
Immunity to Tumors DU Ying Department of Immunology chool of Basic medical scine, Zhengzhou University CONTENTS OVERVIEW OF TUMOR IMMUNITY TUMOR ANTIGENS IMMUNE RESPONSES TO TUMORS EVASION OF IMMUNE RESPONSES BY TUMORS IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR TUMORS
Immunity to Tumors DU Ying Department of Immunology School of Basic medical science , Zhengzhou University OVERVIEW OF TUMOR IMMUNITY CONTENTS TUMOR ANTIGENS IMMUNE RESPONSES TO TUMORS IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR TUMORS EVASION OF IMMUNE RESPONSES BY TUMORS
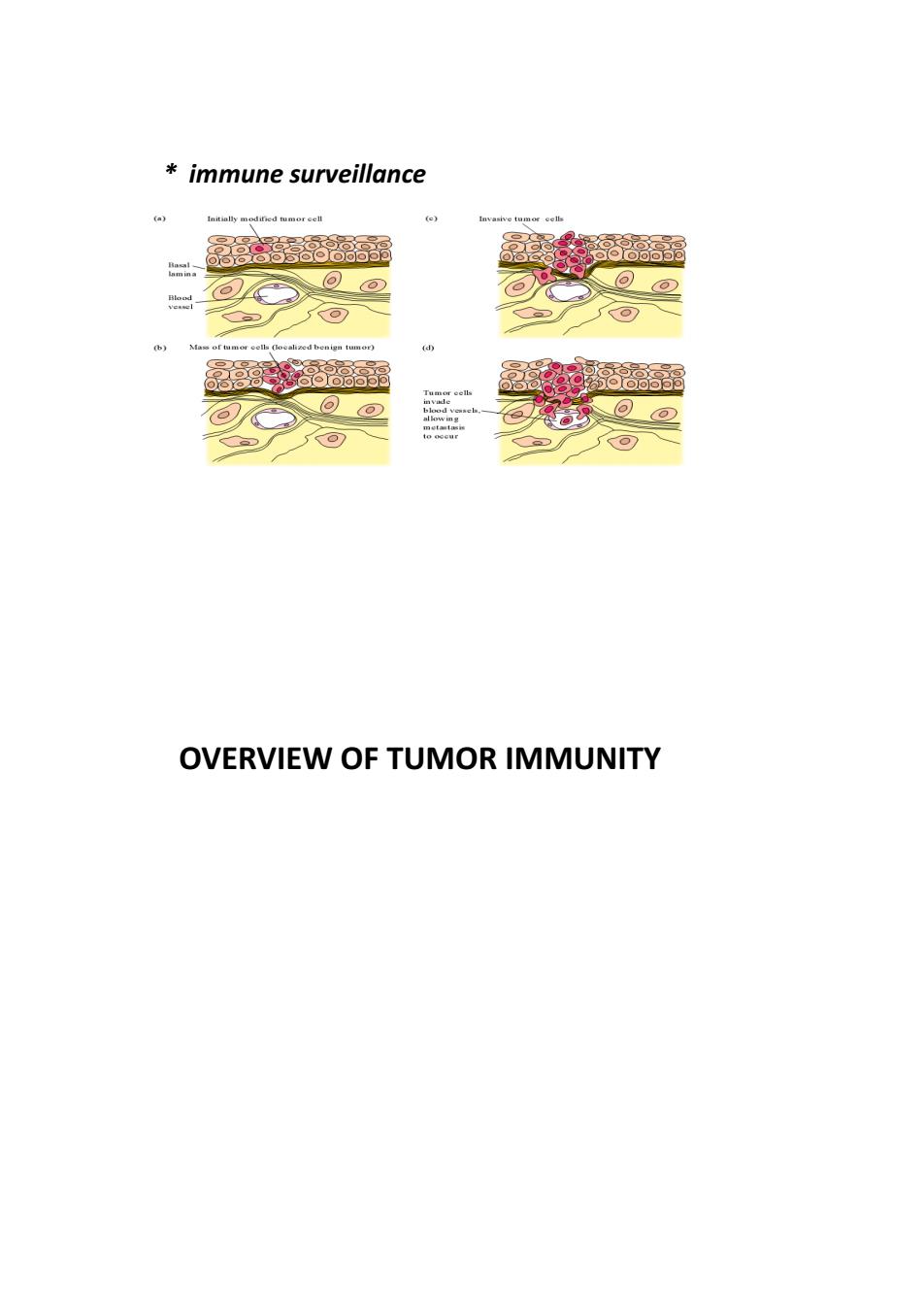
immune surveillance 品蕊 OVERVIEW OF TUMOR IMMUNITY
* immune surveillance OVERVIEW OF TUMOR IMMUNITY
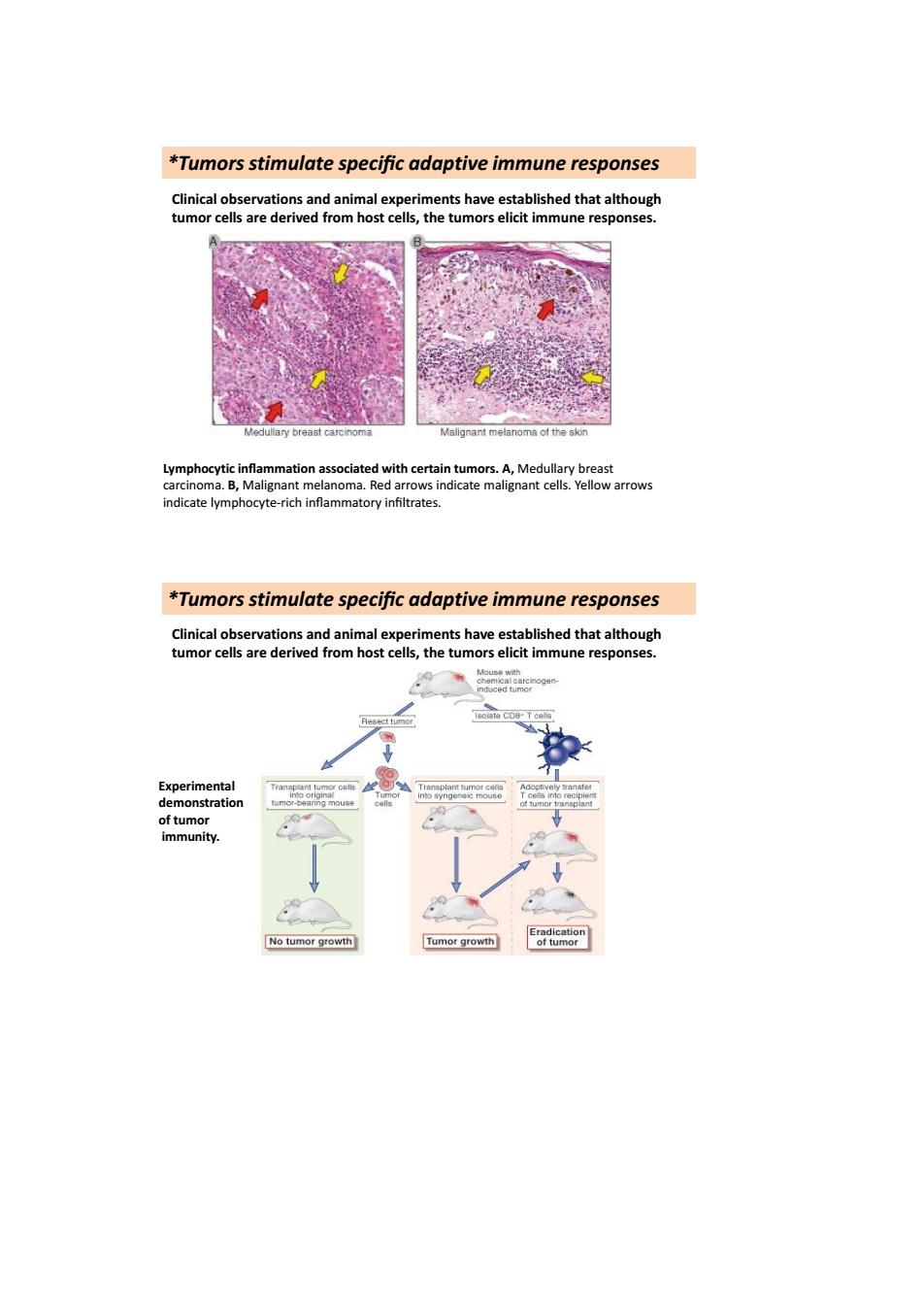
*Tumors stimulate specific adaptive immune responses ation a ndicate b hovte-rich inflammatory *Tumors stimulate specific adaptive immune responses ved from host cells,the tumors e t immune response erimenta No tumor growth Tumor growth
