
电离和斯健 分子量挂 Co“Y射线(RA) A入A MM 直接或间接破坏微生物的核糖核酸、蛋白质和酶 辐射灭菌 会余刹 CHAPTER 8 Sterilization
Chapter 8 Sterilization 辐射灭菌
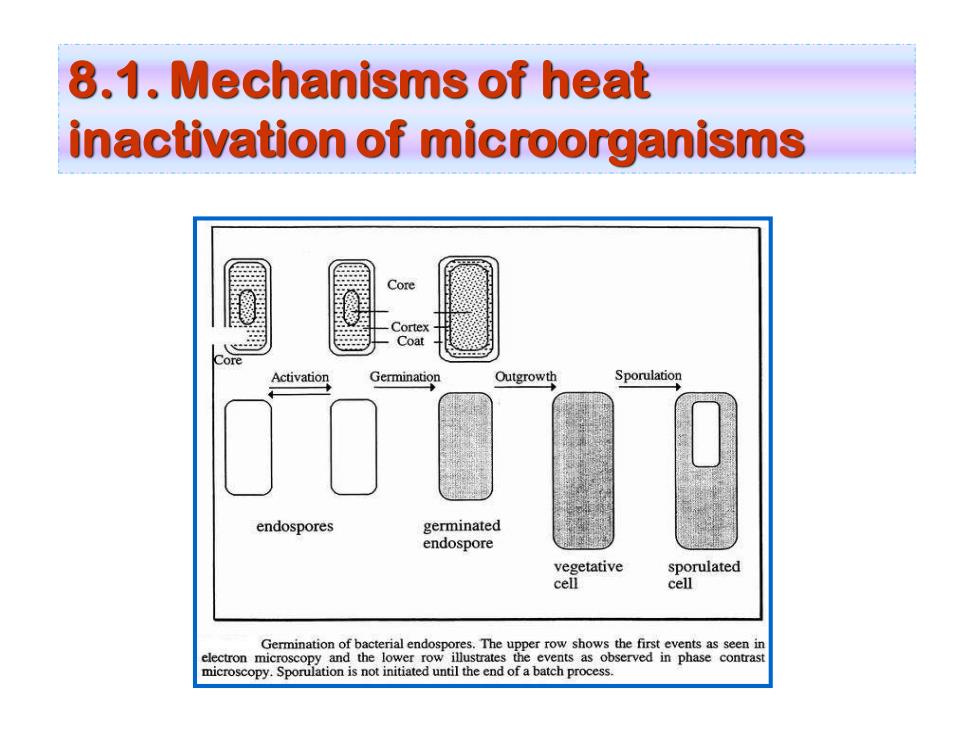
8.1.Mechanisms of heat inactivation of microorganisms Core Coar Activation Germination Outgrowth Sporulation endospores germinated endospore vegetative sporulated cell cell GeotoioanoftaeteoalcentosroiThe,"2ewem events as seen in electron microscopy and the lower row events as observed in phase contrast microscopy.Sporulation is not initiated until the end of a batch process
8.1. Mechanisms of heat inactivation of microorganisms
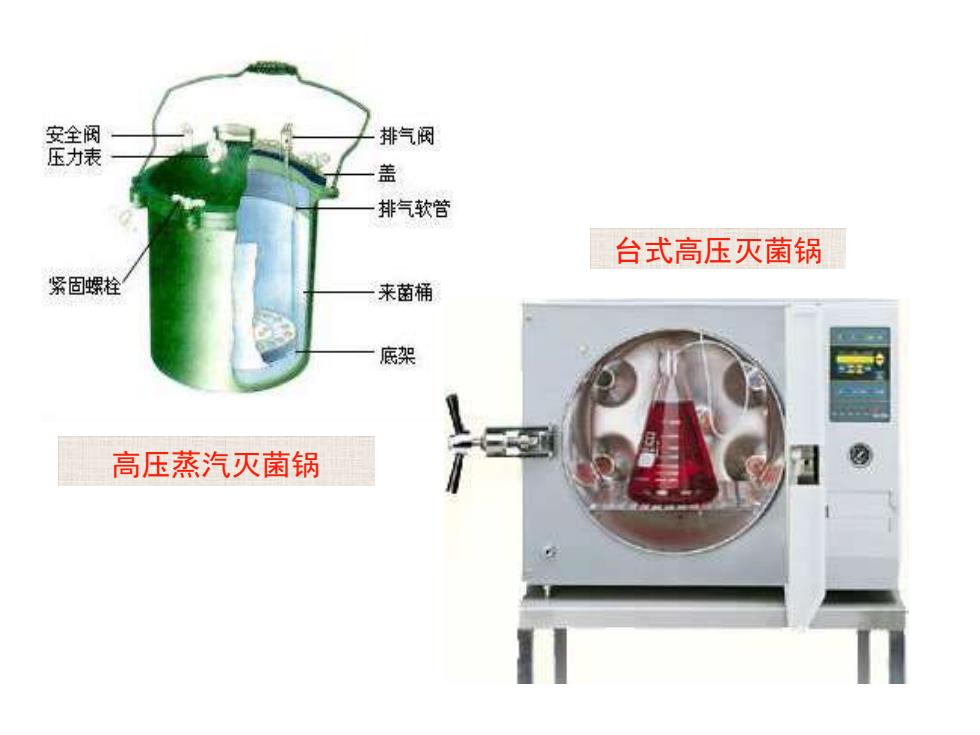

安全阀 排气阀 压力表 盖 排气软管 台式高压灭菌锅 紧固螺栓 来菌桶 底架 高压蒸汽灭菌锅
高压蒸汽灭菌锅 台式高压灭菌锅

Extremophiles Great Salt Lake 硫磺热泉pH海水 晒盐场 海底黑烟囱350℃ 陆地热泉100℃
Great Salt Lake 盐浓度10倍>海水 Extremophiles 晒盐场 海底黑烟囱350℃ 硫磺热泉pH<2-5 陆地热泉 100 ℃
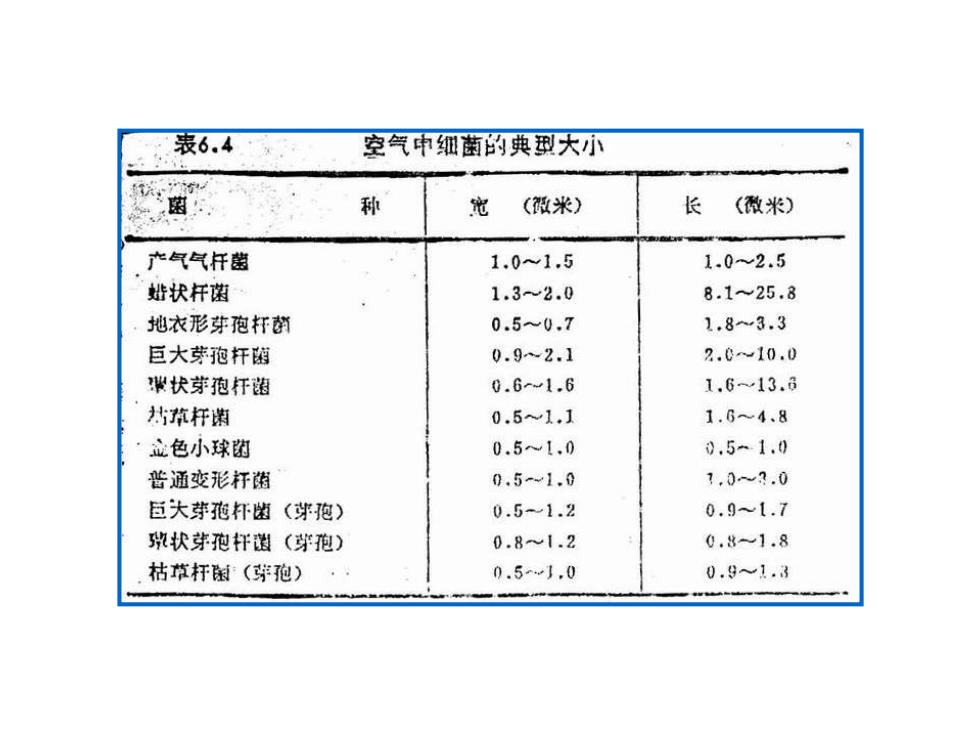
