ME369 Modeling,Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture 141020 Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Ch5.1, Transient,first order systems 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient,second order systems Ch5.3 Week 7# Oct.27(M) Transient,second order system, Ch5.3~5. spec. 6 Transient,higher order system Ch5.45. 0ct.29(W) HW4 Stability,Routh Criterion 7
ME369 Modeling, Analysis and System Control-A --Lecture_141020 Week 6# Oct.20(M) Quiz 1 Transient, first order systems Ch5.1, 5.2 Oct.22(W) Transient, second order systems Ch5.3 Week 7# Oct.27(M) Transient, second order system, spec. Ch5.3~5. 6 Oct.29(W) Transient, higher order system Stability, Routh Criterion Ch5.4~5. 7 HW4
Outline of today's PPT file Transient Response of First-Order Systems 一阶系统的瞬态响应 Step response (阶跃响应) Ramp response (斜坡响应) Impulse response (脉冲响应) Transient Response of Second-Order Systems 二阶系统的瞬态响应 -Step response Ramp response
Outline of today’s PPT file • Transient Response of First-Order Systems 一阶系统的瞬态响应 – Step response (阶跃响应 ) – Ramp response (斜坡响应 ) – Impulse response (脉冲响应 ) • Transient Response of Second-Order Systems 二阶系统的瞬态响应 – Step response – Ramp response
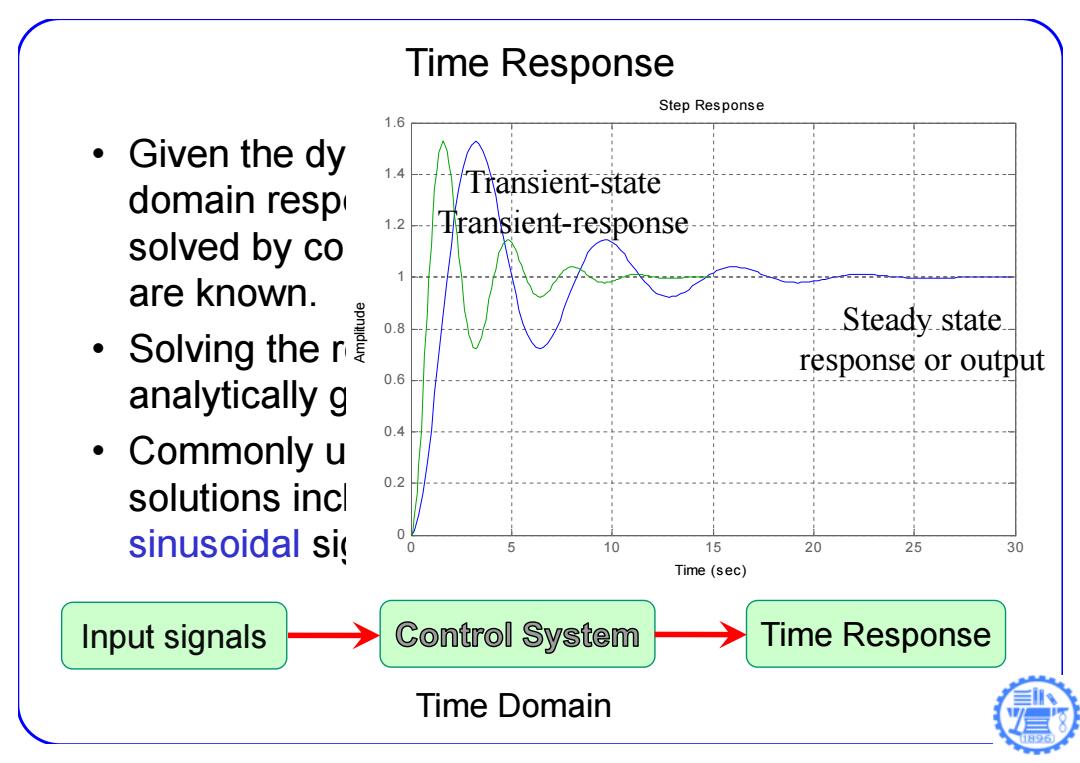
Time Response Step Response 1.6 . Given the dy 1.4 domain resp Transient-state 12Transient-response solved by co are known. Solving the r意 0.8 Steady state. o response or output analytically g 0.6 0.4 Commonly u 0.2 solutions incl sinusoidal sig 10 15 20 25 30 Time (sec) Input signals Control System Time Response Time Domain
Time Response • Given the dynamic model (TF or SS), the time domain response under arbitrary inputs can be solved by computers, if proper initial conditions are known. • Solving the response under simple input analytically gives important insight. • Commonly used input signals for analytical solutions include step, impulse, ramp, and sinusoidal signals. Time Response Time Domain Input signals Step Response Time (sec) Amplitude 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 Transient-state Transient-response Steady state response or output

