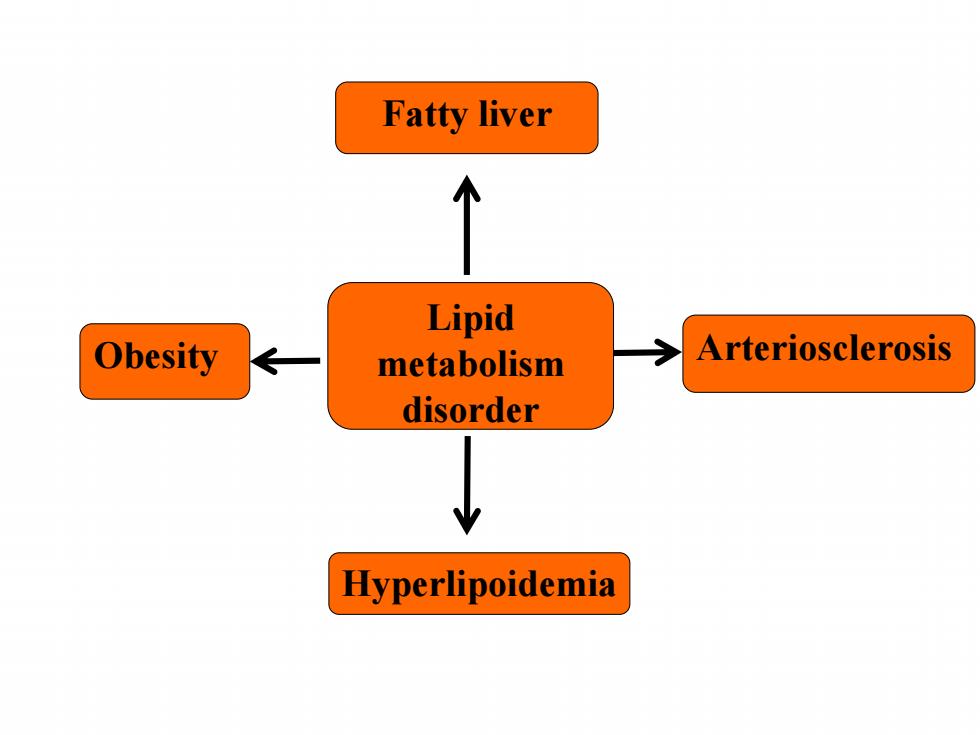
Fatty liver 个 Lipid Obesity metabolism Arteriosclerosis disorder Hyperlipoidemia
Lipid metabolism disorder Obesity Hyperlipoidemia Arteriosclerosis Fatty liver
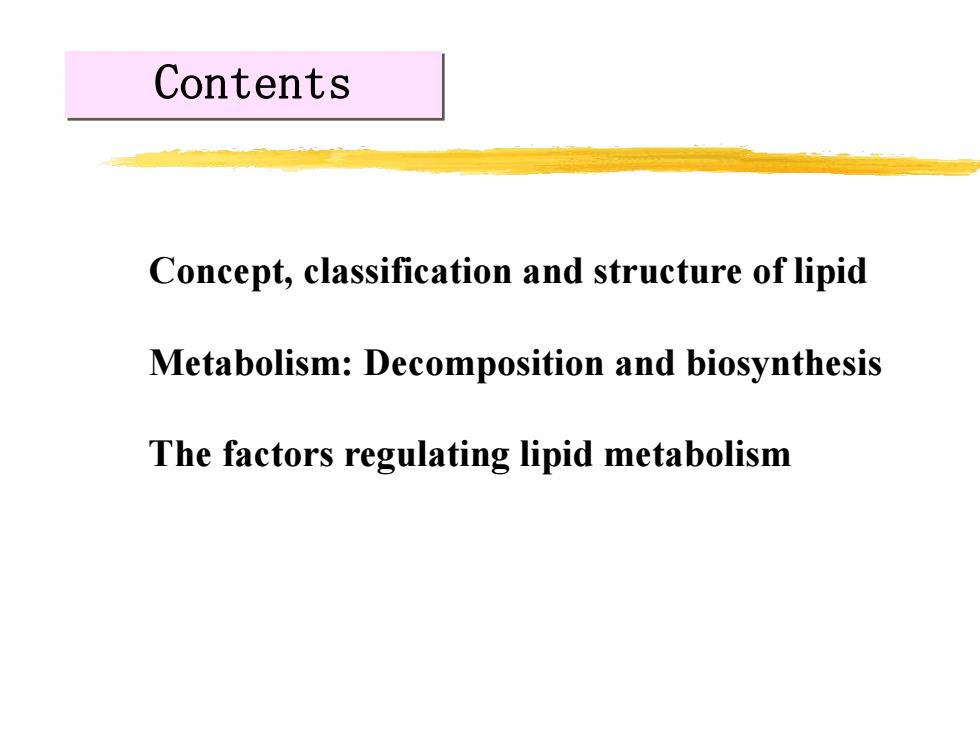
Contents Concept,classification and structure of lipid Metabolism:Decomposition and biosynthesis The factors regulating lipid metabolism
Contents Concept, classification and structure of lipid Metabolism: Decomposition and biosynthesis The factors regulating lipid metabolism
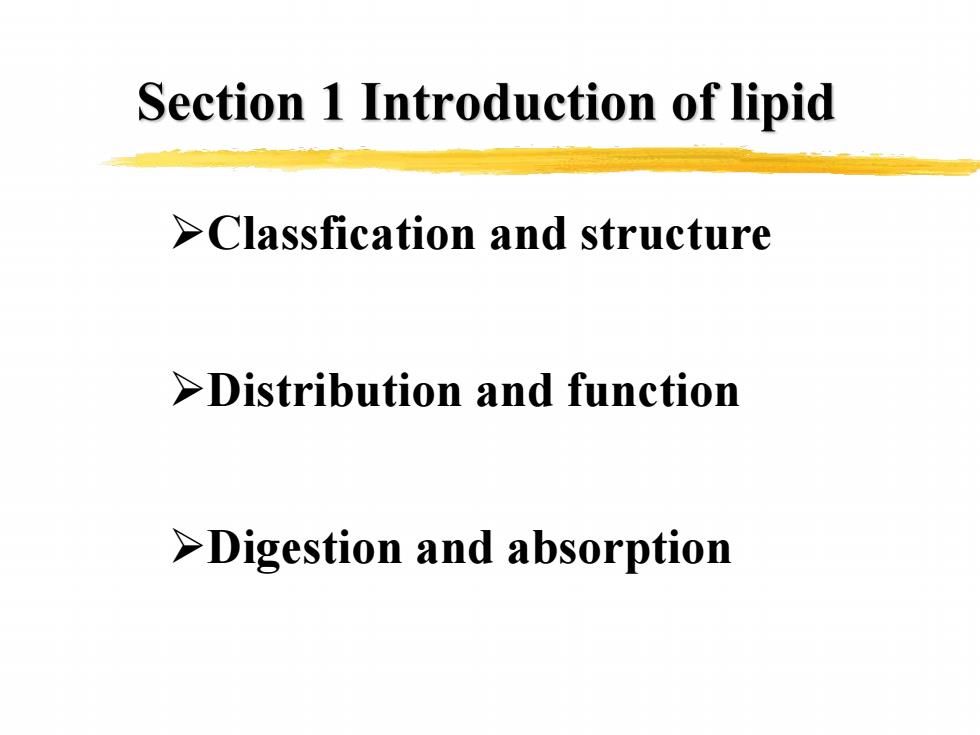
Section 1 Introduction of lipid > Classfication and structure >Distribution and function >Digestion and absorption
ØClassfication and structure ØDistribution and function ØDigestion and absorption
