
Contents of Today S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous Second law Functions F and G Property relation Property relation derived from U,H,F,and G etc. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Contents of Today Review previous Second law Functions F and G Property relation Property relation derived from U, H, F, and G etc

熵增原理 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 卡诺定理/可用热力学第二定律证明 2+0≤1- 式中Q2为从高温热源吸热 T2 Q1为向低温热源放热 1+ 2≤0 克劳修斯等式(可逆)和不等式( T T2 不可逆过程) 更普遍的循环过程 ≤0 δQ为为系统从温度为T的热源吸取的热量 可逆过程的热温商为零,所定义的熵为状态函数 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 熵增原理 卡诺定理 / 可用热力学第二定律证明 2 1 1 2 2 Q Q T 1 Q T + = − 式中Q2为从高温热源吸热 Q1为向低温热源放热 1 2 1 2 Q Q 0 T T + 克劳修斯等式(可逆)和不等式( 不可逆过程) Q 0 T 更普遍的循环过程 Q为为系统从温度为T的热源吸取的热量 可逆过程的热温商为零,所定义的熵为状态函数
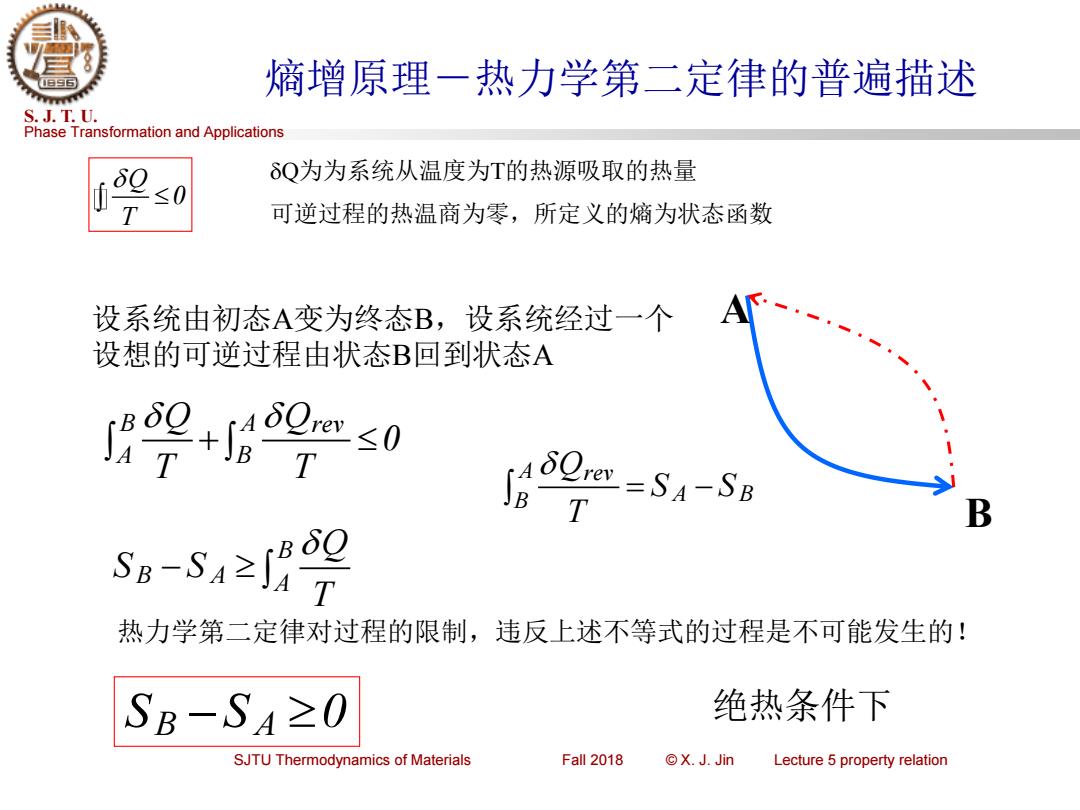
熵增原理一热力学第二定律的普遍描述 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications δQ为为系统从温度为T的热源吸取的热量 ≤0 可逆过程的热温商为零,所定义的熵为状态函数 设系统由初态A变为终态B,设系统经过一个 设想的可逆过程由状态B回到状态A 9+2s0 In50mm-SA-58 B s-5≥2 热力学第二定律对过程的限制,违反上述不等式的过程是不可能发生的! SB-S4≥0 绝热条件下 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 熵增原理-热力学第二定律的普遍描述 Q 0 T Q为为系统从温度为T的热源吸取的热量 