表6.4 空气中细菌的典型大小 种 光 (做米) 长 (酸米) 产气气杆菌 1.01.5 1.02.5 址状杆菌 1.32.0 8.1~25.8 地衣形芽孢杆封 0.5~0.7 1.83.3 巨大芽孢杆蹈 0.92.1 2.010.0 #状芽孢杆随 0.61.6 1.613.6 枯草杆菌 0.51.1 1.64.8 ·立色小球跑 0.51.0 0.51.0 普通变形杆菌 0.5-1.0 1.03.0 巨大芽孢杯堕(茅孢) 0.5-1.2 0.91.7 致状芽孢杆遐(芽孢) 0.8≈1.2 0.81.8 枯草杆闲(芽孢) 0.5w1.0 0.91.3
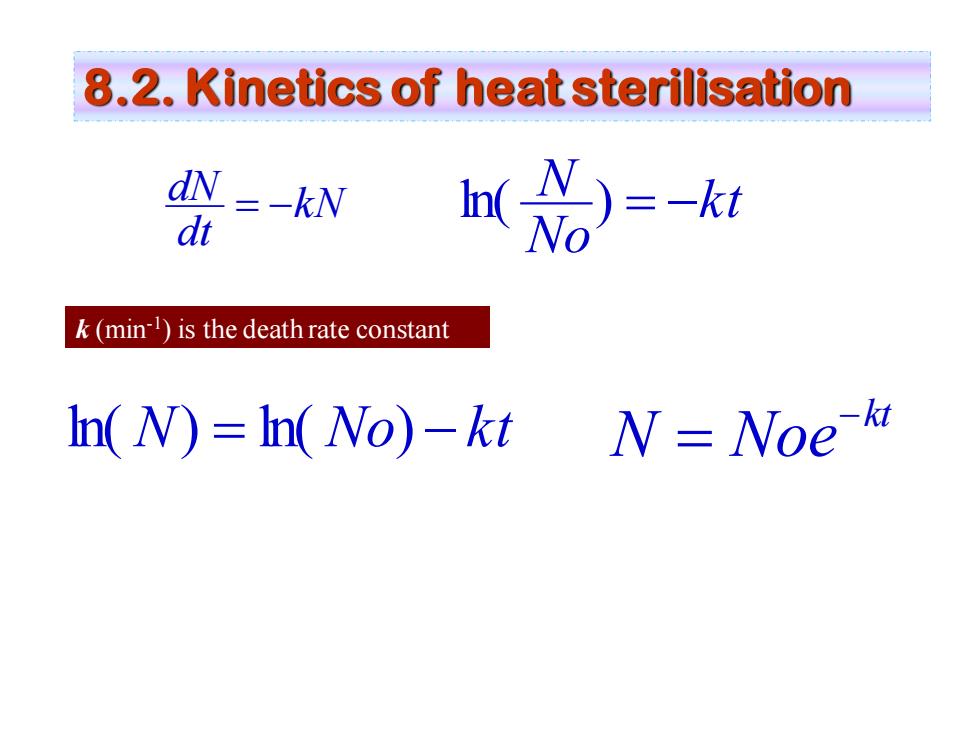
8.2.Kinetics of heat sterilisation dN =-kN dt =知 k(min)is the death rate constant In(N)In(No)-kt N=Noe k
kN dt dN = − kt No N ln( ) = − ln( N) = ln( No) − k t kt N Noe− = k (min-1 ) is the death rate constant 8.2. Kinetics of heat sterilisation
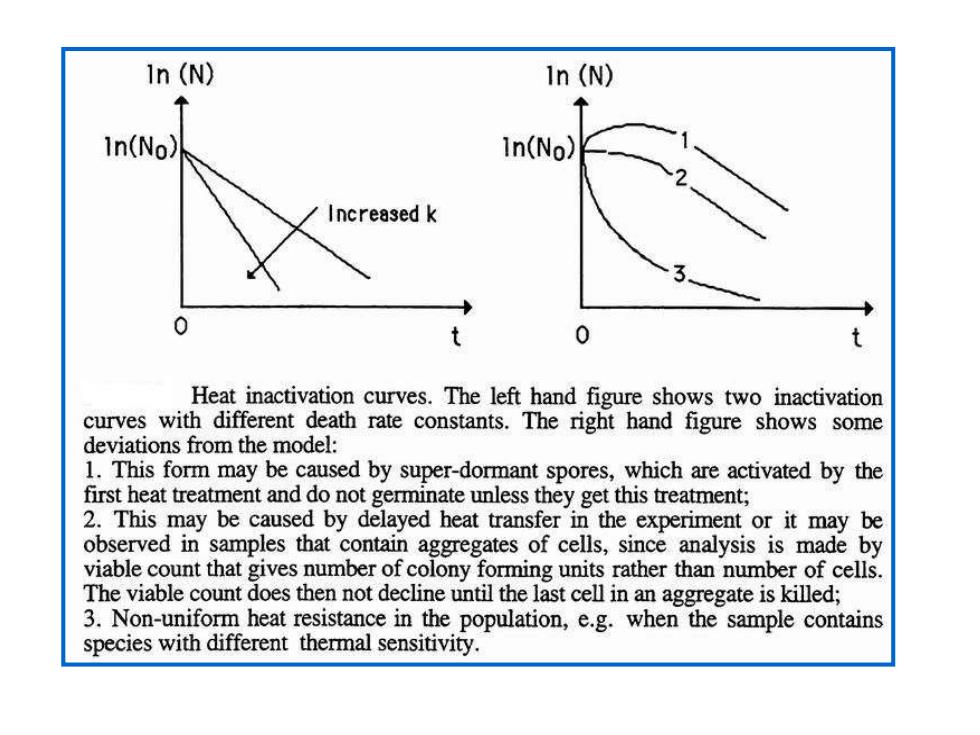
1n(N) 1n(N) In(No) In(No) Increased k 0 t 0 Heat inactivation curves.The left hand figure shows two inactivation curves with different death rate constants.The right hand figure shows some deviations from the model: 1.This form may be caused by super-dormant spores,which are activated by the first heat treatment and do not germinate unless they get this treatment; 2.This may be caused by delayed heat transfer in the experiment or it may be observed in samples that contain aggregates of cells,since analysis is made by viable count that gives number of colony forming units rather than number of cells. The viable count does then not decline until the last cell in an aggregate is killed; 3.Non-uniform heat resistance in the population,e.g.when the sample contains species with different thermal sensitivity

k=Ae-ABIRT 风)=n0-☑习 1.28 ( 0.32 Spores ¥0.08 Thiamine 0.02 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8x103 1T(K) Arrhenius plots of inactivation of B.stearothermophilus spores and thiamine.Note that a temperature increase has a larger effect on the spore inactivation rate than on the vitamin inactivation rate
E RT k Ae− / = R T E k A 1 ln( ) ln( ) = − t c k Co C ln( ) = −

8.3.Calculation of sterilisation time F= 又=Fk,=Frgkrd,F=Re 8.3.1.Batch sterilisation V=th=tAe ABIRT VI=AP (eIRT yit (e-AE/RT)d V=FAe -AE/RTrer Fref(e-EIRT)di
ln( ) f o N N = k F = T ref ref F k F k T = = ( ) 1 1 R Tref T E F F e T ref − − = 8.3.1. Batch sterilisation E RT t t k tAe− / = = t A e dt t E RT − = 0 / ( ) E RTref FAe− / = dt E RT e ref F t dt E RT e t ) / ( 0 ) / ( − − = 8.3. Calculation of sterilisation time

130 100 9 50 0 0 20 40 60 Time (min) Simulation of the progress of sterility (V/V)and inactivation of a temperature sensible compound (C/Co)during a batch sterilisation.The sterility was calculated according to eq.11 and the concentration of compound according to eq.6 and eq.4. Parameters:V=20,A=1035.8 sec-1 and 109 sec-1 for sterilisation and chemical reaction, respectively.AE=282 kJ mole-1 and 92 kJ mole-1,respectively.R=8.31 J mol--1K-1