
.Self-Introduction .Join SJTU in 1996 .PhD.In 2002 Research area:Corporate finance/corporate governance .Course taught:Corporate finance Finance; Economics;Intermediate microeconomics;managerial economics The course information 1-2
The course information •1-2 •Self-Introduction •Join SJTU in 1996 •PhD. In 2002 •Research area:Corporate finance/corporate governance •Course taught:Corporate finance ;Finance; • Economics;Intermediate microeconomics;managerial economics

.The Goals of This Course ●are: To help you develop a financial way of thinking > To enrich your financial knowledge To introduce you to basic financial concepts such as the time value of money, valuation models,and risk and return. >To help you prepare for the advanced financial courses such as corporate finance,investments and financial engineering. Finance Corporate Financial Investments finance Enginering The course information 1-3
The course information •1-3 •The Goals of This Course •are: Ø To help you develop a financial way of thinking Ø To enrich your financial knowledge Ø To introduce you to basic financial concepts such as the time value of money, valuation models, and risk and return. Ø To help you prepare for the advanced financial courses such as corporate finance , investments and financial engineering. Finance Corporate finance Investments Financial Enginering

.Course Materials Textbook:Financial Economics 2e by Zvi Bodie,Robert C.Merton and David L.Cleeton,Pearson publishing house. 。 Reference book:Foundations of finance 7e by Keown.Martin.Petty,Pearson publishing house.You can borrow from School Foundations of finance Materials from the instructor: ·Syllabus ·PPT 。Handouts The Course Information 1-4
The Course Information •1-4 • Textbook: Financial Economics 2e by Zvi Bodie, Robert C. Merton and David L. Cleeton, Pearson publishing house. • Reference book: Foundations of finance 7e by Keown.Martin.Petty, Pearson publishing house. You can borrow from School Foundations of finance • Materials from the instructor: • Syllabus • PPT • Handouts •Course Materials

The Course Schedule 1.Introduction:Finance and Financial system (week1~4) 2.Time and resource allocation (week 5~8 one of the three pillars 3.Valuation models (week9~10 one of the three pillars 4.Risk and risk management (week11~13 one of the three pillars) 5.Asset Pricing (week14~16 extended part) The course of finance
The Course Schedule 1. Introduction: Finance and Financial system (week1~4) 2. Time and resource allocation(week 5~8 one of the three pillars ) 3. Valuation models(week9~10 one of the three pillars ) 4. Risk and risk management(week11~13 one of the three pillars) 5. Asset Pricing(week14~16 extended part) The course of finance
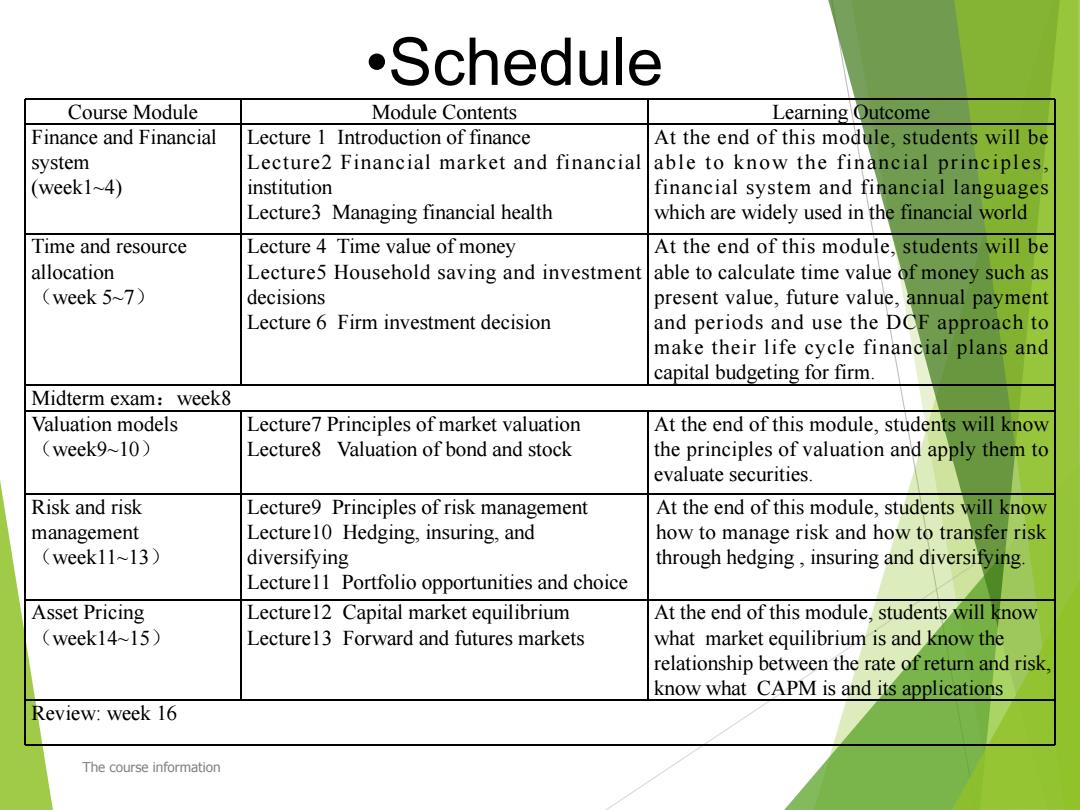
.Schedule Course Module Module Contents Learning Outcome Finance and Financial Lecture 1 Introduction of finance At the end of this module,students will be system Lecture2 Financial market and financial able to know the financial principles, (week1~4) institution financial system and financial languages Lecture3 Managing financial health which are widely used in the financial world Time and resource Lecture 4 Time value of money At the end of this module,students will be allocation Lecture5 Household saving and investment able to calculate time value of money such as (week 5~7) decisions present value,future value,annual payment Lecture 6 Firm investment decision and periods and use the DCF approach to make their life cycle financial plans and capital budgeting for firm. Midterm exam:week8 Valuation models Lecture7 Principles of market valuation At the end of this module,students will know (week9~10) Lecture8 Valuation of bond and stock the principles of valuation and apply them to evaluate securities. Risk and risk Lecture9 Principles of risk management At the end of this module,students will know management Lecture10 Hedging,insuring,and how to manage risk and how to transfer risk (week11~13) diversifying through hedging,insuring and diversifying. Lecture11 Portfolio opportunities and choice Asset Pricing Lecture12 Capital market equilibrium At the end of this module,students will know (week14~15) Lecture13 Forward and futures markets what market equilibrium is and know the relationship between the rate of return and risk. know what CAPM is and its applications Review:week 16 The course information
Course Module Module Contents Learning Outcome Finance and Financial system (week1~4) Lecture 1 Introduction of finance Lecture2 Financial market and financial institution Lecture3 Managing financial health At the end of this module, students will be able to know the financial principles, financial system and financial languages which are widely used in the financial world Time and resource allocation (week 5~7) Lecture 4 Time value of money Lecture5 Household saving and investment decisions Lecture 6 Firm investment decision At the end of this module, students will be able to calculate time value of money such as present value, future value, annual payment and periods and use the DCF approach to make their life cycle financial plans and capital budgeting for firm. Midterm exam:week8 Valuation models (week9~10) Lecture7 Principles of market valuation Lecture8 Valuation of bond and stock At the end of this module, students will know the principles of valuation and apply them to evaluate securities. Risk and risk management (week11~13) Lecture9 Principles of risk management Lecture10 Hedging, insuring, and diversifying Lecture11 Portfolio opportunities and choice At the end of this module, students will know how to manage risk and how to transfer risk through hedging , insuring and diversifying. Asset Pricing (week14~15) Lecture12 Capital market equilibrium Lecture13 Forward and futures markets At the end of this module, students will know what market equilibrium is and know the relationship between the rate of return and risk, know what CAPM is and its applications Review: week 16 •Schedule The course information
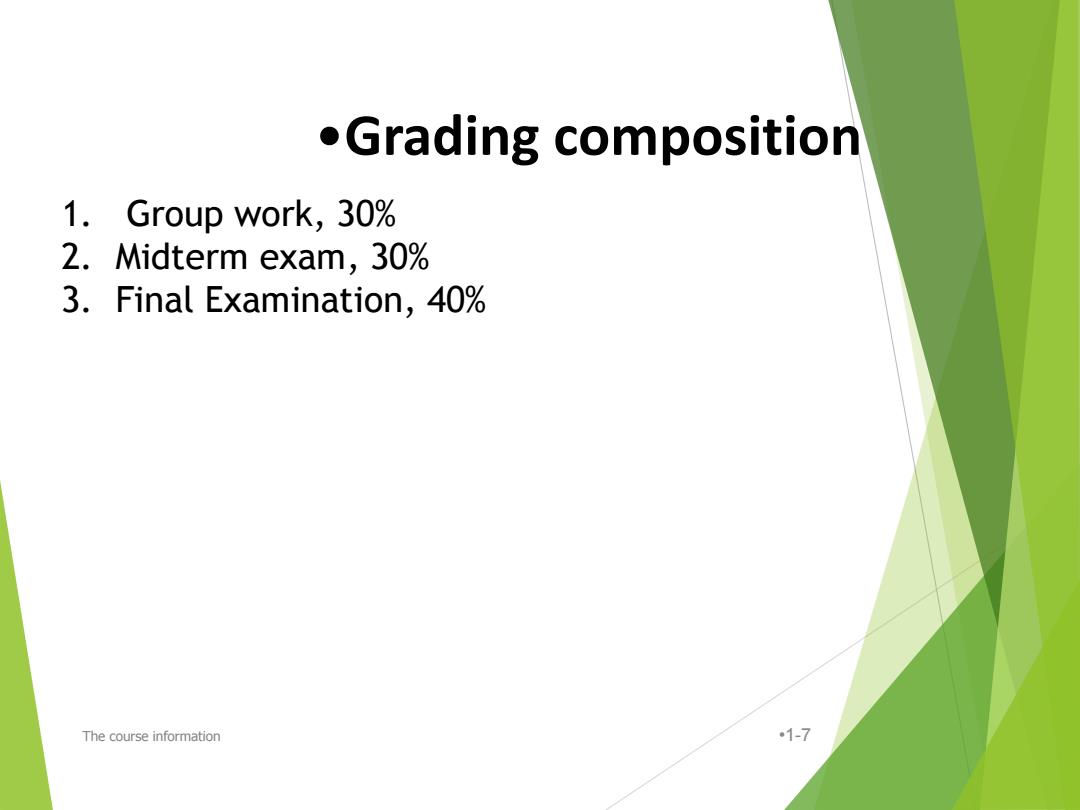
●Grading composition 1.Group work,30% 2.Midterm exam,30% 3.Final Examination,40% The course information 1-7
The course information •1-7 •Grading composition 1. Group work, 30% 2. Midterm exam, 30% 3. Final Examination, 40%

lecture 1: Introduction of Financia Economics Objective To Define Finance 5 financial principles vers and their fin ions THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING
lecture 1: Introduction of Financial Economics THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING •8 Objective To Define Finance 5 financial principles 2 Financial Players and their financial decisions

Chapter 1 Contents 1.1 Defining Finance 1.7 The Goal of 1.2 Why Study Finance Management 1.3 Financial Decisions 1.8 Market Discipline: of Households Takeovers 1.4 Financial Decisions of Firms 1.9 The Role of the Financial Specialist in 1.5 Forms of Business Organization a Corporation 1.6 Separation of Ownership and Management THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING
Chapter 1 Contents 1.1 Defining Finance 1.2 Why Study Finance 1.3 Financial Decisions of Households 1.4 Financial Decisions of Firms 1.5 Forms of Business Organization 1.6 Separation of Ownership and Management 1.7 The Goal of Management 1.8 Market Discipline: Takeovers 1.9 The Role of the Financial Specialist in a Corporation THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING •9

Introduction I'm saving for retirement.Should I use a bank CD,mutual fund,direct stock market investment? I want that new car.Should I use saved cash,lease,borrow? I'm thinking about starting a new business will it reward me adequately? The company is looking to expand into telecommunications. how should you advise the CFO? A Latin American country has asked for major project financing should my organization provide the funds? THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING 10
Introduction I’m saving for retirement. Should I use a bank CD, mutual fund, direct stock market investment? I want that new car. Should I use saved cash, lease, borrow? I’m thinking about starting a new business will it reward me adequately? The company is looking to expand into telecommunications. how should you advise the CFO? A Latin American country has asked for major project financing should my organization provide the funds? THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING •10

1.1 Defining Finance Finance is the study of how people allocate scarce resources over time costs and benefits are distributed over time but the actual timing and size of future cash flows are often known only probabilistically Examples:saving;mortgage loan;capital budgeting Understanding finance helps you evaluate these uncertain cash flows THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING 11
1.1 Defining Finance Finance is the study of how people allocate scarce resources over time costs and benefits are distributed over time but the actual timing and size of future cash flows are often known only probabilistically Examples: saving; mortgage loan; capital budgeting Understanding finance helps you evaluate these uncertain cash flows THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING •11