
同济大学试卷统一命题纸 (A卷答案) 2011-2012学年第二学期 命题教师签名: 审核教师签名: 课号:05028702课名:环境工程微生物学(全英文) 考试考查:考试 此卷选为:期中考试(人期终考试()小补考)试卷 年级 专业 学号」 姓名】 得分 1.Fill in the Blank (1 point each,20 points in total) (1)Microorganism is an organism which is so small that normally it cannot be seen without the use of microscope (2)The systemic taxa of microorganisms follow the systemic taxa built by Linnaeus,including seven grades from top to bottom:Kingdom.Phylum,Class,Oder Family, Genus Species. (3)Viruses consist of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. (4)The methods of virus replication include Lytic cycle and Lysogenic cycle (5)List four morphological shapes of Eubacteria:a Cocus b.Rod c.Vibrio d.Spirillum (6)An antibiotic is a substance produced by microorganisms that inhibits or kills other microorganisms. (7)The carbon source of autotrophic bacteria isCO2 (8)Generally,the ratio of nutrients for aerobic wastewater treatment processes is BOD5:N:P=100:5: (9) Eukaryotic microorganisms include a.Protozoa b.Metozoa c Alga d.Fungi
1 同济大学试卷统一命题纸 (A 卷答案) 2011-2012 学年第二学期 命题教师签名: 审核教师签名: 课号: 05028702 课名:环境工程微生物学(全英文) 考试考查:考试 此卷选为:期中考试( )、期终考试(√)、补考( )试卷 年级 专业 学号 姓名 得分 1. Fill in the Blank(1 point each,20 points in total) (1) Microorganism is an organism which is so small that normally it cannot be seen without the use of microscope . (2) The systemic taxa of microorganisms follow the systemic taxa built by Linnaeus,including seven grades from top to bottom: Kingdom, Phylum , Class, Oder , Family, Genus , Species. (3) Viruses consist of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. (4) The methods of virus replication include Lytic cycle and Lysogenic cycle. (5) List four morphological shapes of Eubacteria: a. Cocus b. Rod c. Vibrio d. Spirillum . (6) An antibiotic is a substance produced by microorganisms that inhibits or kills other microorganisms. (7) The carbon source of autotrophic bacteria is CO2 . (8) Generally, the ratio of nutrients for aerobic wastewater treatment processes is BOD5:N:P = 100 : 5 : 1 . (9) Eukaryotic microorganisms include a. Protozoa b. Metozoa c. Alga d. Fungi

2.True or False.If true,write"T"on the blank;if false write"F"on the blank.(2 point each,20 points in total) (1)TMicrobes are responsible for the geochemical cycles. (2)TMicrobes have been used to produce food(brewing.wine making.).but they are also responsible for food spoilage (3)FAll the viruses can cause illness and they are all pathogenic. (4)FSynergism is an obligatory interrelationship between two populations that benefits both of them. (5)FAll the genes are always expressed at the same time. (6)TUracil (U)can only be found in RNA (7)TTwo strands of DNA are held together by specific hydrogen bonding between A andT or G and C to form a right-handed helix. (8)TThe genetic codes on tRNA are called anticodons. (9)T Ammonification is the process that the amino groups of amino acids are removed and converted into ammonia (10)TChemolithoautotrophs are organisms that oxidize an inorganic compound for energy and obtain their carbon source from carbon dioxide. 2
2 2. True or False. If true, write “ T ” on the blank; if false write “ F ” on the blank. (2 point each,20 points in total) (1) ___T__ Microbes are responsible for the geochemical cycles. (2) ___T__ Microbes have been used to produce food(brewing,wine making...), but they are also responsible for food spoilage. (3) ___F____ All the viruses can cause illness and they are all pathogenic. (4) ___F___ Synergism is an obligatory interrelationship between two populations that benefits both of them. (5) ___F____ All the genes are always expressed at the same time. (6) ___T____ Uracil (U) can only be found in RNA. (7) ___T____ Two strands of DNA are held together by specific hydrogen bonding between A and T or G and C to form a right-handed helix. (8) ___T____ The genetic codes on tRNA are called anticodons. (9) ___T____ Ammonification is the process that the amino groups of amino acids are removed and converted into ammonia. (10)___T___ Chemolithoautotrophs are organisms that oxidize an inorganic compound for energy and obtain their carbon source from carbon dioxide