可逆过程的热温商为零,所定义的熵为状态函数 A B 设系统由初态A变为终态B,设系统经过一个 设想的可逆过程由状态B回到状态A B A rev A B Q Q 0 T T + A rev A B B Q S S T = − B B A A Q S S T − 热力学第二定律对过程的限制,违反上述不等式的过程是不可能发生的! S S 0 B A − 绝热条件下
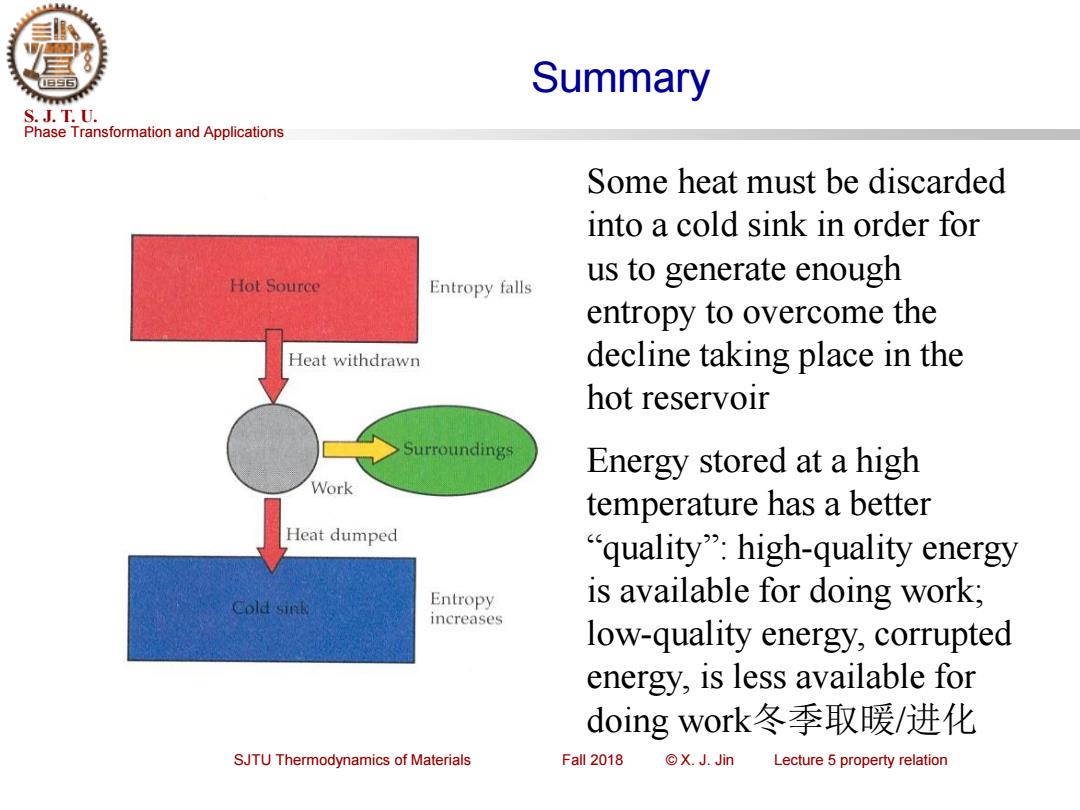
Summary S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Some heat must be discarded into a cold sink in order for Hot Source us to generate enough Entropy falls entropy to overcome the Heat withdrawn decline taking place in the hot reservoir Surroundings Energy stored at a high Work temperature has a better Heat dumped "quality":high-quality energy Cold sink Entropy is available for doing work; increases low-quality energy,corrupted energy,is less available for doing work冬季取暖/进化 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Some heat must be discarded into a cold sink in order for us to generate enough entropy to overcome the decline taking place in the hot reservoir Energy stored at a high temperature has a better “quality”: high-quality energy is available for doing work; low-quality energy, corrupted energy, is less available for doing work冬季取暖/进化 Summary
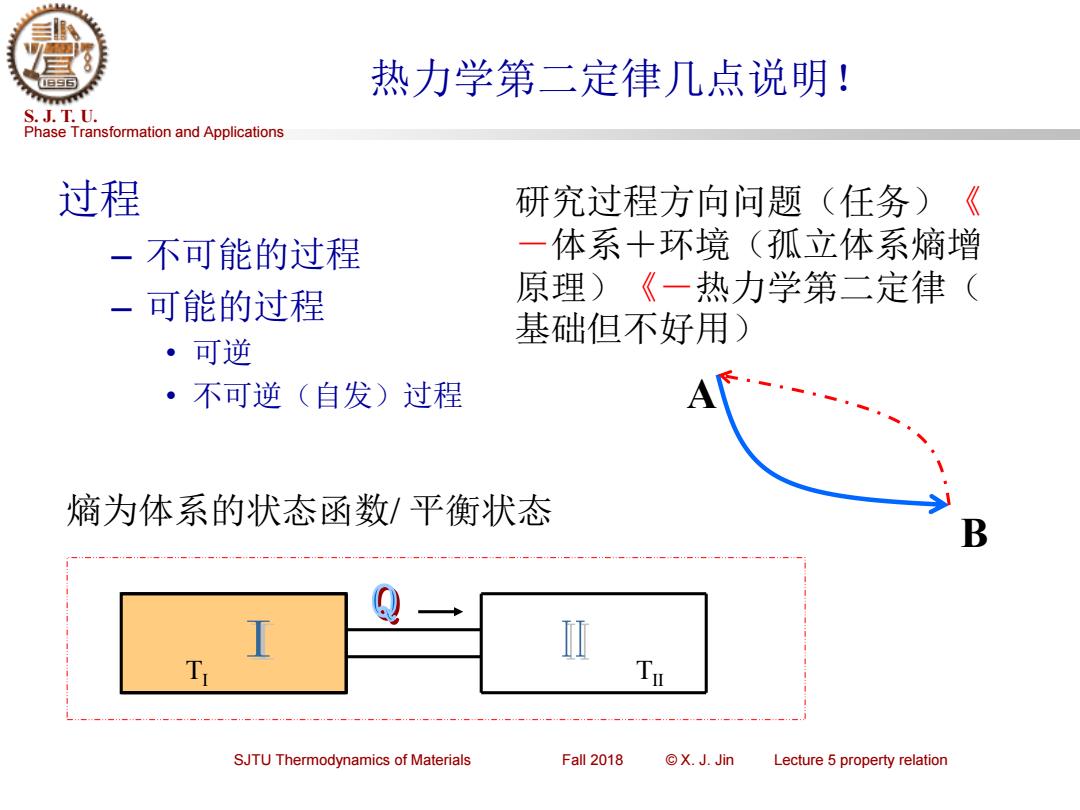
