Contents of Today S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Variation of vapor pressure with particle size Second-order transition SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Contents of Today Review previous Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Variation of vapor pressure with particle size Second-order transition
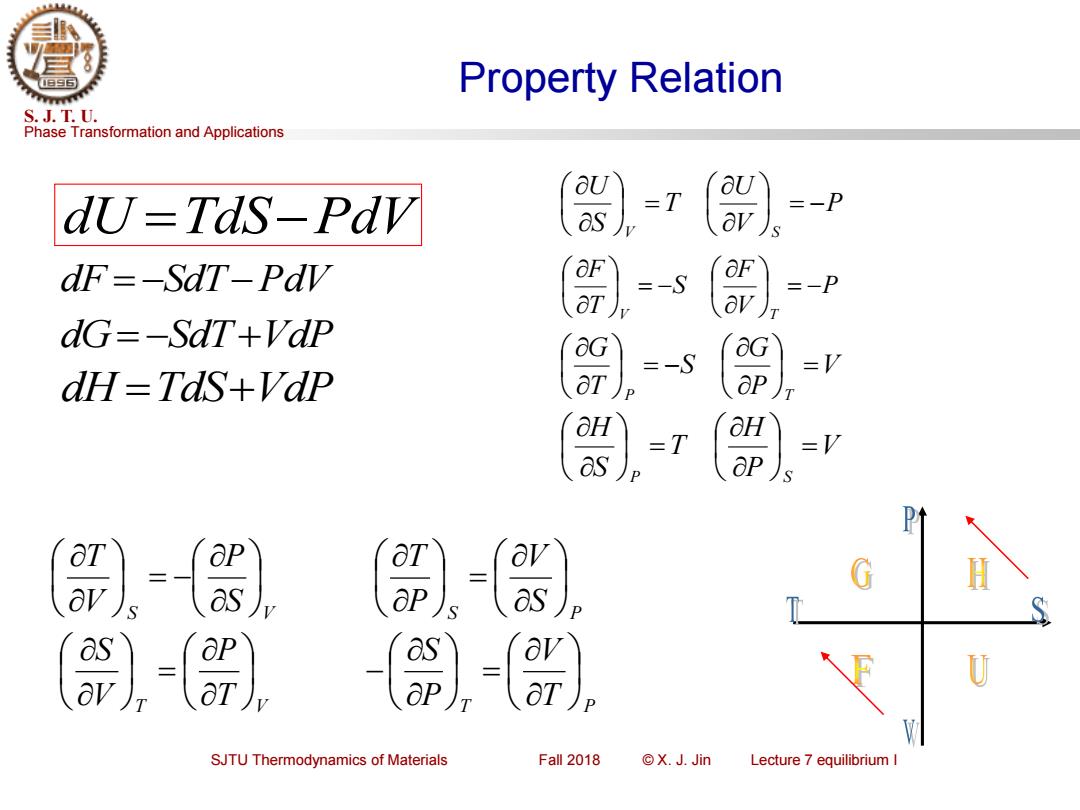
Property Relation S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications aU dU-Tds-Pdv =T =-P dF=-SdT-Pav =-S 8) dG=-SdT+Vdp =-S =V dH=TaS+Vap -T =V 二 as ap) H as aP as ap SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Property Relation S S V P V T = − S S P V P T = T T V P V S = T T P V P S = − dU =TdS−PdV dF = −SdT−PdV dG= −SdT+VdP dH =TdS+VdP P V U T S U V S = − = P V F S T F V T = − = − V P G S T G P T = = − V P H T S H P S = =
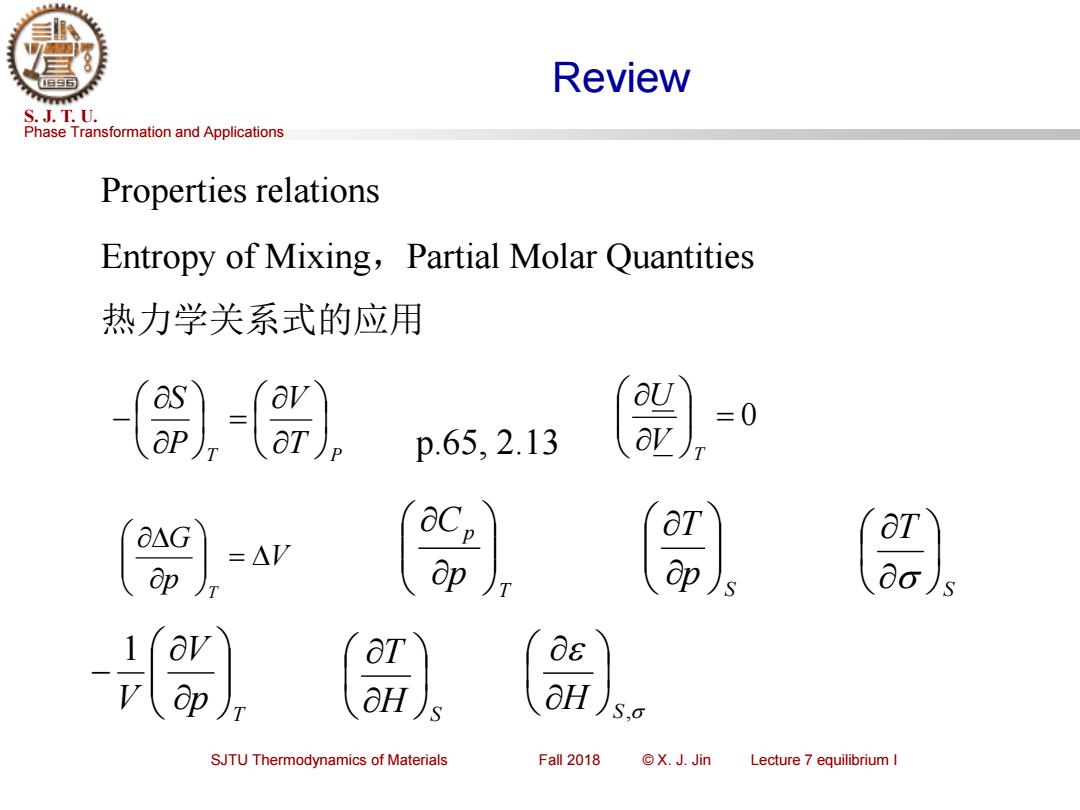
Review S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Properties relations Entropy of Mixing,Partial Molar Quantities 热力学关系式的应用 -) p.65..13 a△G =△V ap ap (av 0s OH aH S,o SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Review Properties relations Entropy of Mixing,Partial Molar Quantities 热力学关系式的应用 T T P V P S = − = 0 T V U p.65, 2.13 V p G T = T p p C S p T S T T p V V − 1 H S T H S,

Quiz Q3 Answer S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 15.进行下述过程时,系统的△U、△H、△S和△G何者为零? (1)非理想气体的卡诺循环; (2)隔离系统中的任意过程: (3)在100℃,01325Pa下1mol水蒸发成水蒸气; (4)绝热可逆过程。 15题:1)内能变化为0,焓变为0,熵变为0,自由能变化为0。 2):内能变化为0, 焓变不一定为0,熵变不一定为0,自由能变化不 一定为0。 3)自由能变化为0。错,主要认为相变过程中内能为0,焓变也为0。 4)只有熵变为0。错误很多。 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Quiz Q3 Answer 15题:1)内能变化为0,焓变为0,熵变为0,自由能变化为0。 2):内能变化为0,焓变不一定为0,熵变不一定为0,自由能变化不 一定为0。 3)自由能变化为0。错,主要认为相变过程中内能为0,焓变也为0。 4)只有熵变为0。错误很多

Problem 3.2 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications At-5 C,the vapor pressure of ice is 3.012 mmHg and that of supercooled liquid water is 3.163 mmHg.Tha latent heat of fusion of ice is 5.85 kJ/mol at -5C.Calculate AG and AS per mole for the transition from water to ice at-5°C. △G1-5C Vapor pressure △G=0 △G=-0 Ice Water △Gand△Sat-5C SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Problem 3.2 At -5 C, the vapor pressure of ice is 3.012 mmHg and that of supercooled liquid water is 3.163 mmHg. Tha latent heat of fusion of ice is 5.85 kJ/mol at -5 C. Calculate G and S per mole for the transition from water to ice at -5C. Ice Water G and S at -5 C G1 -5 C G=0 G=0 Vapor pressure

