
Lecture 11:Hedging,Insuring,and Diversifying refer to Ch.11 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
Lecture 11: Hedging, Insuring, and Diversifying refer to Ch.11 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 1

Chapter 11 Contents 11.1 Using Forward Futures 11.6 Basic Features of Insurance Contracts to Hedge Risks Contracts 11.2 Hedging Foreign-Exchange 11.7 Financial Guarantees Risk with Swap Contracts 11.8 Caps Floors on Interest 11.3 Hedging Shortfall-Risk by Rates Matching Assets to Liabilities 11.9 Options as Insurance 11.4 Minimizing the Cost of 11.10 The Diversification Hedging Principle 11.5 Insuring versus Hedging 11.11 Insuring a Diversified Portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
Chapter 11 Contents 11.1 Using Forward & Futures Contracts to Hedge Risks 11.2 Hedging Foreign-Exchange Risk with Swap Contracts 11.3 Hedging Shortfall-Risk by Matching Assets to Liabilities 11.4 Minimizing the Cost of Hedging 11.5 Insuring versus Hedging 11.6 Basic Features of Insurance Contracts 11.7 Financial Guarantees 11.8 Caps & Floors on Interest Rates 11.9 Options as Insurance 11.10 The Diversification Principle 11.11 Insuring a Diversified Portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 2

objectives Know how to use hedging insuring and diversifying to transfer risk Hedging(11.1-11.4) Insuring (11.5-11.9) Diversifying (11.10-11.11) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 3
objectives Know how to use hedging ,insuring and diversifying to transfer risk Hedging (11.1~11.4) Insuring (11.5~11.9) Diversifying (11.10~11.11) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 3

11.1 Using Forward and Futures Contracts to Hedge Risks Forward Contract an agreement between two parties to exchange something at a specified price and time This is an obligation on both parties Distinguish this from a right of a party to exchange something THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 4
11.1 Using Forward and Futures Contracts to Hedge Risks Forward Contract an agreement between two parties to exchange something at a specified price and time This is an obligation on both parties Distinguish this from a right of a party to exchange something THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 4
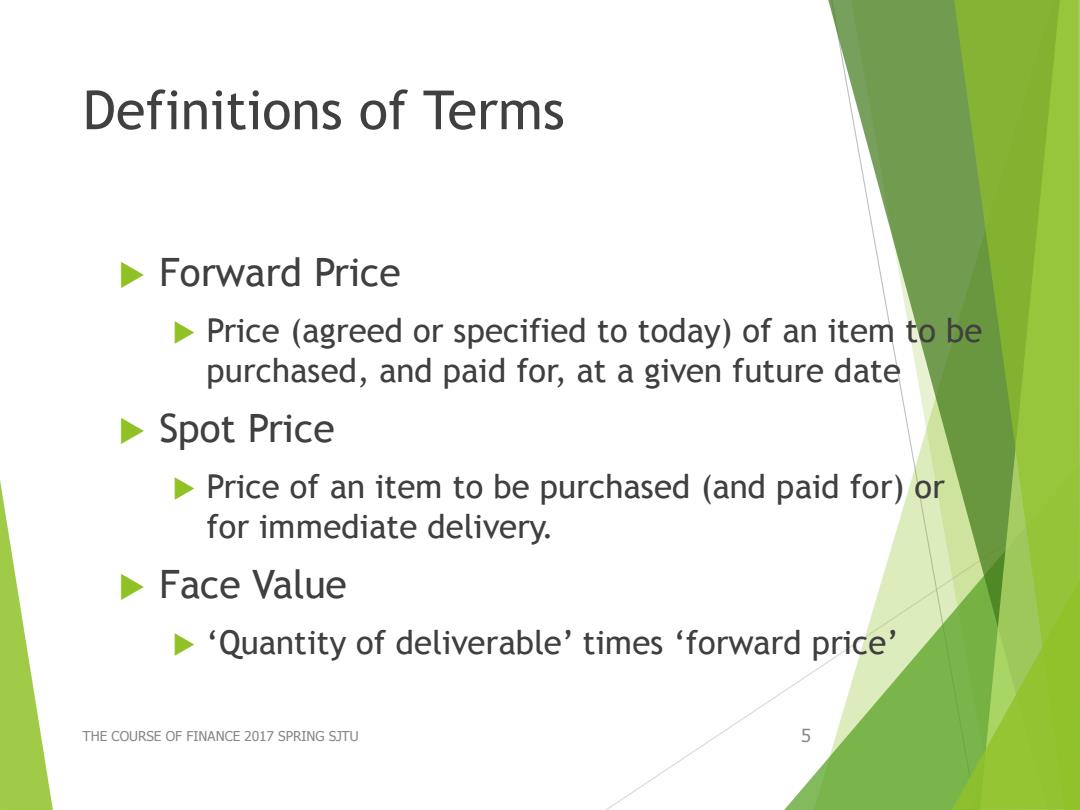
Definitions of Terms Forward Price Price (agreed or specified to today)of an item to be purchased,and paid for,at a given future date Spot Price Price of an item to be purchased (and paid for)or for immediate delivery. Face Value 'Quantity of deliverable'times 'forward price' THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 5
Definitions of Terms Forward Price Price (agreed or specified to today) of an item to be purchased, and paid for, at a given future date Spot Price Price of an item to be purchased (and paid for) or for immediate delivery. Face Value ‘Quantity of deliverable’ times ‘forward price’ THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 5

Definitions of Terms Long Position(多头) The agreement to buy the item (from the person taking the short position) Short Position(空头) The agreement to sell the item (to the person taking the long position) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6
Definitions of Terms Long Position(多头) The agreement to buy the item (from the person taking the short position) Short Position(空头) The agreement to sell the item (to the person taking the long position) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6

Using Forward and Futures Contracts to Hedge Risks Traditionally,no payment is made on a forward contract until the settlement date(交割日) If the parties to a forward contract do not trust the other,then add clauses to provide a sureties to a stakeholder periodically render contract valueless by making cash settlement equal to its current market value THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
Using Forward and Futures Contracts to Hedge Risks Traditionally, no payment is made on a forward contract until the settlement date(交割日) If the parties to a forward contract do not trust the other, then add clauses to provide a sureties to a stakeholder periodically render contract valueless by making cash settlement equal to its current market value THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 7

The Farmer and the Baker (Example) Jamela is a farmer with a wheat crop of about 100,000 bushels,1- month from harvest Mohammed is a baker who will need to restock his inventory of wheat for the coming year THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 8
The Farmer and the Baker (Example) Jamela is a farmer with a wheat crop of about 100,000 bushels, 1- month from harvest Mohammed is a baker who will need to restock his inventory of wheat for the coming year THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 8

The Farmer and the Baker Jamela and Mohammed wish to reduce price uncertainty because: Jamela has a mortgage to pay on her farm,and is concerned about wheat prices falling in the next month Mohammed wishes to close an agreement with a supermarket to supply bread at a fixed price for the coming year THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 9
The Farmer and the Baker Jamela and Mohammed wish to reduce price uncertainty because: Jamela has a mortgage to pay on her farm, and is concerned about wheat prices falling in the next month Mohammed wishes to close an agreement with a supermarket to supply bread at a fixed price for the coming year THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 9

The Farmer and the Baker Jamela and Mohammed agree to a forward contract Jamela agrees to deliver 100,000 bushels of wheat at $2.00 a bushel in one month,and Mohammed agrees to pay the $200,000 on delivery in a forward contract market. Assuming the crop doesn't fail,both parties have hedged their obligations THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 10
The Farmer and the Baker Jamela and Mohammed agree to a forward contract Jamela agrees to deliver 100,000 bushels of wheat at $2.00 a bushel in one month, and Mohammed agrees to pay the $200,000 on delivery in a forward contract market. Assuming the crop doesn't fail, both parties have hedged their obligations THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 10