
第九章交流阻抗谱技术 ●Introduction o Basic elements in an electric circuit Nyquist and Bode plots Data analysis and software ●Examples
第九章 交流阻抗谱技术 Introduction Basic elements in an electric circuit Basic elements in an electric circuit Nyquist and Bode plots Nyquist and Bode plots Data analysis and software Examples

What should you know? ●阻抗谱的原理 ●如何看懂阻抗谱? ●如何解析阻抗谱?(常用软件) ●阻抗谱的常见错误
What should you know? 阻抗谱的原理 如何看懂阻抗谱? 如何解析阻抗谱?(常用软件) 阻抗谱的常见错误

Introduction Terminology: ● AC Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) ● Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) ● Complex Impedance Spectroscopy(CIS) References: ● J.R.MacDonald,Impedance Spectroscopy,Chapel Hill,North Carolina,1987.(John-Wiley,2005?) ● 史美伦,交流阻抗谱原理及应用,国防工业出 版社,2001 曹楚南,张鉴清,电化学阻抗谱导论,科学出版 社,2002
Introduction Terminology: • AC Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) AC Impedance Spectroscopy (IS) • Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) • Complex Impedance Spectroscopy (CIS) Complex Impedance Spectroscopy (CIS) References: • J.R. MacDonald, Impedance Spectroscopy, Chapel Hill N h C li 1987 (J h Hill, North Carolina, 1987. (John-Wil 2005?) Wiley, 2005?) • 史美伦,交流阻抗谱原理及应用,国防工业出 版社,2001. • 曹楚南, 张鉴清,电化学阻抗谱导论,科学出版 社,2002

Introduction ●暂态与稳态:This is a transient technique,but one that requires a general steady state condition. ●可测性质:can be used for determining both: Interfacial parameters(界面参数 a)reaction rates b)rate constants c)capacitance/charge storage abilities d)diffusion coefficients e)adsorption rate constants f)reaction mechanisms And aterial parameters(材料参数 a)conductivity b)dielectric constants c)bulk generation-recombination reaction rates d)charge mobilities e)film thickness f)equilibrium conc.of charged species g)presence of pores and cracks