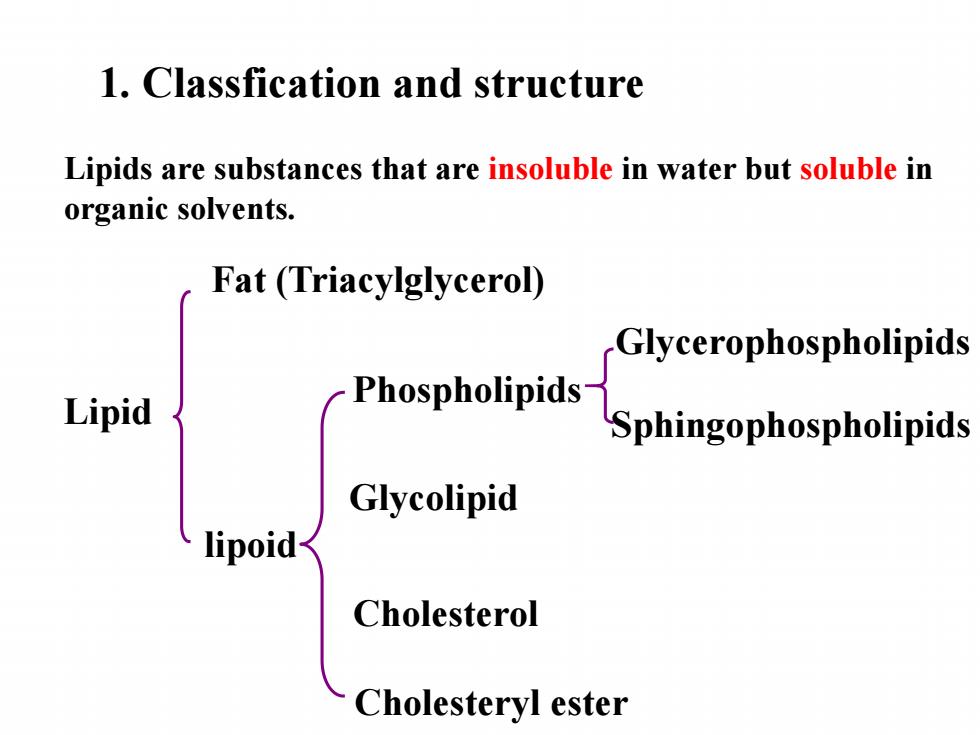
1.Classfication and structure Lipids are substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Fat (Triacylglycerol) Glycerophospholipids Lipid Phospholipids Sphingophospholipids Glycolipid lipoid Cholesterol Cholesteryl ester
Phospholipids lipoid Lipid Glycolipid Fat (Triacylglycerol) Cholesterol Glycerophospholipids Sphingophospholipids 1. Classfication and structure Cholesteryl ester Lipids are substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents

Fat Fat:Triacylglycerols(TAG),esters of fatty acids with glycerol .com
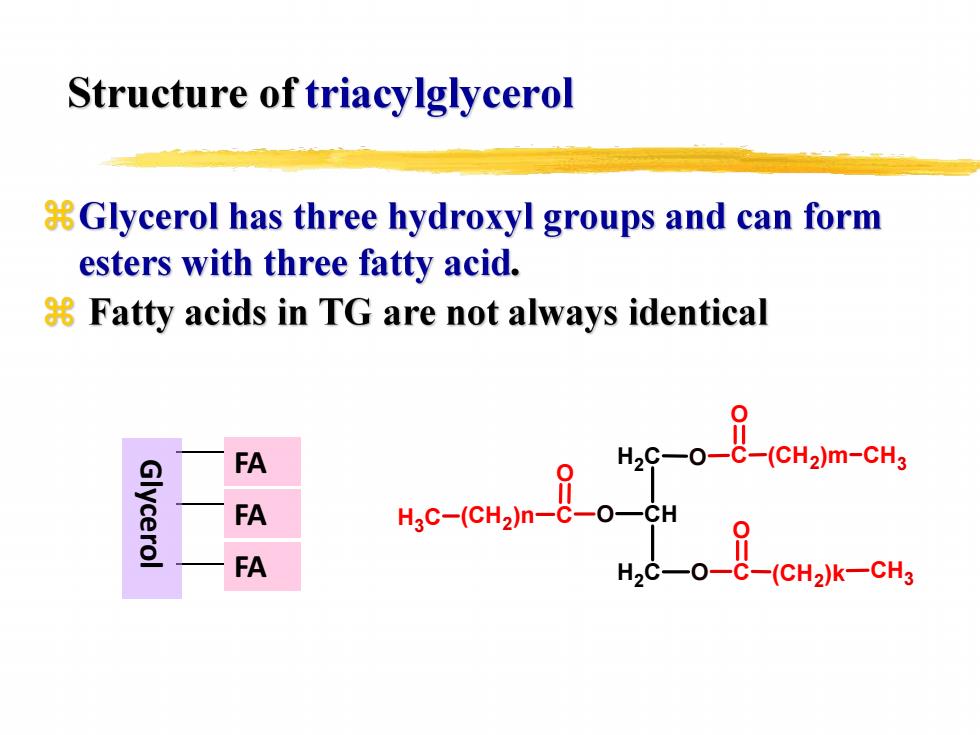
