
Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes
Chapter 13 Industrial Use of Enzymes
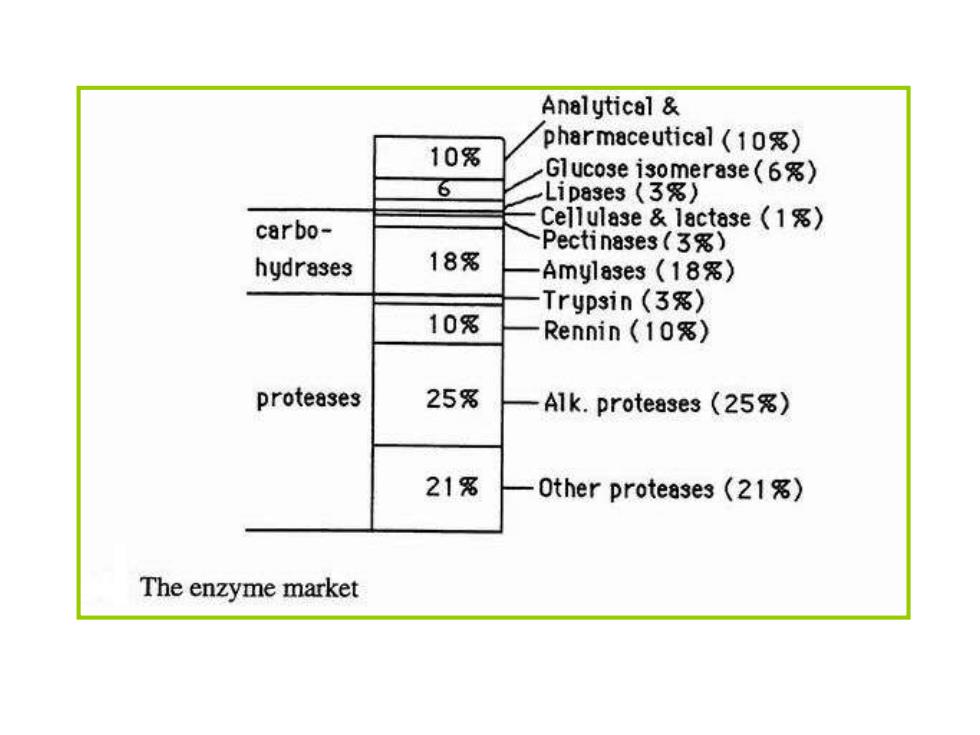
Analytical 10% pharmaceutical (10) Glucose isomerase (6) 6 Lip83e3(3%) carbo- Cellulase lactase (1) Pectinases(3) hydrases 18% Amylases (18) Trypsin (3) 10% Rennin (10%) proteases 25% Alk.proteases(25) 21% Other proteases(21) The enzyme market
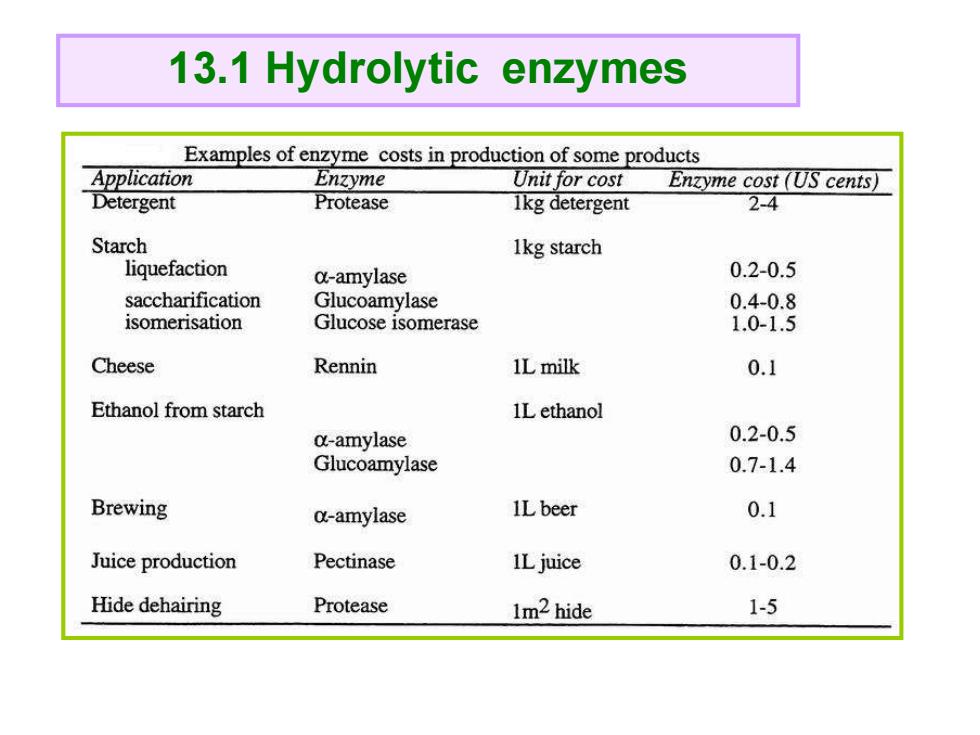
13.1 Hydrolytic enzymes Examples of enzyme costs in production of some products Application Enzyme Unit for cost Enzyme cost (US cents) Detergent Protease 1kg detergent 2-4 Starch 1kg starch liquefaction c-amylase 0.2-0.5 saccharification Glucoamylase 0.4-0.8 isomerisation Glucose isomerase 1.0-1.5 Cheese Rennin 1L milk 0.1 Ethanol from starch 1L ethanol a-amylase 0.2-0.5 Glucoamylase 0.7-1.4 Brewing c-amylase ILbeer 0.1 Juice production Pectinase ILjuice 0.1-0.2 Hide dehairing Protease 1m2hide 1-5
