
Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 1 Overall construction Those machine that can make some form of energy into mechanical energy can be called the engine,such as heat engines,hydraulic engines and wind engines. Heat engine is the machine that can make the heat generated by burning fuel into mechanical energy.Heat engines are divided into two categories:external combustion and internal combustion heat engines. The combustion of fuel is out of the engine that is called the external combustion heat engine;the combustion of fuel is directly in the internal engine known as the internal combustion heat engine. 1.Classification of Internal Combustion Engine (1)Classified by the type of fuel. (2)Classified by the way of fire. (3)Classified by the number of working cycle trips. (4)Classified by the number of cylinders and arrangement. (5)Classified by the way of cooling. (6)Classified by the way of inlet. 械电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Those machine that can make some form of energy into mechanical energy can be called the engine, such as heat engines, hydraulic engines and wind engines. Heat engine is the machine that can make the heat generated by burning fuel into mechanical energy. Heat engines are divided into two categories: external combustion and internal combustion heat engines. The combustion of fuel is out of the engine that is called the external combustion heat engine; the combustion of fuel is directly in the internal engine known as the internal combustion heat engine. 1. Classification of Internal Combustion Engine (1) Classified by the type of fuel. (2) Classified by the way of fire. (3) Classified by the number of working cycle trips. (4) Classified by the number of cylinders and arrangement. (5) Classified by the way of cooling. (6) Classified by the way of inlet. Section 1 Overall construction
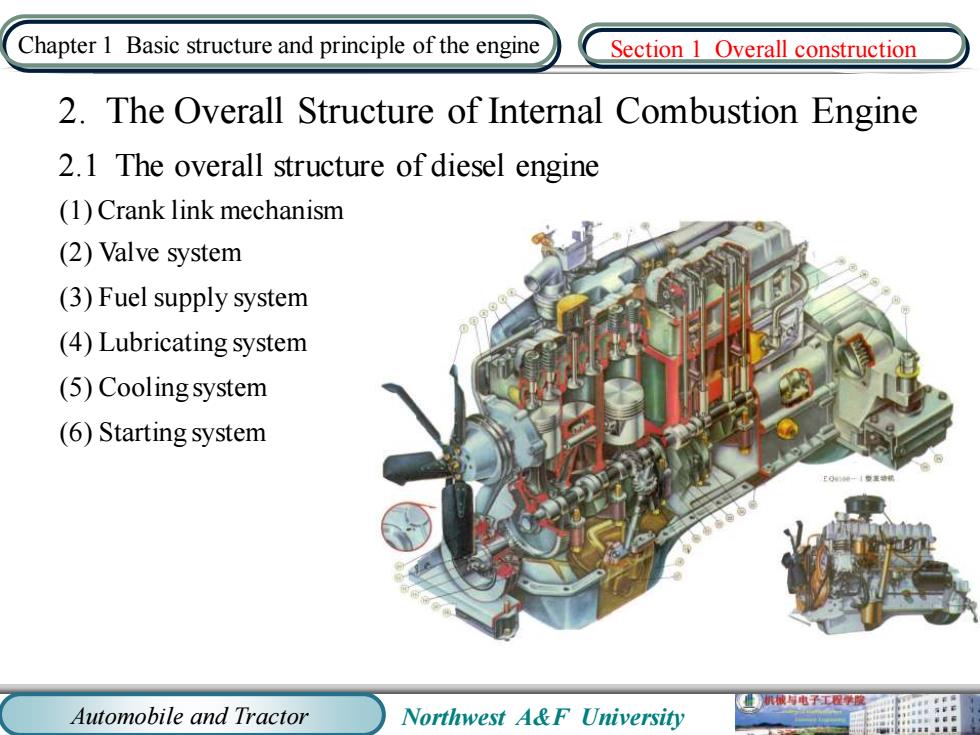
Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 1 Overall construction 2.The Overall Structure of Internal Combustion Engine 2.1 The overall structure of diesel engine (1)Crank link mechanism (2)Valve system (3)Fuel supply system (4)Lubricating system (5)Coolingsystem (6)Starting system 机被电子工学原 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine 2.1 The overall structure of diesel engine (1) Crank link mechanism (2) Valve system (3) Fuel supply system (4) Lubricating system (5) Cooling system (6) Starting system 2. The Overall Structure of Internal Combustion Engine Section 1 Overall construction

