ME369 Modeling,Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture 141013 Week 5# Ch2.1~ Oct.13(M) Transfer function,block diagram HW2 due 2.3 Signal Flow Graphs Ch3.9, Oct.15(W) HW3 Linearization 3.10(4th) Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Ch5.1, Transient,first order systems 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient,second order systems Ch5.3
ME369 Modeling, Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture_141013 Week 5# Oct.13(M) Transfer function, block diagram Ch2.1 ~ 2.3 HW2 due Oct.15(W) Signal Flow Graphs Linearization Ch3.9, 3.10 (4th ) HW3 Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Transient, first order systems Ch5.1, 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient, second order systems Ch5.3

Block Diagram(pp.58) Functional block (block):is a symbol for the mathematical operation on the input signal to the block that produce the output. Transfer Function in block:components/elements... Arrow lines:signals and the signal flow. U(s) Transfer Function Y(s) G(s)
Transfer Function G(s) Block Diagram( pp. 58) Functional block (block): is a symbol for the mathematical operation on the input signal to the block that produce the output. Transfer Function in block: components/elements… Arrow lines: signals and the signal flow. U(s) Y(s)
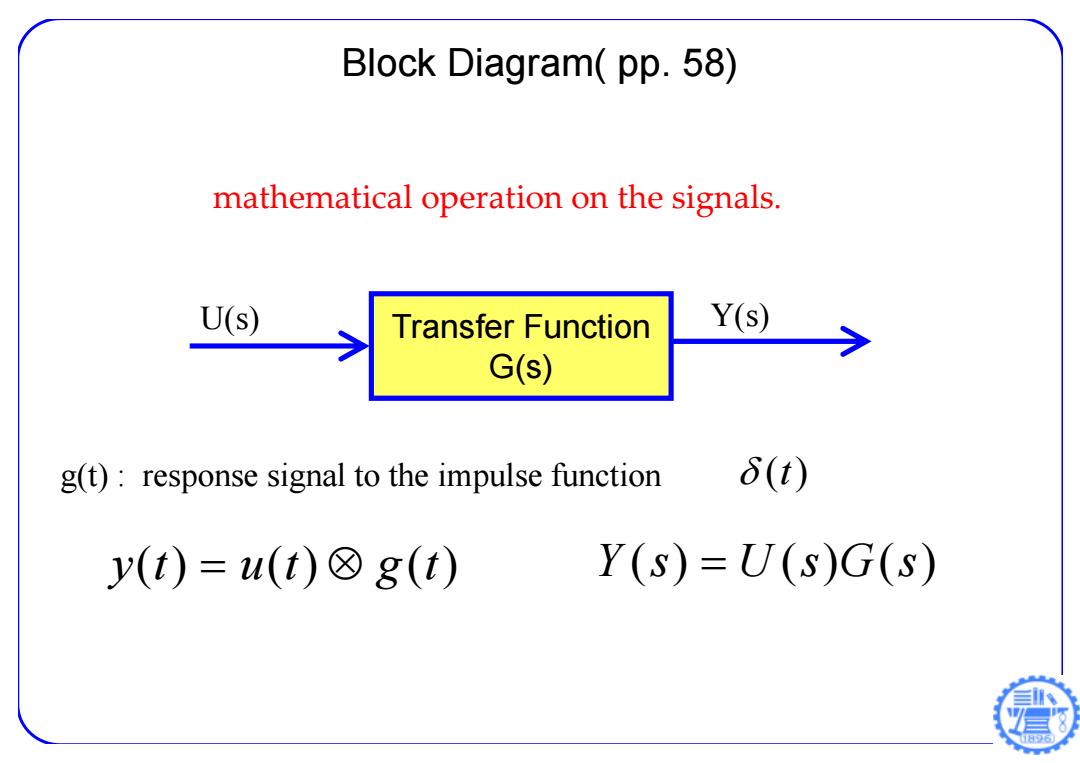
Block Diagram(pp.58) mathematical operation on the signals. U(s) Transfer Function Y(s) G(s) g(t):response signal to the impulse function 6(t) y(t)=u(t)图8(t) Y(s)=U(s)G(s)