Structure of triacylglycerol Glycerol has three hydroxyl groups and can form esters with three fatty acid. 8 Fatty acids in TG are not always identical FA 2s。总-cr3m-cn Glycerol FA MC-(CMa-8 FA
FAFAFA Glycerol H 2 CC H H 2 C O OO CO (C H 2)m C H 3 CO (C H 2)k C H 3 CO (CH2 H C )n 3
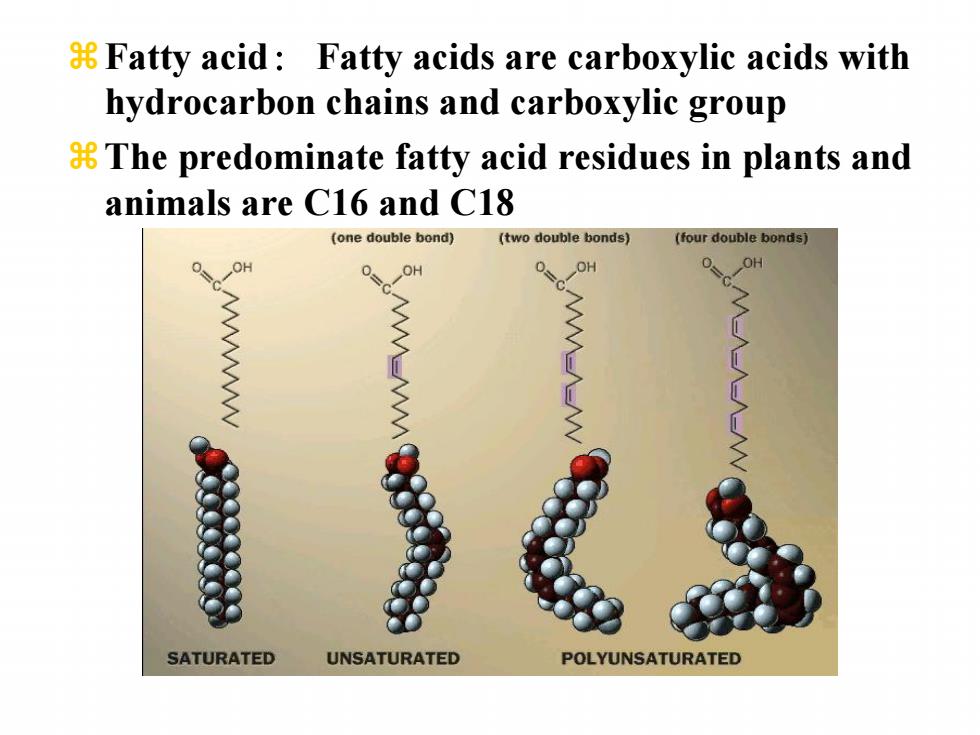
8 Fatty acid:Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains and carboxylic group 8 The predominate fatty acid residues in plants and animals are C16 and C18 (one double bond) (two double bonds】 (four double bonds) OH 0 OH 0 OH OH WWWWWww SATURATED UNSATURATED POLYUNSATURATED
zFatty acid: Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with hydrocarbon chains and carboxylic group zThe predominate fatty acid residues in plants and animals are C16 and C18