热力学第二定律几点说明! S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 过程 研究过程方向问题(任务)《 一不可能的过程 一体系十环境(孤立体系熵增 一可能的过程 原理)《一热力学第二定律( 基础但不好用) ·可逆 ·不可逆(自发)过程 熵为体系的状态函数/平衡状态 B SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 热力学第二定律几点说明! 过程 – 不可能的过程 – 可能的过程 • 可逆 • 不可逆(自发)过程 熵为体系的状态函数/ 平衡状态 研究过程方向问题(任务)《 -体系+环境(孤立体系熵增 原理)《-热力学第二定律( 基础但不好用) TI TII A B
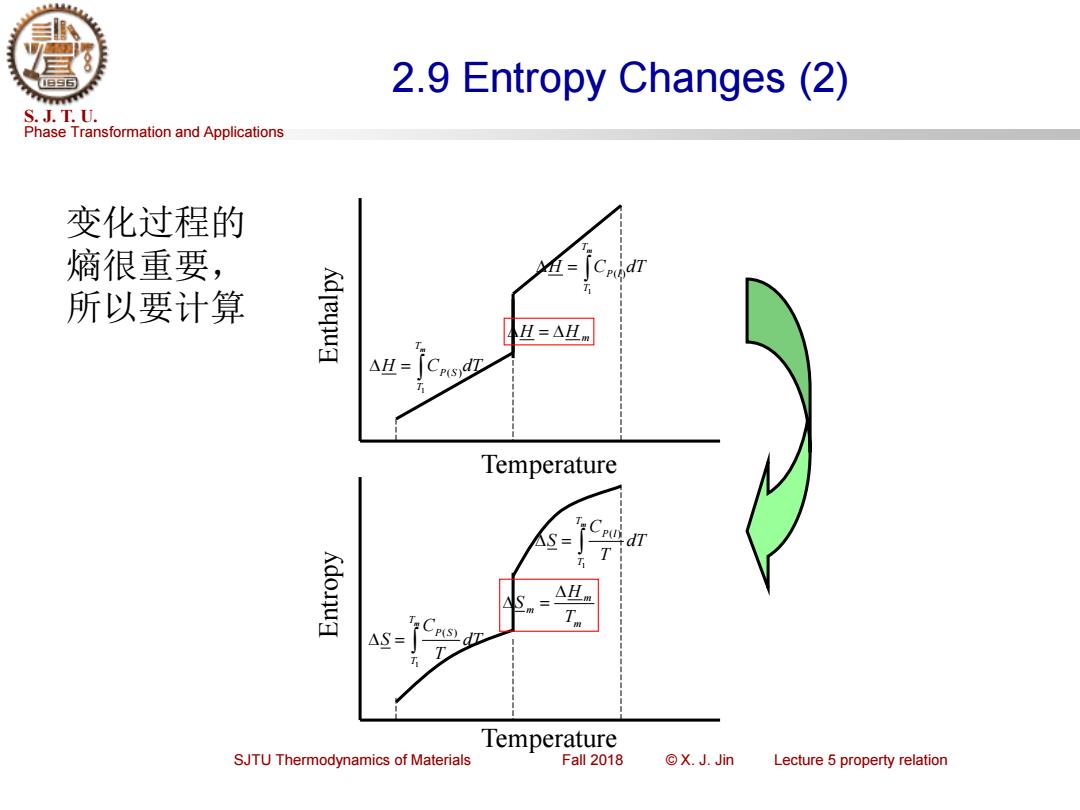
2.9 Entropy Changes(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 变化过程的 熵很重要, 所以要计算 H=△Hm △H= Temperature S= Cpu dT Kdonud △Hm △S= P(S Temperature SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.9 Entropy Changes (2) = Tm T P S dT T C S 1 ( ) = Tm T P l dT T C S 1 ( ) m m m T H S = Temperature Entropy = Tm T H CP S dT 1 ( ) = Tm T H CP l dT 1 ( ) H = H m Temperature Enthalpy 变化过程的 熵很重要, 所以要计算
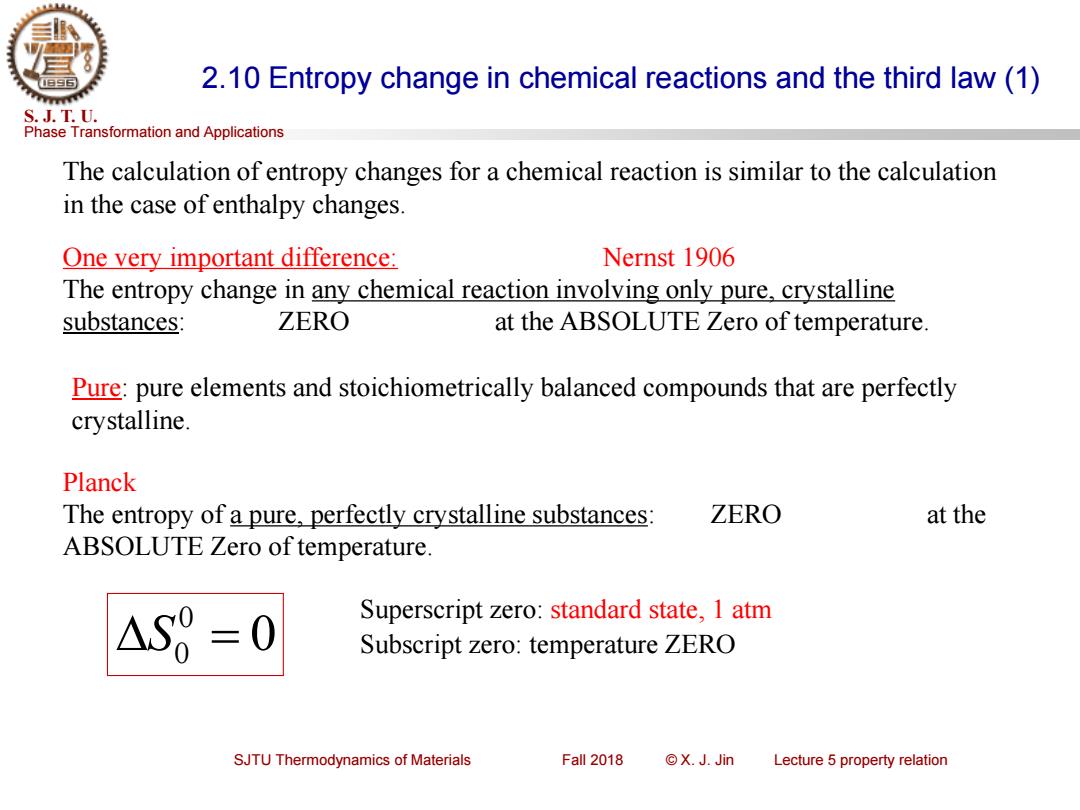
2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law(1) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The calculation of entropy changes for a chemical reaction is similar to the calculation in the case of enthalpy changes. One very important difference: Nernst 1906 The entropy change in any chemical reaction involving