
Conductors,semiconductors and Insulators Conduction LUMO:the Lowest band CB CB Unoccupied MO Band 最低空轨道 g叩 % 带隙 VB HOMO:the Highest Valence VB band Occupied MO Metal Semiconductor Insulator 最高占有轨道 Copyright 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,inc 导带 空带 空带 Most antibonding 000o 价带 价带 导体 半导体 绝缘体 Many Number of interacting atoms
Conductors, semiconductors and Insulators Conduction band Valence band Band gap LUMO: the Lowest Unoccupied MO HOMO: the Highest Occupied MO 带隙 最低空轨道 最高占有轨道

Bonding in Semiconductor 元素半导体 带隙 Elemental Band gap VBT Semiconductors, (e) C 5.5 Si 1.1 Ge 0.67 Sn 0.08 Pb ? 化合物半导体 Compound Band gap Semiconductors, (ev) GaP 2.2 GaAs 1.43 GaP AS1-x 2.2l.43 CdS 2.4 CdSn 1.7 CdTe 1.44
Bonding in Semiconductor Elemental Band gap Semiconductors, (eV) C 5.5 Si 1.1 Ge 0.67 Sn 0.08 Pb ? VBT 元素半导体 带隙 Pb ? Compound Band gap Semiconductors, (eV) GaP 2.2 GaAs 1.43 GaPxAs1-x 2.2 ~1.43 CdS 2.4 CdSn 1.7 CdTe 1.44 化合物半导体

Doping N-style Semiconductor Neutral! Dopant:the atoms from -nergy Explanation the group 54,such as P. CB CB 十4 +41 K3IuH VB VB Intrinsic n-Type N-type Heat added or Negatively charged electrons in in External Electric Field the conduction band increased
N-style Semiconductor Doping Energy Explanation Dopant: the atoms from the group 5A, such as P. Neutral! N-type Heat added or Negatively charged electrons in in External Electric Field the conduction band increased

P-style Semiconductor Dopant:the atoms from the group 34, Neutral! Such as Al,Ga,In. Atomic Explanation Energy Explanation 4 CB CB K3.1Oug 十4 VB VB P-type Intrinsic Positive holes in the PType materials increased. Holes can conduct too
P-style Semiconductor Atomic Explanation Energy Explanation Dopant: the atoms from the group 3A, Such as Al, Ga, In. Energy Explanation Neutral! Heat added or in External Electric Field P-type Positive holes in the materials increased. Holes can conduct too