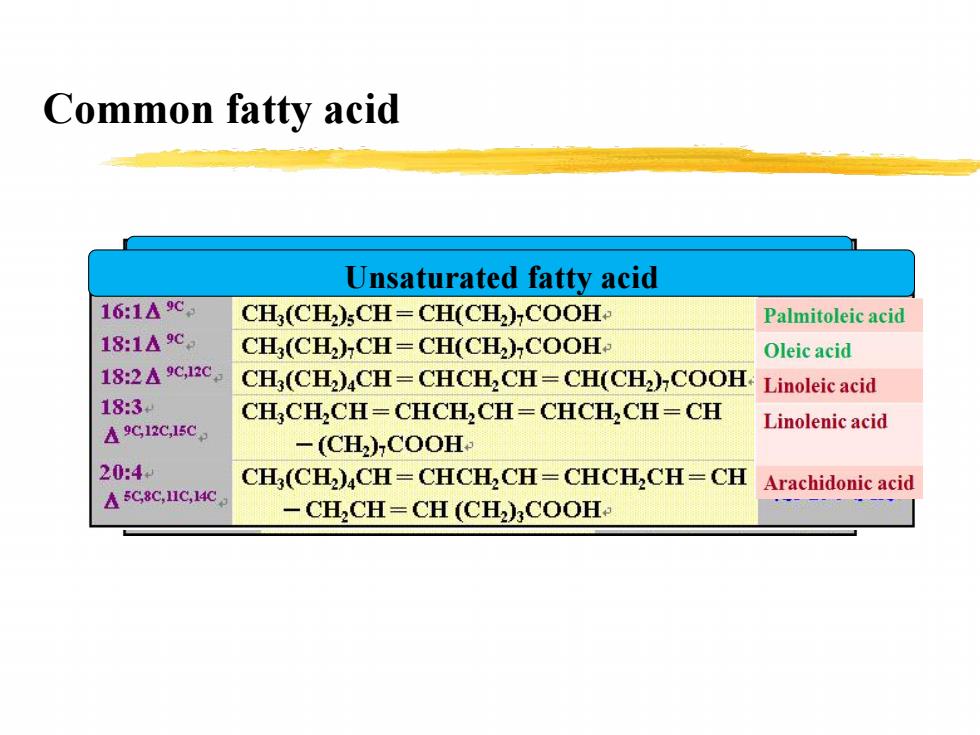
Common fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid 16:1△9℃ CH;(CH);CH=CH(CH2)COOH. Palmitoleic acid 18:1A9℃ CH(CH2)CH=CH(CH2)COOH. Oleic acid 18:2△c,12c CH(CH2)CH=CHCH CH=CH(CH2)COOH.I Linoleic acid 18:3 CH,CH2CH=CHCH CH=CHCH2 CH=CH △9C12C,15C Linolenic acid -(CH2)COOH. 20:4 CH(CH)CH=CHCH CH=CHCH,CH=CH A5C8C,HIC,14C Arachidonic acid -CH2CH=CH(CH)COOH
Common fatty acid Saturated fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid
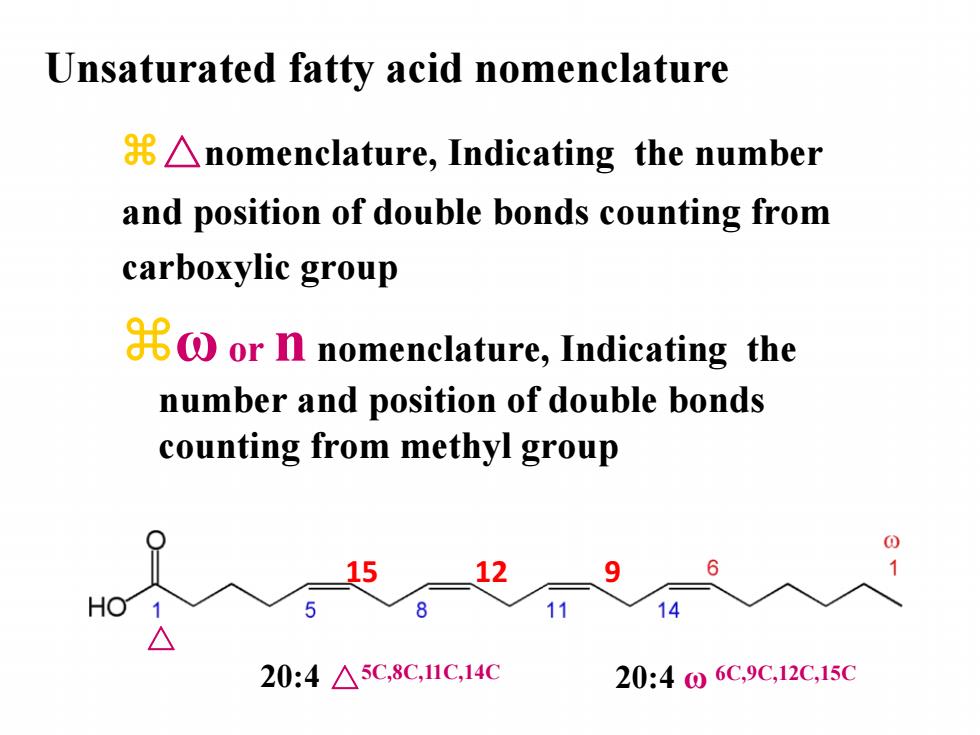
Unsaturated fatty acid nomenclature 8Anomenclature,Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from carboxylic group or n nomenclature,Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from methyl group 9 6 HO 8 11 14 20:4△5C,8C,1C,14C 20:406C,9C,12C,15C
z△nomenclature, Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from carboxylic group zω or n nomenclature, Indicating the number and position of double bonds counting from methyl group 15 12 9 △ Unsaturated fatty acid nomenclature 20:4 △5C,8C,11C,14C 20:4 ω 6C,9C,12C,15C
Essential Fatty Acids(EFA): Some fatty acids that are necessary for human nutrition,but can't synthesis in the body,must obtain from food Including: Linoleic acid (18:2) Linolenic acid (18:3)
Some fatty acids that are necessary for human nutrition, but can’t synthesis in the body, must obtain from food . Including: Essential Fatty Acids(EFA): (18:2) (18:3)