only pure,crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. Pure:pure elements and stoichiometrically balanced compounds that are perfectly crystalline. Planck The entropy of a pure,perfectly crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. AS8=0 Superscript zero:standard state,1 atm Subscript zero:temperature ZERO SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law (1) The calculation of entropy changes for a chemical reaction is similar to the calculation in the case of enthalpy changes. One very important difference: Nernst 1906 The entropy change in any chemical reaction involving only pure, crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. Pure: pure elements and stoichiometrically balanced compounds that are perfectly crystalline. Planck The entropy of a pure, perfectly crystalline substances: ZERO at the ABSOLUTE Zero of temperature. 0 0 S0 = Superscript zero: standard state, 1 atm Subscript zero: temperature ZERO
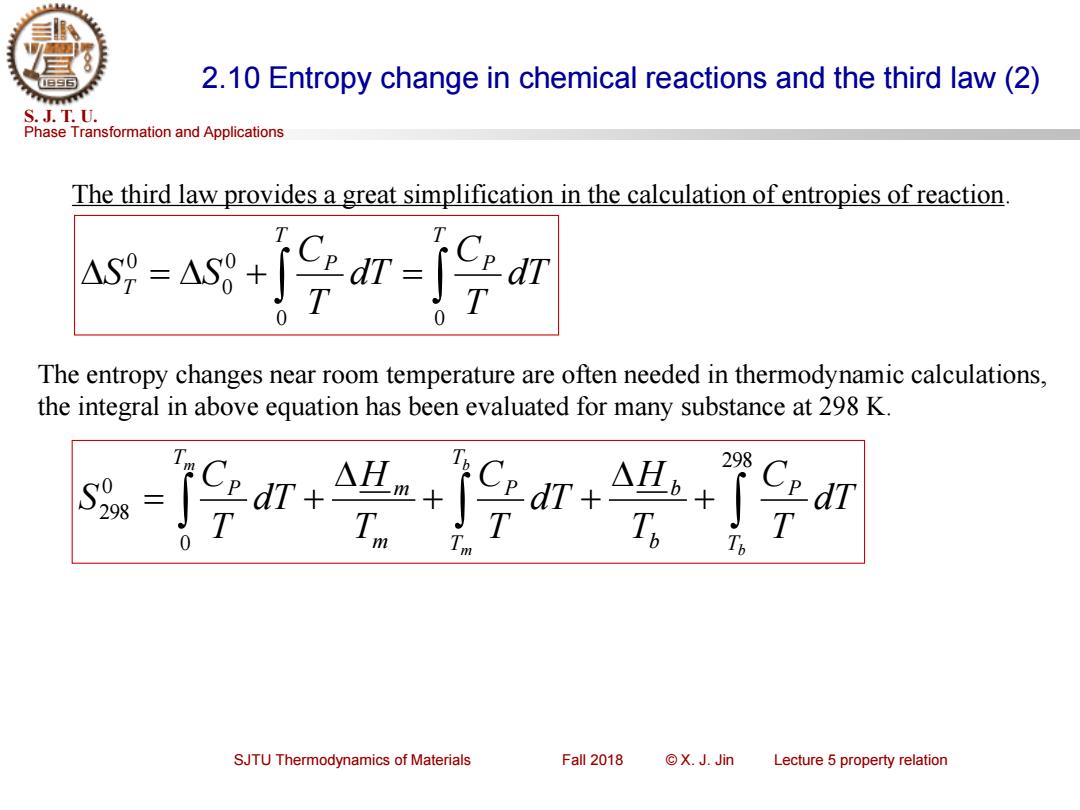