*Tumors stimulate specific adaptive immune responses Lymphocytic inflammation associated with certain tumors. A, Medullary breast carcinoma. B, Malignant melanoma. Red arrows indicate malignant cells. Yellow arrows indicate lymphocyte-rich inflammatory infiltrates. Clinical observations and animal experiments have established that although tumor cells are derived from host cells, the tumors elicit immune responses. *Tumors stimulate specific adaptive immune responses Clinical observations and animal experiments have established that although tumor cells are derived from host cells, the tumors elicit immune responses. Experimental demonstration of tumor immunity
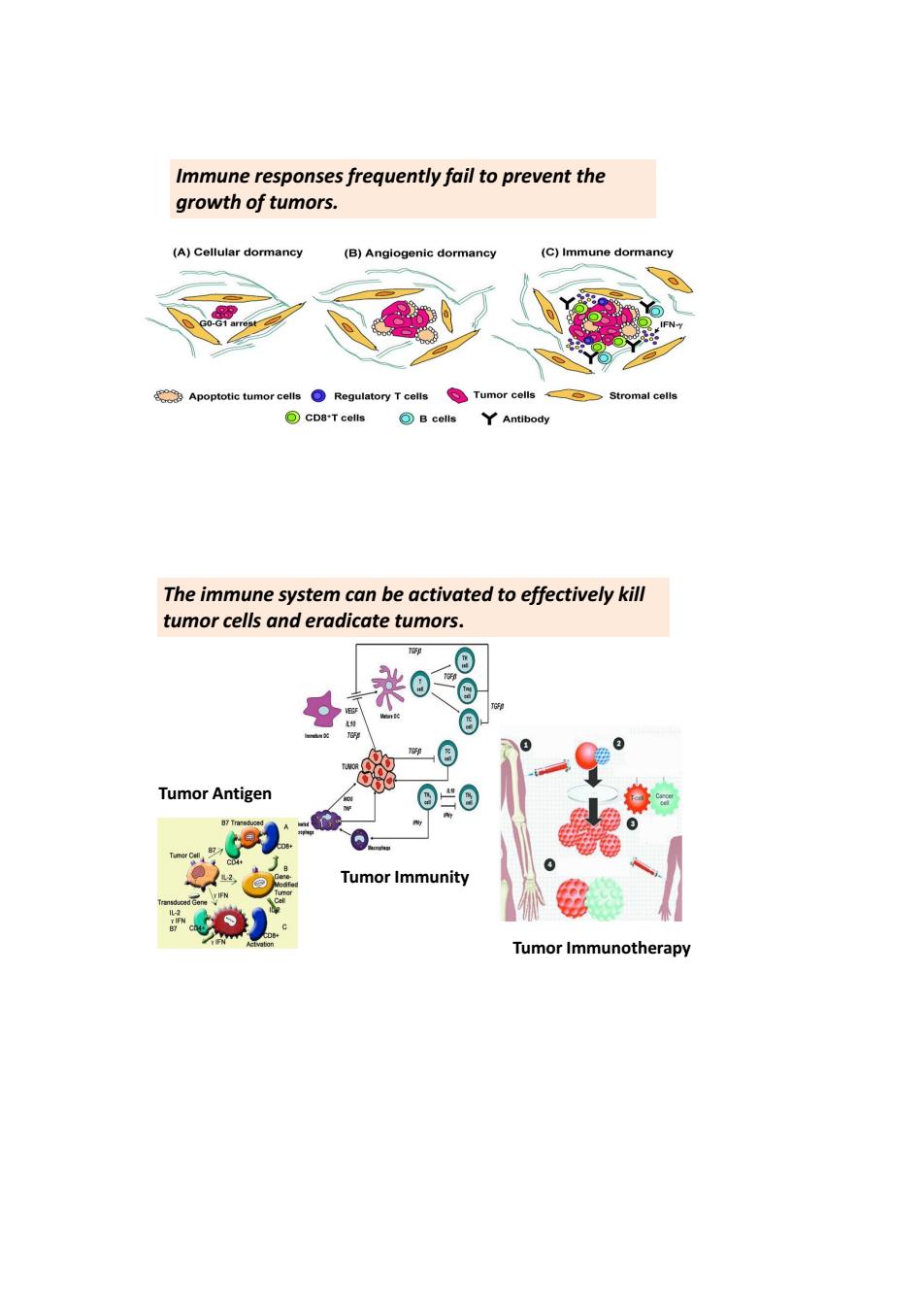
Immune responses frequently fail to prevent the growth of tumors. (B)Anglogenic dormancy (C)Immune dorm Reg The immune system can be activated to effectively kill tumor cells and eradicate tumors. Tumor Antigen Tumor Immunity Tumor Immunothe