13.1 Hydrolytic enzymes

13.1.1 Proteases Cell mass Hemi- Alkaline cellulase B-glucanase protease 仪-8mula3e neutral uoneauaouog protease Fermentation time (h) 100 Typical production pattern for extracellular enzymes in a batch cultivation of a Bacillus
13.1.1 Proteases
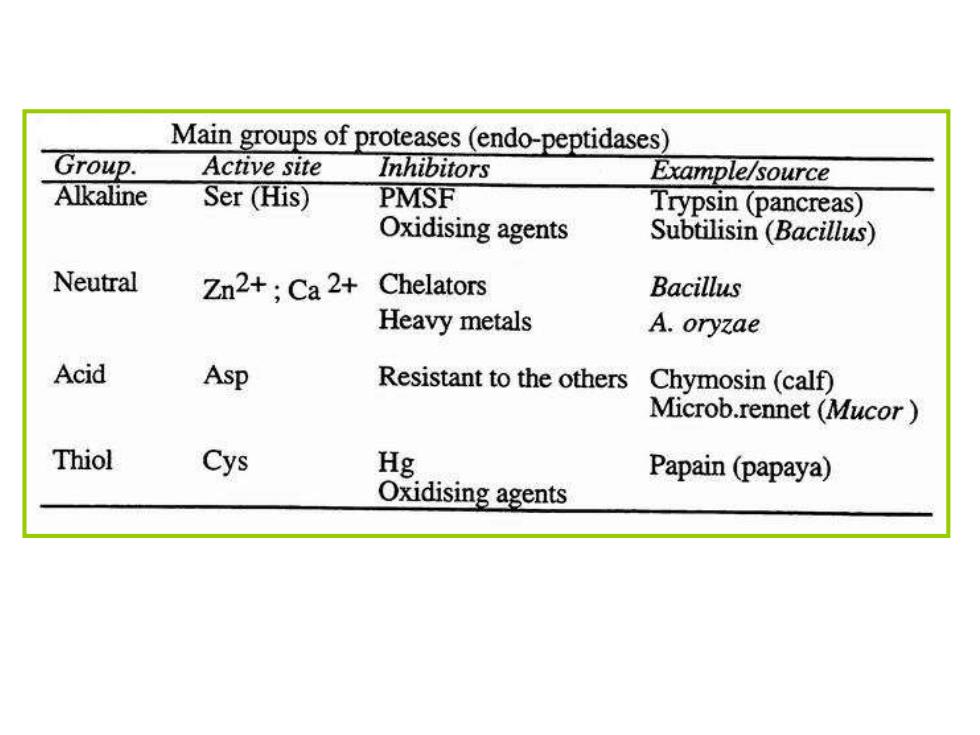
Main groups of proteases(endo-peptidases) Group. Active site Inhibitors Example/source Alkaline Ser(His) PMSF Trypsin(pancreas) Oxidising agents Subtilisin (Bacillus) Neutral Zn2+:Ca2+ Chelators Bacillus Heavy metals A.oryzae Acid Asp Resistant to the others Chymosin(calf) Microb.rennet (Mucor Thiol Cys Hg Papain(papaya) Oxidising agents
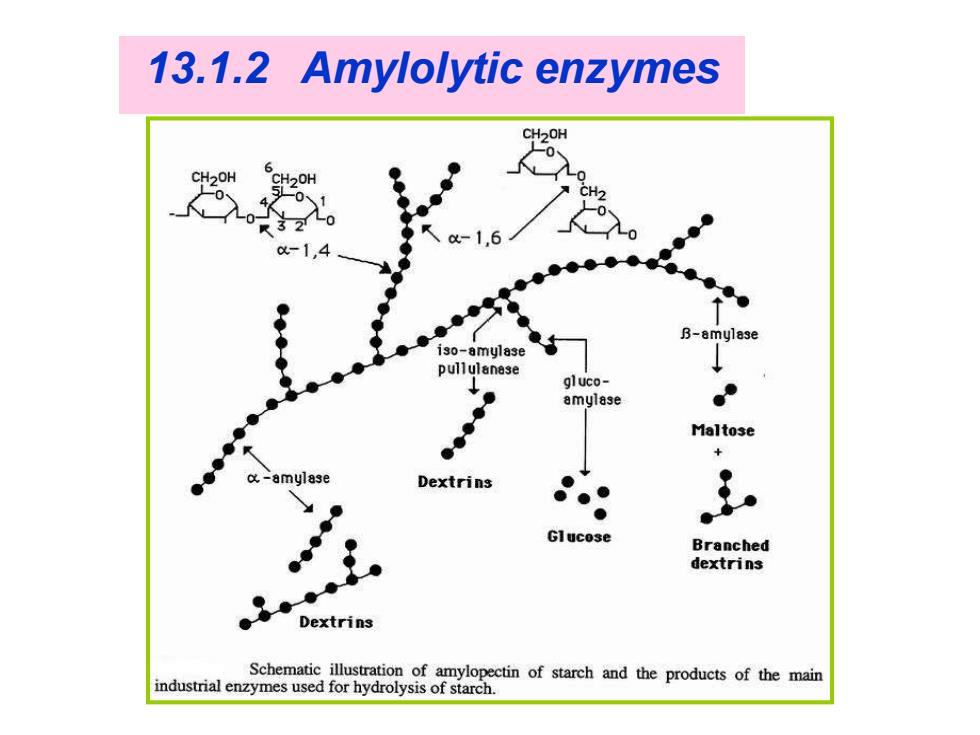
