Chapter 2 Transmission Section 1 Introduction 1.Functions of Transmissions (1)Change the speed and torque; (2)Achieve forward or backward for vehicles; (3)Achieve a long time stop or power output; (4)Achieve the start or idle for the vehicle in off-load conditions. 2.Types of Transmissions 2.1 Transmission Ratio According to different transmission ratio settings,transmissions are divided into mechanical transmission,continuously variable transmission and integrated transmission. (1)Mechanical transmissions have several transmission ratios. They transmit power by gear trains. 机械与电子工程家 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 1. Functions of Transmissions (l) Change the speed and torque; (2) Achieve forward or backward for vehicles; (3) Achieve a long time stop or power output; (4) Achieve the start or idle for the vehicle in off-load conditions. 2. Types of Transmissions 2.1 Transmission Ratio According to different transmission ratio settings, transmissions are divided into mechanical transmission, continuously variable transmission and integrated transmission. (1) Mechanical transmissions have several transmission ratios. They transmit power by gear trains. Section 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 1 Introduction According to the structures of gear trains,transmissions can be divided into ordinary transmissions(axis fixed)and planetary transmissions(axis rotated).According to whether the power transfer is interrupted in transmission process,transmissions are divided into traditional transmissions and loaded shift transmissions. (2)Transmission ratios of continuously variable transmission can be continuously variable within a certain range.Usually they can be divided into hydraulic transmissions and electrical transmissions. (3)Integrated transmissions are composed by a mechanical transmission and a stepless hydraulic torque converter.They are also known as the hydraulic mechanical transmissions.The transmission ratios of them are continuously variable within a number of intervals. 