Immune responses frequently fail to prevent the growth of tumors. Tumor Immunity Tumor Antigen Tumor Immunotherapy The immune system can be activated to effectively kill tumor cells and eradicate tumors

TUMOR ANTIGENS Tumor specific antigens,TSA tumor-associated antigens,TAA Various biochemical and molecular genetic approaches have been used to identify tumor antigens
TUMOR ANTIGENS Tumor specific antigens,TSA tumor-associated antigens,TAA Various biochemical and molecular genetic approaches have been used to identify tumor antigens
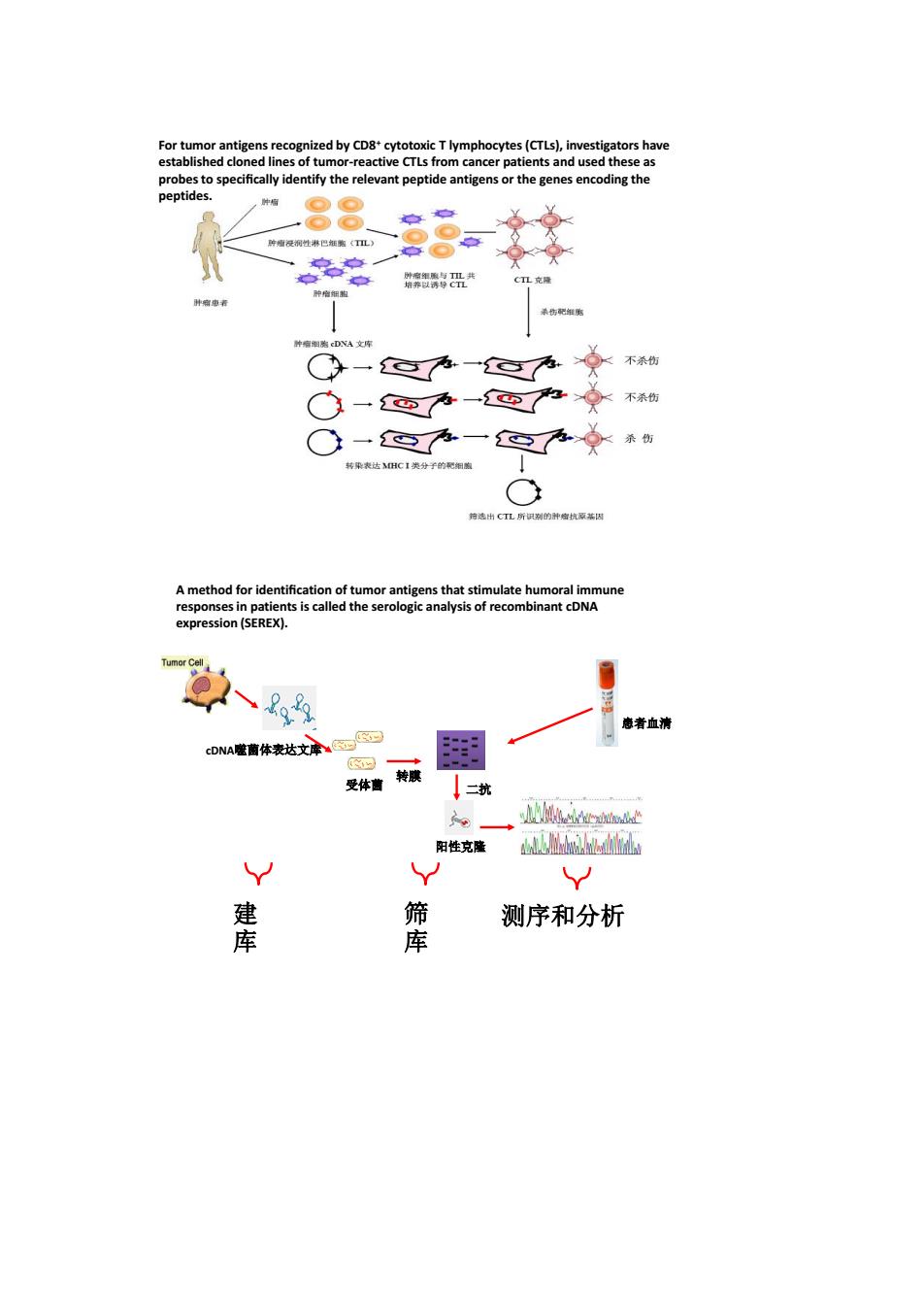
For tumor antige ognized by lymphocytes (CTLs),investigators have 88 裤盘共 D库 年一之示一色产不 心一一色力★ 原 速者血清 cDNA菌体达文康 二抗 。 阳性克隆 hd 辈 测序和分析 库