13.1.2 Amylolytic enzymes CH2OH iso-amylase pullulanese gluco- amylase Maltose 仪-amylase Dextrins Glucose Branched dextrins Dextrins Schematic illustration of amylopectin of starch and the products of the main industrial enzymes used for hydrolysis of starch
13.1.2 Amylolytic enzymes

Cyclodextrin glysytransferase Glucose isomerase high fructose syrups
➢ Cyclodextrin glysytransferase ➢ Glucose isomerase high fructose syrups

13.1.3 Celluloses and hydrolysis of wood cellobiose glucase glucose CH20H CH20H CH20HCH20H CH2OH ↑ B-1,4 The basic structure of cellulose:linear chains of B-1,4 linked poly D-glucose.Enzymatic hydrolysis releases cellobiose which is further degraded to glucose. B-1,4-endo- Cellobiohydrolase Cellobiase glucanase (B-) Cellulose Oligosaccharides →Ce11obio3e ◆G1uc03e (cellodextrins) Cellobiohydrolase (B-1,4-exo-glucanase) Enzymes involved in hydrolysis of cellulose.The dotted lines indicate feed-back inhibition
13.1.3 Celluloses and hydrolysis of wood

13.1.4 Pectinases C-OCH3 HO 0 HO C-OH CH3OH Pectin C-OCH3 HO 2 esterase 0 OH exo-poly(methyl)- Poly- galacturonate OH galacturonase COCH3 1y83e 0 HO C-OCH3 endo-poly(methyl)- galacturonase HO- Basic structure of pectin and the sites of enzymatic hydrolysis.Pectin is a randomly methyl-esterified a-1,4 poly-galacturonic acid 13.1.5 Lipases
13.1.5 Lipases 13.1.4 Pectinases
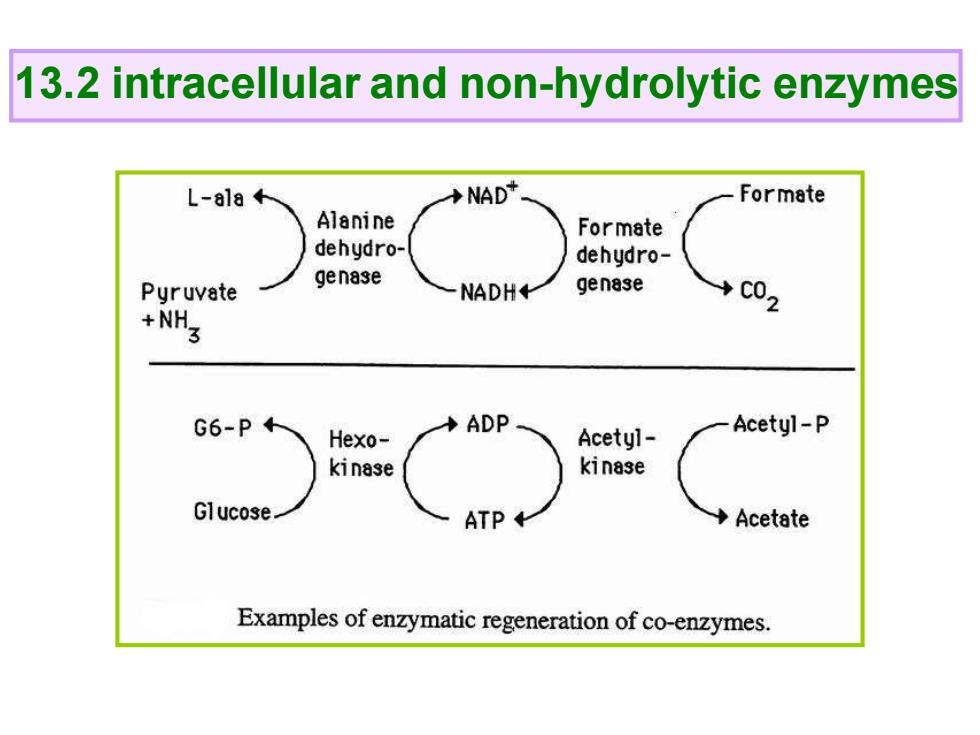
13.2 intracellular and non-hydrolytic enzymes L-ala← NAD+ Formate Alanine Formate dehydro- dehydro- Pyruvate genase NADH+ genase →c02 +NH3 G6-P4 ADP Hexo- Acetyl- Acetyl-P kinase kinase Glucose. ATP+ Acetate Examples of enzymatic regeneration of co-enzymes
13.2 intracellular and non-hydrolytic enzymes