Introduction 暂态与稳态: This is a transient technique, but one that requires a general steady state condition. 可测性质: can be used for determining both: Interfacial parameters ( Interfacial parameters (界面参数) a) reaction rates b) rate constants c) capacitance/charge storage abilities d) diffusion coefficients e) adsorption rate constants f) reaction mechanisms And Material parameters (材料参数) a) conductivity a) conductivity b) dielectric constants b) dielectric constants c) bulk generation-recombination reaction rates d) charge mobilities e) film thickness f) equilibrium conc. of charged species g) presence of pores and cracks
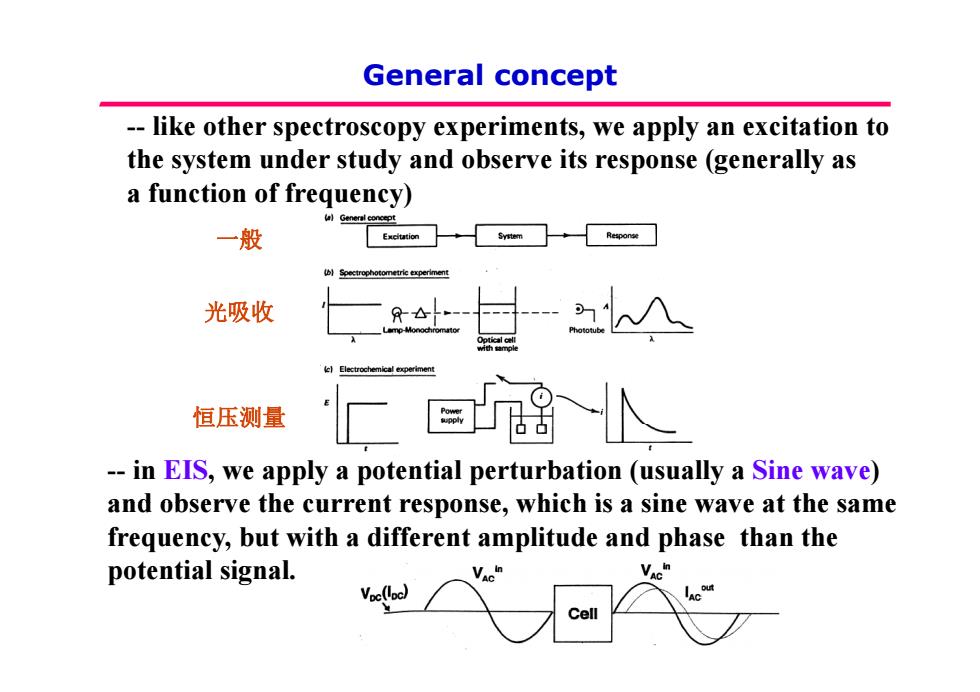
General concept -like other spectroscopy experiments,we apply an excitation to the system under study and observe its response (generally as a function of frequency) 一般 光吸收 恒压测量 厂留人 -in EIS,we apply a potential perturbation (usually a Sine wave) and observe the current response,which is a sine wave at the same frequency,but with a different amplitude and phase than the potential signal. Cell
General concept - like other spectroscopy experiments, we apply an excitation to the system under study and observe its response (generally as a f nction of freq enc ) a function of frequency) 一般 光吸收 恒压测量 - in EIS, we apply a potential perturbation (usually a Sine wave) and observe the current response which is a sine wave at the same 恒压测量 and observe the current response, which is a sine wave at the same frequency, but with a different amplitude and phase than the p g otential signal

