
Chap8非参数密度估计技术 参考:王星2009《非参数统计》 清华大学出版社 主讲:王星 助教:范超 中国人民大学统计学院 办公地点:明德主楼1019 办公电话:82500167 课程网站:https:/dm.ruc.edu.cn 2014年12月24日
Chap8 非参数密度估计技术 参考:王星2009《 非参数统计》 清华大学出版社 主讲:王 星 助教:范 超 中国人民大学统计学院 办公地点:明德主楼1019 办公电话:82500167 课程网站:https://dm.ruc.edu.cn 2014年12月24日

基本概念 ·想一想:什么是分布密度?分布密度有什么用? 色泽不均衡可能是催 熟西瓜 Zipf济普夫定律:在自然语言的 语料库里,一个单词出现的频率 与它在频率表里的排名成反比 分布密度和一个随机变量取值分布的均衡性有关系,不均衡 常常是世界的常态,语言学中重要的词一定被使用的频次高、 食品安全监测中的分布异常可能是风险的一个标志? 通过数据估计分布密度通常都有什么方法?
基本概念 • 想一想:什么是分布密度?分布密度有什么用? Zipf齐普夫定律:在自然语言的 语料库里,一个单词出现的频率 与它在频率表里的排名成反比 色泽不均衡可能是催 熟西瓜 分布密度和一个随机变量取值分布的均衡性有关系,不均衡 常常是世界的常态,语言学中重要的词一定被使用的频次高、 食品安全监测中的分布异常可能是风险的一个标志? 通过数据估计分布密度通常都有什么方法?

非参数密度估计 a直方图 Parzen Windows窗 Kernel density estimator 多元密度估计 判别分析
非参数密度估计 直方图 Parzen Windows窗 Kernel density estimator 多元密度估计 判别分析

Introduction ·大部分的参数密度都是单峰的(have a single local maximum),很多实际问题会涉及多峰问题 ·非参数统计过程将涉及假定宽松的数据结构. ·有两种常见的非参数密度估计问题: -估计似然函数P(回j) -直接估计后验概率 density.default(x iris[n.s =1,1]) N=50 Bandwidth =0.1229
Introduction • 大部分的参数密度都是单峰的 (have a single local maximum), 很多实际问题会涉及多峰问题 • 非参数统计过程将涉及假定宽松的数据结构. • 有两种常见的非参数密度估计问题: – 估计似然函数 P(x|j ) – 直接估计后验概率

密度估计 -Basic idea: Probability that a vector x will fall in region R is: P=p(x')dx (1) Therefore,the ratio k/n is a good estimate for the probability P and hence for the density function p. p(x)dx'=p(x)v (4) p(x)is continuous and that the region is so small that p does not vary significantly within it,we can write: k/n Pn(x)≡ where x is a point within and V the volume enclosed by E. equation(1)and (4)yields histogram:
Therefore, the ratio k/n is a good estimate for the probability P and hence for the density function p. p(x) is continuous and that the region R is so small that p does not vary significantly within it, we can write: where x is a point within R and V the volume enclosed by R. equation (1) and (4) yields histogram: – Basic idea: Probability that a vector x will fall in region R is: 密度估计 ( ') ' ( ) (4) p x d x p x V P = p(x')d x' (1) V k n p x n / ˆ ( )

