
Chapter 10 Fermented Food
Chapter 10 Fermented Food
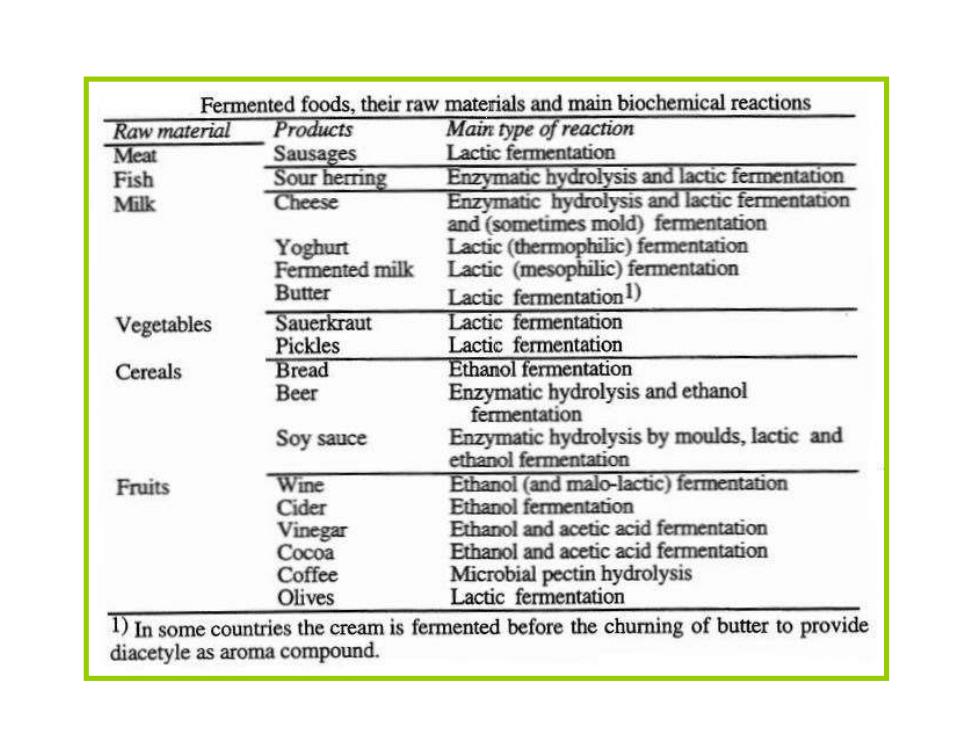
Fermented foods,their raw materials and main biochemical reactions Raw material Products Main type of reaction Meat Sausages Lactic fermentation Fish Sour herring Enzymatic hydrolysis and lactic fermentation Milk Cheese Enzymatic hydrolysis and lactic fermentation and (sometimes mold)fermentation Yoghurt Lactic(thermophilic)fermentation Fermented milk Lactic (mesophilic)fermentation Butter Lactic fermentation1) Vegetables Sauerkraut Lactic fermentation Pickles Lactic fermentation Cereals Bread Ethanol fermentation Beer Enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation Soy sauce Enzymatic hydrolysis by moulds,lactic and ethanol fermentation Fruits Wine Ethanol (and malo-lactic)fermentation Cider Ethanol fermentation Vinegar Ethanol and acetic acid fermentation Cocoa Ethanol and acetic acid fermentation Coffee Microbial pectin hydrolysis Olives Lactic fermentation 1)In some countries the cream is fermented before the churning of butter to provide diacetyle as aroma compound