2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The third law provides a great simplification in the calculation of entropies of reaction A=as+fn号m The entropy changes near room temperature are often needed in thermodynamic calculations, the integral in above equation has been evaluated for many substance at 298 K. 298 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation 2.10 Entropy change in chemical reactions and the third law (2) The third law provides a great simplification in the calculation of entropies of reaction. = + = T P T P T dT T C dT T C S S 0 0 0 0 0 The entropy changes near room temperature are often needed in thermodynamic calculations, the integral in above equation has been evaluated for many substance at 298 K. + + + = + 298 0 0 298 b b m m T P T T b P b m m T P dT T C T H dT T C T H dT T C S

Index of nomenclature S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Helmholtz free energy(F):亥姆赫茨自由能 Gibbs free energy(G):吉布斯自由能 Chemical potential:化学位 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Index of nomenclature Helmholtz free energy (F): 亥姆赫茨自由能 Gibbs free energy (G): 吉布斯自由能 Chemical potential:化学位 Index of nomenclature
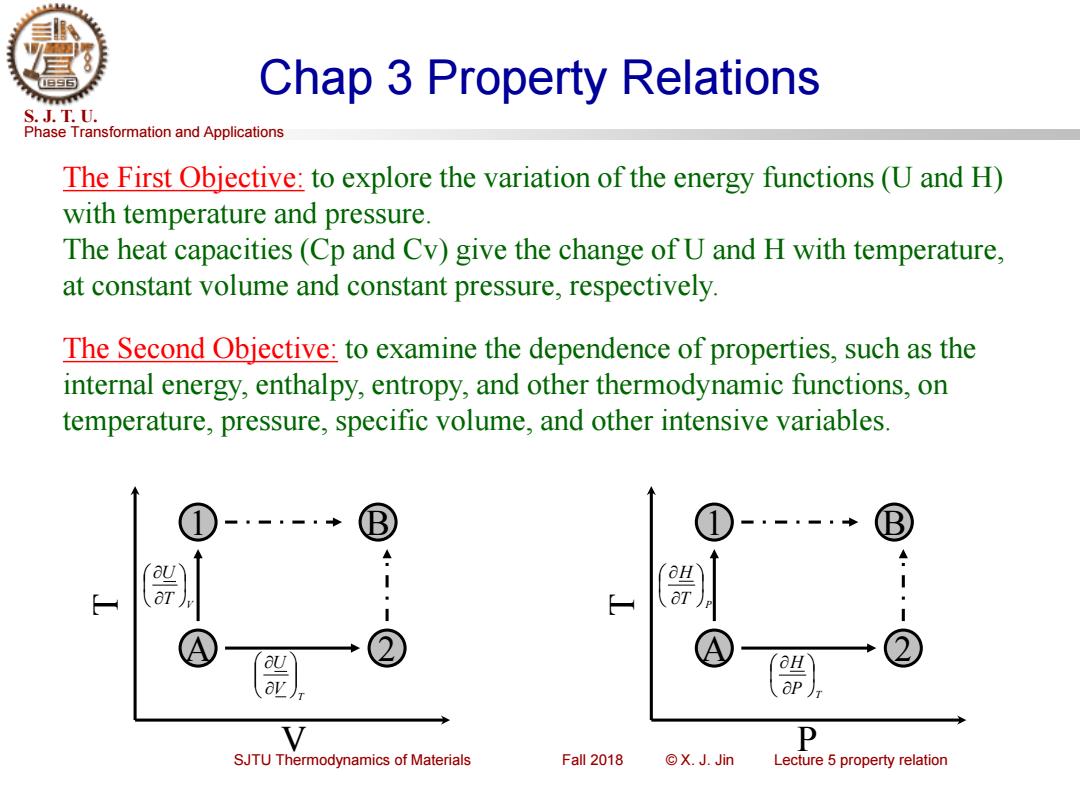
Chap 3 Property Relations S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The First Objective:to explore the variation of the energy functions(U and H) with temperature and pressure. The heat capacities(Cp and Cv)give the change of U and H with temperature, at constant volume and constant pressure,respectively. The Second Objective:to examine the dependence of properties,such as the internal energy,enthalpy,entropy,and other thermodynamic functions,on temperature,pressure,specific volume,and other intensive variables. a av V P SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.JJin Lecture 5 property relation
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation Chap 3 Property Relations The First Objective: to explore the variation of the energy functions (U and H) with temperature and pressure. The heat capacities (Cp and Cv) give the change of U and H with temperature, at constant volume and constant pressure, respectively. The Second Objective: to examine the dependence of properties, such as the internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, and other thermodynamic functions, on temperature, pressure, specific volume, and other intensive variables. 2 1 B A V T T V U T V U 2 1 B A P T P T H T P H