状械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission According to the structures of gear trains, transmissions can be divided into ordinary transmissions(axis fixed) and planetary transmissions(axis rotated). According to whether the power transfer is interrupted in transmission process, transmissions are divided into traditional transmissions and loaded shift transmissions. (2) Transmission ratios of continuously variable transmission can be continuously variable within a certain range. Usually they can be divided into hydraulic transmissions and electrical transmissions. (3) Integrated transmissions are composed by a mechanical transmission and a stepless hydraulic torque converter. They are also known as the hydraulic mechanical transmissions. The transmission ratios of them are continuously variable within a number of intervals. Section 1 Introduction
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 1 Introduction 2.2 Operation Manner According to operation manners,transmissions are divided into three types:manual,automatic and semi-automatic. (1)Manual transmissions rely on drivers direct control of the gear lever to shift. (2)Automatic transmissions rely on drivers control of the accelerator pedal to control the speed. (3)Semi-automatic transmissions can be divided into two forms: one is that several commonly used gears are in automatic control, while other gears are manipulated by the driver;The other is that the driver sets the required gears forward with the button,and then achieve to shift through the accelerator pedal to connect the electromagnetic device or hydraulic device. 机械电子工程学理 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 2.2 Operation Manner According to operation manners, transmissions are divided into three types: manual, automatic and semi-automatic. (1)Manual transmissions rely on drivers direct control of the gear lever to shift. (2)Automatic transmissions rely on drivers control of the accelerator pedal to control the speed. (3) Semi-automatic transmissions can be divided into two forms: one is that several commonly used gears are in automatic control, while other gears are manipulated by the driver; The other is that the driver sets the required gears forward with the button, and then achieve to shift through the accelerator pedal to connect the electromagnetic device or hydraulic device. Section 1 Introduction