Advantageous features of EIS -measurements are made under steady state conditions -all electrical parameters of the system can be determined in a single experiment -a simple measurement,easy to automate -characterize bulk and interfacial properties of all sorts of materials(conductors,semiconductors,ionic transport media, dielectrics(insulators)) -can be used to help verify mechanistic models -works even in low conductivity electrolyte solutions -signal can be averaged over long periods to achieve high precision -non-destructive Caution:Because it is easy to do,it is also easy to collect large amounts of meaningless data!(无效数据/错误数据)
Advantageous features of EIS - measurements are made under steady state conditions - all electrical parameters of the system can be determined in a single e periment single e xperiment - a simple measurement, easy to automate - characterize bulk and interfacial properties of all sorts of characterize bulk and interfacial properties of all sorts of materials (conductors, semiconductors, ionic transport media, dielectrics (insulators)) - can be used to help verify mechanistic models - works even in low conductivity electrolyte solutions - signal can be averaged over long periods to achieve high signal can be averaged over long periods to achieve high precision - non -destructive Caution: Because it is easy to do, it is also easy to collect large amounts of il d ! f mean ing less data!(无效数据 /错误数据)
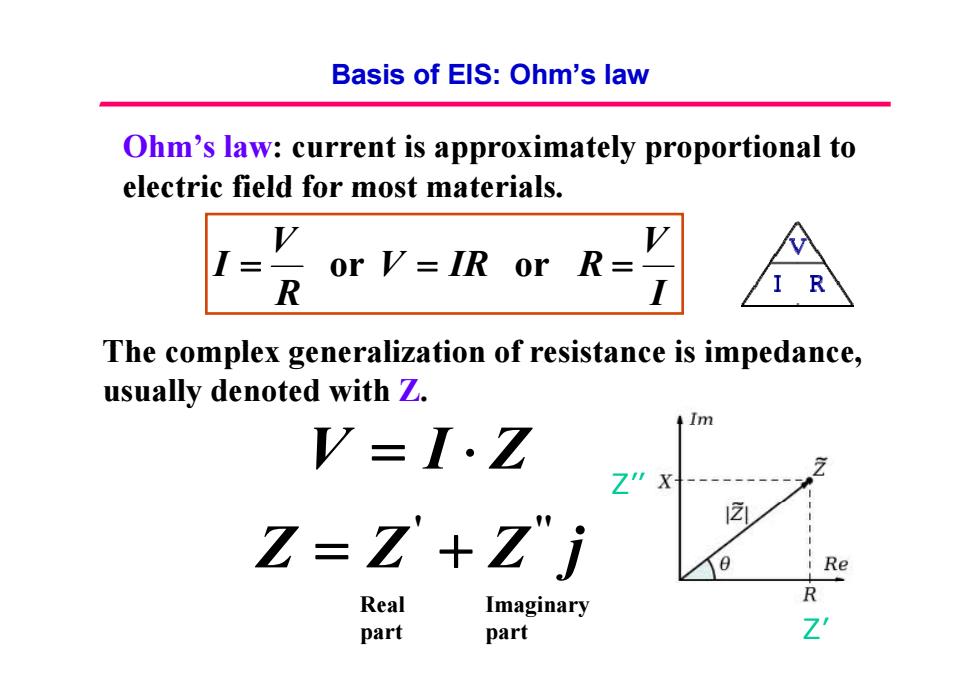
Basis of EIS:Ohm's law Ohm's law:current is approximately proportional to electric field for most materials. I= R or V=IR or R= I R The complex generalization of resistance is impedance, usually denoted with Z. Im V=I.Z X 2 Z-Z+7i Re Real R Imaginary part part Z
Basis of EIS: Ohm’s law Ohm’s law: current is approximately proportional to electric field for most materials electric field for most materials . V V IR R V I or or Th l li ti f i t i i d I V IR R R I or or The comp lex generalization o f res i s tance is impe dance, usually denoted with Z . V I Z Z’’ Z Z Z j ' '' Real part Imaginary part Z’
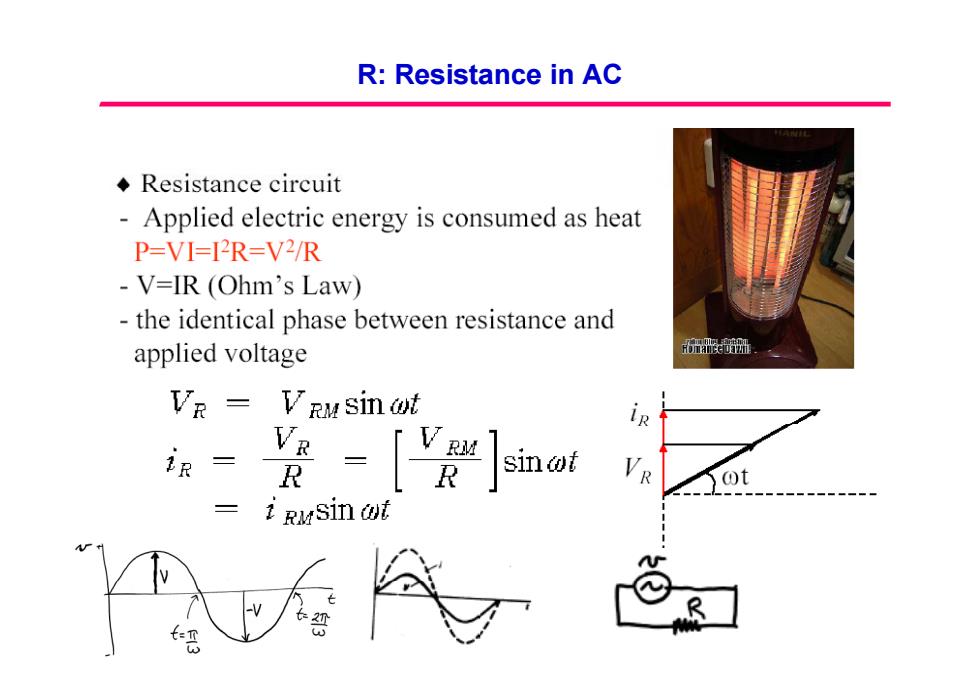
R:Resistance in AC ◆Resistance circuit Applied electric energy is consumed as heat P=VI=I2R=V2/R V=IR (Ohm's Law) the identical phase between resistance and applied voltage 布e班 VR Vrusinot V V助 R sinat VR -1 RuSin ot
R: Resistance in AC
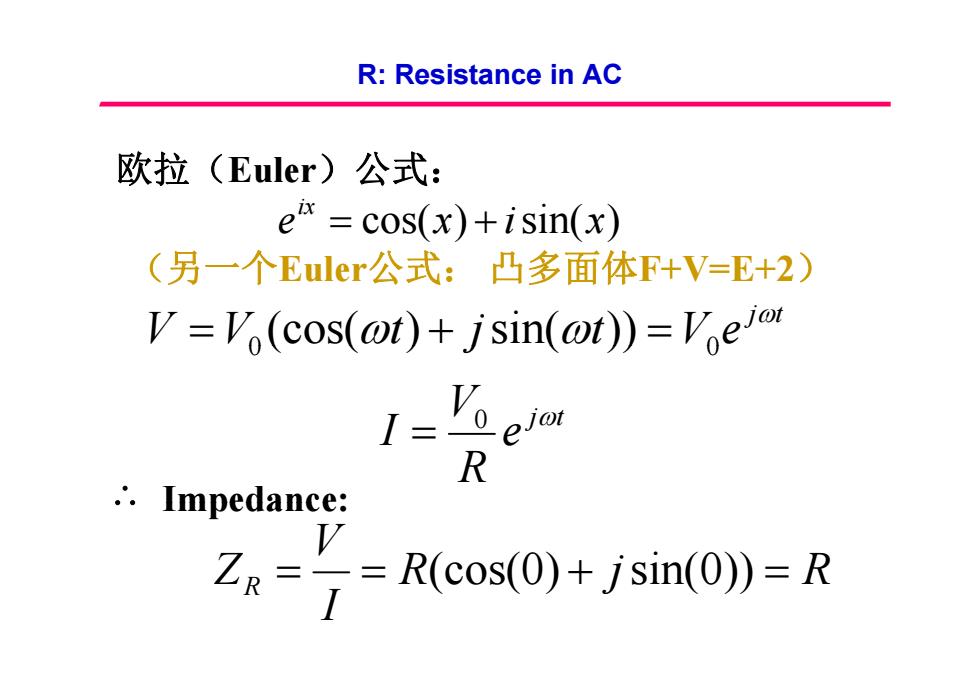
R:Resistance in AC 欧拉(Euler)公式: e=cos(x)+isin(x) (另一个Euler公式:凸多面体F+V=E+2) V=Vo(cos(@t)+jsin(@t))=Ve R ∴.Impedance: V Zg==R(cos(0)+jsin(0))=R
R: Resistance in AC 欧拉(Euler)公式: e cos(x) isin(x) ix (另 个一 Euler公式: 凸多面体F+V=E+2 F+V=E+2) j t V V t j t V e 0 0 0 (cos( ) jsin( )) 0 ( ( ) ( )) V j t I 0 jt e R I 0 Impedance: R j R V ZR R(cos(0) jsin(0)) R I ZR (cos(0) sin(0))
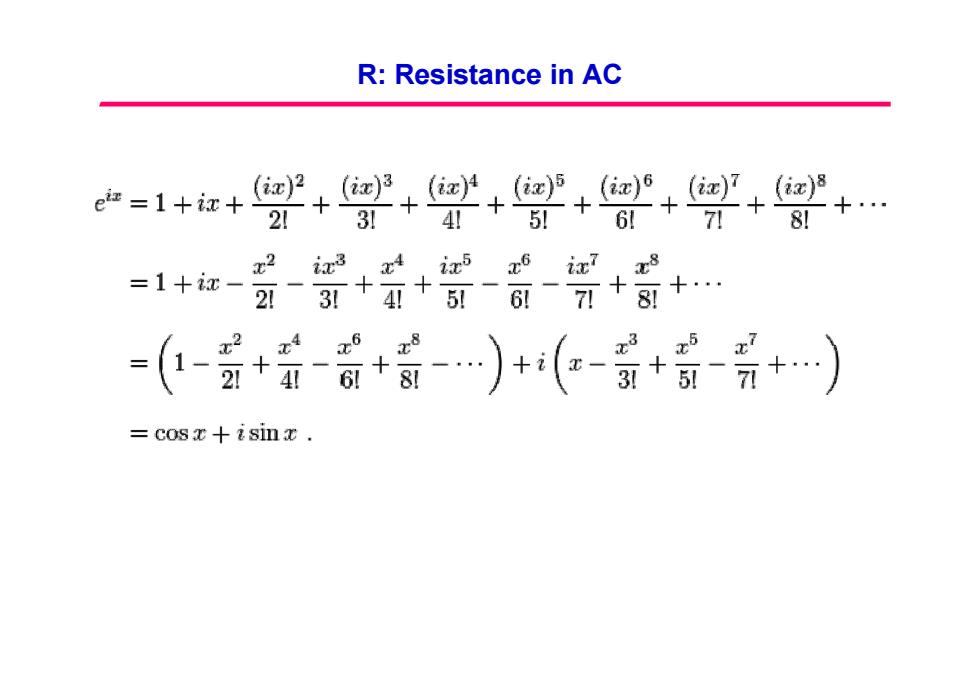
R:Resistance in AC e证=1+x+ +++++++ 21 311 4!51 61 7列 =1+ic- x2 ix3 xi ix5 x6 ix7 x8 2-31+4+5-6-71+8+. =(-豆+-+萄)+(-+罗-员+.) =c0sx十&simx
R: Resistance in AC