
Chapter 6 Brake System Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System 1.Functions and types 1.1 Functions Forcing high-speed vehicles slow down or stop in the shortest distance according to demand;limiting speed when downhill;assisting or achieving to steering;guarantying parked cars immovability to prevent slippery. 1.2 Types Brake systems have many types. Generally,a car should include two separate braking systems:a service braking system and a parking braking system. According to the type of braking energy,they can be divided into: muscular energy braking,dynamic braking,servo brake; According to the transmission forms,they can be divided into: mechanical type,hydraulic type and pneumatic type. 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 1. Functions and types 1.1 Functions Forcing high-speed vehicles slow down or stop in the shortest distance according to demand; limiting speed when downhill; assisting or achieving to steering; guarantying parked cars immovability to prevent slippery. 1.2 Types Brake systems have many types. Generally, a car should include two separate braking systems: a service braking system and a parking braking system. According to the type of braking energy, they can be divided into: muscular energy braking, dynamic braking, servo brake; According to the transmission forms, they can be divided into: mechanical type, hydraulic type and pneumatic type. Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System

Chapter 6 Brake System Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System 2.Ultimate Principle and Requirements 2.1 Ultimate Principle Its ultimate principle is that using friction to make the fixed parts generate a friction torque to the rotating parts,and pass it to the wheels.Then the wheels will generate a forward circumference force to the road because of the adhesive force between the wheels and roads,at the same time the surface will give a backward reaction force to the wheels,which is the braking force.Under the effect of the breaking force,the vehicle will slow down until stop 机械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 2. Ultimate Principle and Requirements 2.1 Ultimate Principle Its ultimate principle is that using friction to make the fixed parts generate a friction torque to the rotating parts, and pass it to the wheels. Then the wheels will generate a forward circumference force to the road because of the adhesive force between the wheels and roads, at the same time the surface will give a backward reaction force to the wheels, which is the braking force. Under the effect of the breaking force, the vehicle will slow down until stop. Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System

Chapter6 Brake System Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System 7777777元 77777T77777 Figure 6-1 Working principle diagram of braking system 1.Brake pedal 2.Push rod 3.Master cylinder piston 4.Brake master cylinder 5.Oil pipe 6.Wheel braking cylinder 7.Wheel braking cylinder piston 8.Brake drum 9.Friction disk 10.Brake shoe 11.Brake bottom plate 12.Support pin 13.Brake shoe return spring 械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System Figure 6-1 Working principle diagram of braking system 1. Brake pedal 2. Push rod 3. Master cylinder piston 4. Brake master cylinder 5. Oil pipe 6. Wheel braking cylinder 7. Wheel braking cylinder piston 8. Brake drum 9. Friction disk 10. Brake shoe 11. Brake bottom plate 12. Support pin 13. Brake shoe return spring Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System

Chapter 6 Brake System Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System 2.2 Requirements To ensure the vehicles to exert high speed capability in safe condition,the brake system must meet the following requirements: (1)Adequate braking reliability Measured by the braking distance,braking deceleration and other indicators. (2)Easy to manipulate Automobiles:Control force no more than 200-300N; Tractors:Control force no more than 300N. (3)Smooth braking The braking force should be gradually increased when braking,but it should be disappeared quickly when relieving brake Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University 业机被与电子工程短
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 2.2 Requirements To ensure the vehicles to exert high speed capability in safe condition , the brake system must meet the following requirements: (1) Adequate braking reliability Measured by the braking distance, braking deceleration and other indicators. (2) Easy to manipulate Automobiles: Control force no more than 200-300N; Tractors: Control force no more than 300N. (3) Smooth braking The braking force should be gradually increased when braking, but it should be disappeared quickly when relieving brake. Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System

Chapter 6 Brake System Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System (4)Good braking stability The braking forces of front and rear wheels should be distributed reasonably,and the braking forces of left and right wheels should be equal. (5)Good heat dissipation Friction discs should have better thermal fade resistance,and should be waterproof,oil-proof and dustproof. 电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System (4) Good braking stability The braking forces of front and rear wheels should be distributed reasonably, and the braking forces of left and right wheels should be equal. (5) Good heat dissipation Friction discs should have better thermal fade resistance, and should be waterproof, oil-proof and dustproof. Section 1 Principle and Type of Brake System