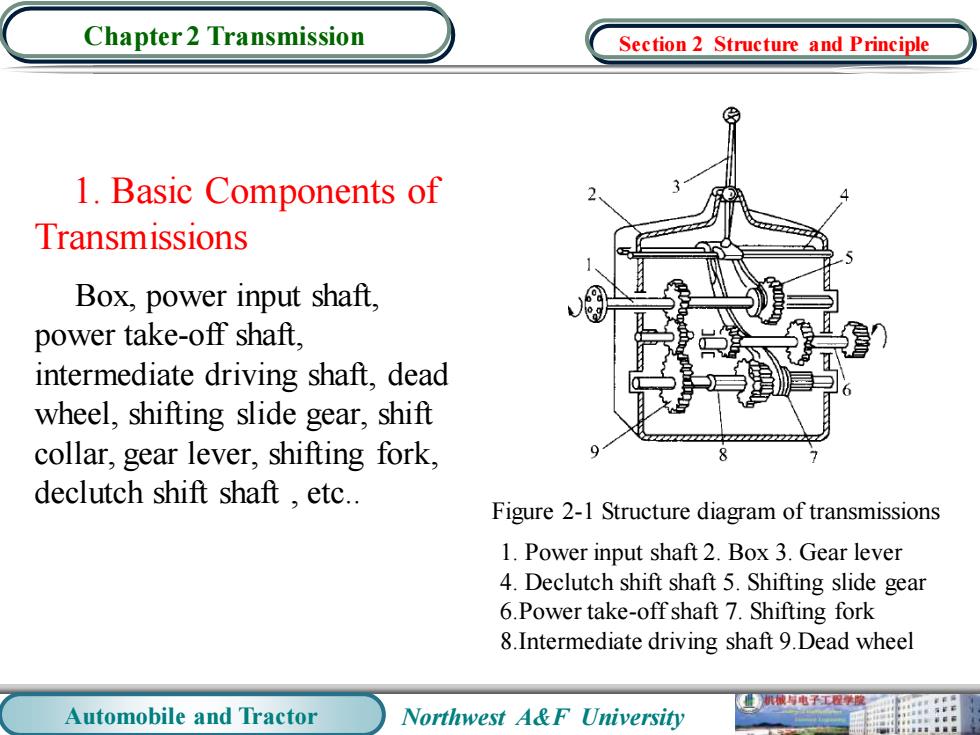
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 2 Structure and Principle 1.Basic Components of Transmissions Box,power input shaft, power take-off shaft. intermediate driving shaft,dead wheel,shifting slide gear,shift collar,gear lever,shifting fork, declutch shift shaft,etc.. Figure 2-1 Structure diagram of transmissions 1.Power input shaft 2.Box 3.Gear lever 4.Declutch shift shaft 5.Shifting slide gear 6.Power take-off shaft 7.Shifting fork 8.Intermediate driving shaft 9.Dead wheel 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 1. Basic Components of Transmissions Box, power input shaft, power take-off shaft, intermediate driving shaft, dead wheel, shifting slide gear, shift collar, gear lever, shifting fork, declutch shift shaft , etc.. 1. Power input shaft 2. Box 3. Gear lever 4. Declutch shift shaft 5. Shifting slide gear 6.Power take-off shaft 7. Shifting fork 8.Intermediate driving shaft 9.Dead wheel Figure 2-1 Structure diagram of transmissions Section 2 Structure and Principle
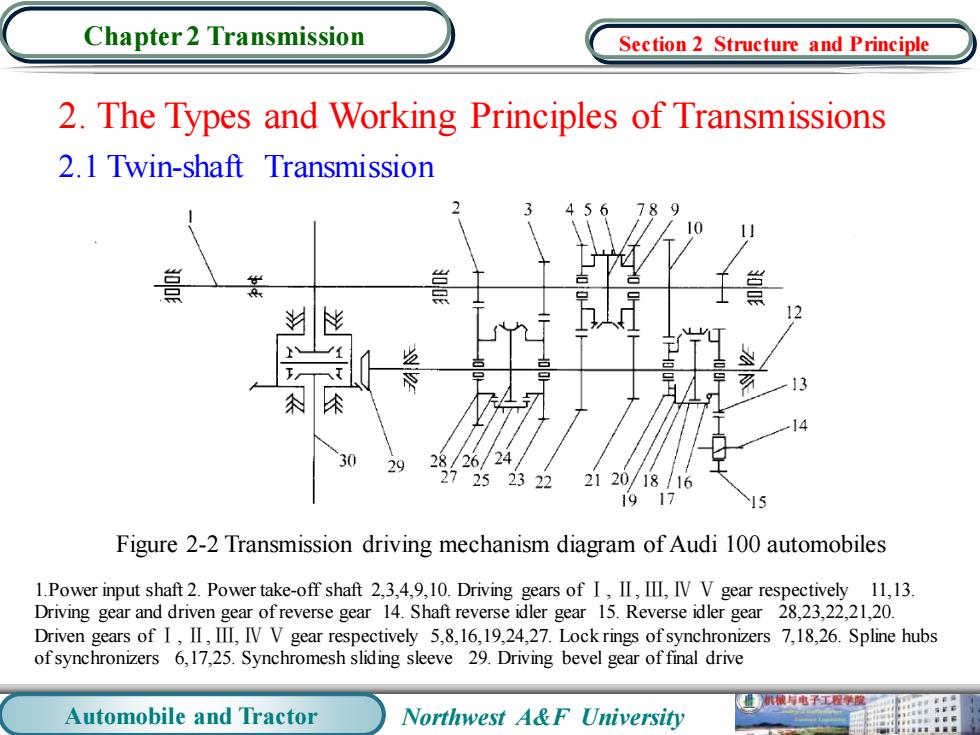
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 2 Structure and Principle 2.The Types and Working Principles of Transmissions 2.1 Twin-shaft Transmission 10 13 不 29 28/26/24 27252322 2120/18/16 1917 Figure 2-2 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Audi 100 automobiles 1.Power input shaft 2.Power take-off shaft 2,3,4,9,10.Driving gears of I,II,III,IV V gear respectively 11,13. Driving gear and driven gear ofreverse gear 14.Shaft reverse idler gear 15.Reverse idler gear 28,23,22,21,20. Driven gears of I,II,III,IV V gear respectively ,8,16,19,24,27.Lock rings of synchronizers 7,18,26.Spline hubs of synchronizers 6,17,25.Synchromesh sliding sleeve 29.Driving bevel gear of final drive 机被有电子工学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University 用
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 2. The Types and Working Principles of Transmissions 2.1 Twin-shaft Transmission Figure 2-2 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Audi 100 automobiles 1.Power input shaft 2. Power take-off shaft 2,3,4,9,10. Driving gears of Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ Ⅴ gear respectively 