
18 Hydrogen and the rare gases 8.1 The discovery of the rare gases 18.2 Properties and uses of the rare gases -18.3 The existence and recovery of the rare gases -18.4 The rare gas compounds -18.5 Summarry on the main group elements
18.1 The discovery of the rare gases §18 Hydrogen and the rare gases 18.4 The rare gas compounds 18.3 The existence and recovery of the rare gases 18.2 Properties and uses of the rare gases 18.5 Summarry on the main group elements

18.1 The discovery of the rare gases Rare gases:He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Valence e:ns2npo “第三位小数的胜利” fractionate N2 from air:1.2572 gL Ar Chemical preparation of N2:1.2505gL-1
18.1 The discovery of the rare gases Ar Rare gases:He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn “第三位小数的胜利” fractionate N2 from air:1.2572 g•L-1 Chemical preparation of N2:1.2505g•L-1 Valence e-:ns 2np 6
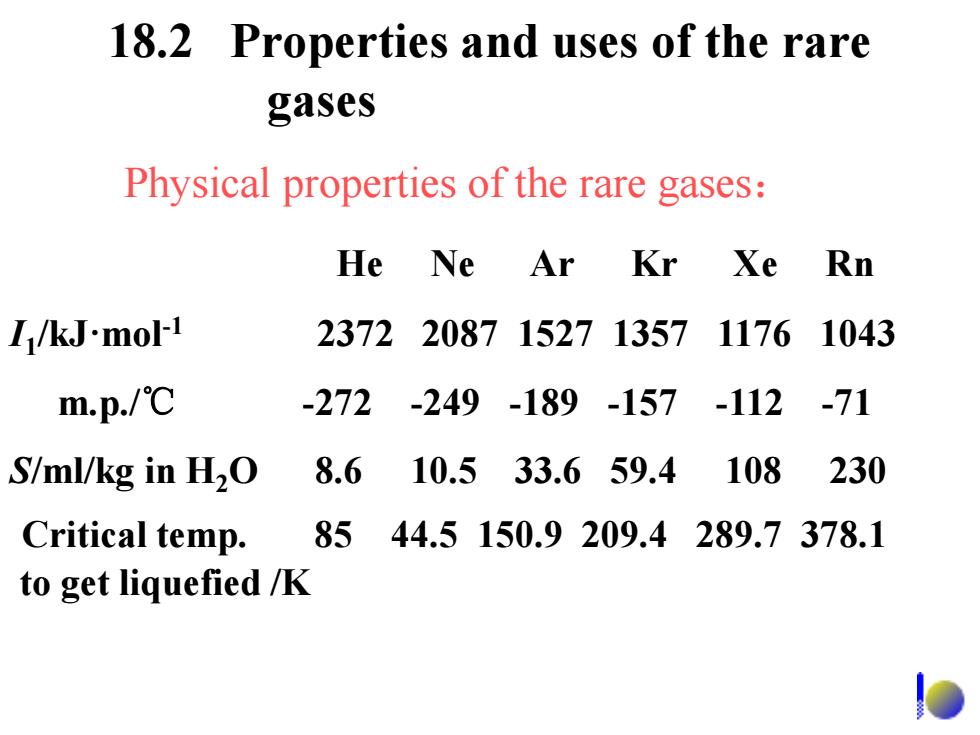
18.2 Properties and uses of the rare gases Physical properties of the rare gases: He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn I/kJ-mol-1 237220871527135711761043 m.p./℃ -272-249-189-157-112 -71 S/ml/kg in H2O 8.6 10.533.659.4 108 230 Critical temp. 8544.5150.9209.4289.7378.1 to get liquefied /K
18.2 Properties and uses of the rare gases He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn I1 /kJ·mol-1 2372 2087 1527 1357 1176 1043 m.p./℃ -272 -249 -189 -157 -112 -71 S/ml/kg in H2O 8.6 10.5 33.6 59.4 108 230 Physical properties of the rare gases: to get liquefied /K Critical temp. 85 44.5 150.9 209.4 289.7 378.1
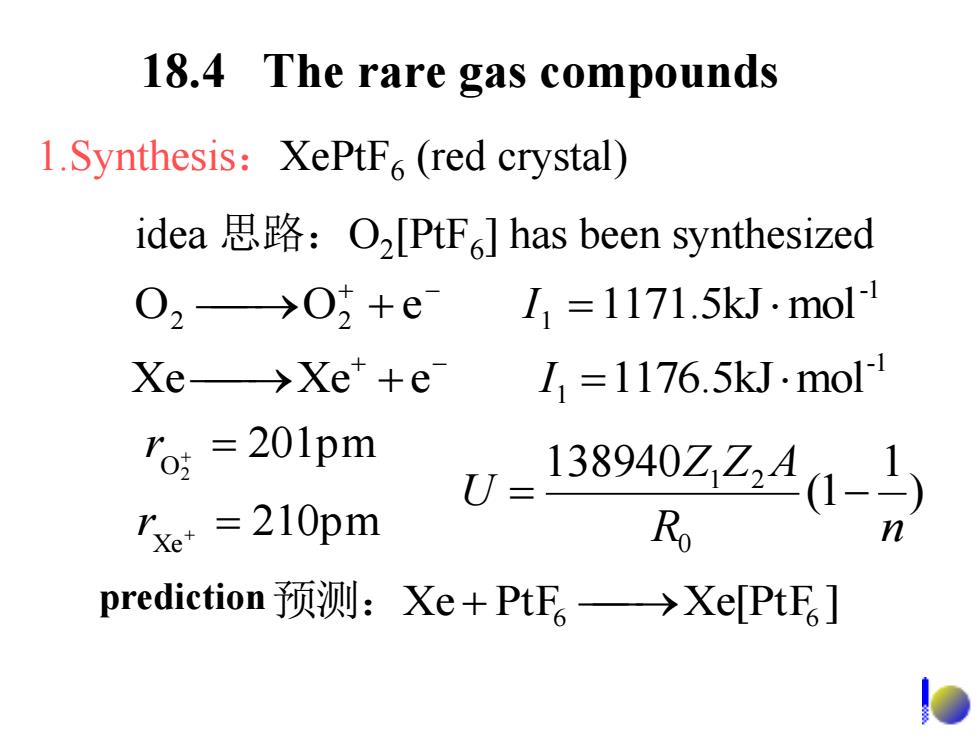
18.4 The rare gas compounds 1.Synthesis:XePtF(red crystal) idea思路:O2[PtF6]has been synthesized 02→0+eL1=1171.5 kJ.mol Xe→Xe+e 11=1176.5kJ.mol 'o=201pm 138940Z,Z41-〉 rxe =210pm R prediction预测:Xe+PtF。→Xe[PtE。]