Chapter 6 Brake System Section2 Brake 1.Brake Types Brakes have many types.They can be divided into the wheel brakes and parking brakes according to their application.According to their structures,wheel brakes can be divided into band brakes,drum brakes and disc brakes;Parking brakes can be divided into shoe disc brakes and drum parking brakes. 2.Drum Brake 2.1 Wheel Cylinder Brake 2.1.1 Simple non-balancing brake N1N2, F1F2, The braking torques of left and right shoes are not equal.The torque of tight shoe is 2 to 2.5 times than that of the loose shoe. 机械电子工程学 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 1. Brake Types Brakes have many types. They can be divided into the wheel brakes and parking brakes according to their application. According to their structures, wheel brakes can be divided into band brakes, drum brakes and disc brakes; Parking brakes can be divided into shoe disc brakes and drum parking brakes. 2. Drum Brake 2.1 Wheel Cylinder Brake 2.1.1 Simple non-balancing brake N1≠N2, F1≠F2, The braking torques of left and right shoes are not equal. The torque of tight shoe is 2 to 2.5 times than that of the loose shoe. Section 2 Brake
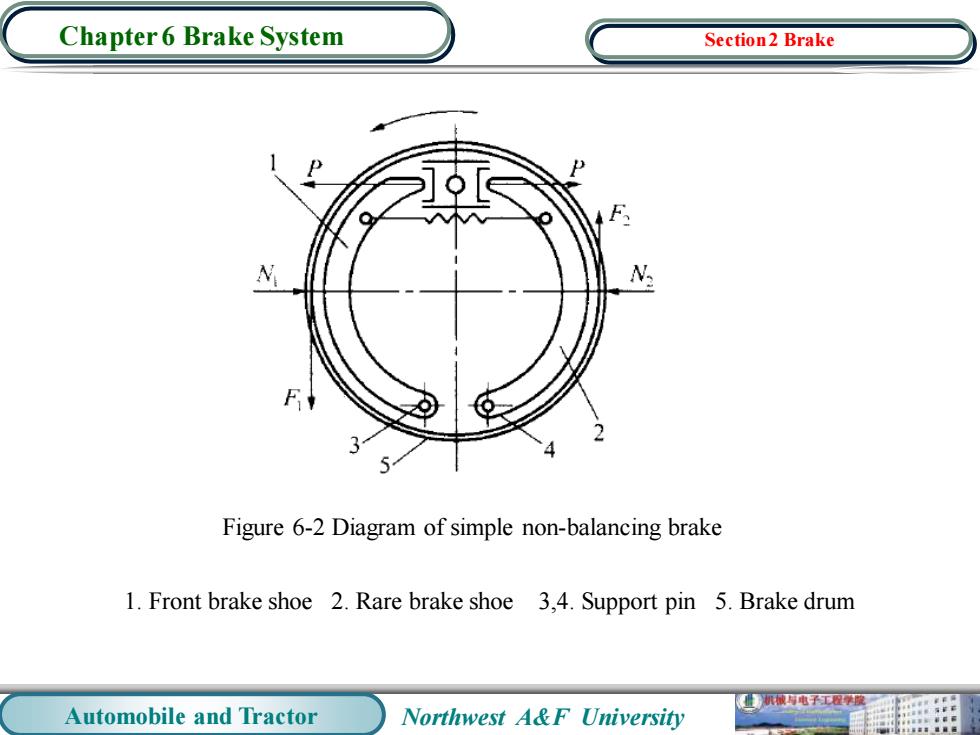
Chapter 6 Brake System Section2 Brake Figure 6-2 Diagram of simple non-balancing brake 1.Front brake shoe 2.Rare brake shoe 3,4.Support pin 5.Brake drum 机械电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System Figure 6-2 Diagram of simple non-balancing brake 1. Front brake shoe 2. Rare brake shoe 3,4. Support pin 5. Brake drum Section 2 Brake
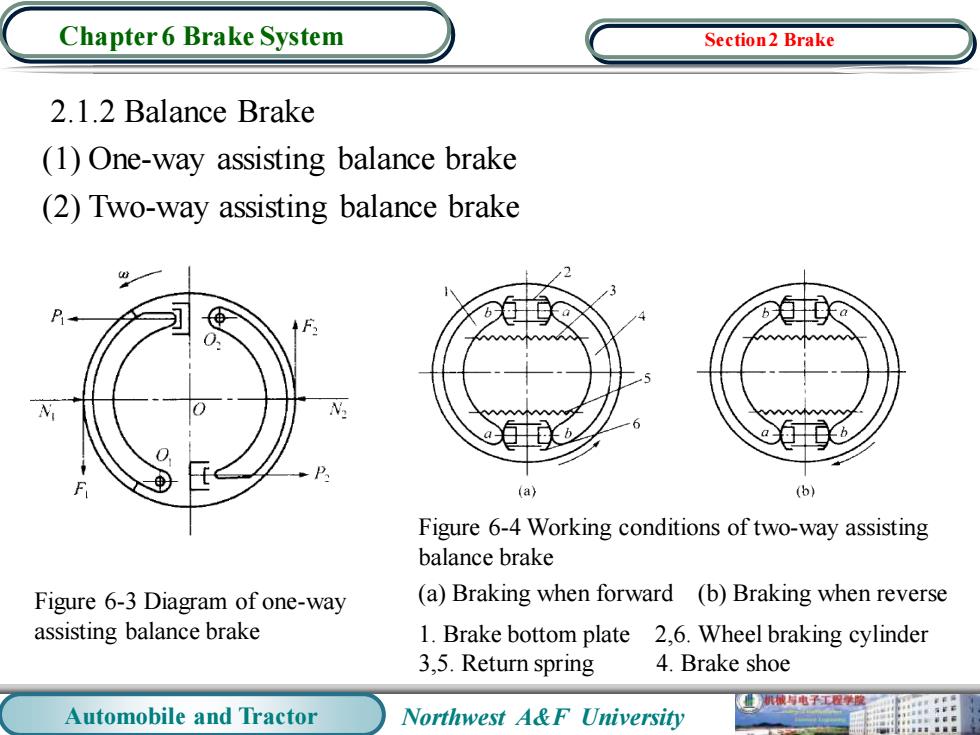
Chapter 6 Brake System Section2 Brake 2.1.2 Balance Brake (1)One-way assisting balance brake (2)Two-way assisting balance brake N (a) (b) Figure 6-4 Working conditions of two-way assisting balance brake Figure 6-3 Diagram of one-way (a)Braking when forward (b)Braking when reverse assisting balance brake 1.Brake bottom plate 2,6.Wheel braking cylinder 3.5.Return spring 4.Brake shoe 机被有电子工程聚 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 2.1.2 Balance Brake (1) One-way assisting balance brake (2) Two-way assisting balance brake Figure 6-3 Diagram of one-way assisting balance brake Figure 6-4 Working conditions of two-way assisting balance brake (a) Braking when forward (b) Braking when reverse 1. Brake bottom plate 2,6. Wheel braking cylinder 3,5. Return spring 4. Brake shoe Section 2 Brake