11,13. Driving gear and driven gear of reverse gear 14. Shaft reverse idler gear 15. Reverse idler gear 28,23,22,21,20. Driven gears of Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ Ⅴ gear respectively 5,8,16,19,24,27. Lock rings of synchronizers 7,18,26. Spline hubs of synchronizers 6,17,25. Synchromesh sliding sleeve 29. Driving bevel gear of final drive Section 2 Structure and Principle
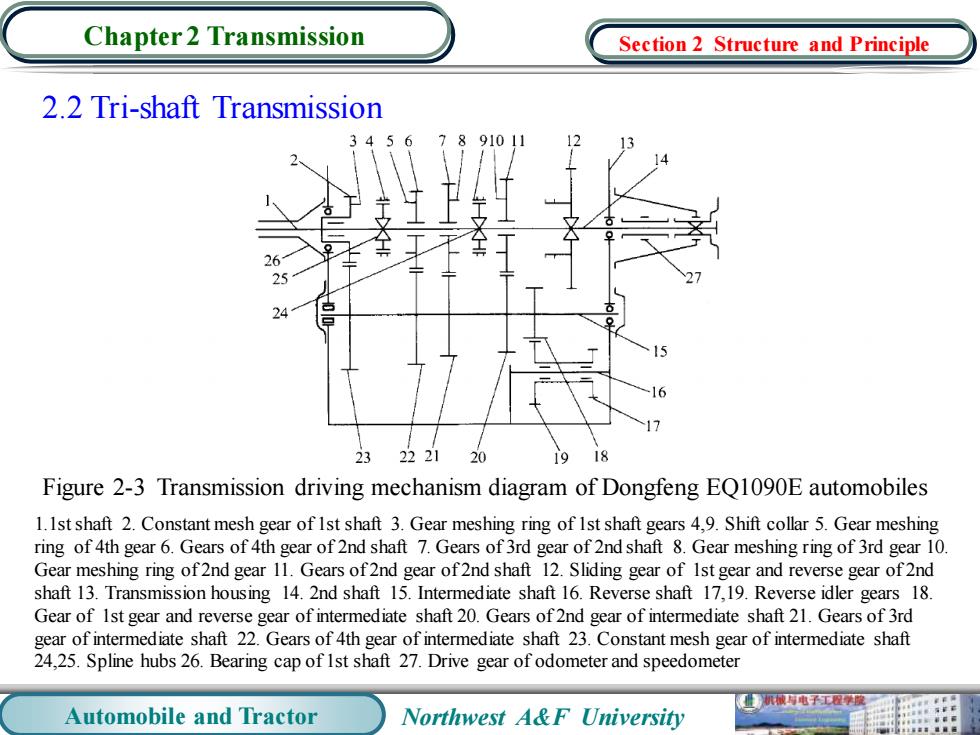
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 2 Structure and Principle 2.2 Tri-shaft Transmission 891011 23222120 19 18 Figure 2-3 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Dongfeng EQ1090E automobiles 1.Ist shaft 2.Constant mesh gear of Ist shaft 3.Gear meshing ring of Ist shaft gears 4,9.Shift collar 5.Gear meshing ring of 4th gear 6.Gears of 4th gear of 2nd shaft 7.Gears of 3rd gear of 2nd shaft 8.Gear meshing ring of 3rd gear 10 Gear meshing ring of2nd gear 11.Gears of2nd gear of2nd shaft 12.Sliding gear of Ist gear and reverse gear of 2nd shaft 13.Transmission housing 14.2nd shaft 15.Intermediate shaft 16.Reverse shaft 17,19.Reverse idler gears 18 Gear of Ist gear and reverse gear of intermediate shaft 20.Gears of2nd gear of intermediate shaft 21.Gears of 3rd gear of intermediate shaft 22.Gears of 4th gear of intermediate shaft 23.Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 24,25.Spline hubs 26.Bearing cap of Ist shaft 27.Drive gear of odometer and speedometer 业机械电子工程学二 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 2.2 Tri-shaft Transmission Figure 2-3 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Dongfeng EQ1090E automobiles 1.1st shaft 2. Constant mesh gear of 1st shaft 3. Gear meshing ring of 1st shaft gears 4,9. Shift collar 5. Gear meshing ring of 4th gear 6. Gears of 4th gear of 2nd shaft 7. Gears of 3rd gear of 2nd shaft 8. Gear meshing ring of 3rd gear 10. Gear meshing ring of 2nd gear 11. Gears of 2nd gear of 2nd shaft 12. Sliding gear of 1st gear and reverse gear of 2nd shaft 13. Transmission housing 14. 2nd shaft 15. Intermediate shaft 16. Reverse shaft 17,19. Reverse idler gears 18. Gear of 1st gear and reverse gear of intermediate shaft 20. Gears of 2nd gear of intermediate shaft 21. Gears of 3rd gear of intermediate shaft 22. Gears of 4th gear of intermediate shaft 23. Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 24,25. Spline hubs 26. Bearing cap of 1st shaft 27. Drive gear of odometer and speedometer Section 2 Structure and Principle