3.Explain the following scientific terms.(3 point each,30 points in total) (1)Plasmid:Small extrachromosomal genetic elements in Prokaryotic cells. (2)Eutrophication:the process by which a body of water becomes enriched in dissolved nutrients (as phosphates)that stimulate the growth of aquatic plant life usually resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen (3)Enzyme:A protein with catalytic properties due to its power of specific activation (4)Complimentary Base Pairing:Principle of Nitrogenous bases pairing in DNA or RNA:A-T(U) and G-C. (5)Commensalism:a unidirectional relationship betwen populations in which one population benefits and the other one is unaffected. (6)Biofilm:an assemblage of microorganisms and its associated extracellular products at an interface and typically attached to a surface. (7)Operon:a series of structural genes which are under the control of a Regulatory Gene and functions in a coordinated manner by means of an operator,a promoter,and one or more structural genes. (8)Cell Yield Coefficient(Y):the unit amount of cell mass produced per unit amount of substrate consumed (9)Mesophiles:microorganisms which prefer living at temperature of 25 to 45 degrees. (10)Fluorescence in situ Hybridization(FISH):a process which vividly paints chromosomes or portions of chromosomes with fluorescent molecules 3
3 3. Explain the following scientific terms. (3 point each,30 points in total) (1) Plasmid: Small extrachromosomal genetic elements in Prokaryotic cells. (2) Eutrophication: the process by which a body of water becomes enriched in dissolved nutrients (as phosphates) that stimulate the growth of aquatic plant life usually resulting in the depletion of dissolved oxygen. (3) Enzyme: A protein with catalytic properties due to its power of specific activation. (4) Complimentary Base Pairing: Principle of Nitrogenous bases pairing in DNA or RNA: A – T (U) and G – C. (5) Commensalism: a unidirectional relationship betwen populations in which one population benefits and the other one is unaffected. (6) Biofilm: an assemblage of microorganisms and its associated extracellular products at an interface and typically attached to a surface. (7) Operon: a series of structural genes which are under the control of a Regulatory Gene and functions in a coordinated manner by means of an operator, a promoter, and one or more structural genes. (8) Cell Yield Coefficient (Y): the unit amount of cell mass produced per unit amount of substrate consumed. (9) Mesophiles: microorganisms which prefer living at temperature of 25 to 45 degrees. (10) Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH): a process which vividly paints chromosomes or portions of chromosomes with fluorescent molecules

4.Briefly answer the following questions.(5 point each,30 points in total) (1)What are the main functions of cell membrane in prokaryotic microorganisms? 1)Permeability barrier prevents leakage and function as gate way for transport of nutrients into and out of the cell. 2)Protein anchor site of many proteins involved in transport,bioenergetics,and chemotaxis. 3)Energy conservation site of generation and use of the proton motive force. (2)What are the three components of nucleotide?Please draw the schematic structure of nucleotide Phosphate Nitrogenous base Pentose sugar
