
Chapter 13 Nutrient Cycling and Pollution 1
1 Chapter 13 Nutrient Cycling and Pollution

What we are going to learn in this chapter? ·Material cycling·Pollution -Vater水 -Eutrophication(富营养化) -Carbon碳 -Heavy metal toxicity -Nitrogen氮 -Alkaline wastes(碱性废弃物) -Phosphorous磷 -Acid rain -Sulfur硫 -Pesticides -Potassium钾 CFCs and the ozone layer radioactivity 2
2 What we are going to learn in this chapter? • Material cycling – Water 水 – Carbon 碳 – Nitrogen 氮 – Phosphorous 磷 – Sulfur 硫 – Potassium 钾 • Pollution – Eutrophication(富营养化) – Heavy metal toxicity – Alkaline wastes(碱性废弃物) – Acid rain – Pesticides – CFCs and the ozone layer – radioactivity
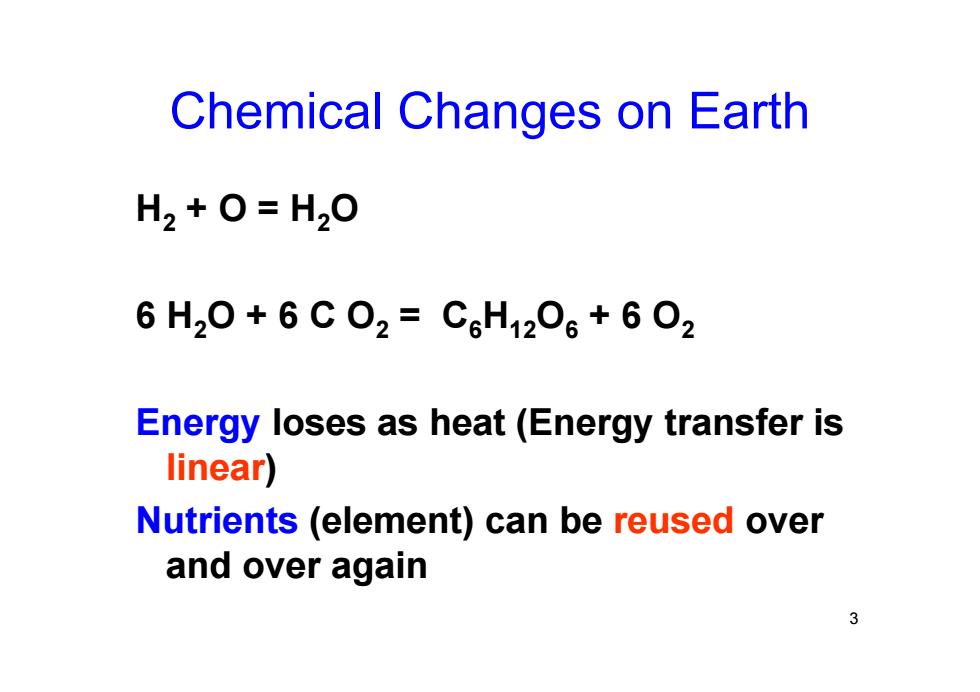
Chemical Changes on Earth H2+0=H20 6H20+6C02=C6H1206+602 Energy loses as heat(Energy transfer is linear) Nutrients (element)can be reused over and over again
3 Chemical Changes on Earth H 2 + O = H 2 O 6 H 2O + 6 C O 2 = C 6 H12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Energy loses as heat (Energy transfer is linear ) Nutrients (element) can be reused over and over again

Material Cycling and G0 0 energy transfer 。8380o Abiotic chemicals (carbon dioxide, Heat Heat Solar oxygen,nitrogen, energy minerals) Heat Decomposers Producers (bacteria,fungus) (plants) Consumers (herbivores Heat carnivores) Heat 2002 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