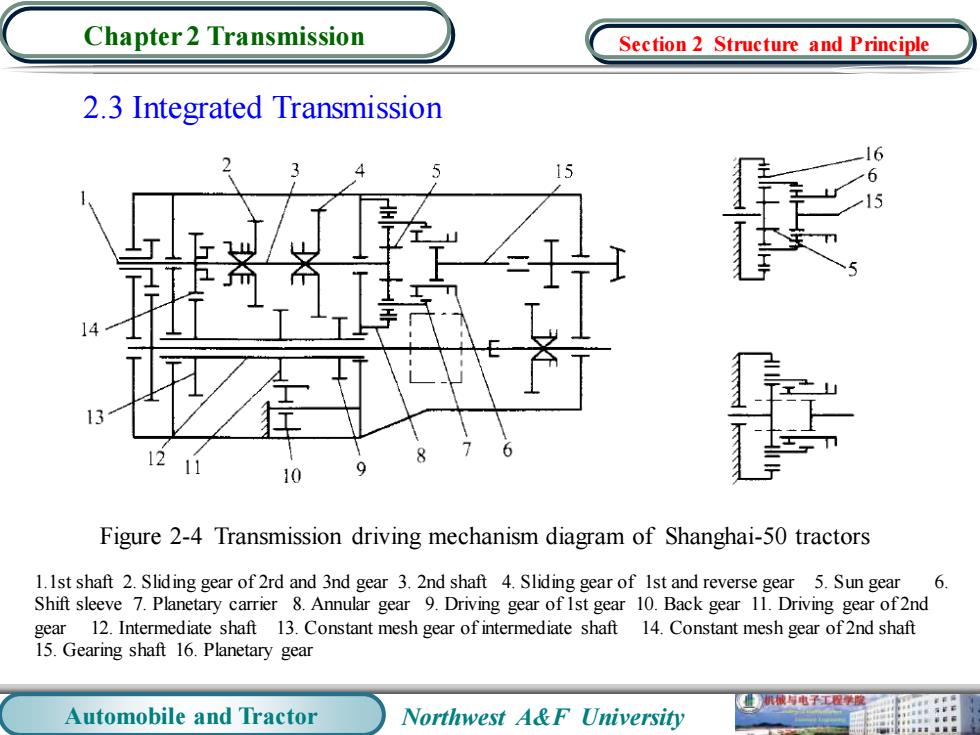
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 2 Structure and Principle 2.3 Integrated Transmission 5 L丁 12 10 Figure 2-4 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Shanghai-50 tractors 1.1st shaft 2.Sliding gear of 2rd and 3nd gear 3.2nd shaft 4.Sliding gear of Ist and reverse gear 5.Sun gear 6 Shift sleeve 7.Planetary carrier 8.Annular gear 9.Driving gear of Ist gear 10.Back gear 11.Driving gear of2nd gear 12.Intermediate shaft 13.Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 14.Constant mesh gear of2nd shaft 15.Gearing shaft 16.Planetary gear 机被电子工程聚 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 2.3 Integrated Transmission Figure 2-4 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Shanghai-50 tractors 1.1st shaft 2. Sliding gear of 2rd and 3nd gear 3. 2nd shaft 4. Sliding gear of 1st and reverse gear 5. Sun gear 6. Shift sleeve 7. Planetary carrier 8. Annular gear 9. Driving gear of 1st gear 10. Back gear 11. Driving gear of 2nd gear 12. Intermediate shaft 13. Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 14. Constant mesh gear of 2nd shaft 15. Gearing shaft 16. Planetary gear Section 2 Structure and Principle

Chapter 2 Transmission Section 3 Synchronizer Currently,there are three ways to shift gears in automobiles and tractors using gear transmission:using shifting slide gear,using shift collar and using synchronizer. Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission Currently, there are three ways to shift gears in automobiles and tractors using gear transmission: using shifting slide gear, using shift collar and using synchronizer. Section 3 Synchronizer
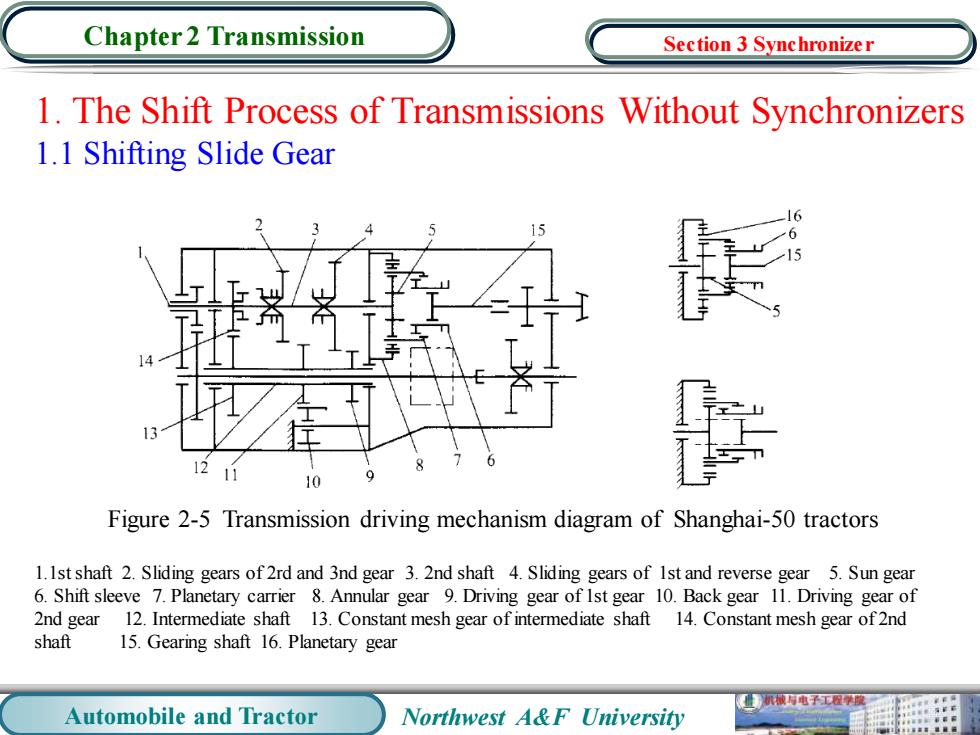
