
Contents of Today S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous /Quiz Equlibrium Thermodynamic activity Chemical equilibrium Gaseous equilibrium Solid-vapor equilibrium Sources of information on Chemical equilibrium and adiabatic flame temperature etc. Science research is an adventure,is an interest-driving learning process. It takes more time to think than to do.-Ke Lu SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Contents of Today Review previous / Quiz Equlibrium Science research is an adventure, is an interest-driving learning process. It takes more time to think than to do. – Ke Lu Thermodynamic activity Chemical equilibrium Gaseous equilibrium Solid-vapor equilibrium Sources of information on Chemical equilibrium and adiabatic flame temperature etc

Review previous lecture (1) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium相平衡/化学反应的平衡 8W,en1>2=0 4,2=41G2=G1 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Review previous lecture (1) Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium相平衡/化学反应的平衡 Wrev.1→2 = 0 i,2 i,1 Gi,2 = Gi,1 =
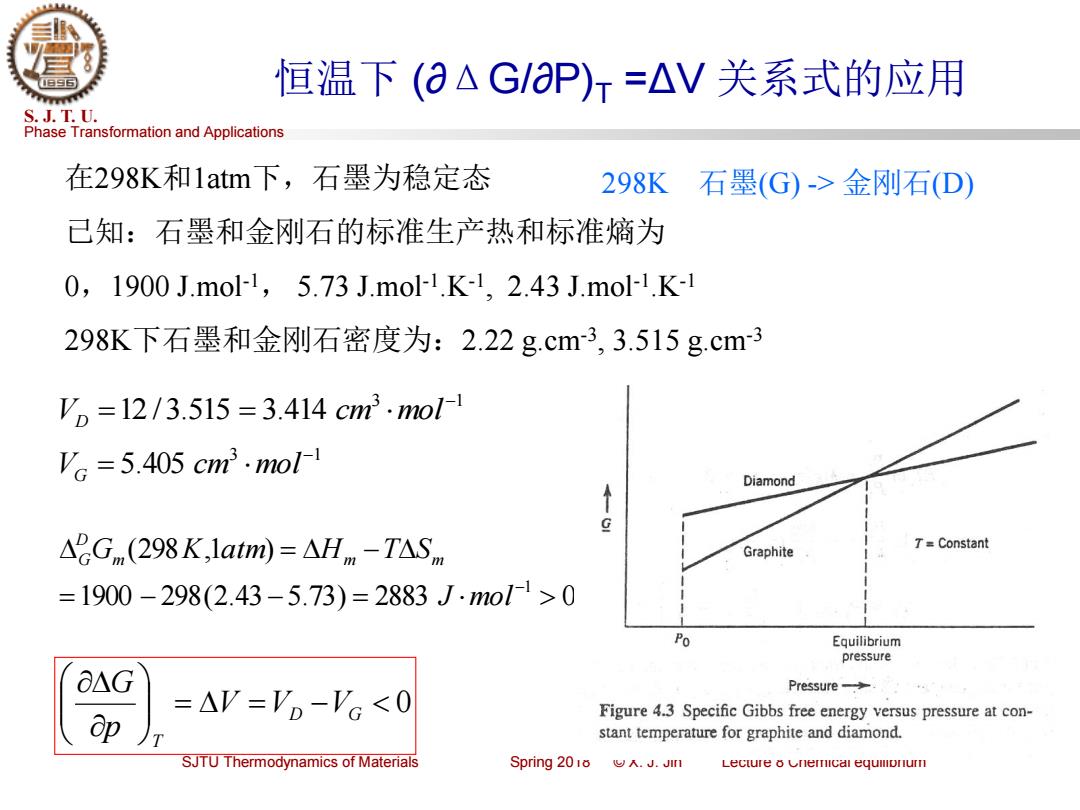
恒温下(aAG/aP)r=△V关系式的应用 S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 在298K和1atm下,石墨为稳定态 298K 石墨(G)->金刚石(D) 已知:石墨和金刚石的标准生产热和标准熵为 0,1900J.mol1,5.73J.mol1.K-1,2.43J.mo1.K-1 298K下石墨和金刚石密度为:2.22g.cm-3,3.515g.cm3 V,=12/3.515=3.414cm3.mol1 'c=5.405cm3.mol1 Diamond ↑ g △2Gnm(298K,1atm)=△Hm-T△S,m Graphite 7=Constant =1900-298(2.43-5.73)=2883J.mo1>0 Po Equilibrium pressure O△G Pressure-> =AV='o-'c<0 op Figure 4.3 Specific Gibbs free energy versus pressure at con- stant temperature for graphite and diamond. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018.J.Jin Lecture 8 Cnemical equllonur
