
Preface 1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity 1.2 Features of chemical changes 1.3 History,revival and development of inorganic chemistry 1.4 How to study easily and efficiently inorganic chemistry
1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity 1.2 Features of chemical changes 1.3 History, revival and development of inorganic chemistry 1.4 How to study easily and efficiently inorganic chemistry Preface
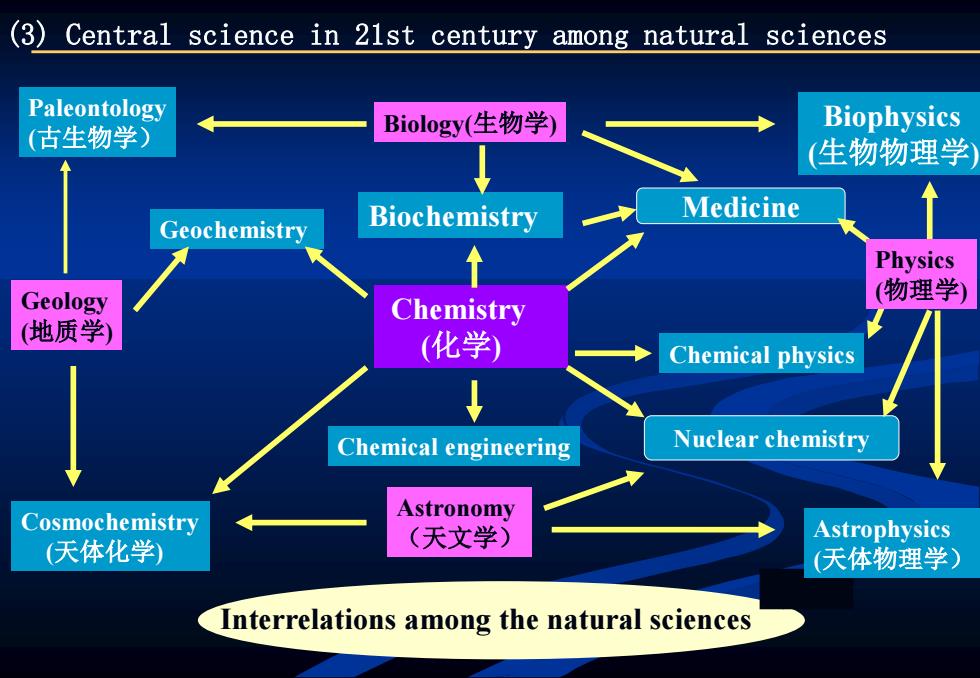
(3)Central science in 21st century among natural sciences Paleontology (古生物学) Biology(生物学) Biophysics (生物物理学 Biochemistry Medicine Geochemistry ↑ Physics Geology (物理学) Chemistry (地质学) (化学) Chemical physics Chemical engineering Nuclear chemistry Cosmochemistry Astronomy 天体化学) (天文学) Astrophysics (天体物理学) Interrelations among the natural sciences
Chemistry (化学) Biochemistry Medicine Nuclear chemistry Biophysics (生物物理学) Paleontology (古生物学) Biology(生物学) Chemical physics Chemical engineering Geology (地质学) Geochemistry Cosmochemistry (天体化学) Astronomy (天文学) Physics (物理学) Astrophysics (天体物理学) (3) Central science in 21st century among natural sciences Interrelations among the natural sciences

Preface 1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity 1.2 Features of chemical changes 1.3 History,revival and development of inorganic chemistry 1.4 How to study easily while efficiently inorganic chemistry
1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity 1.2 Features of chemical changes 1.3 History, revival and development of inorganic chemistry 1.4 How to study easily while efficiently inorganic chemistry Preface
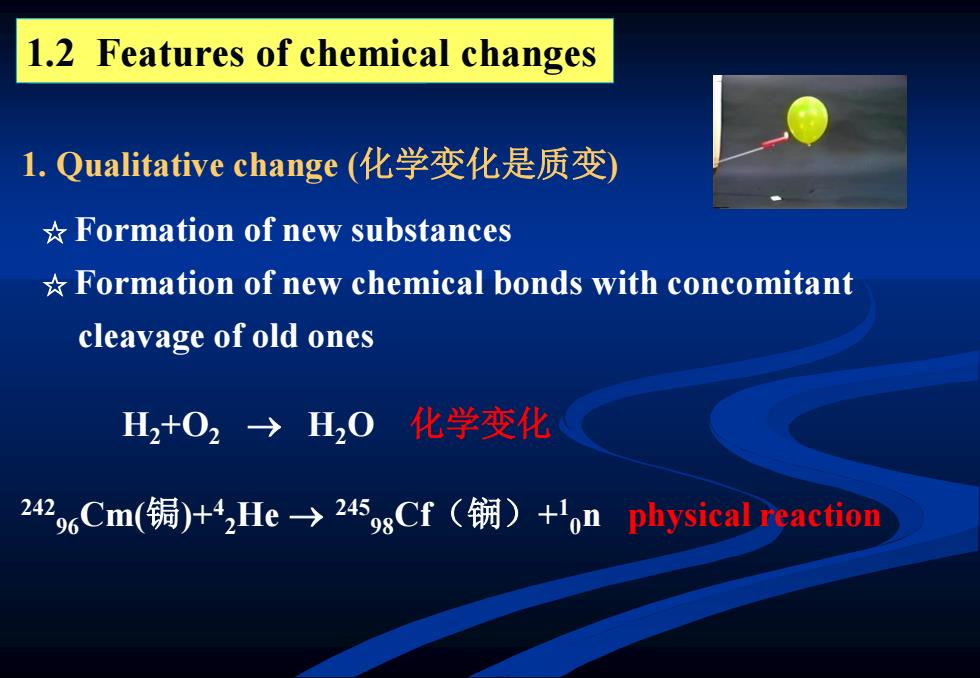
1.2 Features of chemical changes l.Qualitative change(化学变化是质变) *Formation of new substances *Formation of new chemical bonds with concomitant cleavage of old ones H2+02→H20 化学变化 242,oCm(锔)+He-→25gCf(锎)+'on physical reaction
1.2 Features of chemical changes 1. Qualitative change (化学变化是质变) 242 96Cm(锔)+4 2He 245 98Cf(锎)+ 1 0n physical reaction H2+O2 H2O 化学变化 ☆ Formation of new substances ☆ Formation of new chemical bonds with concomitant cleavage of old ones

2.Chemical reactions obey the law of mass conservation 化学反应过程中各元素的原子数和核外电子的总数没有变化 ,并且参与反应的各种物质之间有确定的计量关系 3.Chemical reactions always occur companying energy changes 化学键的断裂和形成,电子的转移伴随能量的吸收和释放,如 石油燃烧等
2. Chemical reactions obey the law of mass conservation 化学反应过程中各元素的原子数和核外电子的总数没有变化 ,并且参与反应的各种物质之间有确定的计量关系 3. Chemical reactions always occur companying energy changes 化学键的断裂和形成,电子的转移伴随能量的吸收和释放, 如 石油燃烧等

1.3.1 Classification of chemistry Classifications of chemistry in terms of objects studied 除了碳氢化合物及其衍生物外,以元素周期系和物质结构 inorganic 理论为基础研究一切元素及其化合物的学科。无机化学就 有稀士元素化学、配位化学、无机合成化学、生物无机化 学、固体无机化学、物理无机化学、金属有机化学、无机 材料化学等。 analytical 分析化学是研究物质化学组成的鉴定方法、测定方法、 测定步骤以及有关原理的学科。细分为:化学容量分析、 Chemistry 重量分析、光学分析、电化学分析、色谱分析、各种波谱 分析、结构分析、表面分析 包括化学热力学、化学动力学和结构化学三个方面。细分 physical 为:热化学、电化学、溶液化学、胶体化学、催化剂及催 化动力学、结构化学、量子化学、分子设计学、表面结构 化学 organic 有机化学是研究碳氢化合物及其衍生物的化学分支。 derivatives:polymer,nuclear,radiative biochem,et al
inorganic analytical physical organic Chemistry 除了碳氢化合物及其衍生物外,以元素周期系和物质结构 理论为基础研究一切元素及其化合物的学科。无机化学就 有稀土元素化学、配位化学、无机合成化学、生物无机化 学、固体无机化学、物理无机化学、金属有机化学、无机 材料化学等。 分析化学是研究物质化学组成的鉴定方法、测定方法、 测定步骤以及有关原理的学科。细分为:化学容量分析、 重量分析、光学分析、电化学分析、色谱分析、各种波谱 分析、结构分析、表面分析 包括化学热力学、化学动力学和结构化学三个方面。细分 为:热化学、电化学、溶液化学、胶体化学、催化剂及催 化动力学、结构化学、量子化学、分子设计学、表面结构 化学 有机化学是研究碳氢化合物及其衍生物的化学分支。 Classifications of chemistry in terms of objects studied 1.3.1 Classification of chemistry derivatives: polymer, nuclear, radiative biochem, et al

Today's thriving inorganic chemistry Sub-branches of inorganic chemistry: .Organometallics chem. 如环戊二烯基金属化合物,G.ilkinson .Coordination chem. Werner .Bio-inorganic chem. 如细胞离子通道,Peter Agre,.R.MacKinno业 .Solid state inorg.Chem. 如无机超导体 .Inorganic material chem. 磁性材料半导体材料超导材料纳米材料 .Non-metal chem.: 如硼烷化学、富勒烯化学 R.Curl,S.H.Kroto,R.Smalley .Supra-mol.chem. Lehn等 Inorg.chem.with brighter tomorrow
Today’s thriving inorganic chemistry •Organometallics chem. •Coordination chem. •Bio-inorganic chem. •Solid state inorg. Chem. •Inorganic material chem. •Non-metal chem.: •Supra-mol. chem. Sub-branches of inorganic chemistry: 如环戊二烯基金属化合物,G. Wilkinson 如细胞离子通道, Peter Agre, R. MacKinnon 如无机超导体 磁性材料,半导体材料,超导材料,纳米材料 如硼烷化学、富勒烯化学 R. Curl, S. H. Kroto, R. Smalley Lehn等 Werner

Outline of this course Chapter 0 Introduction (0.5) Part 1.Principles of chemical reactions (11) Chapter 1 The basic knowledge of chemistry (1) Chapter 2 Basic of chemical thermodynamics (6) Chapter 3 Chemical kineties Chapter 4 Chemical equilibrium Part 2.The basis of material structure (16) Chapter 5 Atomic structure and periodic law of elements (6) Chapter 6 Molecular structure and covalent bond theory (6) Chapter 7 Crystal structure (4)
Chapter 1 The basic knowledge of chemistry (1) Chapter 2 Basic of chemical thermodynamics (6) Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics Chapter 4 Chemical equilibrium (4) Outline of this course Part 1. Principles of chemical reactions (11) Chapter 5 Atomic structure and periodic law of elements (6) Chapter 6 Molecular structure and covalent bond theory (6) Chapter 7 Crystal structure (4) Part 2. The basis of material structure (16) Chapter 0 Introduction (0.5)

Outline of this course Part 3.The four types of chemical equilibria (22.5) Chapter 8 Acid-base equilibria (6) Chapter 9 Precipitation-solubility equilibria (3.5) Chapter 10 Reduction and oxidation (Redox)reactions (7) Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination chemistry (6 Part 4.Chemistry of the elements (22) Chapter 12 The alkali and alkaline earth metals (2) Chapter 13 The boron group elements (5)
Outline of this course Part 3. The four types of chemical equilibria (22.5) Chapter 8 Acid-base equilibria (6) Chapter 9 Precipitation-solubility equilibria (3.5) Chapter 10 Reduction and oxidation (Redox) reactions (7) Chapter 11 Basic of Coordination chemistry (6) Part 4. Chemistry of the elements (22) Chapter 12 The alkali and alkaline earth metals (2) Chapter 13 The boron group elements (5)

Outline of this course Chapter 14 The carbon group elements (6.5) Chapter 15 The nitrogen group elements (2.5) Chapter 16 T oxygen group elements (I)(5) Chapter 17 The halogen group elements (II)(3) Chapter 18 Hydrogen and rare gas (6.5) Chapter 19 The copper and zinc group elements (2.5) Chapter 20 The titanium and vanadium group elements (5 Chapter 21 The chromium and manganese group elements (3) Chapter 22 The iron and platinum group elements (2.5) Chapter 23 The lanthanide and actinide group elements (5) Chapter 24 The introduction on inorganic frontiers (3)
Outline of this course Chapter 16 T oxygen group elements (I) (5) Chapter 14 The carbon group elements (6.5) Chapter 15 The nitrogen group elements (2.5) Chapter 17 The halogen group elements (II) (3) Chapter 20 The titanium and vanadium group elements (5) Chapter 18 Hydrogen and rare gas (6.5) Chapter 19 The copper and zinc group elements (2.5) Chapter 21 The chromium and manganese group elements (3) Chapter 23 The lanthanide and actinide group elements (5) Chapter 22 The iron and platinum group elements (2.5) Chapter 24 The introduction on inorganic frontiers (3)