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 3 Synchronizer 1.The Shift Process of Transmissions Without Synchronizers 1.1 Shifting Slide Gear 10 Figure 2-5 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Shanghai-50 tractors 1.Ist shaft 2.Sliding gears of 2rd and 3nd gear 3.2nd shaft 4.Sliding gears of Ist and reverse gear 5.Sun gear 6.Shift sleeve 7.Planetary carrier 8.Annular gear 9.Driving gear of Ist gear 10.Back gear 11.Driving gear of 2nd gear 12.Intermediate shaft 13.Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 14.Constant mesh gear of2nd shaft 15.Gearing shaft 16.Planetary gear 机械电子工程学原 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 1. The Shift Process of Transmissions Without Synchronizers 1.1 Shifting Slide Gear Figure 2-5 Transmission driving mechanism diagram of Shanghai-50 tractors 1.1st shaft 2. Sliding gears of 2rd and 3nd gear 3. 2nd shaft 4. Sliding gears of 1st and reverse gear 5. Sun gear 6. Shift sleeve 7. Planetary carrier 8. Annular gear 9. Driving gear of 1st gear 10. Back gear 11. Driving gear of 2nd gear 12. Intermediate shaft 13. Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 14. Constant mesh gear of 2nd shaft 15. Gearing shaft 16. Planetary gear Section 3 Synchronizer
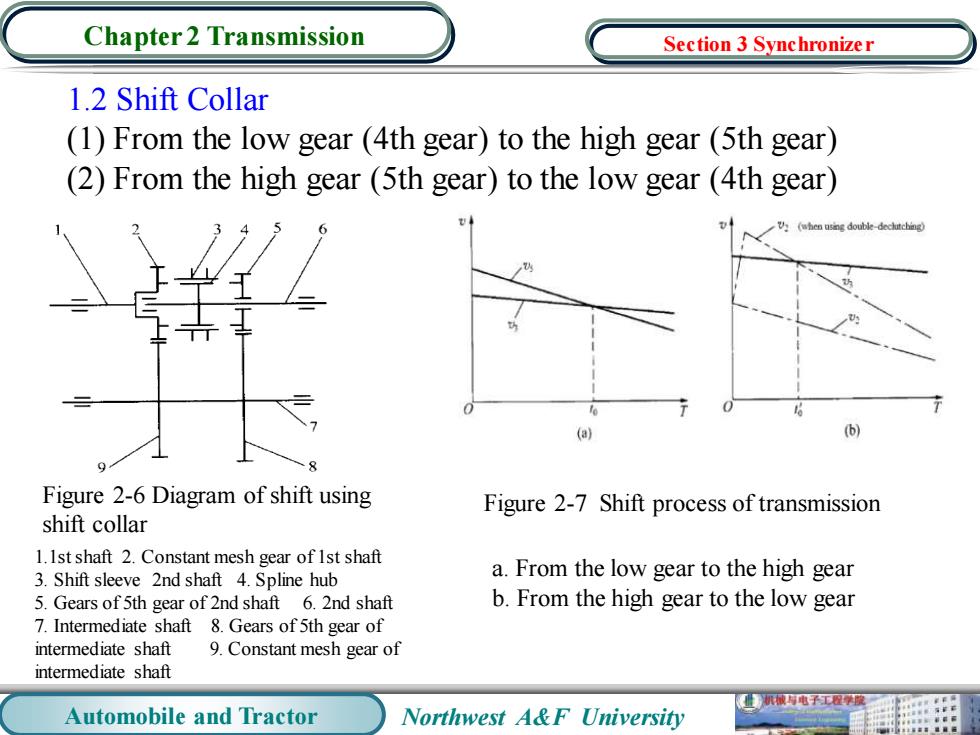
Chapter 2 Transmission Section 3 Synchronizer 1.2 Shift Collar (1)From the low gear(4th gear)to the high gear(5th gear) (2)From the high gear(5th gear)to the low gear(4th gear) ,h(double-d女cb恤g (a) 6 Figure 2-6 Diagram of shift using Figure 2-7 Shift process of transmission shift collar 1.Ist shaft 2.Constant mesh gear of Ist shaft 3.Shift sleeve 2nd shaft 4.Spline hub a.From the low gear to the high gear 5.Gears of 5th gear of 2nd shaft 6.2nd shaft b.From the high gear to the low gear 7.Intermediate shaft 8.Gears of 5th gear of intermediate shaft 9.Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 2 Transmission 1.2 Shift Collar (1) From the low gear (4th gear) to the high gear (5th gear) (2) From the high gear (5th gear) to the low gear (4th gear) Figure 2-6 Diagram of shift using shift collar Figure 2-7 Shift process of transmission 1.1st shaft 2. Constant mesh gear of 1st shaft 3. Shift sleeve 2nd shaft 4. Spline hub 5. Gears of 5th gear of 2nd shaft 6. 2nd shaft 7. Intermediate shaft 8. Gears of 5th gear of intermediate shaft 9. Constant mesh gear of intermediate shaft a. From the low gear to the high gear b. From the high gear to the low gear Section 3 Synchronizer