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium 恒温下 (∂ΔG/∂P)T =ΔV 关系式的应用 在298K和1atm下,石墨为稳定态 已知:石墨和金刚石的标准生产热和标准熵为 0,1900 J.mol-1 , 5.73 J.mol-1 .K-1 , 2.43 J.mol-1 .K-1 298K下石墨和金刚石密度为:2.22 g.cm-3 , 3.515 g.cm-3 = = − 0 D G T V V V p G 298K 石墨(G) -> 金刚石(D) 1900 298(2.43 5.73) 2883 0 (298 ,1 ) 1 = − − = = − − J mol Gm K atm Hm T Sm D G 3 1 12 /3.515 3.414 − V = = cm mol D 3 1 5.405 − V = cm mol G
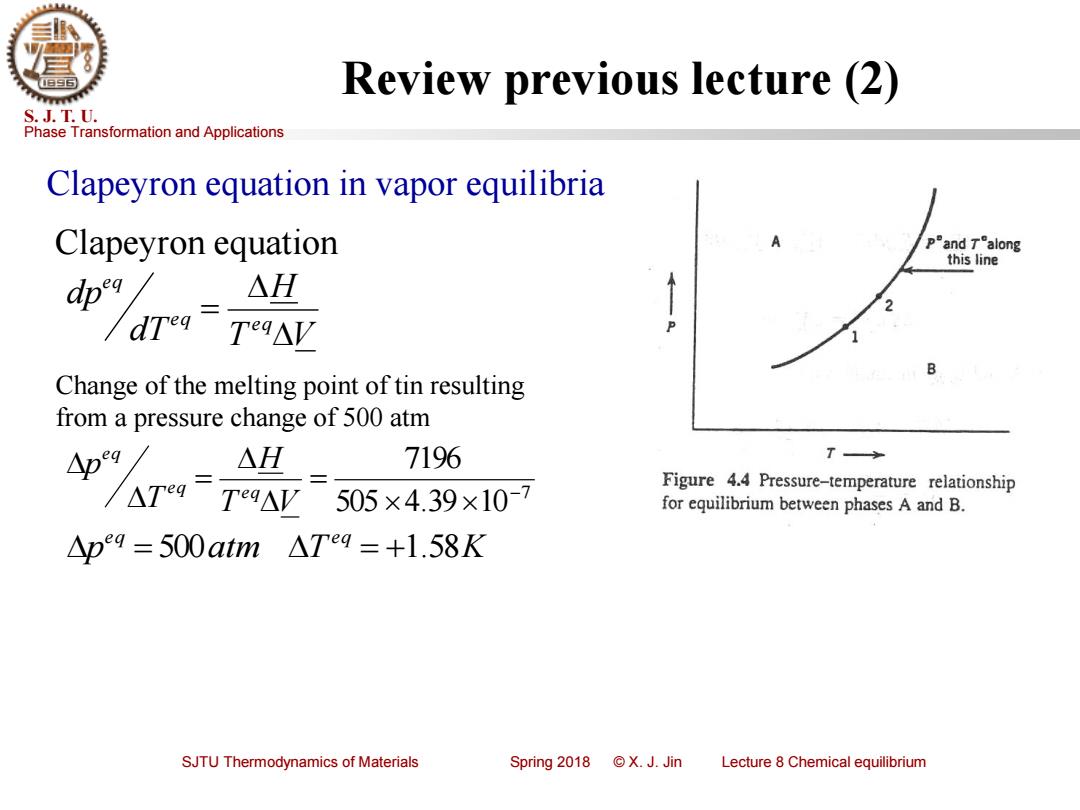
Review previous lecture (2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Clapeyron equation pand Talong this line △H Teg△V B Change of the melting point of tin resulting from a pressure change of 500 atm 人 AH 7196 T Figure 4.4 Pressure-temperature relationship Teg△V 505×4.39×10-7 for equilibrium between phases A and B. △p9=500atm△Teg=+1.58K SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Review previous lecture (2) Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria T V H dT dp e q e q e q = Clapeyron equation Change of the melting point of tin resulting from a pressure change of 500 atm 7 505 4.39 10 7196 − = = T V H T p e q e q e q p atm T K e q e q = 500 = +1.58
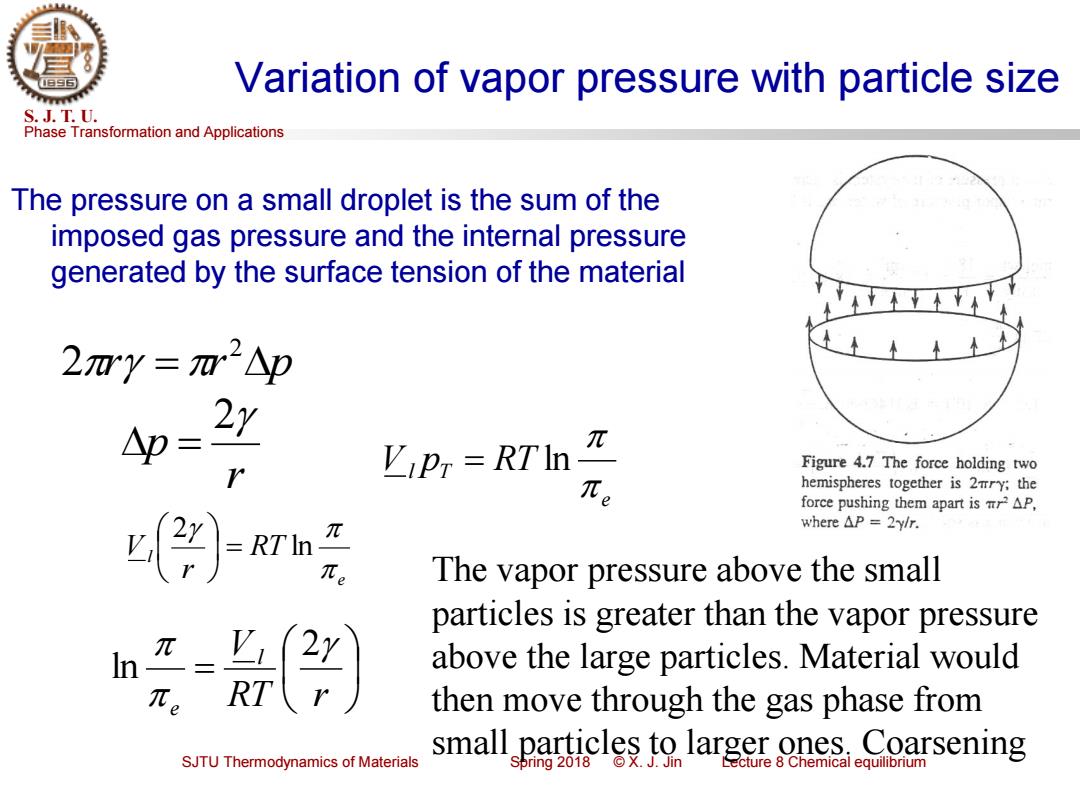
Variation of vapor pressure with particle size S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications The pressure on a small droplet is the sum of the imposed gas pressure and the internal pressure generated by the surface tension of the material 2mY=m2△p △p= π ViPT RTIn Figure 4.7 The force holding two hemispheres together is 2mry:the force