Control methods 1.Inoculation with a microflora 2.Adjustment of the oxygen concentration 3.Reduction of water activity
1. Inoculation with a microflora 2. Adjustment of the oxygen concentration 3. Reduction of water activity Control methods
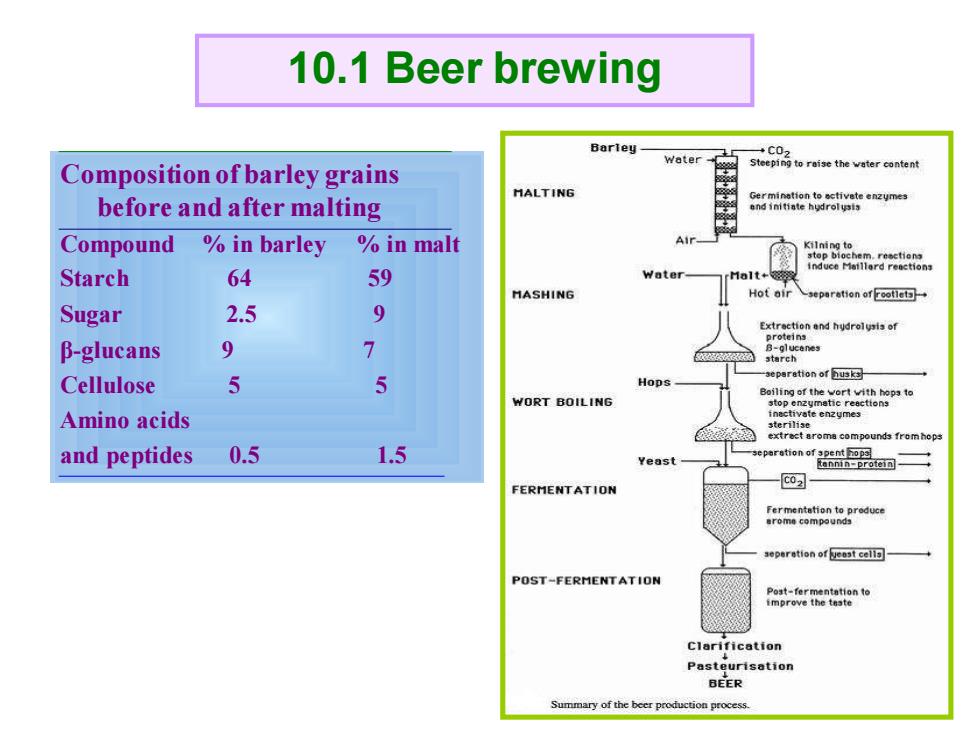
10.1 Beer brewing Barley Water Composition of barley grains Steeping to reise the water content MALTING before and after malting Compound in barley in malt induce Maillerd reaction Starch 64 59 Water MASHING Hot air Sugar 2.5 9 B-glucans 9 7 Cellulose 5 5 -aepsretion of husks- Hops WORT BOILING eawp2giere2oeno Amino acids sterilise extrect aroma compounds fromhops and peptides 0.5 1.5 Yeast FERMENTATION C02 POST-FERMENTATION ntaieno Clarification Pasteurisation BEER Summary of the beer production process
Composition of barley grains before and after malting Compound % in barley % in malt Starch 64 59 Sugar 2.5 9 β-glucans 9 7 Cellulose 5 5 Amino acids and peptides 0.5 1.5 10.1 Beer brewing

Malting Germination Mashing Enzymes:protease glucanases amylase
Malting Germination Mashing Enzymes : protease glucanases amylase
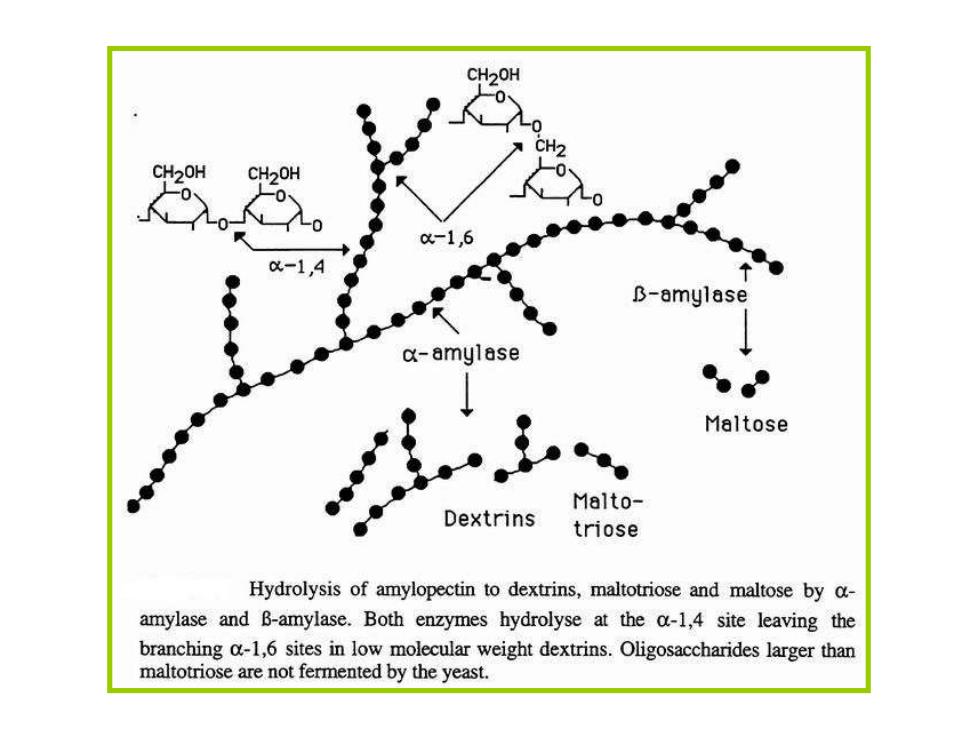
CH20H 0 CH20H CH20H B-amylase a-amylase Maltose Malto- Dextrins triose Hydrolysis of amylopectin to dextrins,maltotriose and maltose by c- amylase and B-amylase.Both enzymes hydrolyse at the a-1,4 site leaving the branching a-1,6 sites in low molecular weight dextrins.Oligosaccharides larger than maltotriose are not fermented by the yeast

Wort boiling aromatic compounds from hops sterilise Fermentation top fermentation bottom fermentation ethanol and other aroma compounds Post fermentation decarboxylation
Wort boiling aromatic compounds from hops sterilise Fermentation top fermentation bottom fermentation ethanol and other aroma compounds Post fermentation decarboxylation
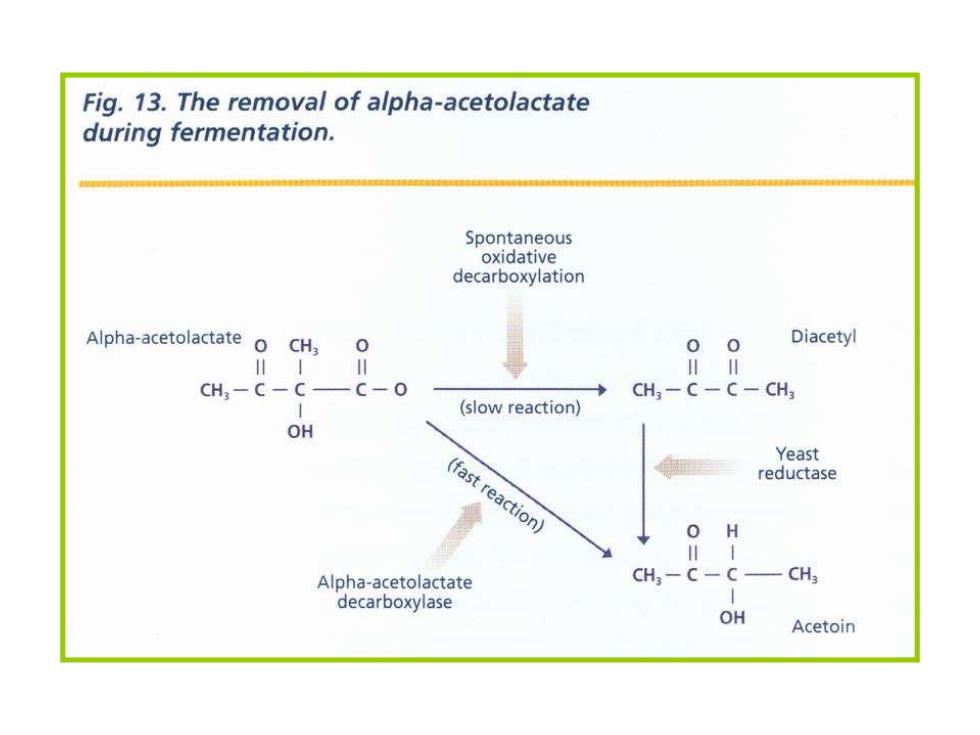
Fig.13.The removal of alpha-acetolactate during fermentation. Spontaneous oxidative decarboxylation Alpha-acetolactate o CH3 0 00 Diacetyl CH-C-C一C-O CH3-C-C-CH3 (slow reaction) OH Yeast (fast reaction) reductase 0 H Alpha-acetolactate CH;-C-C- CH3 decarboxylase OH Acetoin