2.2 The overall structure of gasoline engmes Gasoline and diesel fuel supply systemsgreatly and the gasoline engine is also equipped with the ignition syrom ● Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine 2.2 The overall structure of gasoline engines Gasoline and diesel fuel supply systems vary greatly, and the gasoline engine is also equipped with the ignition system

Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle 1.Basic Terms of Internal Combustion Engine (1)upper dead point(UDP) (2)lower dead point(LDP) UDP (3)strokeS Stroke (4)fuel chamber volume Vc (5)cylinder working volume Vh V=80s×10 (L) 4 (6)total volume ofcylinder Va Va=V。+V (7)compressionratio s Figure 1.3 Internal combustion engine VV+V.=1+7 e-V.-V schematic diagram 1.intake valve 2.exhaust valve 3.cylinder (8)total swept volume of piston Vz 4.piston 5.connecting rod 6.crankshaft center Vz=Vh·i 7.crank 机被电子工程模 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine (1) upper dead point(UDP) (2) lower dead point(LDP) (3) stroke S (4) fuel chamber volume Vc (5) cylinder working volume Vh (6) total volume of cylinder Va (7) compression ratio ε ε (8) total swept volume of piston Vz Vz=Vh·i S 10 (L) 4 D V 3 2 h − = ð Va = Vc + Vh c h c c h c a V V 1 V V V V V = + + = = 1. Basic Terms of Internal Combustion Engine Figure 1.3 Internal combustion engine schematic diagram 1. intake valve 2. exhaust valve 3. cylinder 4. piston 5.connecting rod 6. crankshaft center 7. crank Section 2 Basic working principle
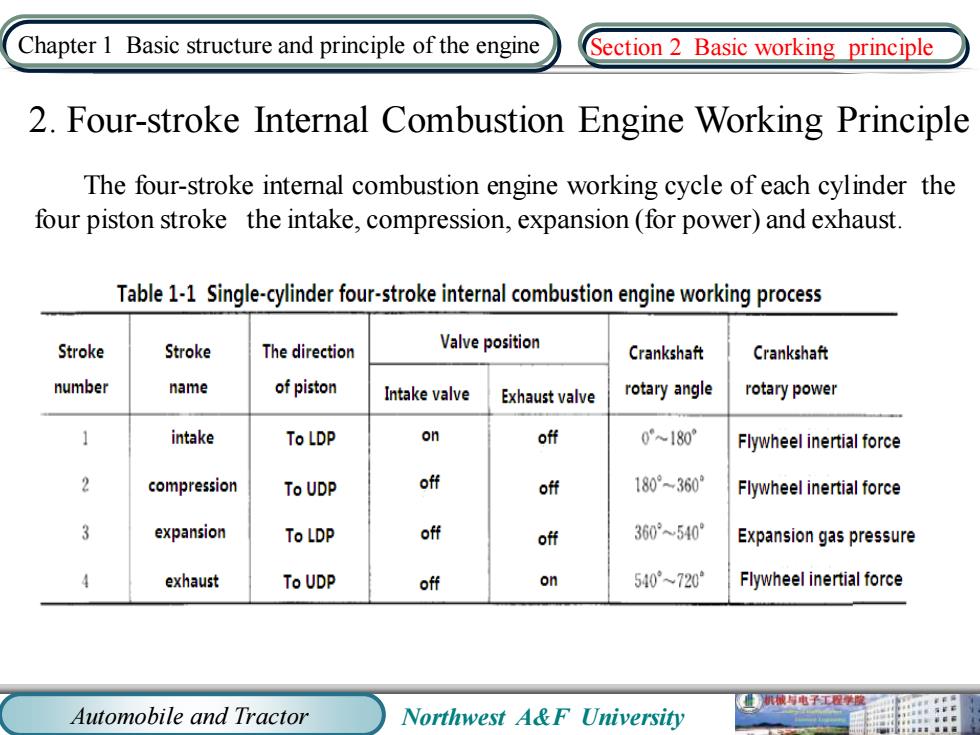
Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle 2.Four-stroke Internal Combustion Engine Working Principle The four-stroke internal combustion engine working cycle of each cylinder the four piston stroke the intake,compression,expansion(for power)and exhaust. Table 1-1 Single-cylinder four-stroke internal combustion engine working process Stroke Stroke The direction Valve position Crankshaft Crankshaft number name of piston Intake valve Exhaust valve rotary angle rotary power intake To LDP on off 0180 Flywheel inertial force 2 compression To UDP off off 180°-360 Flywheel inertial force 3 expansion To LDP off off 360°~540 Expansion gas pressure exhaust To UDP off on 540°~720 Flywheel inertial force 业机械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine 2. Four-stroke Internal Combustion Engine Working Principle The four-stroke internal combustion engine working cycle of each cylinder the four piston stroke the intake, compression, expansion (for power) and exhaust. Section 2 Basic working principle
Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle

Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle 2.1 Four-stroke gasoline engine working principle inlet inlet intake stroke port fuel/air mixture mixture. intake Atmospheric pressure line connecting rod crankshaft otation (a) 业机电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine 2.1 Four-stroke gasoline engine working principle intake stroke Section 2 Basic working principle

Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle valves( compression stroke closed compression Atmospheric pressure line (b) Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine compression stroke Section 2 Basic working principle
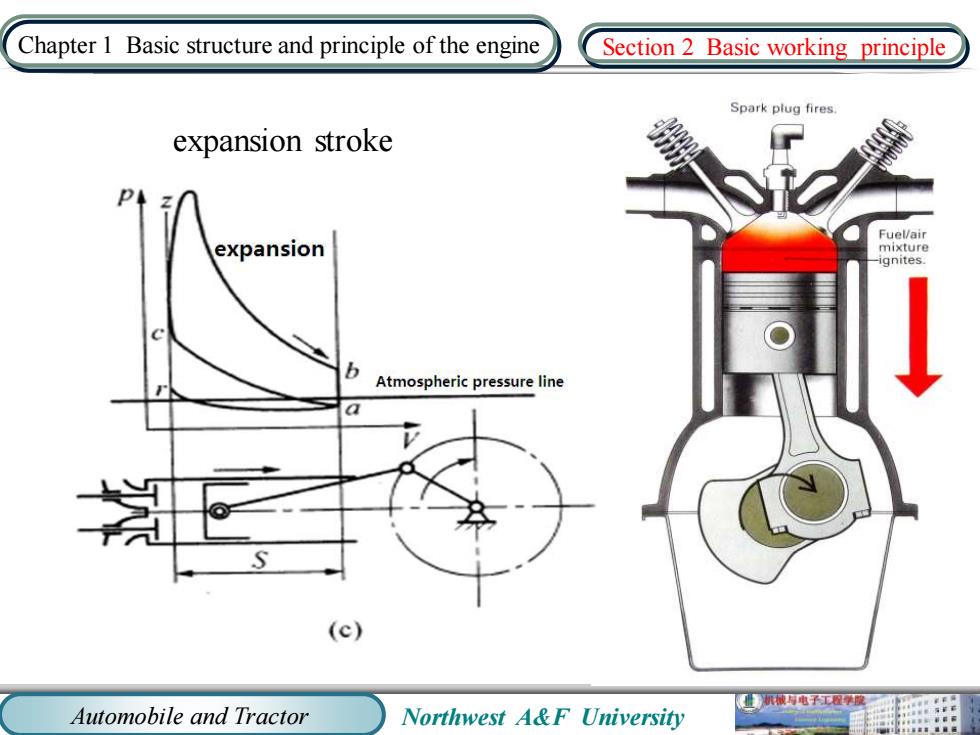
Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle Spark plug fires. expansion stroke Fuel/air expansion mixture ignites. Atmospheric pressure line (c) 业机电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine expansion stroke Section 2 Basic working principle

Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine Section 2 Basic working principle exhaus valve inlet exhaust stroke exhaust D out Piston rises. forcing waste exhaust Atmospheric pressure line (d) Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 1 Basic structure and principle of the engine exhaust stroke Section 2 Basic working principle