pushing them apart is AP, RTI- where△P=2ylr. The vapor pressure above the small particles is greater than the vapor pressure I=Y (2x above the large particles.Material would RT then move through the gas phase from Coarsening SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials small particles to largerones..Coar Spring 2018
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Variation of vapor pressure with particle size The pressure on a small droplet is the sum of the imposed gas pressure and the internal pressure generated by the surface tension of the material r = r p 2 2 r p 2 = e Vl pT RT = ln e l RT r V ln 2 = = RT r V l e 2 ln The vapor pressure above the small particles is greater than the vapor pressure above the large particles. Material would then move through the gas phase from small particles to larger ones. Coarsening

Second-order transition S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications First derivatives of G with respect to T and p are continuous and the second derivatives of G with respect to T and P are discontinuous SA=SB S=S(T,p) dS dT+ dp T dS= d7- C。=T T dp n SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Second-order transition First derivatives of G with respect to T and p are continuous and the second derivatives of G with respect to T and P are discontinuous S A = S B S = S(T, p) dp p S dT T S dS p T + = dp T V dT T C d S p p = − p p T S C T =

Second-order transition(2) S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications ds=dt-ar T dp ds,=dsB dsas。-0-CsC≥rm-eas-ra,p Teq VA=VR=V ACp The thermal expansion dTeg VTe△a coefficient does change! dp △ dTeg △B SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Second-order transition (2) dp T V dT T C d S p p = − dS A = dS B ( ) e q B B A A e q e q p B p A A B dT V V dp T C C dS dS − − − − = = , , 0 V A =V B =V = e q p e q e q VT C dT dp The thermal expansion coefficient does change! = e q e q dT dp
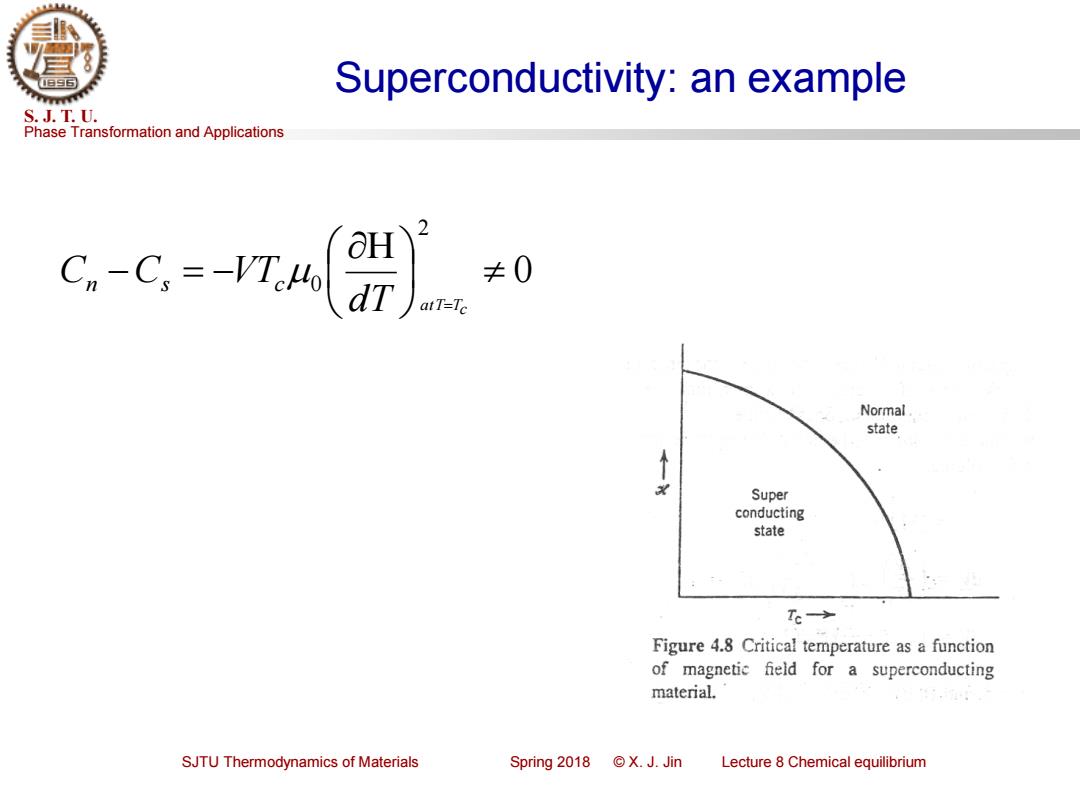
Superconductivity:an example S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications 2 C,-C.=-VTMh dr ≠0 atT-Tc Normal state Super conducting state Tc→ Figure 4.8 Critical temperature as a function of magnetie field for a superconducting material. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Superconductivity: an example 0 2 0 − = − d T atT=Tc Cn Cs VTc
Index of nomenclature S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Activity:活度 Fugacity:逸度 Reference state/standard state:参考态/标准态 Equilibrium constant:平衡常数 Ellingham diagrams:Ellingham SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Index of nomenclature Activity:活度 Fugacity:逸度 Reference state / standard state:参考态 / 标准态 Equilibrium constant:平衡常数 Ellingham diagrams: Ellingham图
Introduction S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Physical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium. Activity Fugacity dG=VdrdG=-SdT+Vdp,withdT=O) dG=RTP RTdln P P SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2018©X.J.Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2018 © X. J. Jin Lecture 8 Chemical equilibrium Introduction Physical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium. Activity Fugacity dG =VdP(dG = −SdT +VdP,withdT = 0) RTd P P dP dG = R T = ln