
Random Network
Random Network

Section 3.2 The random network model
The random network model Section 3.2
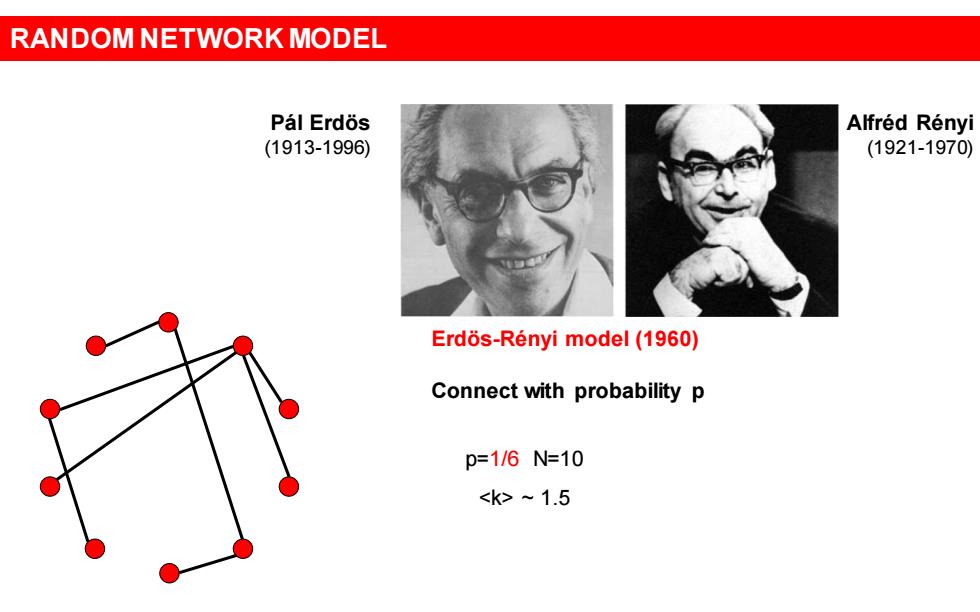
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL Pal Erdos Alfred Renyi (1913-1996) (1921-1970) Erdos-Renyi model(1960) Connect with probability p p=1/6N=10 ~1.5
Erdös-Rényi model (1960) Connect with probability p p=1/6 N=10 ~ 1.5 Pál Erdös (1913-1996) Alfréd Rényi (1921-1970) RANDOM NETWORK MODEL
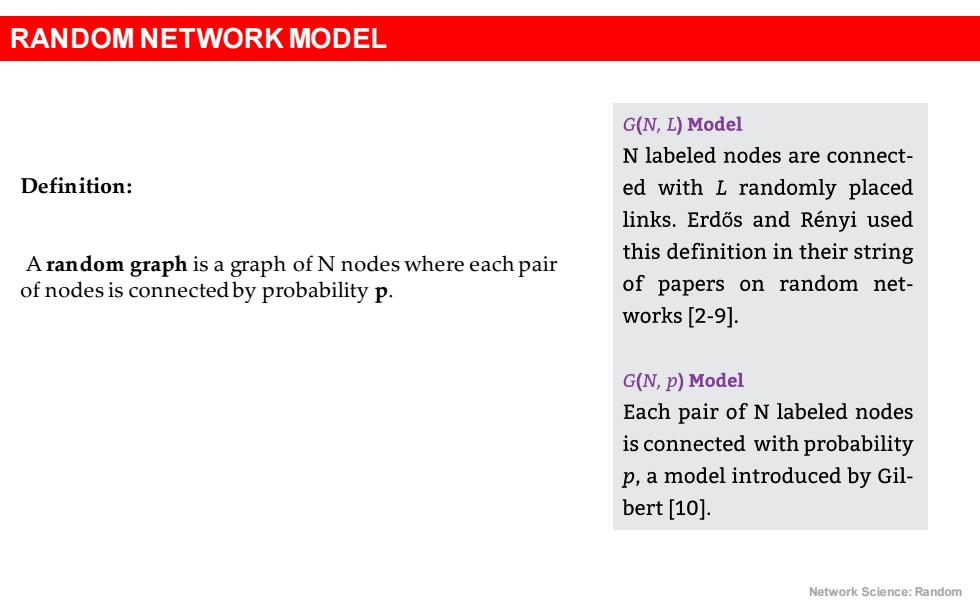
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL G(N,L)Model N labeled nodes are connect- Definition: ed with L randomly placed links.Erdos and Renyi used A random graph is a graph of N nodes where each pair this definition in their string of nodes is connectedby probability p. of papers on random net- works [2-9]. G(N,p)Model Each pair of N labeled nodes is connected with probability p,a model introduced by Gil- bert [10]. Network Science:Random
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL Network Science: Random Definition: A random graph is a graph of N nodes where each pair of nodes is connected by probability p
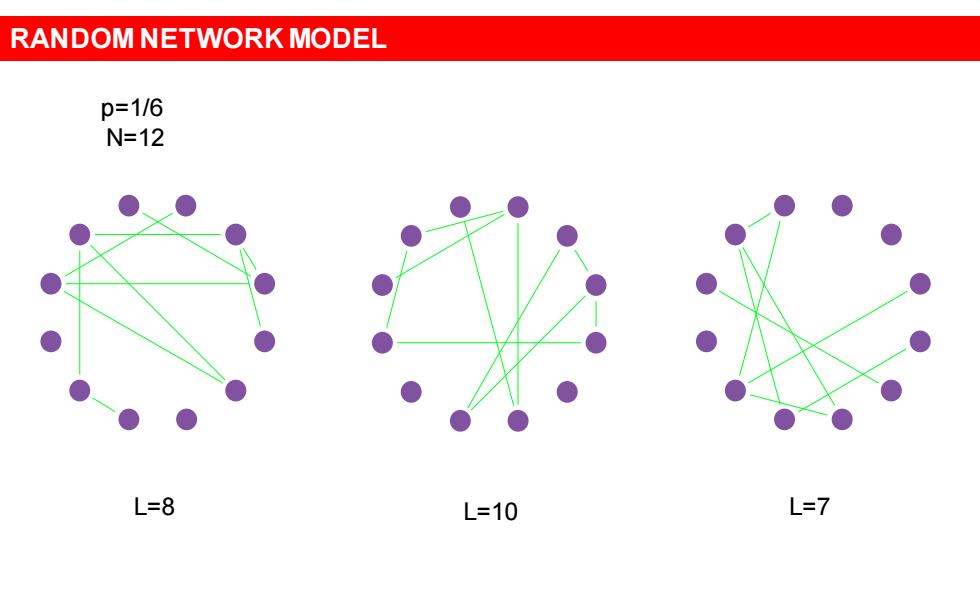
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=1/6 N=12 L=8 L=10 L=7
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=1/6 N=12 L=8 L=10 L=7

RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=0.03 N=100 00000
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=0.03 N=100

Section 3.3 The number of links is variable
The number of links is variable Section 3.3
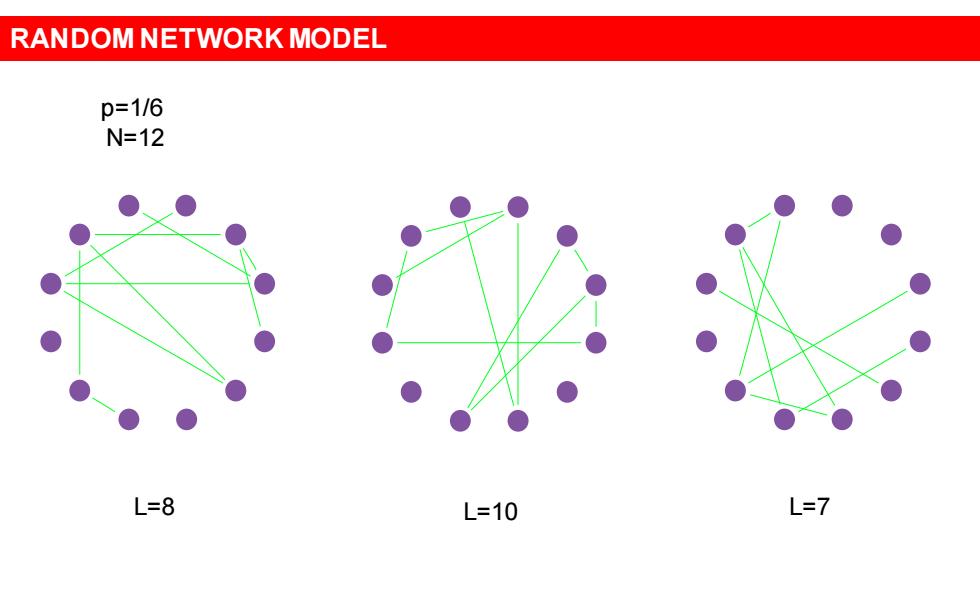
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=1/6 N=12 L=8 L=10 L=7
RANDOM NETWORK MODEL p=1/6 N=12 L=8 L=10 L=7
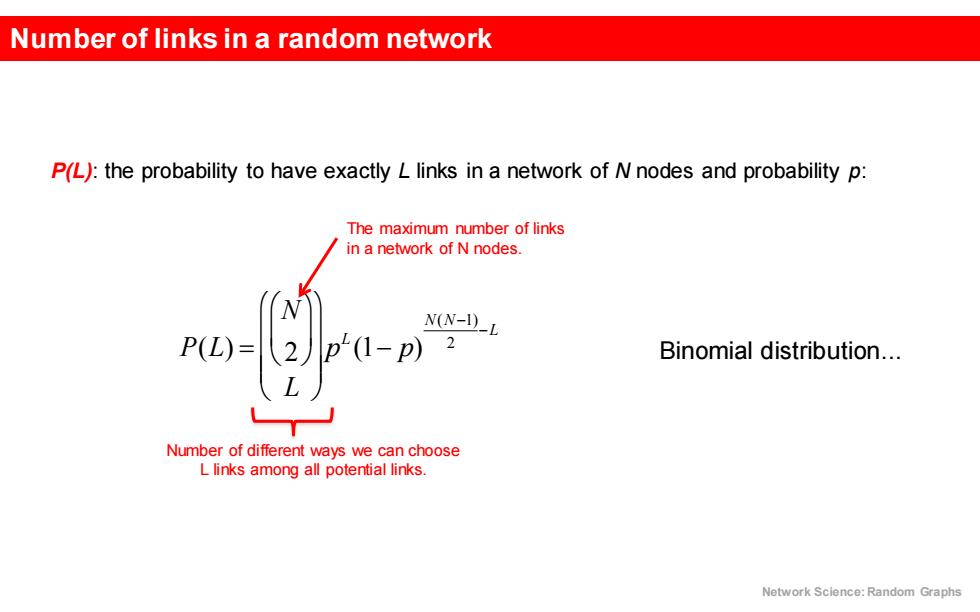
Number of links in a random network P(L):the probability to have exactly L links in a network of N nodes and probability p: The maximum number of links in a network of N nodes. N(N-D)_L P(L)= (1-p) Binomial distribution... Number of different ways we can choose L links among all potential links. Network Science:Random Graphs
Number of links in a random network P(L): the probability to have exactly L links in a network of N nodes and probability p: Network Science: Random Graphs P(L) = N 2 æ è ç ö ø ÷ L æ è ç ç ç ö ø ÷ ÷ ÷ p L (1- p) N(N-1) 2 -L The maximum number of links in a network of N nodes. Number of different ways we can choose L links among all potential links. Binomial distribution
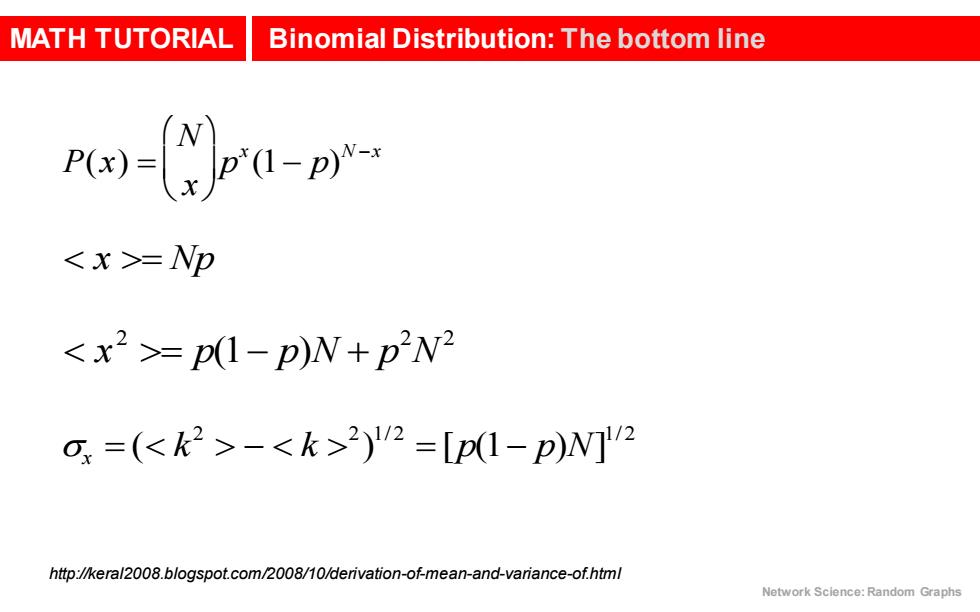
MATH TUTORIAL Binomial Distribution:The bottom line -r- =Np =p1-p)N+p2W2 o=(-2)2=[p1-p)N]V2 http://keral2008.blogspot.com/2008/10/derivation-of-mean-and-variance-of.html Network Science:Random Graphs
MATH TUTORIAL Binomial Distribution: The bottom line Network Science: Random Graphs http://keral2008.blogspot.com/2008/10/derivation-of-mean-and-variance-of.html P(x) = N x æ è ç ö ø ÷p x (1- p) N -x = Np = p(1- p)N + p 2 N 2 sx = ( - 2 ) 1/ 2 =[p(1- p)N] 1/ 2