直方图 ni 当xeI,i=1,2,…,k 0, 其他 既是归一化参数,又表示每一组的组距,称为带宽或窗宽, Dissects the range of the data into bins of equal width along the horizontal axis Vertical axis represents the frequency counts(or percents,proportions)-Bars represent the counts Fewer bins,smoother histogram,but less detail about the distribution Trade-off between smoothness and detail:We want to preserve as much detail as possible but we do not want the graph to be too rough(difficult to discern shape)
直方图 • Dissects the range of the data into bins of equal width along the horizontal axis • Vertical axis represents the frequency counts (or percents, proportions)—Bars represent the counts • Fewer bins, smoother histogram, but less detail about the distribution • Trade-off between smoothness and detail: We want to preserve as much detail as possible but we do not want the graph to be too rough (difficult to discern shape)
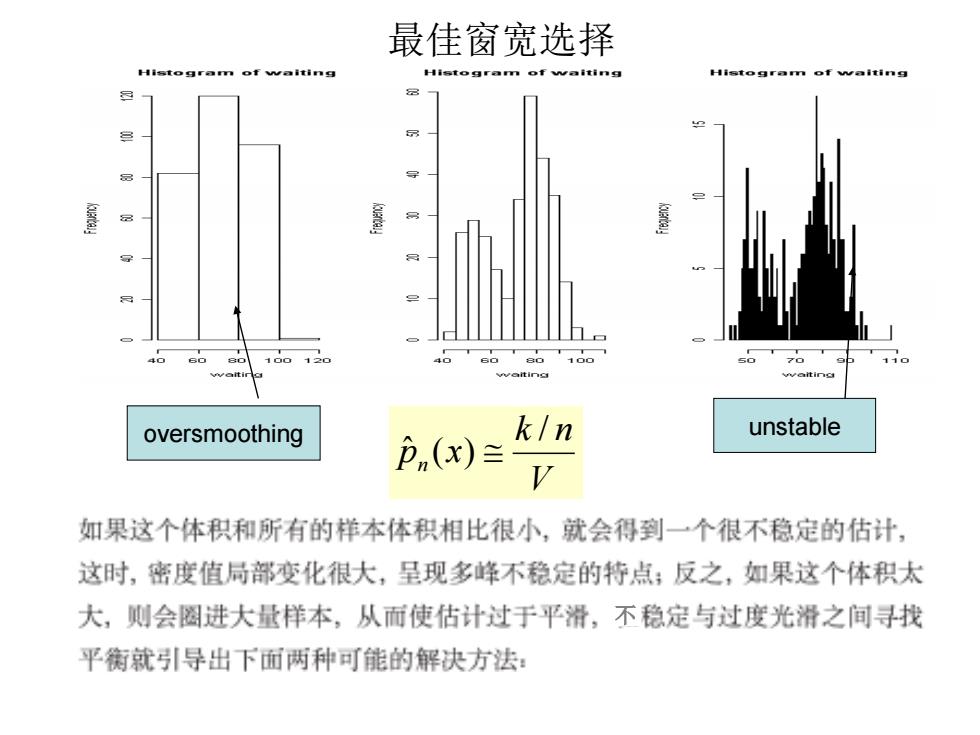
最佳窗宽选择 Histogram of waiting Histogram of weiting Histogram of walting 100120 100 11 waiting oversmoothing k/n unstable Pn(x) 如果这个体积和所有的样本体积相比很小,就会得到一个很不稳定的估计, 这时,密度值局部变化很大,呈现多峰不稳定的特点;反之,如果这个体积太 大,则会圈进大量样本,从而使估计过于平滑,不稳定与过度光滑之间寻找 平衡就引导出下而两种可能的解决方法:
V k n p x n / ˆ ( ) unstable oversmoothing 不 最佳窗宽选择

最优理论窗宽Histogram 定理:∫(∫'(u)2du<+o则L2损失下的最优风险为: rfn(x),f)≈jf'(u2a+ 极小化上面的式子,可以得到理想的窗宽: 1/3 =(Ta 在这个窗宽的选择下 R(f,f)≈nS
定理: 则L2损失下的最优风险为: 极小化上面的式子,可以得到理想的窗宽: 在这个窗宽的选择下 最优理论窗宽 Histogram

定理8.1 固定和h,令估计的密度是p,如果x∈马,=p)d,有 Ep(x)=Pi/h, apc)=P51-卫 nh2 证明提示:注意到E=nn= p()da,varpj pi(1-Pj)/n. 考察平方损失风险: R(p,p)=EL(p(x),p(x)) =(D(z)-p(z))2 dz -(Ep(=)-pz)dr+(p()-Epz))2 dzr =Bias()dr+v()回dk

积分均方误(Mean Integral Square Error,简称:MISE) MISE-E(P(z)-p(z))2 dzr AMISE-[(Bias())+Var()dz