
中国科学院数学与系统科学研究院 Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science Chinese Academy of Sciences Introduction to Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong March 17,2021
Introduction to Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong March 17, 2021

CONTENTS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Quantitative Features of Modern Economics 1.3 Mathematical Modeling 1.4 Empirical Validation 1.5 lllustrative Examples 1.6 Limitations of Econometric Analysis ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 2
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 2 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Quantitative Features of Modern Economics 1.3 Mathematical Modeling 1.4 Empirical Validation 1.5 Illustrative Examples 1.6 Limitations of Econometric Analysis CONTENTS

Introduction Econometrics has become an integrated part of teaching and research in modern economics. Core courses in economics: microeconomics macroeconomics (financial econometrics economics) ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 3
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 3 Introduction • Econometrics has become an integrated part of teaching and research in modern economics. • Core courses in economics: microeconomics macroeconomics econometrics (financial economics)
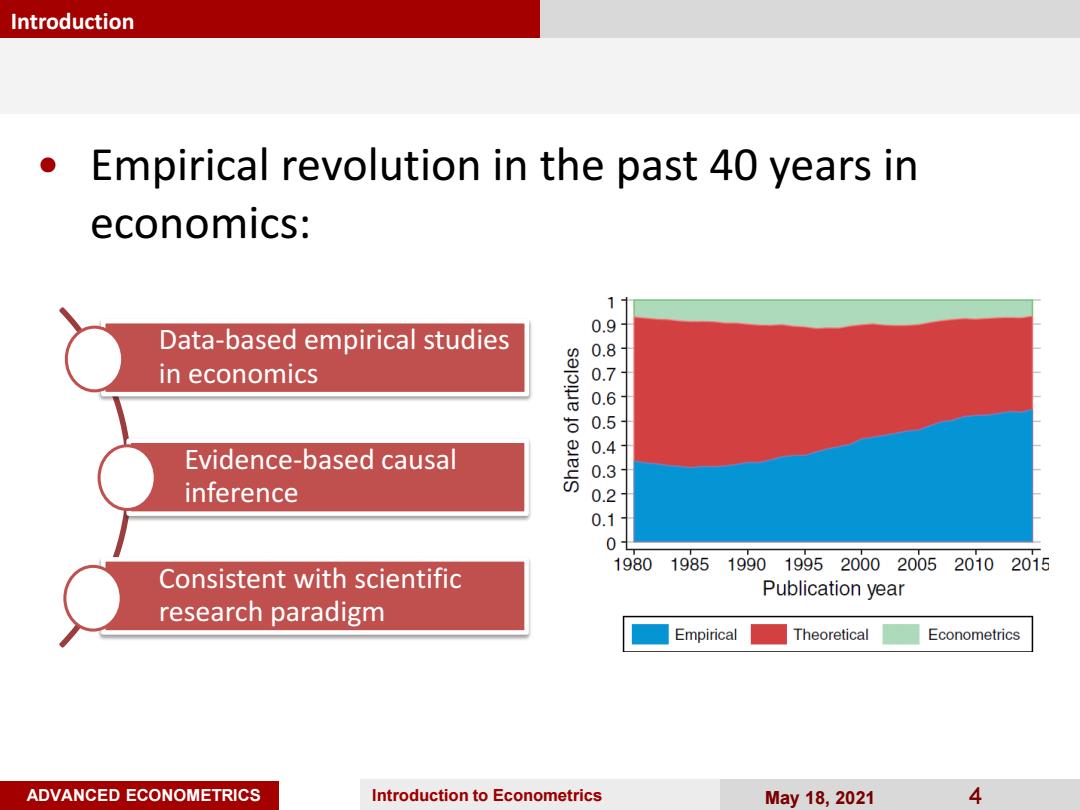
Introduction Empirical revolution in the past 40 years in economics: 1 Data-based empirical studies 0.9 in economics 8s 0.5 Evidence-based causal 0.4 0.3 inference 0.1 0 1980 1985199019952000200520102015 Consistent with scientific Publication year research paradigm Empirical Theoretical Econometrics ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 4
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 4 Introduction • Empirical revolution in the past 40 years in economics: Data-based empirical studies in economics Evidence-based causal inference Consistent with scientific research paradigm

Introduction Key differences of empirical studies between economics and natural sciences: Controlled experiements in natural sciences Nonexperimental nature of economic system and economic data The importance of econometrics as a general methodology of empirical research in economics has been increasingly recognized over the past several decades ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 5
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 5 Introduction • Key differences of empirical studies between economics and natural sciences: • The importance of econometrics as a general methodology of empirical research in economics has been increasingly recognized over the past several decades Controlled experiements in natural sciences Nonexperimental nature of economic system and economic data

Introduction Big data in economics: Traditional structured data New structured data:(e.g.)interval-valued data,symbolic data,functional data Unstructured data,e.g.,text data,photo data,video data,audio data ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 6
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 6 Introduction • Big data in economics: Traditional structured data New structured data: (e.g.) interval-valued data, symbolic data, functional data Unstructured data, e.g., text data, photo data, video data, audio data

Introduction New forms of data call for innovation and development of theory,methods and tools in modern econometrics. Heatmap for each joint Height Growth tor 10 Giris e 60 a 30 ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 7
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 7 Introduction • New forms of data call for innovation and development of theory, methods and tools in modern econometrics

CONTENTS 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Quantitative Features of Modern Economics 1.3 Mathematical Modeling 1.4 Empirical Validation 1.5 lllustrative Examples 1.6 Limitations of Econometric Analysis ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 8
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 8 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Quantitative Features of Modern Economics 1.3 Mathematical Modeling 1.4 Empirical Validation 1.5 Illustrative Examples 1.6 Limitations of Econometric Analysis CONTENTS
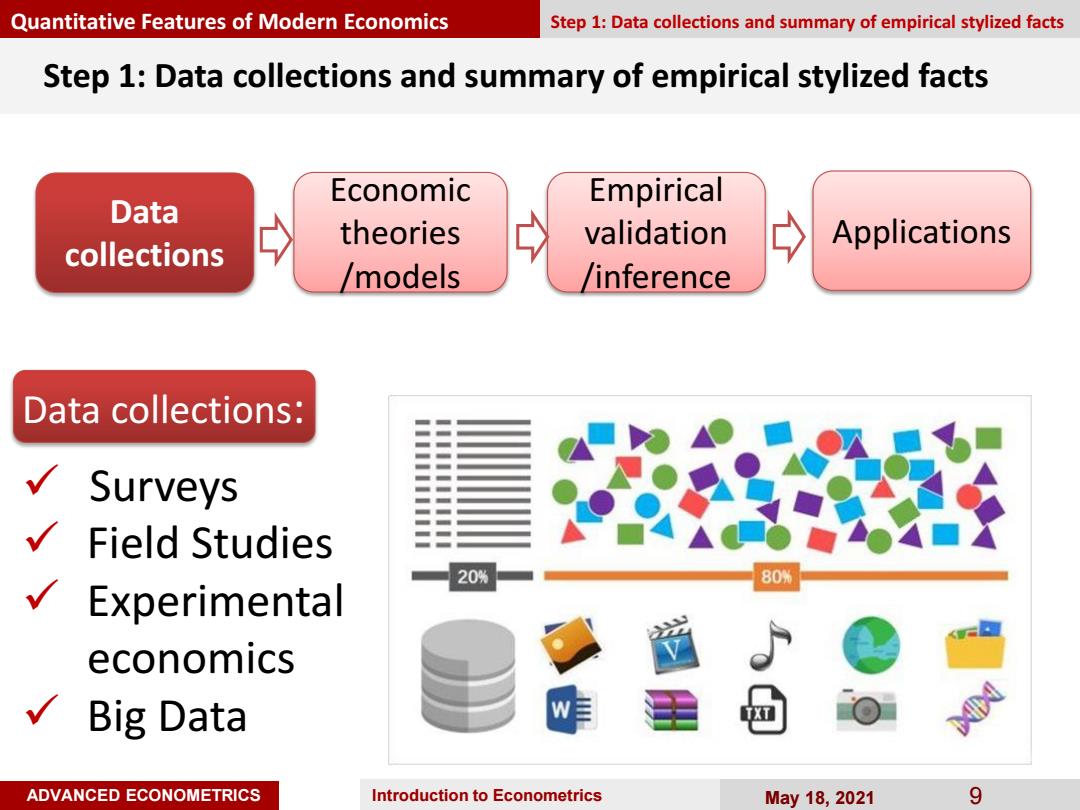
Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections /models /inference Data collections: Surveys Field Studies 20% 80% Experimental economics √Big Data ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 9
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 9 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections: Surveys Field Studies Experimental economics Big Data Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections Economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications

Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics Engel Curves The share of a Income (per month) 30 consumer's Inferior expenditure on a Engel curves slope 20 backward bending for inferior goods. commodity out of her Normal or his total income 10 will vary as his/her income changes; Food(units 8 12 16 per month) ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May18,2021 10
ADVANCED ECONOMETRICS Introduction to Econometrics May 18, 2021 10 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. Quantitative Features of Modern Economics Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics The share of a consumer’s expenditure on a commodity out of her or his total income will vary as his/her income changes;