
Is nucleic acid dietarily essential? Nucleic acid health product
Nucleic acid health product Is nucleic acid dietarily essential?

What makes up of our DNA and RNA? Cytosine Cytosine NH ucleobases NH Guanine Guanine H Base pair Adenine Adenine H2N Uracil Thymine m, helix of sugar-phosphates Nucleobases Nucleobases of RNA of DNA RNA DNA Ribonucleic acid Deoxyribonucleic acid
What makes up of our DNA and RNA?

Learning Objectives After completion of this section,you should be able to 1.Indicate the source of each atom in purine and pyrimidine ring. 2.Describe anabolism (de novo and salvage)and catabolism of purine and pyrimidine. 3.Outline the sequence of reactions in de novo and salvage and the conversion of IMP to AMP or GMP,and UMP to CTP or TMP. 4.Understand the mechanism of anticancer drugs and allopurinol in treating gout
Learning Objectives After completion of this section, you should be able to : 1. Indicate the source of each atom in purine and pyrimidine ring. 2. Describe anabolism (de novo and salvage) and catabolism of purine and pyrimidine. 3. Outline the sequence of reactions in de novo and salvage and the conversion of IMP to AMP or GMP, and UMP to CTP or TMP. 4. Understand the mechanism of anticancer drugs and allopurinol in treating gout

Outline of the section 1.Nomenclature and structure of nucleotide. 2.Biosynthesis of purine and pyrimidine 3.Feedback inhibition and cross regulation in purine and pyrimidine synthesis. 4.Catabolism of purine and pyrimidine. 5.Clinical significance
Outline of the section 1. Nomenclature and structure of nucleotide. 2. Biosynthesis of purine and pyrimidine 3. Feedback inhibition and cross regulation in purine and pyrimidine synthesis. 4. Catabolism of purine and pyrimidine. 5. Clinical significance

Section 1 Nomenclature and structure of nucleotide
Section 1 Nomenclature and structure of nucleotide