For tumor antigens recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), investigators have established cloned lines of tumor-reactive CTLs from cancer patients and used these as probes to specifically identify the relevant peptide antigens or the genes encoding the peptides. cDNA噬菌体表达文库 受体菌 转膜 患者血清 二抗 阳性克隆 建 库 筛 库 测序和分析 A method for identification of tumor antigens that stimulate humoral immune responses in patients is called the serologic analysis of recombinant cDNA expression (SEREX)

Products of Mutated Genes Type of Antigen Examples of Human Tumor Antigens Products of mutated oncogene products:Ras mutations oncogenes (~10%of human carcinomas), p210 product of Bcr/Abl rearrangements(CmL) Tumor suppressor gene products: mutated p53(present in~50%of human tumors) Tumor antigens may be produced by randomly mutated genes whose products are not related to the malignant phenotype. Abnormally Expressed but Unmutated Cellular Proteins Type of Antigen Examples of Human Tumor Antigens HER2/neu(breast and other carcinomas Products of genes that are silent in most Cancer/testis antigens expressed in normal tissues expre normal nonone tenic proteins overexpressed in tumor cells hormaWopeegnmehngn Tyrosinase,gp100,MART in melanc Products of oncogenic viruses oeoon on antigens normally present in in prostate
• Oncogenes and mutated tumor suppressor genes produce proteins that differ from normal cellular proteins and, therefore, can induce immune responses. Products of Mutated Genes Products of mutated oncogenes tumor suppressor genes Type of Antigen Examples of Human Tumor Antigens oncogene products: Ras mutations (∼10% of human carcinomas), p210 product of Bcr/Abl rearrangements (CmL) Tumor suppressor gene products: mutated p53 (present in ∼50% of human tumors) Tumor antigens may be produced by randomly mutated genes whose products are not related to the malignant