Outline of today's PPT file Transient Response of First-Order Systems √Step response (阶跃响应) Ramp response Impulse response Transient Response of Second-Order Systems - Step response - Ramp response
Outline of today’s PPT file Transient Response of First-Order Systems Step response (阶跃响应 ) – Ramp response – Impulse response • Transient Response of Second-Order Systems – Step response – Ramp response
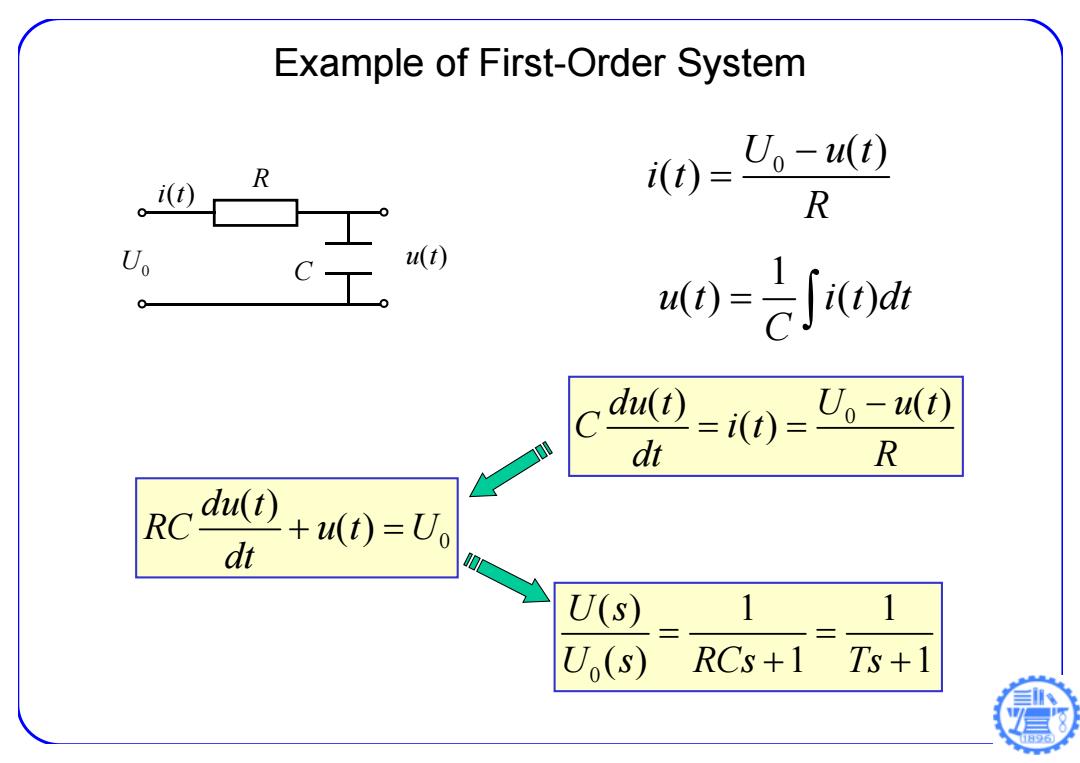
Example of First-Order System U。-(t) R R u(t) M0=己Jd 0-i0=。-0 dt R RC du(=Uo dt U(s) 1 1 U.(s) RCs+1 Ts+1
Example of First-Order System 0 ( ) ( ) U ut i t R 0 () () ( ) du t U u t C it dt R 0 ( ) ( ) du t RC u t U dt U0 u t( ) R C i t( ) 1 u t i t dt () () C 0 () 1 1 () 1 1 U s U s RCs Ts
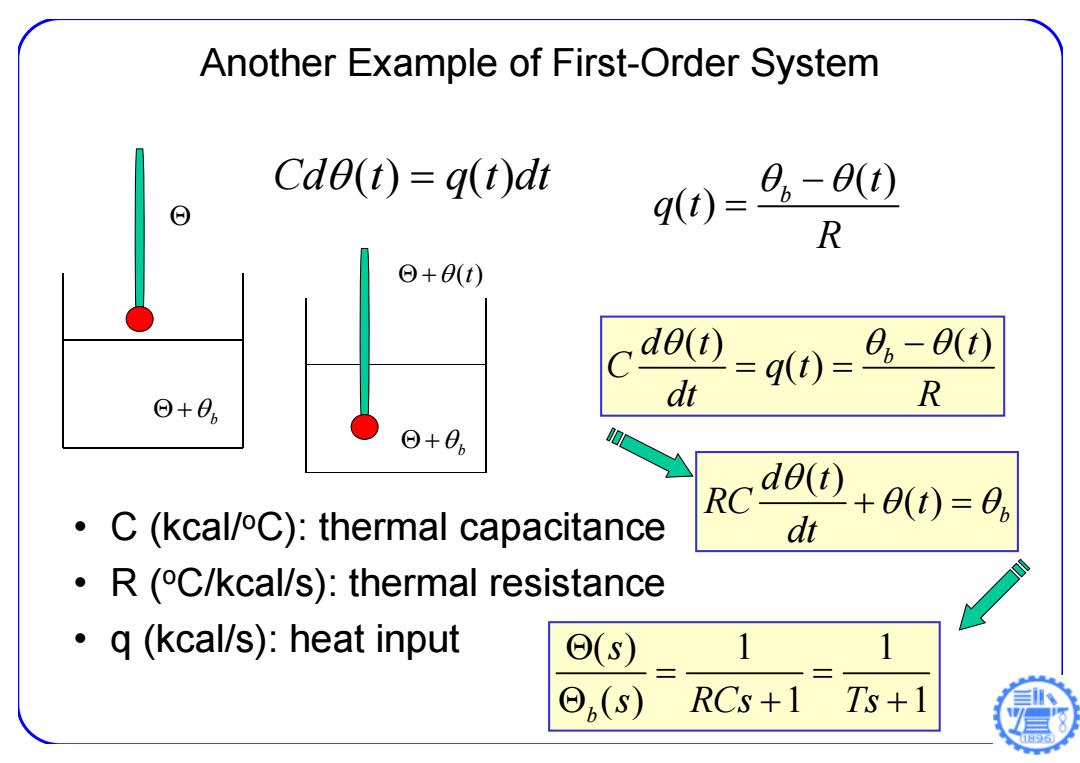
Another Example of First-Order System Cde(t)=q(t)dt 900=-6 R Θ+θ(t) de(t) =q0)= e。-(t) ⊙+0n dt R ⊙+0。 Rcd90+80)=9, C(kcal/C):thermal capacitance dt R(C/kcal/s):thermal resistance q (kcal/s):heat input 1 1 ⊙,(s) RCs+1 Ts+1