4 4. Briefly answer the following questions. (5 point each,30 points in total) (1) What are the main functions of cell membrane in prokaryotic microorganisms? 1) Permeability barrier prevents leakage and function as gate way for transport of nutrients into and out of the cell. 2) Protein anchor site of many proteins involved in transport, bioenergetics, and chemotaxis. 3) Energy conservation site of generation and use of the proton motive force. (2) What are the three components of nucleotide? Please draw the schematic structure of nucleotide. Phosphate Nitrogenous base Pentose sugar

(3)What is the Nitrogen Cycle in the nature?Describe the main processes of nitrogen cycle and draw a schematic graph Almost all the nitrogen in the soil exists in organic molecules,primarily in proteins.When an organism dies.the process of microbial decomposition results in the hydrolytic breakdown of proteins into amino acids.The amino groups of amino acids are removed and converted into ammonia(NH3). Ammonification is brought about by numerous bacteria and fungi.Then ammonia are oxidized by nitrifying bacteria into nitrite and nitrate,which are converted into nitrogen gas by denitrification. (4)What are the fundamental biochemical mechanisms of enhanced biological phosphorus remova process for municipal wastewater treatment? 1)Under anaerobic conditions,phosphorus accumulating organisms (PAOs)release P to bulk liquid. 2)Under aerobic conditions,PAOs adsorb and utilize more P than it released. 3)The P was removed from wastewater water together with excessive waste sludge discharge
5 (3) What is the Nitrogen Cycle in the nature? Describe the main processes of nitrogen cycle and draw a schematic graph. Almost all the nitrogen in the soil exists in organic molecules, primarily in proteins. When an organism dies, the process of microbial decomposition results in the hydrolytic breakdown of proteins into amino acids. The amino groups of amino acids are removed and converted into ammonia (NH3). Ammonification is brought about by numerous bacteria and fungi. Then ammonia are oxidized by nitrifying bacteria into nitrite and nitrate, which are converted into nitrogen gas by denitrification. (4) What are the fundamental biochemical mechanisms of enhanced biological phosphorus removal process for municipal wastewater treatment? 1) Under anaerobic conditions, phosphorus accumulating organisms (PAOs) release P to bulk liquid. 2) Under aerobic conditions, PAOs adsorb and utilize more P than it released. 3) The P was removed from wastewater water together with excessive waste sludge discharge
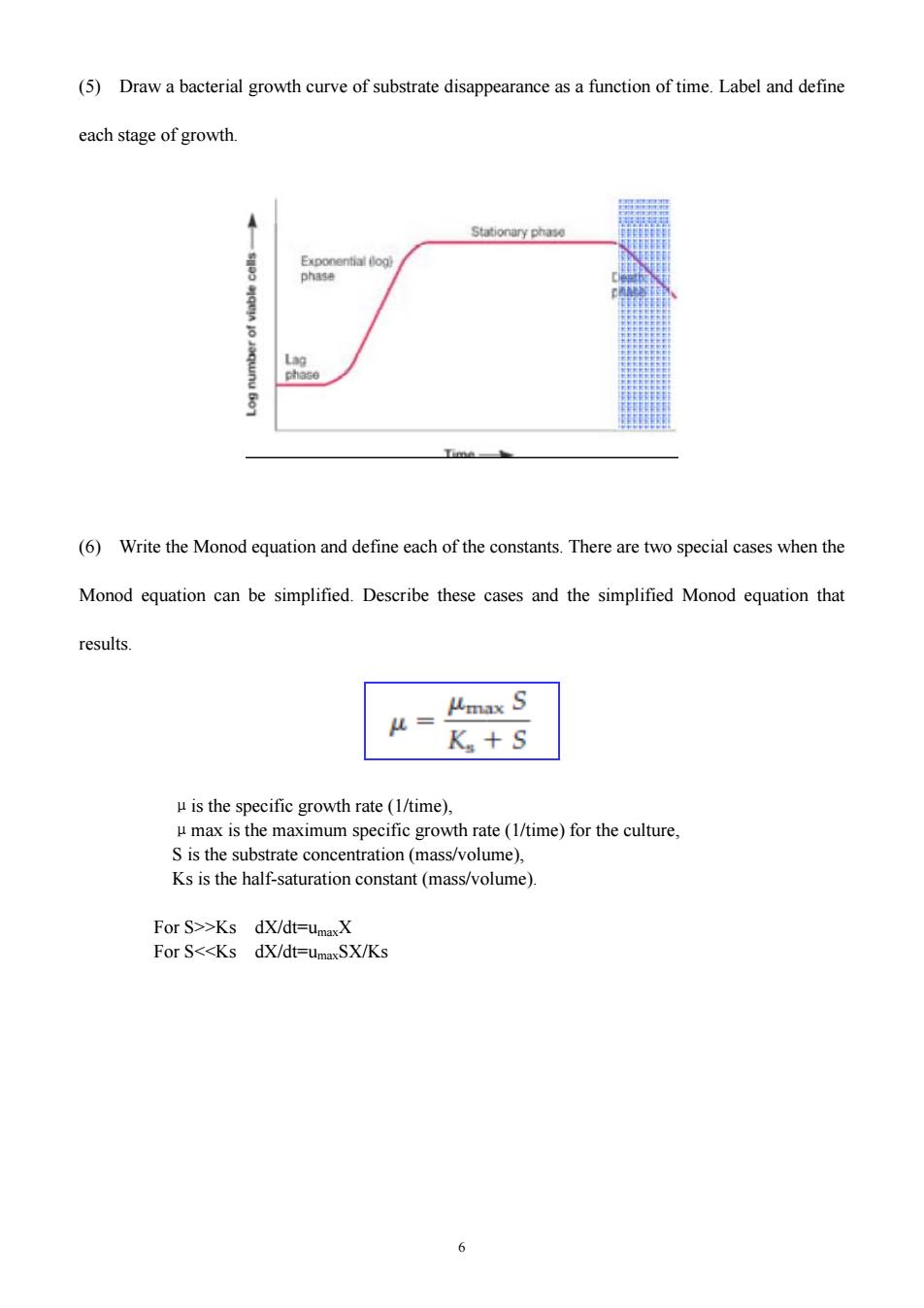
(5)Draw a bacterial growth curve of substrate disappearance as a function of time.Label and define each stage of growth (6)Write the Monod equation and define each of the constants.There are two special cases when the Monod equation can be simplified.Describe these cases and the simplified Monod equation that results. 从= K+S uis the specific growth rate(1/time). umax is the maximum specific growth rate (1/time)for the culture, S is the substrate concentration(mass/volume), Ks is the half-saturation constant (mass/volume) For S>>Ks dX/dt=umaX For S<<Ks dX/dt=umaxSX/Ks 6
6 (5) Draw a bacterial growth curve of substrate disappearance as a function of time. Label and define each stage of growth. (6) Write the Monod equation and define each of the constants. There are two special cases when the Monod equation can be simplified. Describe these cases and the simplified Monod equation that results. μis the specific growth rate (1/time), μmax is the maximum specific growth rate (1/time) for the culture, S is the substrate concentration (mass/volume), Ks is the half-saturation constant (mass/volume). For S>>Ks dX/dt=umaxX For S<<Ks dX/dt=umaxSX/Ks