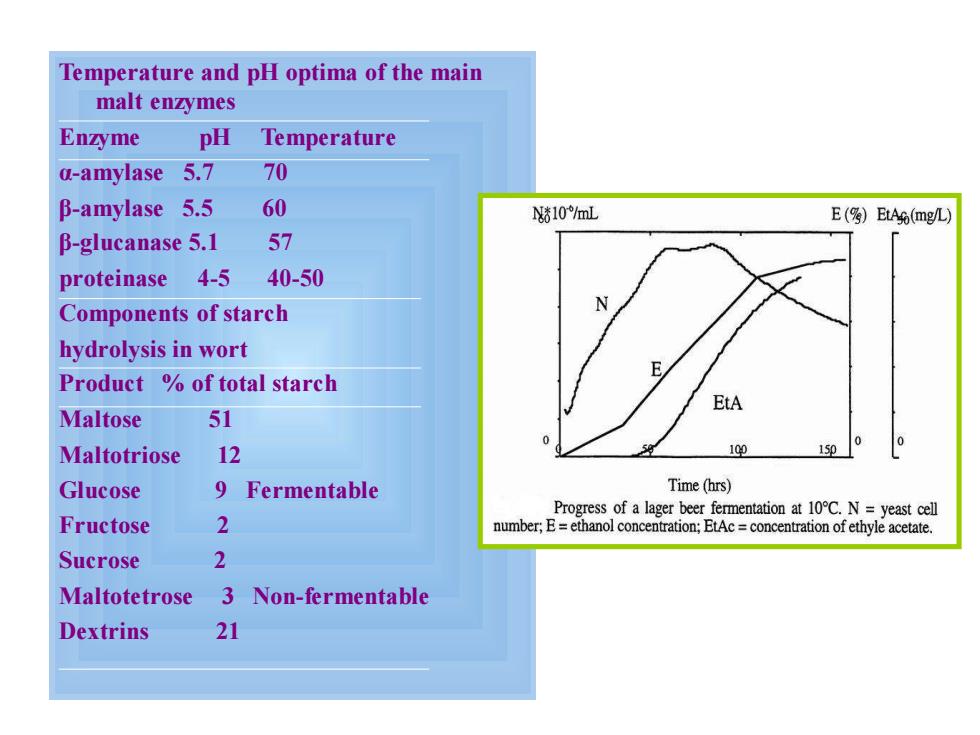
Temperature and pH optima of the main malt enzymes Enzyme pH Temperature a-amylase 5.7 70 B-amylase 5.5 60 N10/mL E(图)EtAg (mg/L) B-glucanase 5.1 57 proteinase 4-5 40-50 Components of starch hydrolysis in wort Product of total starch EtA Maltose 51 0 Maltotriose 12 109 15p Glucose 9 Fermentable Time(hrs) Progress of a lager beer fermentation at 10C.N=yeast cell Fructose 2 number;E=ethanol concentration;EtAc concentration of ethyle acetate. Sucrose 2 Maltotetrose Non-fermentable Dextrins 21
Temperature and pH optima of the main malt enzymes Enzyme pH Temperature α-amylase 5.7 70 β-amylase 5.5 60 β-glucanase 5.1 57 proteinase 4-5 40-50 Components of starch hydrolysis in wort Product % of total starch Maltose 51 Maltotriose 12 Glucose 9 Fermentable Fructose 2 Sucrose 2 Maltotetrose 3 Non-fermentable Dextrins 21
纳精中的 挤压机 加腾赫停止发 大部分前萄在榨计前都码 过在 神汁 显线的西榨过程才轴产生银化的 的计液 有链的超在神汁解未经情压 酒精强化葡萄酒酿造过程 究烧罐 葡萄酒生产 发酵 一步可在情性net容 消结大储中其行。情美 而言,如课撑本是新的 诊增最超计中,益加株着 千兰anla的香精 葡萄酒酿造工艺
酒精强化葡萄酒酿造过程 葡萄酒酿造工艺 葡萄酒生产