Another Example of First-Order System b ( )t Cd t q t dt () () • C (kcal/ oC): thermal capacitance • R ( oC/kcal/s): thermal resistance • q (kcal/s): heat input ( ) ( ) b t q t R () () ( ) b dt t C qt dt R ( ) ( ) b d t RC t dt b () 1 1 () 1 1 b s s RCs Ts
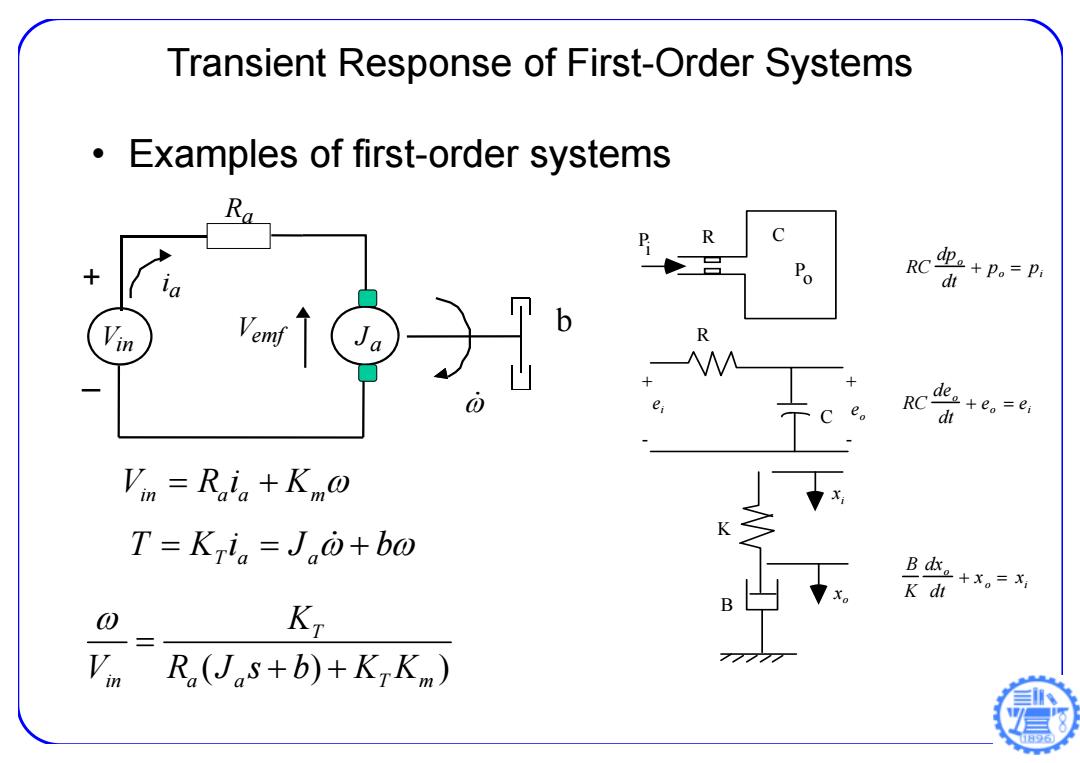
Transient Response of First-Order Systems Examples of first-order systems Ra R C + P RC- .=P b R R de。+e=ei d Vin =Rgia +Km@ T=Ki。=J.o+bw L Bdk。+x。=X K dt 0 KT 二 R(Jas+b)+KKm)
Transient Response of First-Order Systems • Examples of first-order systems + _ Vemf J a R a i a Vin b V Ri K in a a m T Ki J b Ta a () ) T in a a T m K V R Js b KK P i Po R C RC dpo dt po pi R C RC deo dt eo ei ei + - + - eo K B B K dxo dt x o xi xi xo
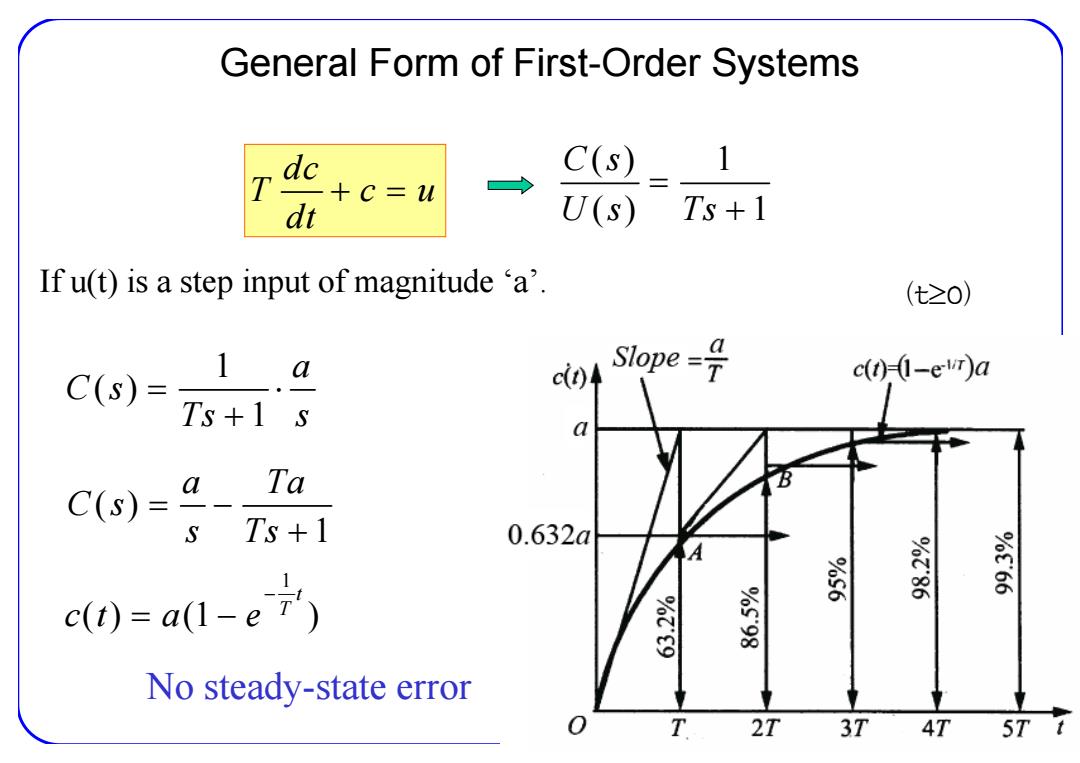
General Form of First-Order Systems C(s)_ T dc +c=u dt U(s) Ts+1 Ifu(t)is a step input of magnitude a'. (t≥0) a C(S)= 1 c04 ope=号 c(t)(-eir)a Ts+1s a Ta C(s)= a S Ts+1 0.632a 960.66 c0=a1-e不 261:P0 No steady-state error T 2T 3T 4T 577