4 Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Abiotic chemicals (carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen, minerals) Producers (plants) Decomposers (bacteria, fungus) Consumers (herbivores, carnivores) Solar energy Material Cycling and energy transfer
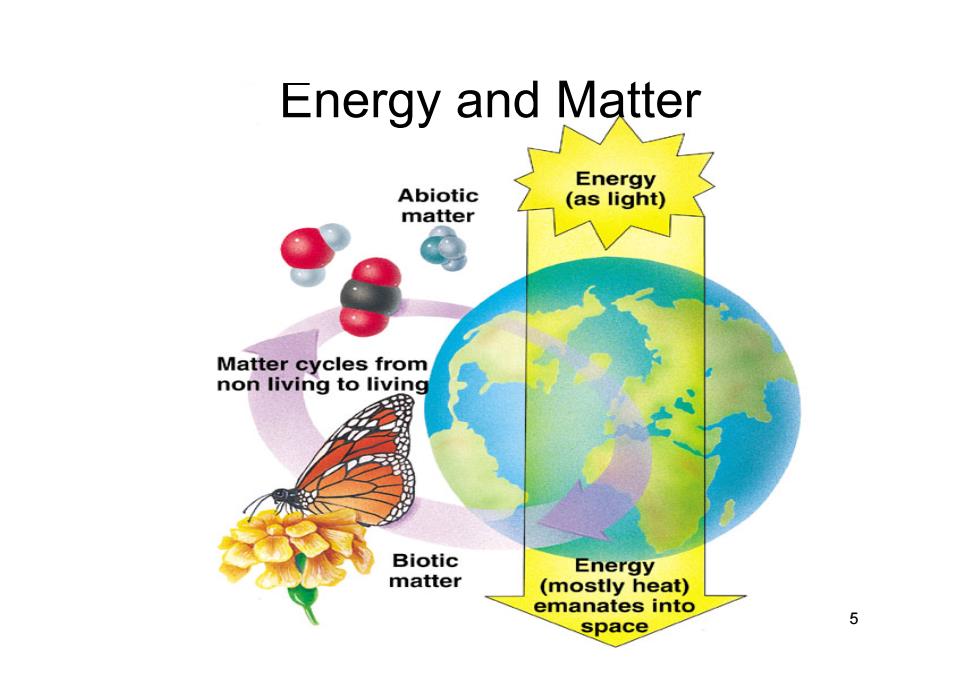
Energy and Matter Energy Abiotic (as light) matter Matter cycles from non living to living Biotic Energy matter (mostly heat) emanates into space
5 Energy and Matter
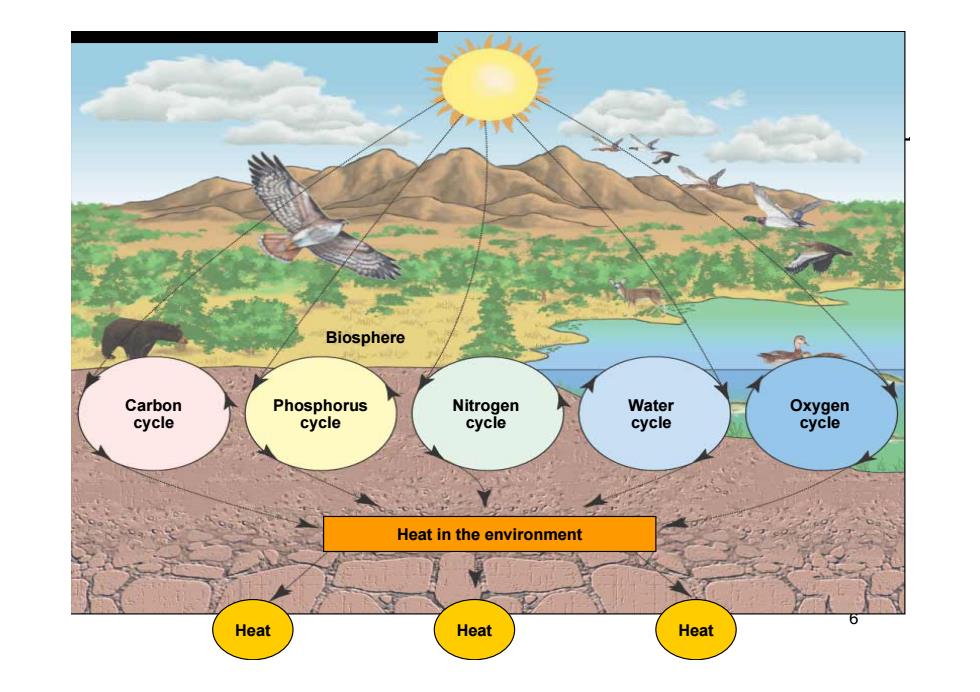
Biosphere Carbon Phosphorus Nitrogen Water Oxygen cycle cycle cycle cycle cycle Heat in the environment Heat Heat Heat
6 Biosphere Carbon cycle Phosphorus cycle Nitrogen cycle Water cycle Oxygen cycle Heat in the environment Heat Heat Heat
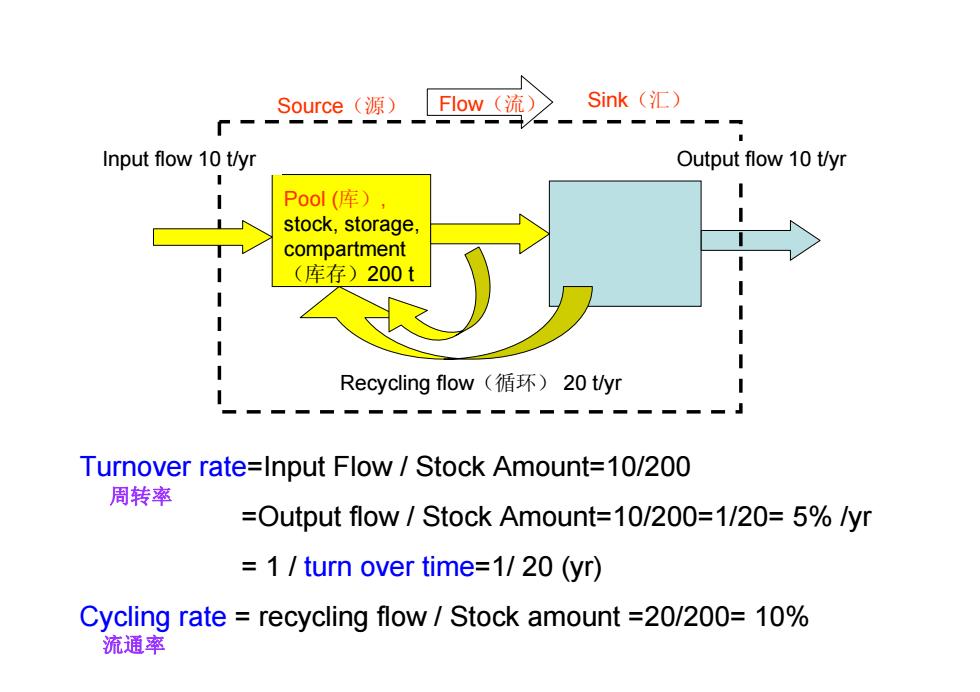
Source(源)FIow(流)> -_Source Sink(汇) Input flow 10 t/yr Output flow 10 t/yr Pool(库) stock,storage. compartment (库存)200t 1 1 Recycling flow(循环)20tyr Turnover rate=Input Flow/Stock Amount=10/200 周转率 =Output flow Stock Amount=10/200=1/20=5%/yr 1 turn over time=1/20(yr) Cycling rate recycling flow Stock amount =20/200=10% 流通率
7 Pool (库), stock, storage, compartment (库存)200 t Source(源) Flow(流) Sink(汇) Recycling flow(循环) 20 t/yr Input flow 10 t/yr Output flow 10 t/yr Turnover rate=Input Flow / Stock Amount=10/200 =Output flow / Stock Amount=10/200=1/20= 5% /yr = 1 / turn over time=1/ 20 (yr) Cycling rate = recycling flow / Stock amount =20/200= 10% 周转率 流通率

库(poo1) 物质在运动过程中被暂时固定、贮存 的场所,称为库 •生态系统的各组分都是物质循环的库。 等分为(著整赛:果洋林本繁转 等, 永体库。 流(f1ow) ·能量和物质通过食物链形成的转移运动状态,为流。 ·生态系统中主要的流有物质流、能量流和信息流。 ·生态系统要获得高的生产力,就要使系统内的能量和 物质的流量大,流速快且畅通无阻。 8
8 库(pool)——物质在运动过程中被暂时固定、贮存 的场所,称为库。 •生态系统的各组分都是物质循环的库。 •可分为植物库(农作物、蔬菜、果树、林木、牧草 等),动物库(畜、禽,虫等)、土壤库、大气库和 水体库。 流(flow) • 能量和物质通过食物链形成的转移运动状态,为流。 • 生态系统中主要的流有物质流、能量流和信息流。 • 生态系统要获得高的生产力,就要使系统内的能量和 物质的流量大,流速快且畅通无阻
源(source)和汇(sink)。源是产生和释放物质的 库,汇是吸收和固定物质的库。如化石燃料 燃烧是温室气体CO,的一个重要的源,海洋 则是CO,的汇之一。 C02 源 9
9 源(source )和汇(sink)。源是产生和释放物质的 库,汇是吸收和固定物质的库。如化石燃料 燃烧是温室气体CO2的一个重要的源,海洋 则是CO2 的汇之一。 源 汇 CO2

流通率(Cycling rate):物质在生态系统单位 面积(或单位体积)和单位时间的移动量。 流通量是指单位时间、单位面积内通过的营养物 质的绝对值。 用周转时间(turnover time)和周转率 (turnover rate)表示有关库的相对重要性。 ·周转时间(turnover time)表示该库的全部物质全部 更换一次平均需要的时间 ·周转时间=库中营养物质总量/流通率 ·周转率=1/周转时间 ·周转率=流通率/库中营养物质总量 10
10 流通率(Cycling rate):物质在生态系统单位 面积(或单位体积)和单位时间的移动量。 流通量是指单位时间、单位面积内通过的营养物 质的绝对值。 用周转时间(turnover time)和周转率 (turnover rate)表示有关库的相对重要性。 •周转时间(turnover time)表示该库的全部物质全部 更换一次平均需要的时间 •周转时间=库中营养物质总量/流通率 •周转率=1/周转时间 •周转率=流通率/库中营养物质总量