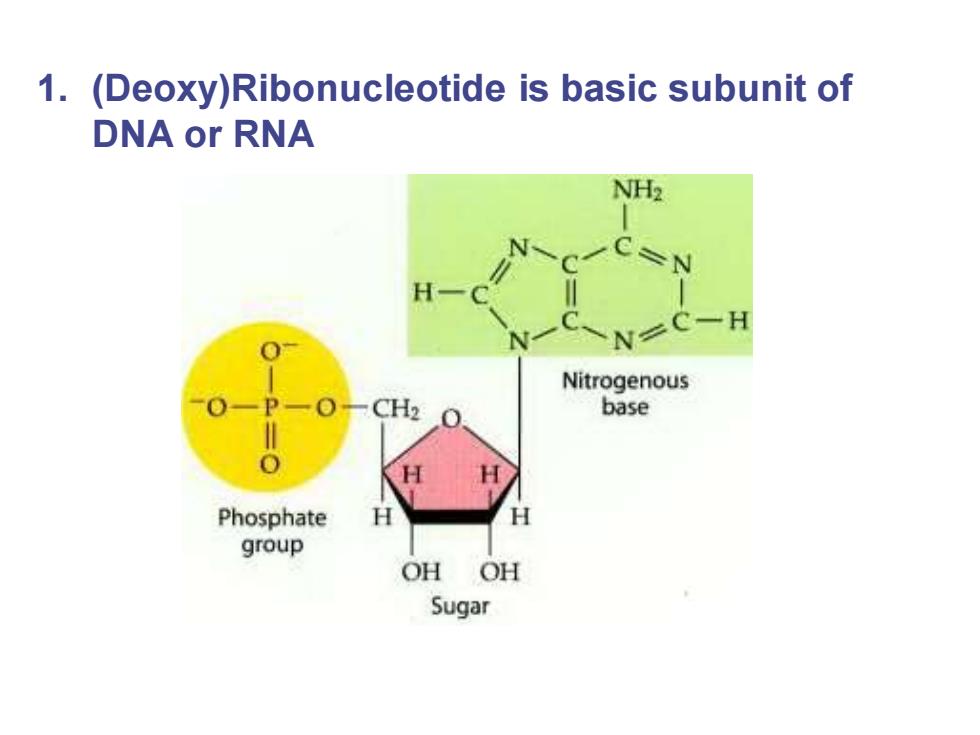
1.(Deoxy)Ribonucleotide is basic subunit of DNA or RNA NH2 N C一H Nitrogenous base Phosphate H group OHOH Sugar
1. (Deoxy)Ribonucleotide is basic subunit of DNA or RNA
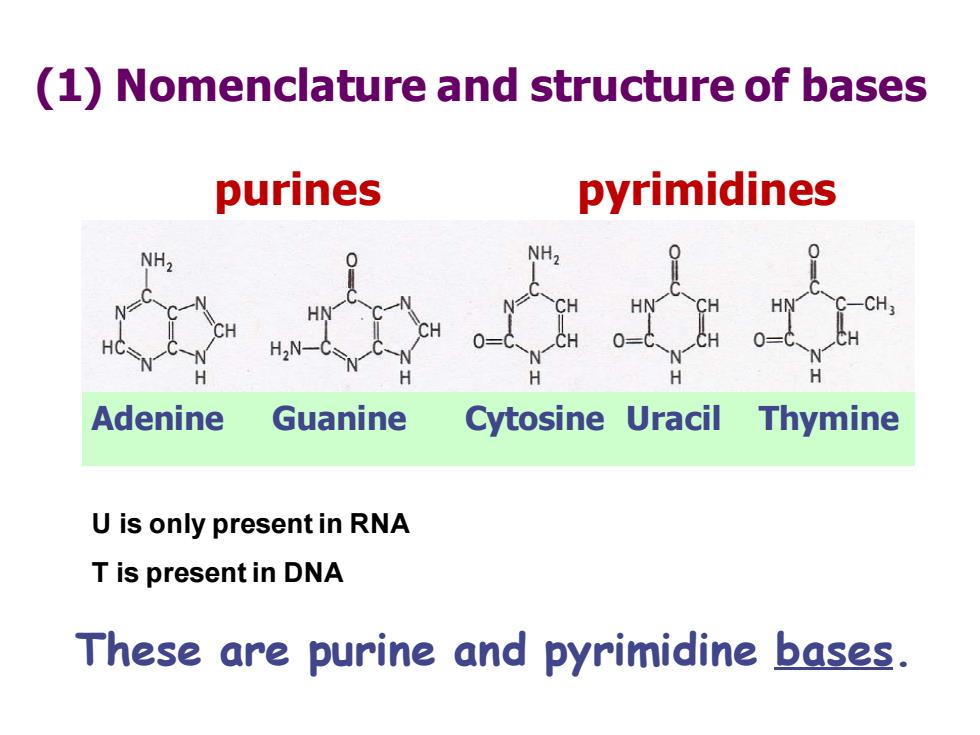
(1)Nomenclature and structure of bases purines pyrimidines NH2 Adenine Guanine Cytosine Uracil Thymine U is only present in RNA T is present in DNA These are purine and pyrimidine bases
(1) Nomenclature and structure of bases Adenine Guanine Cytosine Uracil Thymine These are purine and pyrimidine bases. purines pyrimidines U is only present in RNA T is present in DNA
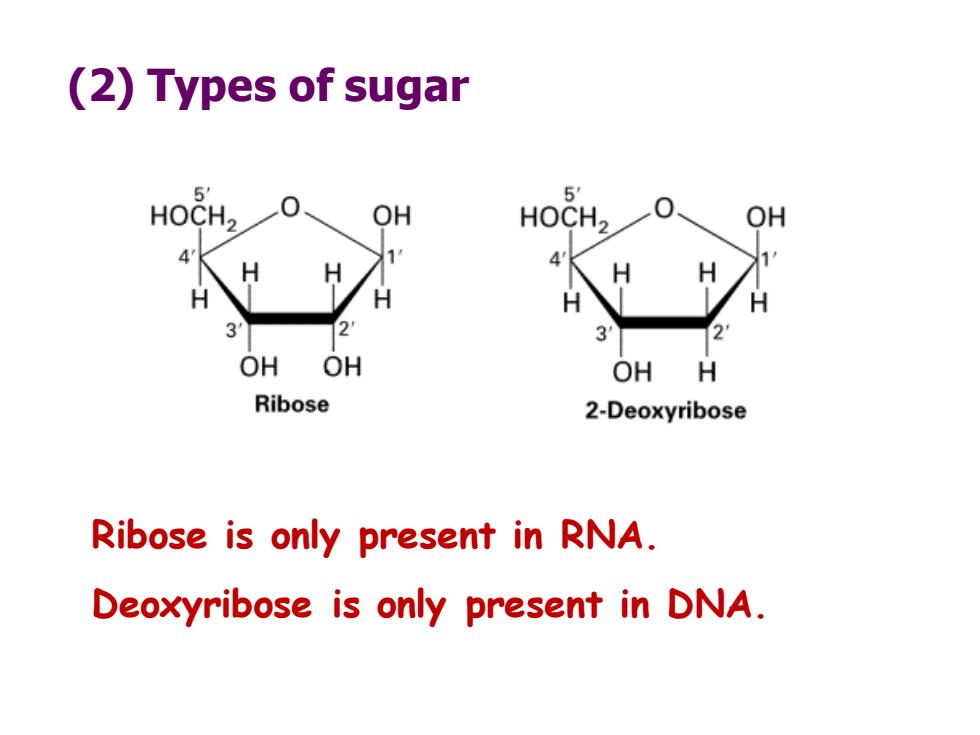
(2)Types of sugar 5 5 HOCH2 OH HOCH2 OH H 3 OH OH OH H Ribose 2-Deoxyribose Ribose is only present in RNA. Deoxyribose is only present in DNA
(2) Types of sugar Ribose is only present in RNA. Deoxyribose is only present in DNA
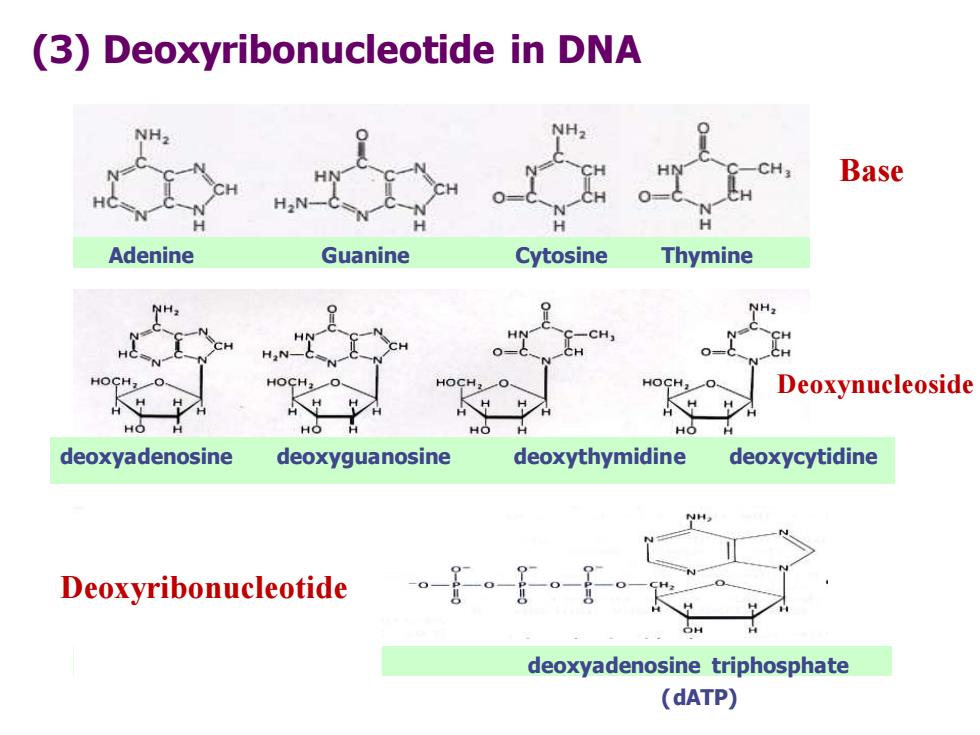