Chapter6 Brake System Section2 Brake (3)Self-servo brake 10 Figure 6-5 Bi-directional-servo brake 1.Brake bottom plate 2.Rare brake shoe 3.Return spring of rare brake shoe 4.Clamp 5.Wheel braking cylinder 6.Return spring of front brake shoe 7.Front brake shoe 8.Adjustable push rod 9.Stretched spring 10.Adjusting screw 11.Push rod sleeve 业机电子工程学度 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System (3) Self-servo brake Figure 6-5 Bi-directional-servo brake 1. Brake bottom plate 2. Rare brake shoe 3. Return spring of rare brake shoe 4. Clamp 5. Wheel braking cylinder 6. Return spring of front brake shoe 7. Front brake shoe 8. Adjustable push rod 9. Stretched spring 10. Adjusting screw 11. Push rod sleeve Section 2 Brake

Chapter 6 Brake System Section2 Brake 2.2 Cam Brake Pneumatic transmission brakes normally adopt cam type expander. 10 Figure 6-6 Cam brake Figure 6-7 Brake plunger arm 1.Axle journal of knuckle 2.Brake shoe 3.Return spring 4.Brake camshaft 5.Brake plunger arm 1.Spring 2.Dust guard 3.Worm 6.Brake repair room 7.Brake bottom plate shaft 4.Lock-up sleeve 5.Lock 8.Brake drum 9.Shoe shaft 10.Cotter bolt 6.Worm 7.Housing 机械与电子工程学聚 Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University
Automobile and Tractor Northwest A&F University Chapter 6 Brake System 2.2 Cam Brake Pneumatic transmission brakes normally adopt cam type expander. Figure 6-6 Cam brake Figure 6-7 Brake plunger arm 1. Axle journal of knuckle 2. Brake shoe 3. Return spring 4. Brake camshaft 5. Brake plunger arm 6. Brake repair room 7. Brake bottom plate 8. Brake drum 9. Shoe shaft 10. Cotter 1. Spring 2. Dust guard 3. Worm shaft 4. Lock-up sleeve 5. Lock bolt 6. Worm 7. Housing Section 2 Brake