phenotype. Abnormally Expressed but Unmutated Cellular Proteins HER2/neu (breast and other carcinomas) Type of Antigen Examples of Human Tumor Antigens unmutated but overexpressed products of oncogenes Products of genes that are silent in most normal tissues Cancer/testis antigens expressed in melanomas and many carcinomas; normally expressed mainly in the testis and placenta normal nononcogenic proteins overexpressed in tumor cells Tyrosinase, gp100, MART in melanomas (normally expressed in melanocytes) Products of oncogenic viruses Papillomavirus E6 and E7 proteins EBnA-1 protein of EBV Differentiation antigens normally present in tissue of origin Prostate-specific antigen in prostate carcinomas CD20 on B cell lymphomas
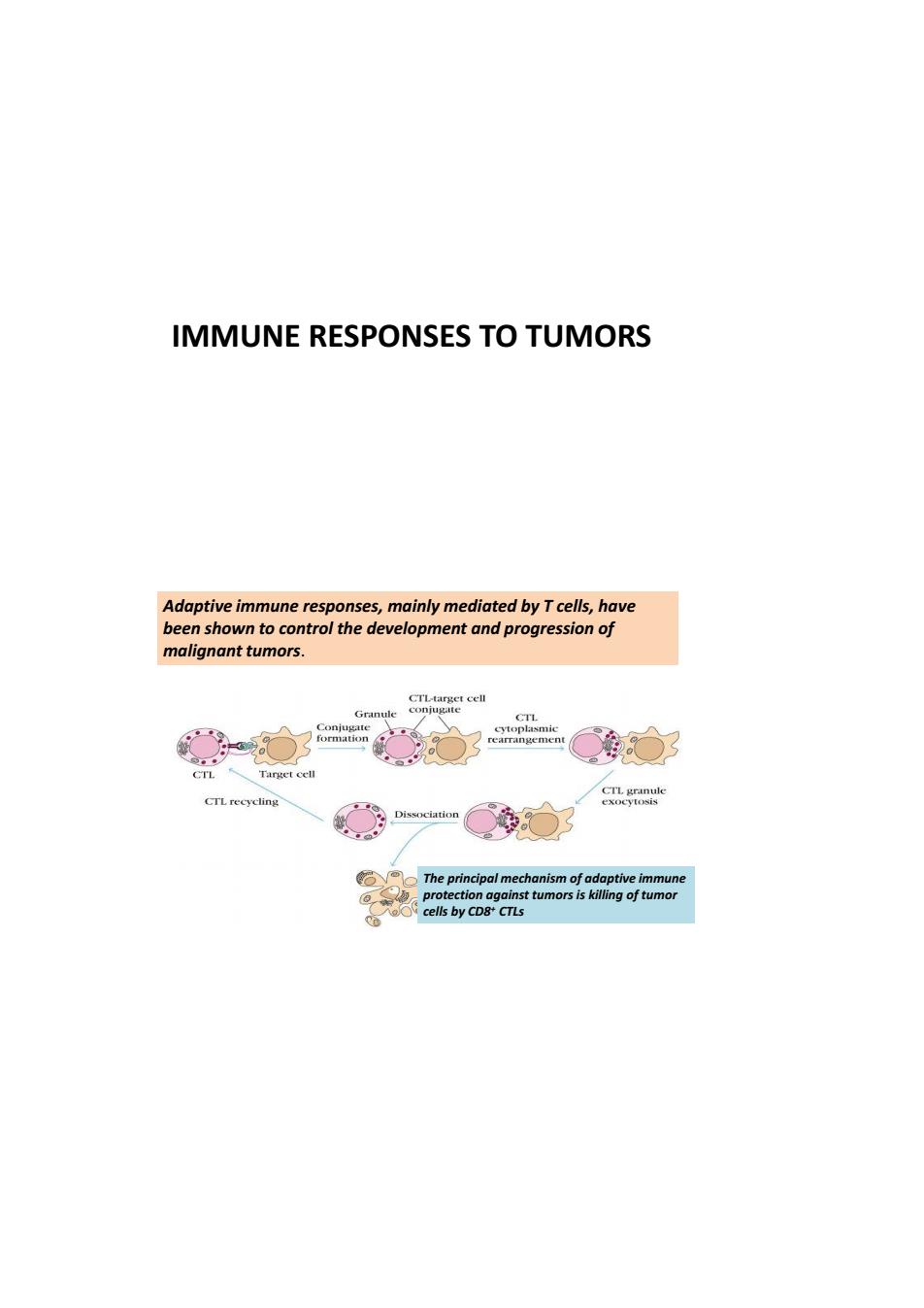
IMMUNE RESPONSES TO TUMORS Adaptive immne responses,mainly mediated byTcells,have been shown to control the development and progression of malignant tumors 品 Target cel The principal mechanism of adaptive im