Chapter 11 Intermolecular forces 11.1 A molecular comparison of gases, liquids and solids 11.2 Intermolecular Forces 11.3 Some Properties of Liquids 11.4 Phase Changes 11.5 Vapor pressure 11.6 Phase Diagrams 11.8 Bonding in solids
Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces 11.1 A molecular comparison of gases, liquids and solids 11.2 Intermolecular Forces 11.3 Some Properties of Liquids 11.4 Phase Changes 11.5 Vapor pressure 11.6 Phase Diagrams 11.8 Bonding in solids
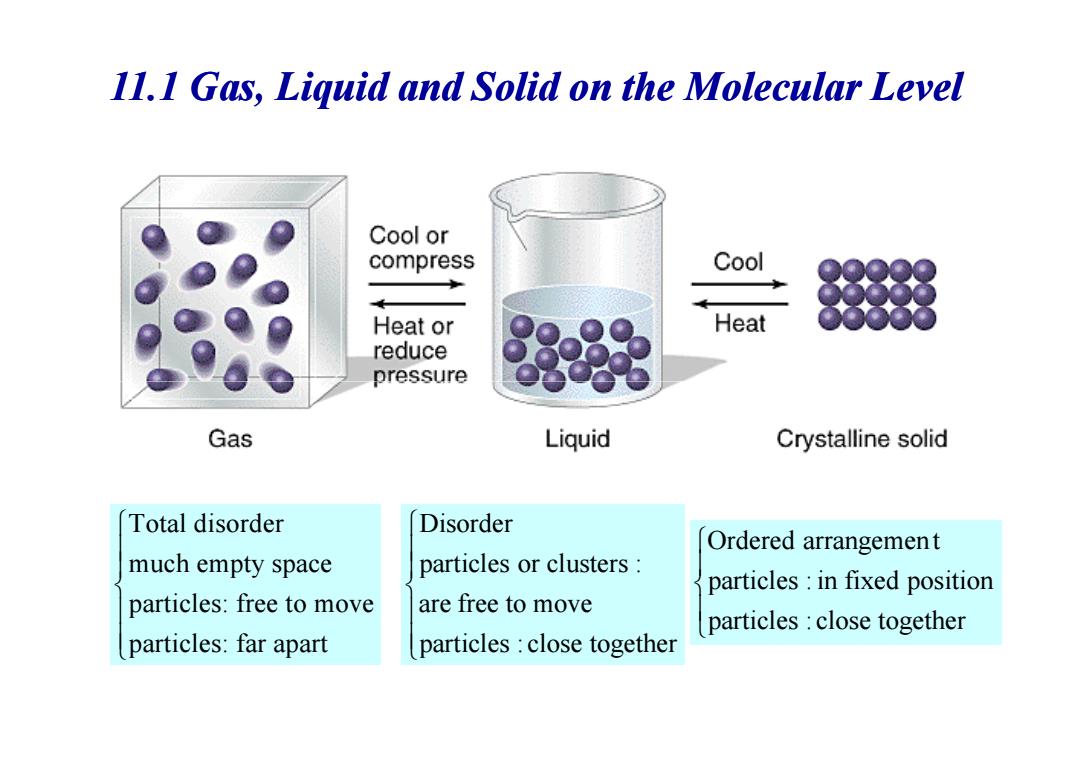
11.I Gas,Liquid and Solid on the Molecular Level Cool or compress Cool Heat or Heat reduce pressure Gas Liquid Crystalline solid Total disorder Disorder Ordered arrangement much empty space particles or clusters: particles in fixed position particles:free to move are free to move particles:close together particles:far apart particles close together
11.1 Gas, Liquid and Solid on the Molecular Level Total disorder much empty space particles: free to move particles: far apart particles : close together are free to move particles or clusters : Disorder particles : close together particles : in fixed position Ordered arrangemen t

Gas,Liquid and Solid on the Molecular Level 3 states of matter are closely related to Intermolecular forces Gaseous state: Kinetic energy completely overcomes intermolecular forces. Particles move freely unrelated to each other. ·Liquid state:. Intermolecular forces hold particles close together. Kinetic energy keeps them moving around each other. ●Solid state:. Intermolecular forces hold particles in fixed positions -Kinetic energy keeps them vibrating in place
• Gaseous state: – Kinetic energy completely overcomes intermolecular forces. – Particles move freely & unrelated to each other. Gas, Liquid and Solid on the Molecular Level 3 states of matter are closely related to Intermolecular forces E >>E kinetic attraction • Liquid state: – Intermolecular forces hold particles close together. – Kinetic energy keeps them moving around each other. • Solid state: – Intermolecular forces hold particles in fixed positions. –Kinetic energy keeps them vibrating in place. E < E kinetic attraction

Intermolecular Forces I (van der Waals forces) The van der Waals force is the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules 偶极子 1.Ion-Dipole Attraction: Interaction between an ion and a dipole (a) (b) The Strongest in all intermolecular forces
1. Ion-Dipole Attraction: • Interaction between an ion and a dipole Intermolecular Forces I (van der Waals forces Waals forces) The van The van der Waals force Waals force is the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules 偶极子 • Interaction between an ion and a dipole The Strongest in all intermolecular forces σ - σ +

Intermolecular Forces I (van der Waals forces) 1.Ion-Dipole Attraction: Interaction between an ion and a dipole NaCl aqueous solution
1. Ion-Dipole Attraction: • Interaction between an ion and a dipole Intermolecular Forces I (van der Waals forces) NaCl aqueous solution

Intermolecular Forces i (van der Waals forces) Weaker than 偶极 2.Dipole-Dipole Attraction: ion-dipole forces Interaction between polar molecules Dipole-dipole forces among polar molecules cause them to have "preferred"orientations in the liquid or solid states
2. Dipole-Dipole Attraction Dipole Attraction: Interaction between polar molecules Intermolecular Forces I (van der Waals forces) Weaker than ion-dipole forces 偶极 Dipole-dipole forces among polar molecules cause them to have “preferred” orientations in the liquid or solid states