
0院究研清想南臣王季大門厦 8.XIAM Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University May13,2019
Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics Professor Yongmiao Hong Cornell University May 13, 2019

CONTENTS 1.1 General methodology of modern economic research 1.2 Roles of Econometrics 1.3 Illustrative Examples 1.4 Roles of Probability and Statistics Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 2
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 2 1.1 General methodology of modern economic research 1.2 Roles of Econometrics 1.3 Illustrative Examples 1.4 Roles of Probability and Statistics CONTENTS
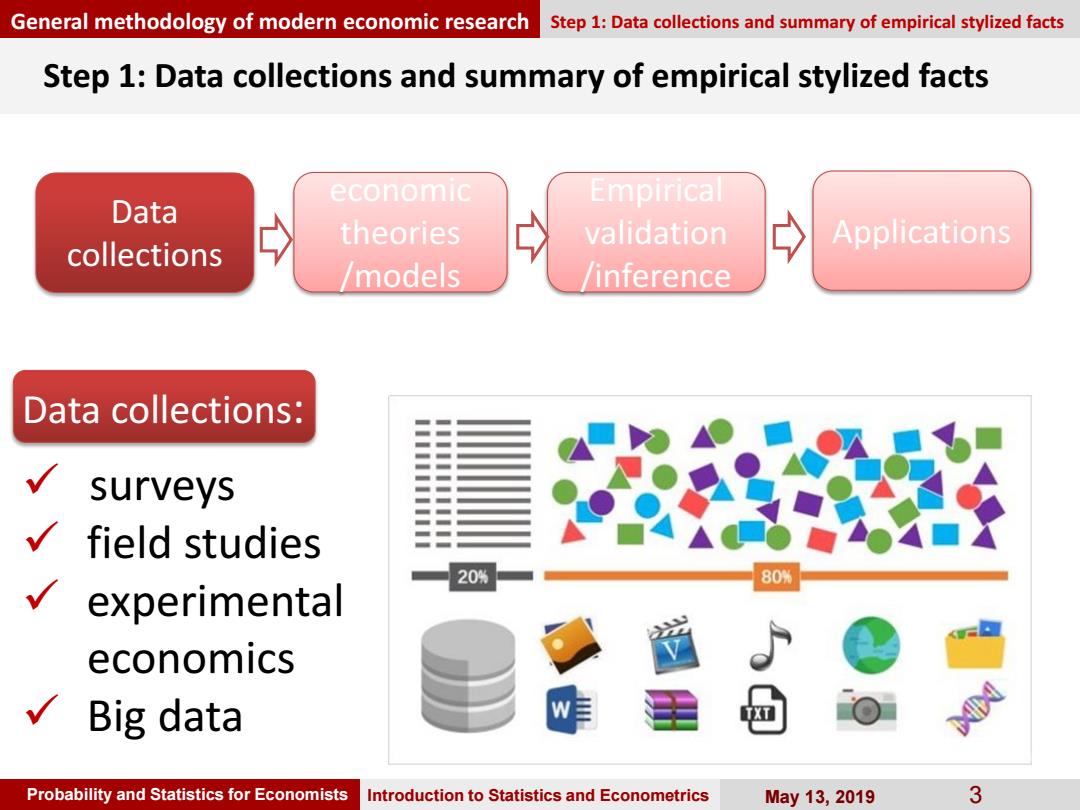
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections models inference Data collections: surveys field studies 20% 80% experimental economics Big data Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 3
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 3 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections: surveys field studies experimental economics Big data General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications
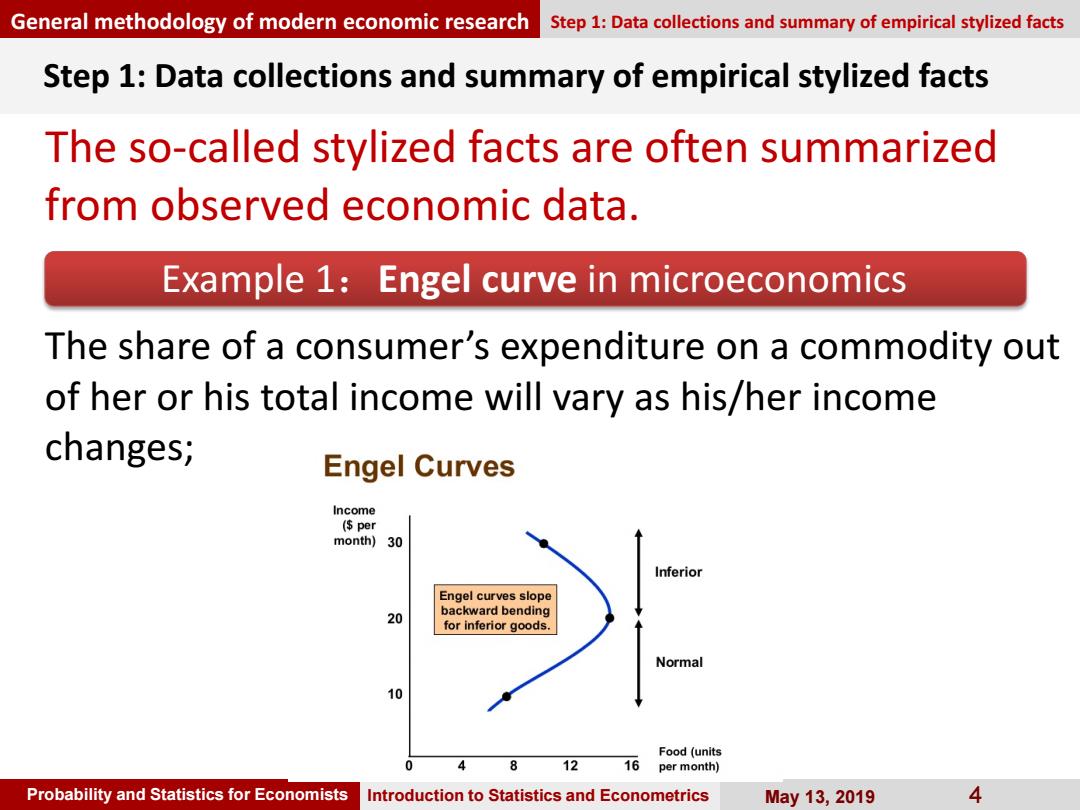
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics The share of a consumer's expenditure on a commodity out of her or his total income will vary as his/her income changes; Engel Curves Income (per month) 30 Inferior Engel curves slope 20 backward bending for inferior goods. Normal 10 Food(units 8 12 16 per month) Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 4
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 4 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts The so-called stylized facts are often summarized from observed economic data. General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 1:Engel curve in microeconomics The share of a consumer’s expenditure on a commodity out of her or his total income will vary as his/her income changes;

General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2:Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: A negative correlation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate in an aggregate economy; Inflation rate (% E E Phillips curve Unemployment rate(%) Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 5
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 5 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 2: Phillips Curve in macroeconomics: A negative correlation between the inflation rate and the unemployment rate in an aggregate economy; General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts
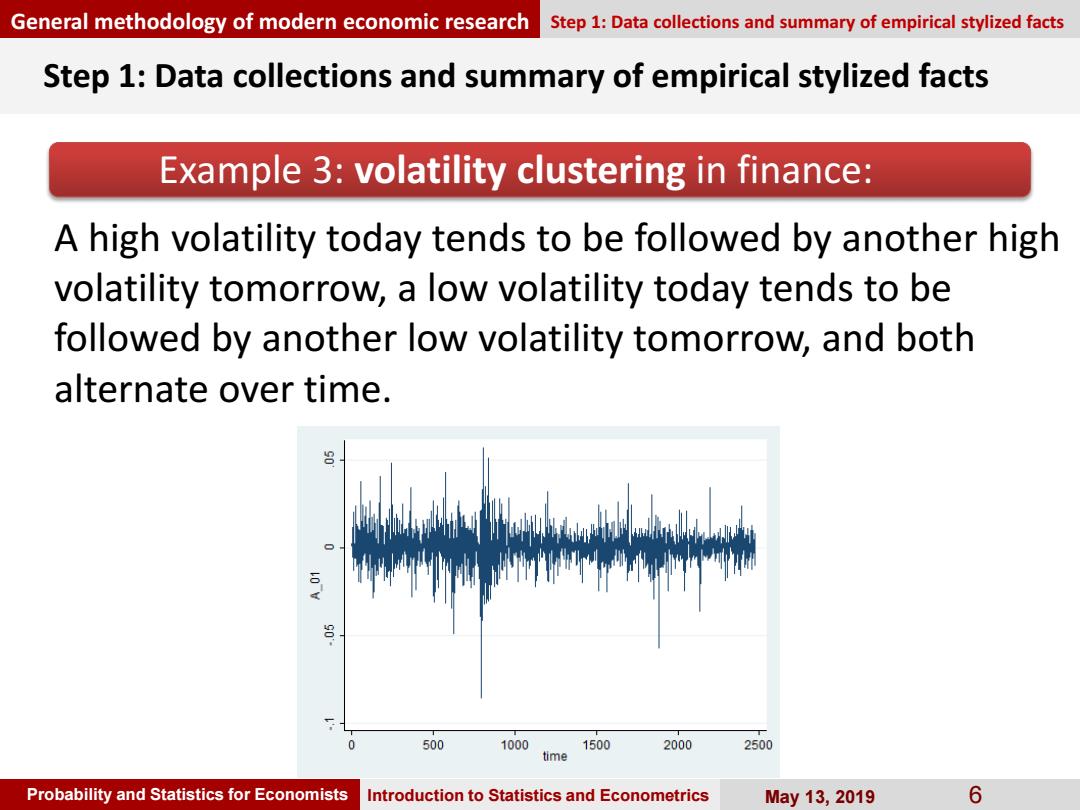
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3:volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow,a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow,and both alternate over time. m 500 10001500 2000 2500 time Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 6
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 6 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Example 3: volatility clustering in finance: A high volatility today tends to be followed by another high volatility tomorrow, a low volatility today tends to be followed by another low volatility tomorrow, and both alternate over time. General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts
General methodology of modern economic research Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts Step 1:Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts a starting point the empirical serve as for economic stylized facts research Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 7
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 7 Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts General methodology of modern economic research Step 1: Data collections and summary of empirical stylized facts the empirical stylized facts a starting point for economic research serve as

General methodology of modern economic research Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections /models inference With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. ● This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 8
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 8 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models ● With the empirical stylized facts in mind, economists then develop an economic theory or model. ● This usually calls for specifying a mathematical model of economic theory. General methodology of modern economic research Step 2: Development of economic theories/models Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications
General methodology of modern economic research Step 2:Development of economic theories/models Step 2:Development of economic theories/models An example is the Euler equation for rational expectations in macroeconomics. The objective of economic modeling is not merely to explain the stylized facts,but also to understand the economic mechanism. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 9
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 9 Step 2: Development of economic theories/models • An example is the Euler equation for rational expectations in macroeconomics. • The objective of economic modeling is not merely to explain the stylized facts, but also to understand the economic mechanism. General methodology of modern economic research Step 2: Development of economic theories/models
General methodology of modern economic research Step 3:Empirical validation/inference of economic models Step 3:Empirical validation/inference of economic models economic Empirical Data theories validation Applications collections models /inference A key is to transform an economic model into a testable empirical econometric model. One often has to assume some functional form, up to some unknown model parameters,or to choose suitable instrumental variables to form a set of moment conditions. Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May13,2019 10
Probability and Statistics for Economists Introduction to Statistics and Econometrics May 13, 2019 10 Step 3: Empirical validation/inference of economic models General methodology of modern economic research Step 3: Empirical validation/inference of economic models • A key is to transform an economic model into a testable empirical econometric model. • One often has to assume some functional form, up to some unknown model parameters, or to choose suitable instrumental variables to form a set of moment conditions. Data collections economic theories /models Empirical validation /inference Applications