
Lecture I5 Capital Market Equilibriu Refer to chapter THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
Lecture 13: Capital Market Equilibrium Refer to chapter13 THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 1

Objectives .The Theory of the CAPM .Use of CAPM in benchmarking .Using CAPM to determine correct rate for discounting THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 2
Objectives THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 2 •The Theory of the CAPM •Use of CAPM in benchmarking •Using CAPM to determine correct rate for discounting

Chapter 13 Contents 13.1 The Capital Asset Pricing Model in Brief 13.2 Determining of the Risk Premium on the Market Portfolio 13.3 Beta and Risk Premiums on Individual Securities 13.4 Using the CAPM in Portfolio Selection 13.5 Valuation Regulating Rates of Return THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 3
Chapter 13 Contents 13.1 The Capital Asset Pricing Model in Brief 13.2 Determining of the Risk Premium on the Market Portfolio 13.3 Beta and Risk Premiums on Individual Securities 13.4 Using the CAPM in Portfolio Selection 13.5 Valuation & Regulating Rates of Return THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 3

CAPM in bri CAPM is a theory about equilibrium prices in the markets for risky assets It is important because it provides a justification for the widespread practice of passive investing called indexing a way to estimate expected rates of return for use in evaluating stocks and projects THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 4
CAPM in bri CAPM is a theory about equilibrium prices in the markets for risky assets It is important because it provides a justification for the widespread practice of passive investing called indexing a way to estimate expected rates of return for use in evaluating stocks and projects THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 4

13.1 The Capital Asset Pricing Model in Brief Developed in the 1960's by Sharp,and independently by Lintner,and Mossin It answers the question What would equilibrium risk premiums be if people had the same set of forecasts of expected returns,risk,and correlations and all chose their portfolios according the principles of efficient diversification (Refer to chapter12) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
13.1 The Capital Asset Pricing Model in Brief Developed in the 1960’s by Sharp, and independently by Lintner, and Mossin It answers the question What would equilibrium risk premiums be if people had the same set of forecasts of expected returns, risk, and correlations and all chose their portfolios according the principles of efficient diversification (Refer to chapter12) THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 5

Two Assumptions Investors forecasts agree with respect to expectations,standard deviations,and correlations of the returns of risky securities. Therefore all investors hold risky assets in the same relative proportions Investors behave optimally In equilibrium,prices adjust so that aggregate demand for each security is equal to its supply THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6
Two Assumptions Investors forecasts agree with respect to expectations, standard deviations, and correlations of the returns of risky securities. Therefore all investors hold risky assets in the same relative proportions Investors behave optimally :In equilibrium, prices adjust so that aggregate demand for each security is equal to its supply THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 6

CML and Market Portfolio Since every investor's relative holdings of the risky security is the same,the only way the asset market can clear is if those optimal relative proportions are the proportions in which they are valued in the market place that proportions are called Market Portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU
CML and Market Portfolio Since every investor’s relative holdings of the risky security is the same, the only way the asset market can clear is if those optimal relative proportions are the proportions in which they are valued in the market place ,that proportions are called Market Portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 7

CML and the CAPM CAPM says that in equilibrium, any investor's relative holding of risky assets will be the same as in the market portfolio Depending on their risk aversions, different investors hold portfolios with different mixes of riskless asset and the market portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 8
CML and the CAPM CAPM says that in equilibrium, any investor’s relative holding of risky assets will be the same as in the market portfolio Depending on their risk aversions, different investors hold portfolios with different mixes of riskless asset and the market portfolio THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 8
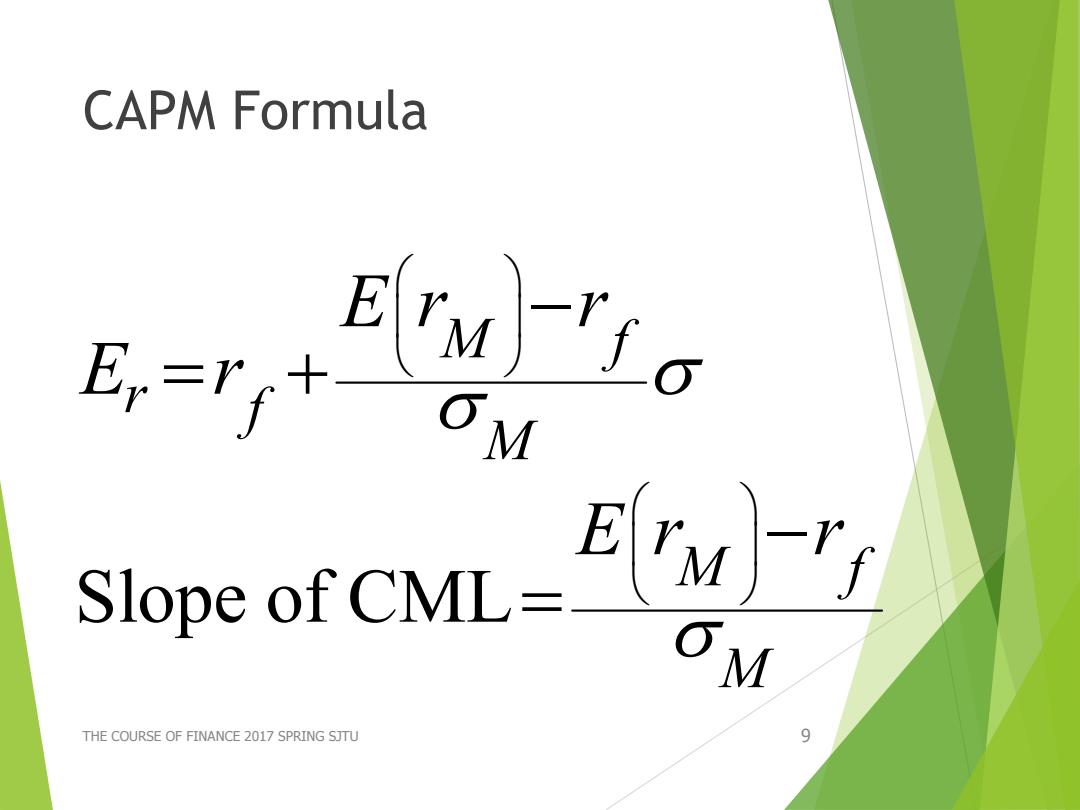
CAPM Formula En=rf十 M Slope of CML= M THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 9
CAPM Formula THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 9 Slope of CML M f r f M M f M E r r E r E r r

The Capital Market Line 18 16 1 M uImed panoadxy 120 8 6 4 2 5 10 15 20 25 30 Standard Deviation THE COUROL Ur FLNMINCL ZUL Fo
The Capital Market Line THE COURSE OF FINANCE 2017 SPRING SJTU 10