Transfer Function G(s) Block Diagram( pp. 58) mathematical operation on the signals. U(s) Y(s) g(t) : response signal to the impulse function (t) y(t) u(t) g (t) Y (s) U (s)G(s)
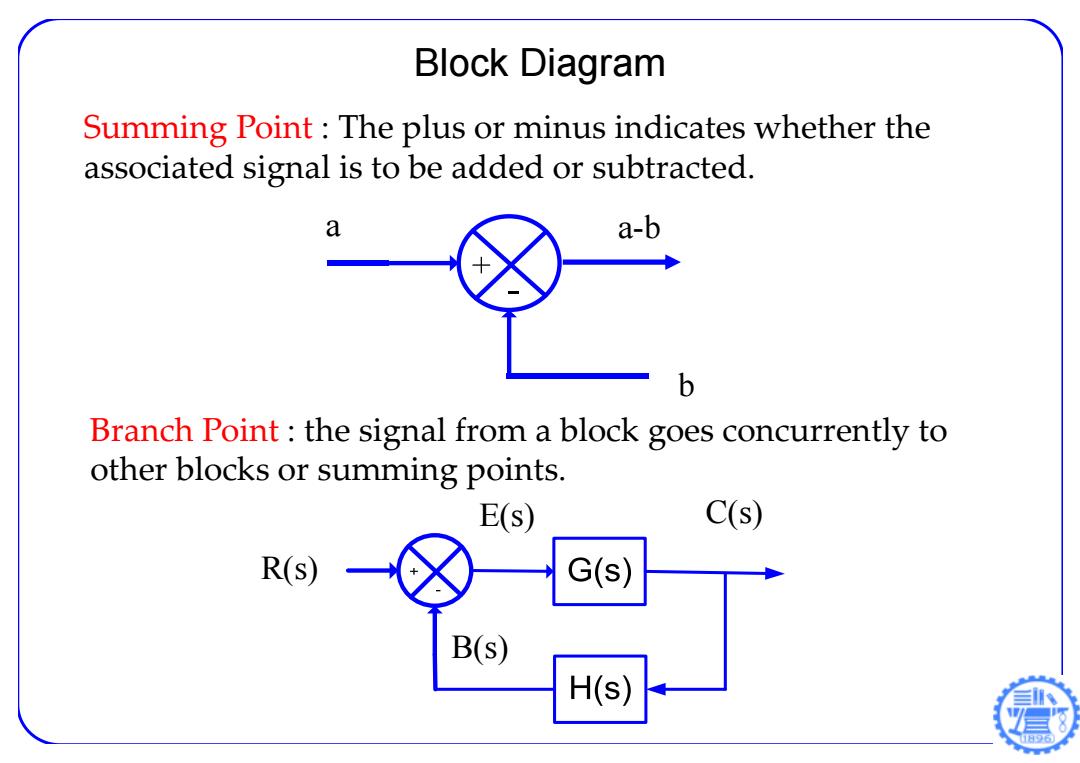
Block Diagram Summing Point:The plus or minus indicates whether the associated signal is to be added or subtracted. a a-b b Branch Point the signal from a block goes concurrently to other blocks or summing points. E(s) C(s) R(s) G(s) B(s) H(s)
Summing Point : The plus or minus indicates whether the associated signal is to be added or subtracted. a b a-b Block Diagram Branch Point : the signal from a block goes concurrently to other blocks or summing points. R(s) B(s) E(s) C(s)