Index of nomenclature S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Equilibrium:平衡 Phase equilibrium:相平衡 First order transitions:一级相变 Second-order transition:二级相变 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Index of nomenclature Equilibrium: 平衡 Phase equilibrium: 相平衡 First order transitions: 一级相变 Second-order transition: 二级相变
Introduction to equilibrium S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The concept of equilibrium is fundamental Stable,unchanging with time and certain properties of the system are uniform throughout The system may not be homogeneous in form Co-existence of ice and water Phase A portion of matter that is uniform throughout,not only in chemical composition,but also in physical state - The usefulness of many metallic,polymeric,and ceramic systems depends on the presence,at equilibrium,of various different phases in the material 组织 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Introduction to equilibrium • The concept of equilibrium is fundamental • Stable, unchanging with time and certain properties of the system are uniform throughout • The system may not be homogeneous in form – Co-existence of ice and water • Phase – A portion of matter that is uniform throughout, not only in chemical composition, but also in physical state – The usefulness of many metallic, polymeric, and ceramic systems depends on the presence, at equilibrium, of various different phases in the material 组织
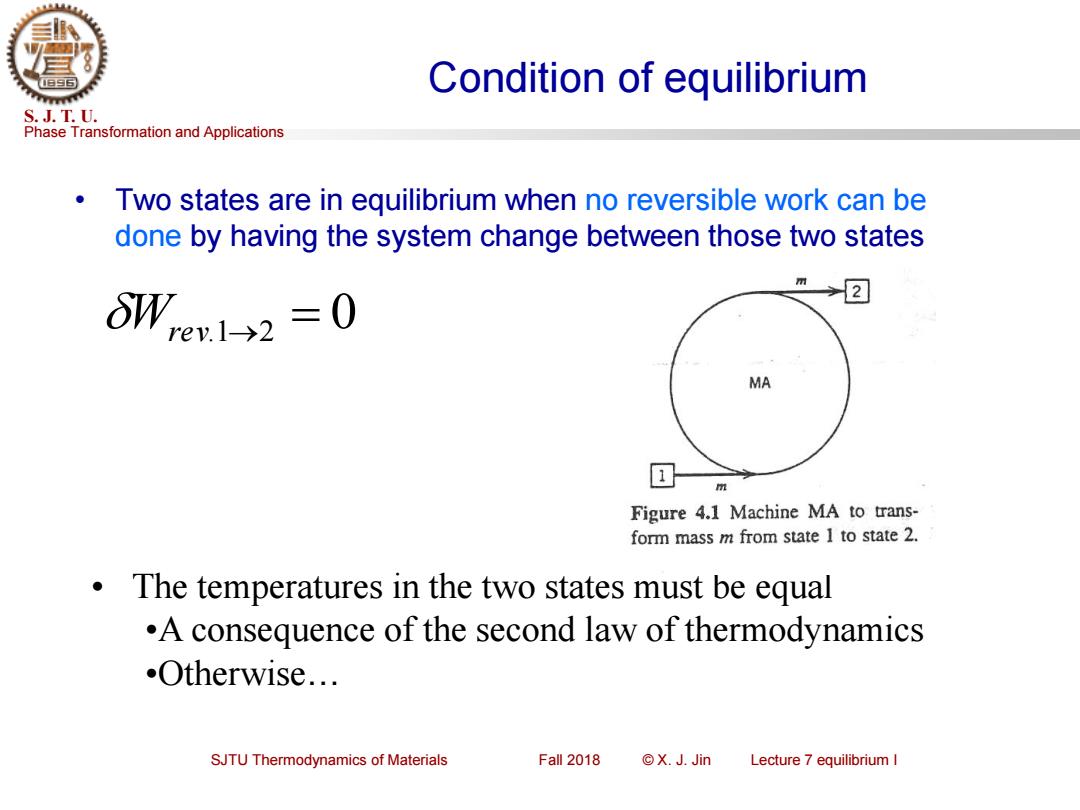
Condition of equilibrium S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Two states are in equilibrium when no reversible work can be done by having the system change between those two states 2 6W,ev1->2=0 MA m Figure 4.1 Machine MA to trans- form mass m from state I to state 2. The temperatures in the two states must be equal .A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics .Otherwise... SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium • Two states are in equilibrium when no reversible work can be done by having the system change between those two states Wrev.1→2 = 0 • The temperatures in the two states must be equal •A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics •Otherwise…

Condition of equilibrium(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Deal with partial molar quantities First law +PE+KE)a dn.-(+PE+KE).2dn2++W=du Second law 51-5,dm2+9 =ds T -TSdn.+TS,.dn.2-80+8w=-TdS The poperties of the machine do not change at steady state du-0and ds-0 G+PE+KE)dn2-G+PE+KE)dn.=OWc SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium (2) dS T lw T Q Si dni −Si dni + − = ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 (H + PE + KE)i,1 d ni,1 −(H + PE + KE)i,2 d ni,2 +Q +W = dU Deal with partial molar quantities −TSi,1 dni,1 +TSi,2 dni,2 −Q +lw= −TdS First law Second law The properties of the machine do not change at steady state dU=0 and dS=0 ( ) ( ) G + PE + KE i,2 d ni,2 − G + PE + KE i,1 d ni,1 = Wrev
Condition of equilibrium(3) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications G+PE+KE)dn,-G+PE+KE)dn,=OW Condition of equilibrium W,e1-→2=0 G+PE+KE)dn,=G+PE+KE)dn, At the same potential energy level and kinetic level (G,2-G,)dn,=AG,=0 G,2-G 4,2=4,1 In term of the chemical potential of i States 1 and 2 are in equilibrium with respect to material i if the partial molar Gibbs free energy (or chemical potential)of i is the same in both states. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 ©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Fall 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium (3) ( ) ( ) G + PE + KE i,2 d ni − G + PE + KE i,1 d ni = Wrev Condition of equilibrium Wrev.1→2 = 0 ( ) ( ) G + PE + KE i,2 d ni = G + PE + KE i,1 d ni (Gi,2 −Gi,1 )dni = Gi = 0 Gi,2 = Gi,1 At the same potential energy level and kinetic level i,2 = i,1 In term of the chemical potential of i States 1 and 2 are in equilibrium with respect to material i if the partial molar Gibbs free energy (or chemical potential) of i is the same in both states