(3)Deoxyribonucleotide in DNA CH Base H.N- Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine HN -CH CH CH H2N- HOCH,0 Deoxynucleoside HO HO HO H HO deoxyadenosine deoxyguanosine deoxythymidine deoxycytidine Deoxyribonucleotide 。-官。8。-g deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP)
(3) Deoxyribonucleotide in DNA Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine deoxyadenosine deoxyguanosine deoxythymidine deoxycytidine adenosine monophosphate deoxyadenosine triphosphate (AMP) (dATP) Base Deoxynucleoside Deoxyribonucleotide
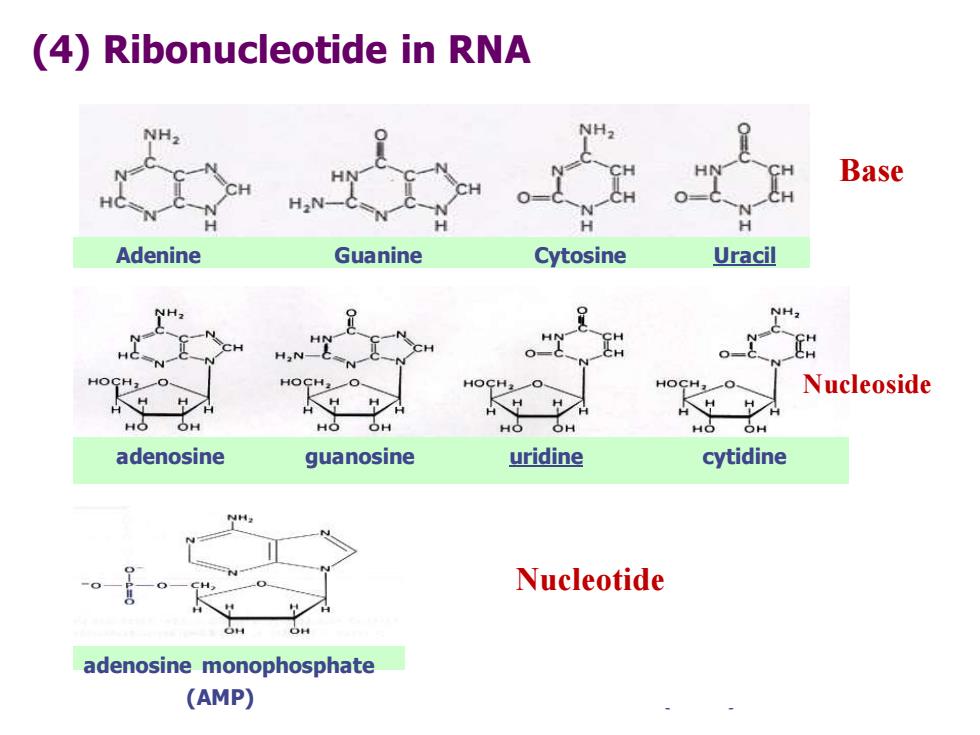
(4)Ribonucleotide in RNA Base H.N- Adenine Guanine Cytosine Uracil NH H,N- CH Nucleoside OH OH OH adenosine guanosine uridine cytidine Nucleotide adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
(4) Ribonucleotide in RNA Adenine Guanine Cytosine Uracil adenosine guanosine uridine cytidine adenosine monophosphate deoxyadenosine triphosphate (AMP) (dATP) Base Nucleotide Nucleotide Nucleoside