18.4 The rare gas compounds 1.Synthesis:XePtF6 (red crystal) idea 思路:O2 [PtF6 ] has been synthesized Xe PtF Xe[PtF ] 预测: 6 6 ) 1 (1 138940 0 1 2 R n Z Z A U r Xe 210pm 201pm O2 r -1 Xe Xe e 1 1176.5kJmol I -1 O2 O2 e 1 1171.5kJmol I prediction

2.Molecular structure VSEPR theory: XeOF,V.P.-(8+0+4)-6 squarepyramidal 2 XeF,V.P.)7distroted octahedral Question:Describe the molecular shape of XeF,and XeF2
2. Molecular structure VSEPR theory: (8 6) 7 distrotedoctahedral 2 1 XeF V.P. (8 0 4) 6 square pyramidal 2 1 XeOF V.P. 6 4 Question:Describe the molecular shape of XeF4 and XeF2 ?
18.5 Summarry on the main group elements *18.5.1 The general properties of the s-block elements 18.5.2 Outline on the p-block elements 18.5.3 The property variations for compounds of p-block elements
§ 18.5 Summarry on the main group elements *18.5.1 The general properties of the s-block elements 18.5.2 Outline on the p-block elements 18.5.3 The property variations for compounds of p-block elements
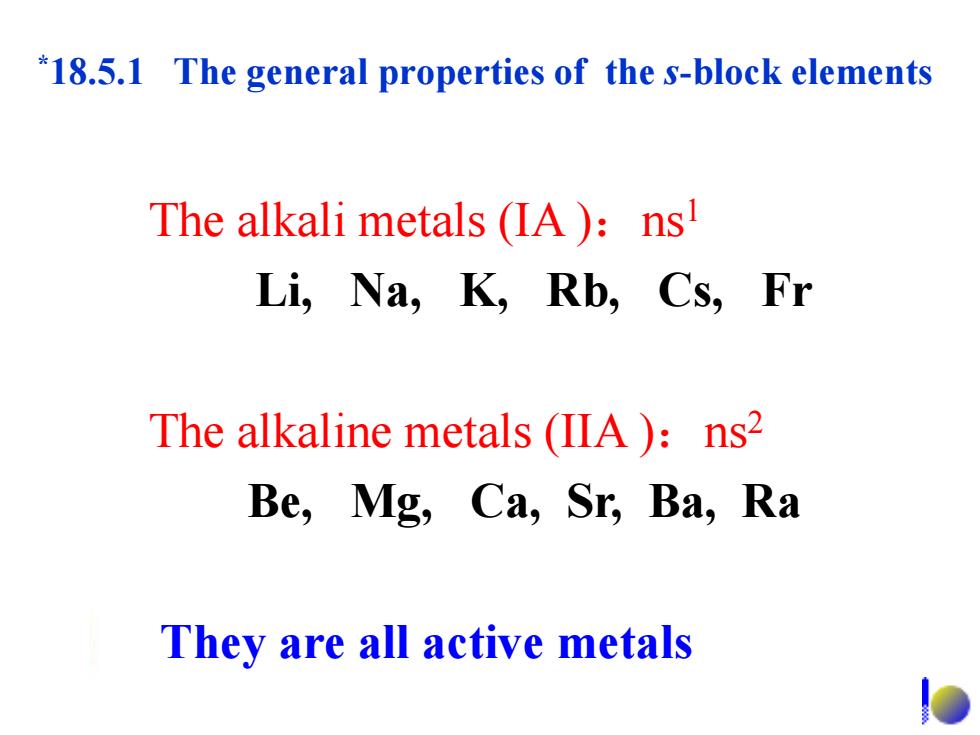
*18.5.1 The general properties of the s-block elements The alkali metals (IA):ns Li,Na,K,Rb,Cs,Fr The alkaline metals(IIA):ns2 Be,Mg,Ca,Sr,Ba,Ra They are all active metals D
*18.5.1 The general properties of the s-block elements The alkali metals (IA ):ns1 Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr The alkaline metals (IIA ):ns2 Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra They are all active metals

IA IIA electronegativity Decreasing ionization energy and Increasing metallicity Increasing atomic Li Be Na Mg K Ca Rb Sr and radius Cs Ba reductibility Decreasing atomic radius Decreasing metallicity and reductibility Increasing ionization energy and electronegativity
electronegativity Decreasing ionization energy and Increasing metallicity and reductibility Increasing atomic radius IA IIA Li Be Na Mg K Ca Rb Sr Cs Ba Decreasing atomic radius Decreasing metallicity and reductibility Increasing ionization energy and electronegativity
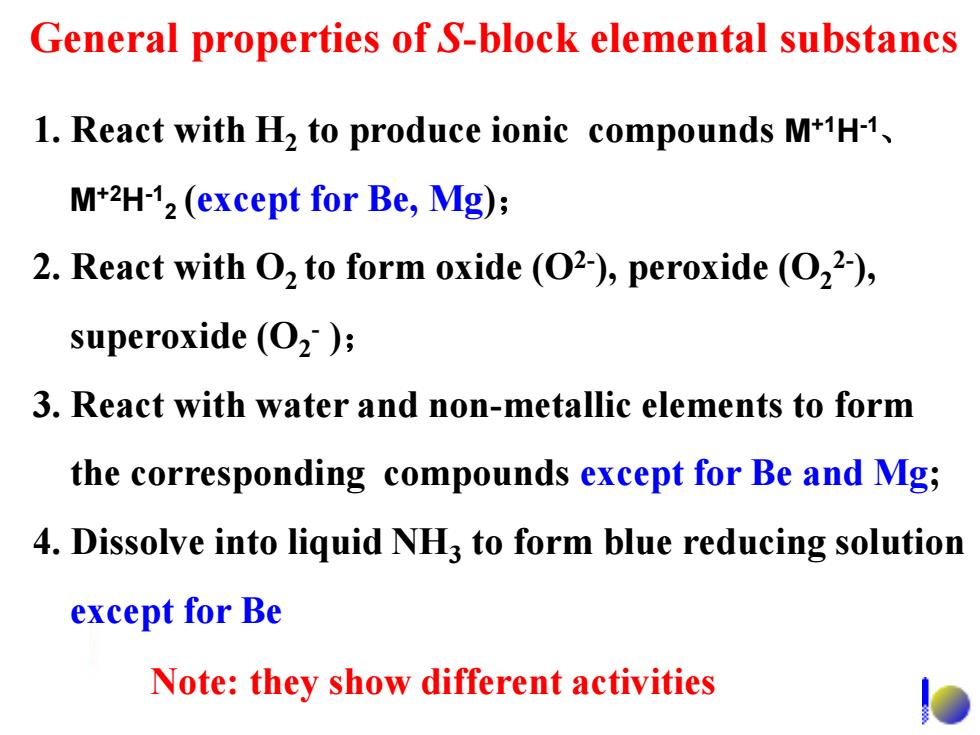
General properties of S-block elemental substancs 1.React with H2 to produce ionic compounds M+1H-1. M+2H-12(except for Be,Mg); 2.React with O2 to form oxide (O2),peroxide (O22), superoxide (O2); 3.React with water and non-metallic elements to form the corresponding compounds except for Be and Mg; 4.Dissolve into liquid NH3 to form blue reducing solution except for Be Note:they show different activities
1. React with H2 to produce ionic compounds M+1H-1 、 M+2H-1 2 (except for Be, Mg); 2. React with O2 to form oxide (O2- ), peroxide (O2 2- ), superoxide (O2 - ); 3. React with water and non-metallic elements to form the corresponding compounds except for Be and Mg; 4. Dissolve into liquid NH3 to form blue reducing solution except for Be General properties of S-block elemental substancs Note: they show different activities

18.5.2 Outline on the p-block elements 鳎 1 18 IA 13 1415 16 17 0 H IIIA IVA VA VIA VIA He Li Be B 0 F Ne 3 5 6 7 8 9 1011 12 Na g IIIB IVB VB VIB VIB 四 IB IIB Al Si P c1 Ax K Ca Se Ti Cr n Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Bx Kr Rb Y Zx b Mo Tc Ru R贴h Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Xe Cs Ba Lu Ha Ta Re 0s Pt Au Pb Bi Po At Rn Ra Lx Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 调系 Px Nb Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Ex Tm Yb 铜系 Th Pa Pu An Cm Bk cEsEm Md No
18.5.2 Outline on the p-block elements