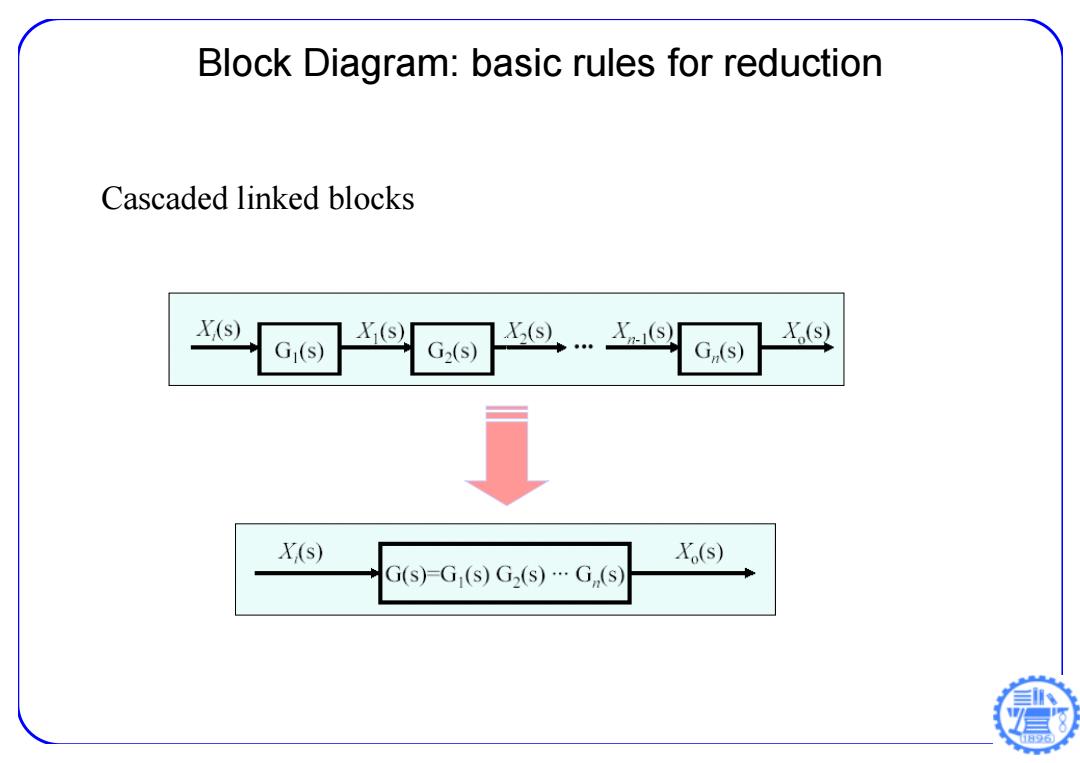
Block Diagram:basic rules for reduction Cascaded linked blocks X,(s) X(s) G2(s) X(s) G1(S) G,(s) X(s) Xo(s) G(s)=G (s)G2(s).G(s) 日96
Block Diagram: basic rules for reduction Cascaded linked blocks
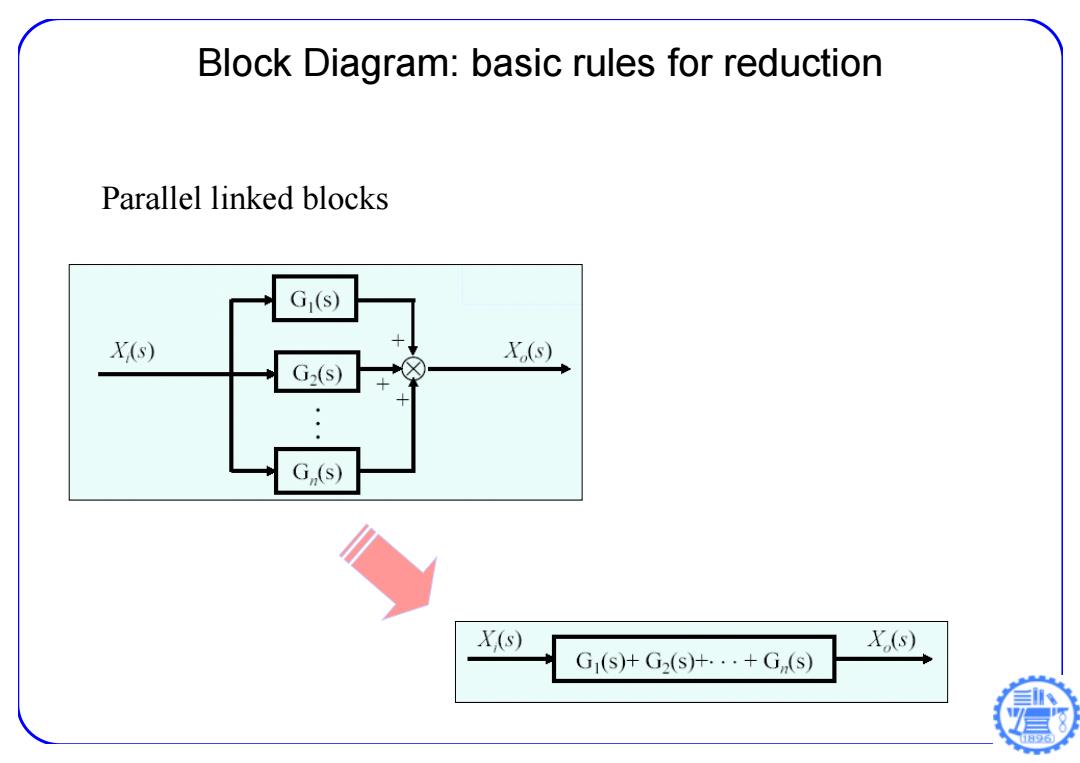
Block Diagram:basic rules for reduction Parallel linked blocks G1(S) X(s) X(s) G(s) G,(s) X(s) X(s) G1(s)G2(s)十.·+G(S)
Block Diagram: basic rules for reduction Parallel linked blocks
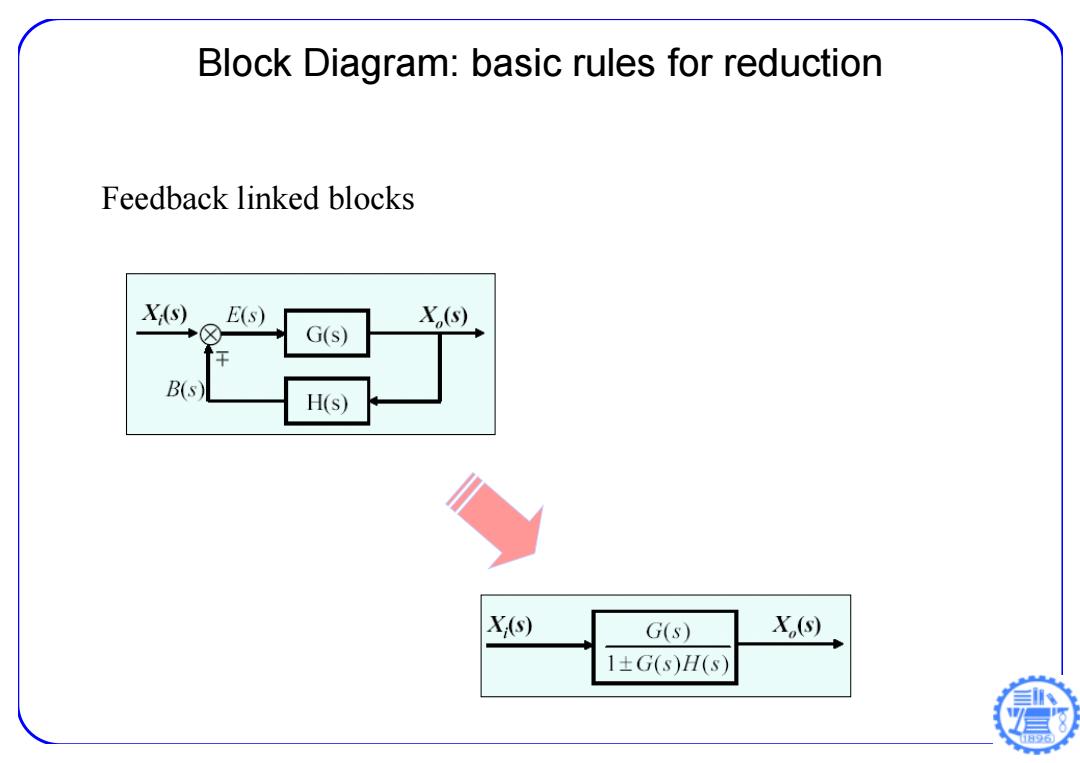
Block Diagram:basic rules for reduction Feedback linked blocks X(s) E(s) X,(s) ⑧ G(s) B(s) H(s) X(s) G(s) X,(s) 1±G(s)H(s)
Block Diagram: basic rules for reduction Feedback linked blocks

Block Diagram:basic rules for reduction Exchanging of summing points B A-B A-B+C B 4+C A+C-B B ←→ 4 A-B+C C 日96
Block Diagram: basic rules for reduction Exchanging of summing points
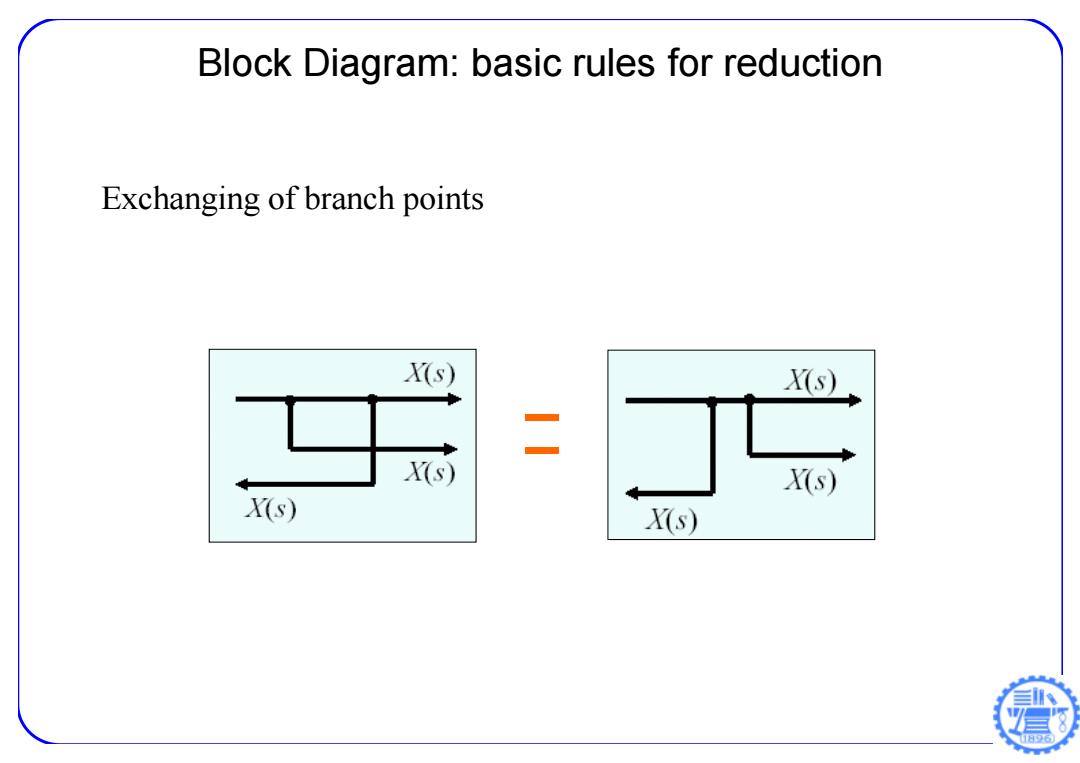
Block Diagram:basic rules for reduction Exchanging of branch points X(s) X(s) 二 X(s) X(s) X(s) X(s) 日96
Block Diagram: basic rules for reduction Exchanging of branch points
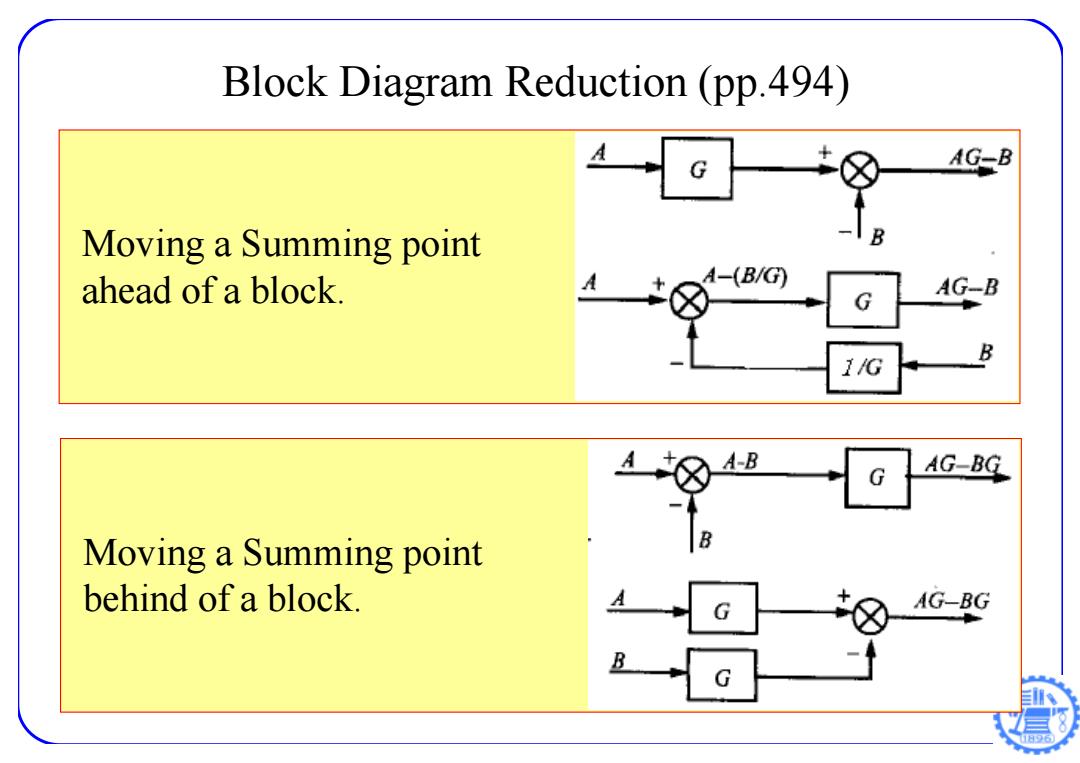
Block Diagram Reduction (pp.494) G AG-B Moving a Summing point B ahead of a block -(B/G AG-B G B 1/G A-B G AG-BG Moving a Summing point behind of a block. AG-BG 1日6
Block Diagram Reduction (pp.494) Moving a Summing point ahead of a block. Moving a Summing point behind of a block