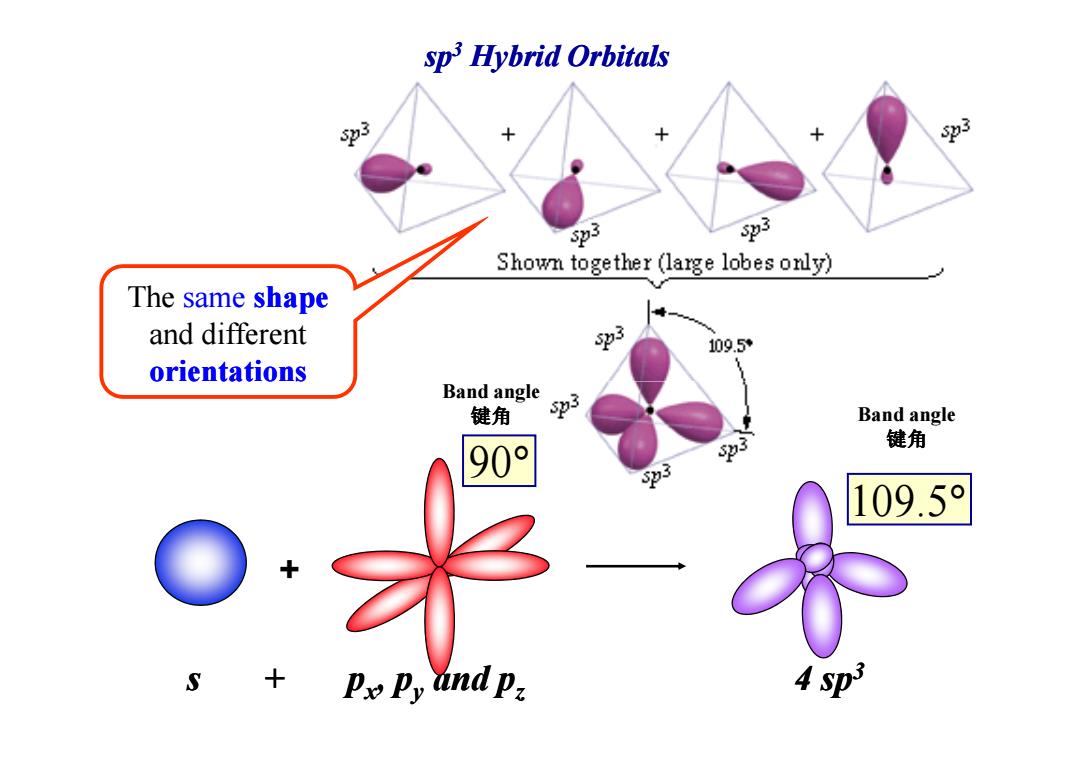
sp Hybrid Orbitals %3 % 3 23 Shown together (large lobes only) The same shape and different 3 109.5 orientations Band angle 键角 3 Band angle 3 键角 90° 3 109.5 + S + Pe卫y and p, 4 sp3
The same shape and different orientations sp3 Hybrid Orbitals Band angle + s + px, py and pz 4 sp3 90° 109.5° orientations Band angle 键角 Band angle 键角