IMMUNE RESPONSES TO TUMORS The principal mechanism of adaptive immune protection against tumors is killing of tumor cells by CD8+ CTLs Adaptive immune responses, mainly mediated by T cells, have been shown to control the development and progression of malignant tumors
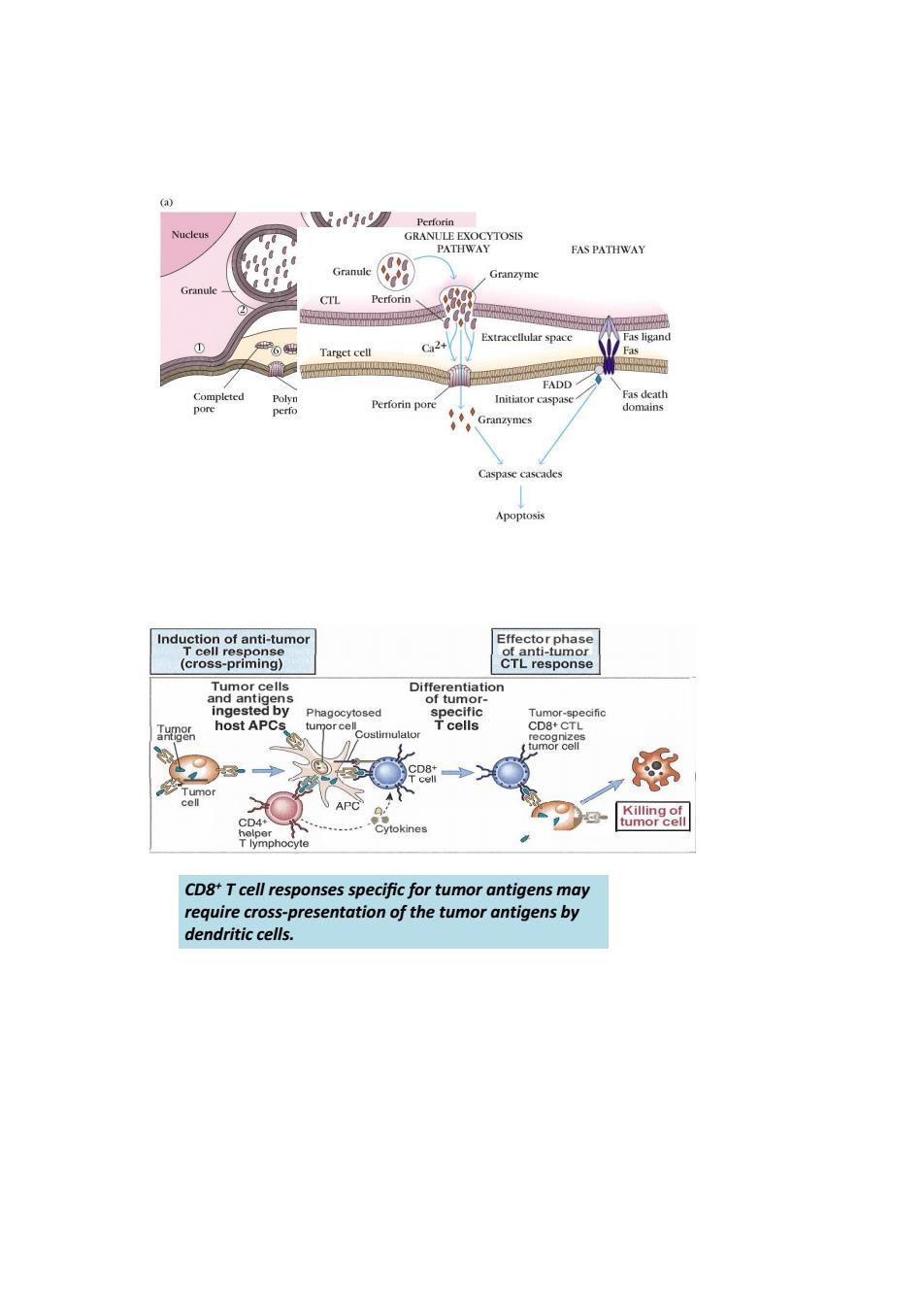
nd Differentiation Tcells D8+CTL tumor CD8*T cell responses specific for tumor antigens may require cross-presentation of the tumor antigens by dendritic cells
CD8+ T cell responses specific for tumor antigens may require cross-presentation of the tumor antigens by dendritic cells

IL-4 →米g 北4 TGF-B e→Yg 霸记忆B细胞 Antibodies m ay kill tumor cells by activatin ment or by antibody ndent cel mediated cytotox cit FcyR(CD16)
Antibodies may kill tumor cells by activating complement or by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity