
Lecture 4: Allocating Resources Over Time (textbook Ch.4 referencebook ch.5) Objective Explain the concept of compounding and discounting Know how these concepts are applied in financial decision THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU
Lecture 4: Allocating Resources Over Time (textbook Ch.4\referencebook ch.5) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 1 Objective u Explain the concept of compounding and discounting u Know how these concepts are applied in financial decision

Chapter 4 Contents 4.1 compounding 4.6 annuities 4.2 the frequency of 4.7 perpetual annuities compounding 4.8 loan amortization 4.3 present value and 4.9 exchange rates and discounting time value of money 4.4 alternative 4.10 inflation and discounted cash flow discounted cash flow decision rules analysis 4.5 multiple cash flows 4.11 taxes and investment decision THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU
Chapter 4 Contents 4.1 compounding 4.2 the frequency of compounding 4.3 present value and discounting 4.4 alternative discounted cash flow decision rules 4.5 multiple cash flows 4.6 annuities 4.7 perpetual annuities 4.8 loan amortization 4.9 exchange rates and time value of money 4.10 inflation and discounted cash flow analysis 4.11 taxes and investment decision THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU •2

Selected Contents FV PV Compounding interest;simple interest Discounting and DCF approach Annuity,perpetuity,preferred stock Using Excel functions of FV,PV,PMT,RATE,and NPER to compute time value of money THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU 3
Selected Contents FV, PV Compounding interest; simple interest Discounting and DCF approach Annuity, perpetuity, preferred stock Using Excel functions of FV, PV, PMT, RATE, and NPER to compute time value of money THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 3
Introduction:Time Value of Money (TVM) $1 today is worth more than the expectation of $1 tomorrow because: a bank would pay interest on the $1 inflation makes tomorrows s1 less valuable than today's uncertainty of receiving tomorrow's $1 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU
Introduction: Time Value of Money (TVM) $1 today is worth more than the expectation of $1 tomorrow because: a bank would pay interest on the $1 inflation makes tomorrows $1 less valuable than today’s uncertainty of receiving tomorrow’s $1 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 4

Two methods to offer interest Simple interest Compound interest THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU 5
Two methods to offer interest Simple interest Compound interest THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 5

Simple Interest Interest is earned only on principal. Example:Compute simple interest on $100 invested at 6%per year for three years. 1st year interest is S6.00 2nd yearinterest is S6.00 3rd year interest is $6.00 Total interest earned:$18.00 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6-6
Simple Interest Interest is earned only on principal. Example: Compute simple interest on $100 invested at 6% per year for three years. 1st year interest is $6.00 2nd yearinterest is $6.00 3rd year interest is $6.00 Total interest earned: $18.00 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6-6

Compound Interest Compounding is when interest paid on an investment during the first period is added to the principal;then, during the second period,interest is earned on the new sum (that includes the principal and interest earned so far). THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU 6-7
Compound Interest Compounding is when interest paid on an investment during the first period is added to the principal; then, during the second period, interest is earned on the new sum (that includes the principal and interest earned so far). THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6-7

Compound Interest Example:Compute compound interest on $100 invested at 6%for three years with annual compounding. 1st year interest is $6.00 Principal now is $106.00 2nd year interest is S6.36 Principal now is $112.36 3rd year interest is $6.74 Principal now is S119.11 Total interest earned:S19.10 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6-8
Compound Interest Example: Compute compound interest on $100 invested at 6% for three years with annual compounding. 1st year interest is $6.00 Principal now is $106.00 2nd year interest is $6.36 Principal now is $112.36 3rd year interest is $6.74 Principal now is $119.11 Total interest earned: $19.10 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6-8
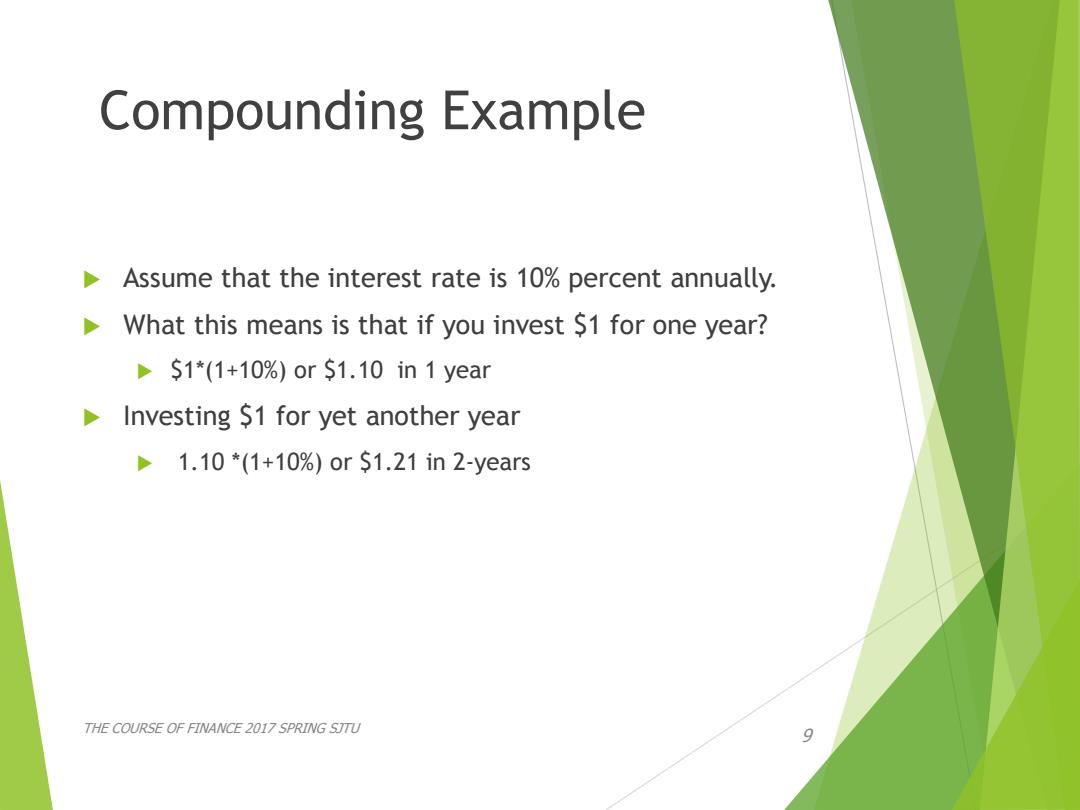
Compounding Example Assume that the interest rate is 10%percent annually. What this means is that if you invest $1 for one year? DS1*(1+10%)or$1.10in1year Investing $1 for yet another year 1.10*(1+10%)orS1.21in2-years THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU 9
Compounding Example Assume that the interest rate is 10% percent annually. What this means is that if you invest $1 for one year? $1*(1+10%) or $1.10 in 1 year Investing $1 for yet another year 1.10 *(1+10%) or $1.21 in 2-years THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 9
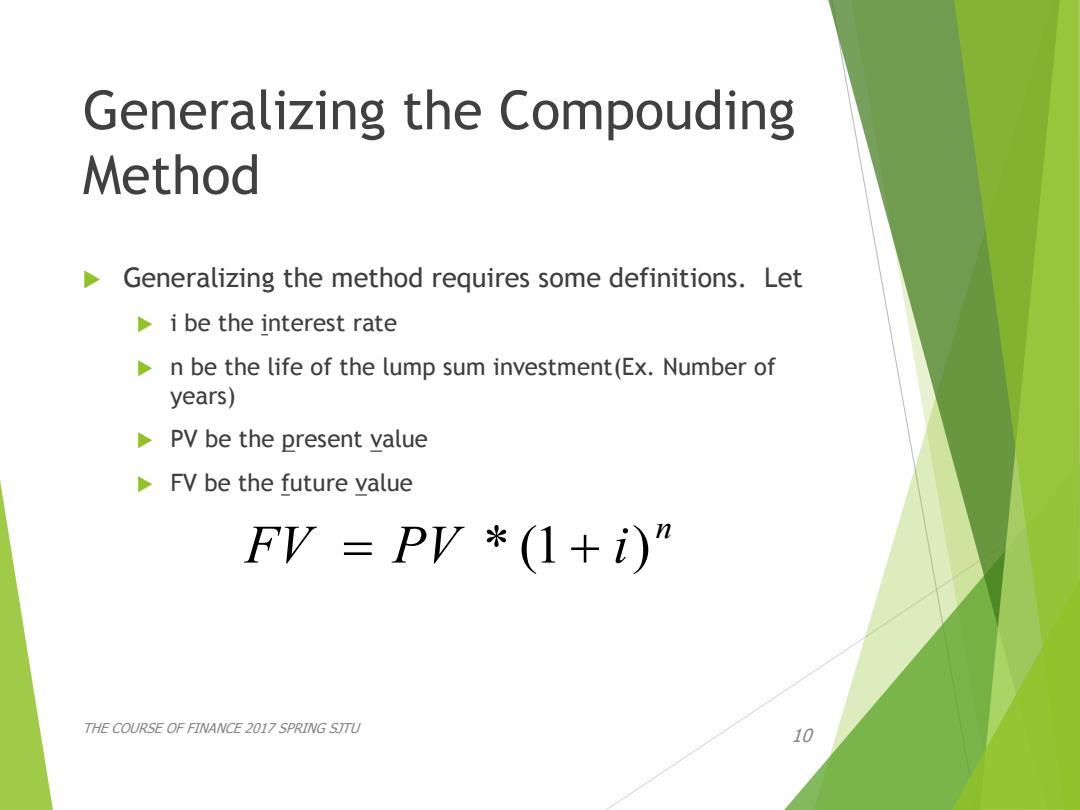
Generalizing the Compouding Method Generalizing the method requires some definitions.Let i be the interest rate n be the life of the lump sum investment(Ex.Number of years) PV be the present value FV be the future value FV=PV*(1+i)” THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING STTU 10
Generalizing the Compouding Method Generalizing the method requires some definitions. Let i be the interest rate n be the life of the lump sum investment(Ex. Number of years) PV be the present value FV be the future value THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 10 n FV PV * (1 i)