General Form of First-Order Systems If u(t) is a step input of magnitude ‘a’. No steady-state error 1 ( ) 1 a C s Ts s (t 0) ( ) 1 a Ta C s s Ts 1 ( ) (1 )t T ct a e dc T cu dt () 1 () 1 C s U s Ts

c)4 Stope-号 c(1)-(1-evr)a Characteristics 1 a S plane 0.632a 968.66 0 O66 267:Pm Slope T 2T 3T 4T 577 dt l=0= c0=a1-e六) Treduce of transient portion response time distance toj T reduce of transient portionT response time distance to jo 响应时间 日6
T reduce of transient portion response time distance to j T reduce of transient portion response time distance to j 1 ( ) (1 ) t T ct a e (t0) Characteristics 1 T a e T a dt dc t t t T t 0 1 0 | | ( ) Slope 响应时间
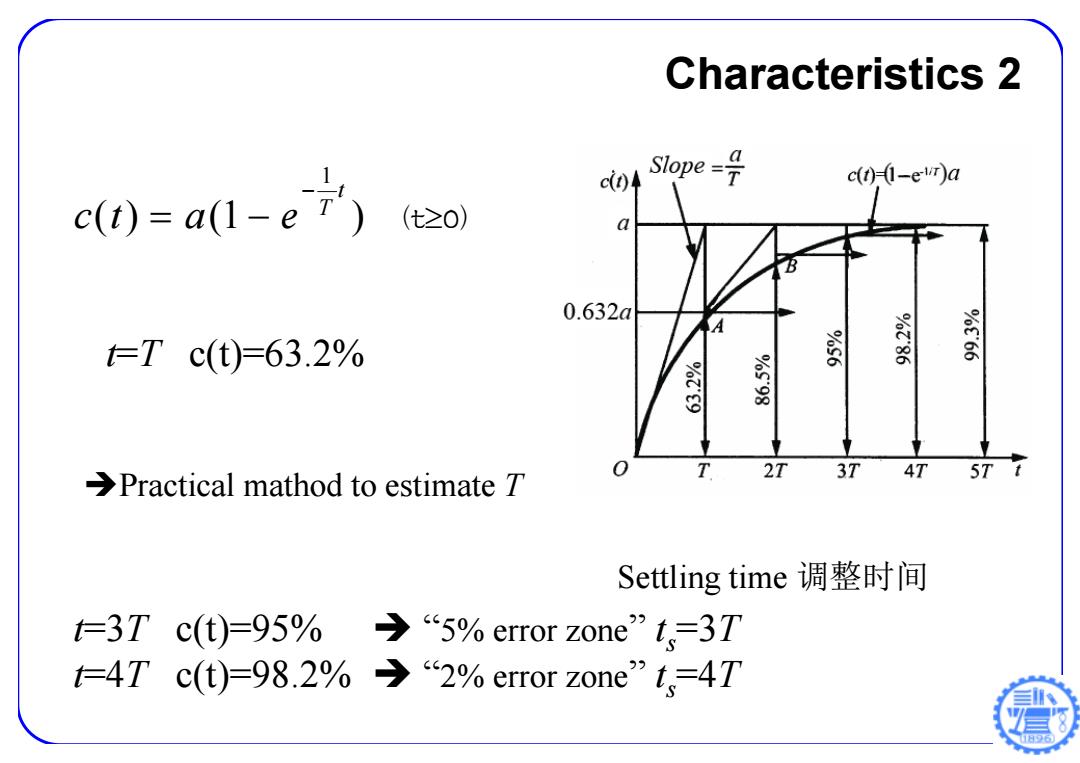
Characteristics 2 c(0=a1-e7) c)4 Sope-÷ c(t)1-evr)a 0.632a =Tc(t)=63.2% 茶 866.66 T Practical mathod to estimate T 2T 3T 4T 5T7 Settling time调整时间 t=3Tc(t)=95%· →“5%error zone'”t,=3T t仁4Tc(t)=98.2%→2%error zone'”t,=4T
1 ( ) (1 ) t T ct a e (t0) Characteristics 2 t=T c(t)=63.2% t=3T c(t)=95% “5% error zone” ts=3T t=4T c(t)=98.2% “2% error zone” ts=4T Practical mathod to estimate T Settling time 调整时间