
/936 Frontiers of Physical and Chemical Power Sources Part ll Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020
Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020 Frontiers of Physical and Chemical Power Sources Part II

196 Lecture 1 Background of Batteries 6
6 Lecture 1 Background of Batteries
Contents /986 ● Definition of battery >Working mechanism ●History of batteries Technology development Important types of batteries Characteristics,Comparisons 7
7 Contents Definition of battery Working mechanism History of batteries Technology development Important types of batteries Characteristics, Comparisons
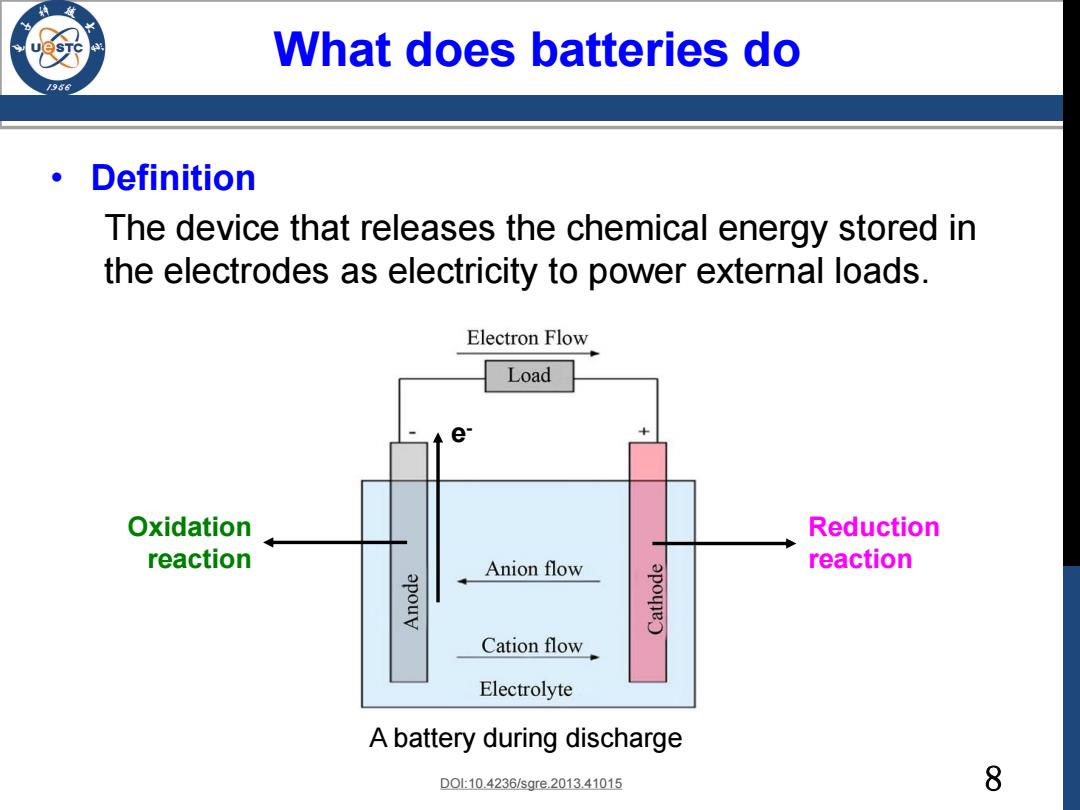
What does batteries do /98 Definition The device that releases the chemical energy stored in the electrodes as electricity to power external loads. Electron Flow Load Oxidation Reduction reaction Anion flow reaction Cation flow Electrolyte A battery during discharge D010.4236/sgre.2013.41015 8
8 What does batteries do • Definition The device that releases the chemical energy stored in the electrodes as electricity to power external loads. A battery during discharge DOI:10.4236/sgre.2013.41015 Oxidation reaction Reduction reaction e -
Battery Chemistry /98 Electrochemical reaction >A pair of redox reactions between elements at the two electrodes that involves the change of valence state > Oxidation at anode.reduction at cathode ●Free electrons > Free electrons are generated by the reactions at the electrodes ●Complete circuit > Electrons flow through the outer circuit to power up the external loads 9
9 Battery Chemistry Electrochemical reaction A pair of redox reactions between elements at the two electrodes that involves the change of valence state Oxidation at anode, reduction at cathode Free electrons Free electrons are generated by the reactions at the electrodes Complete circuit Electrons flow through the outer circuit to power up the external loads
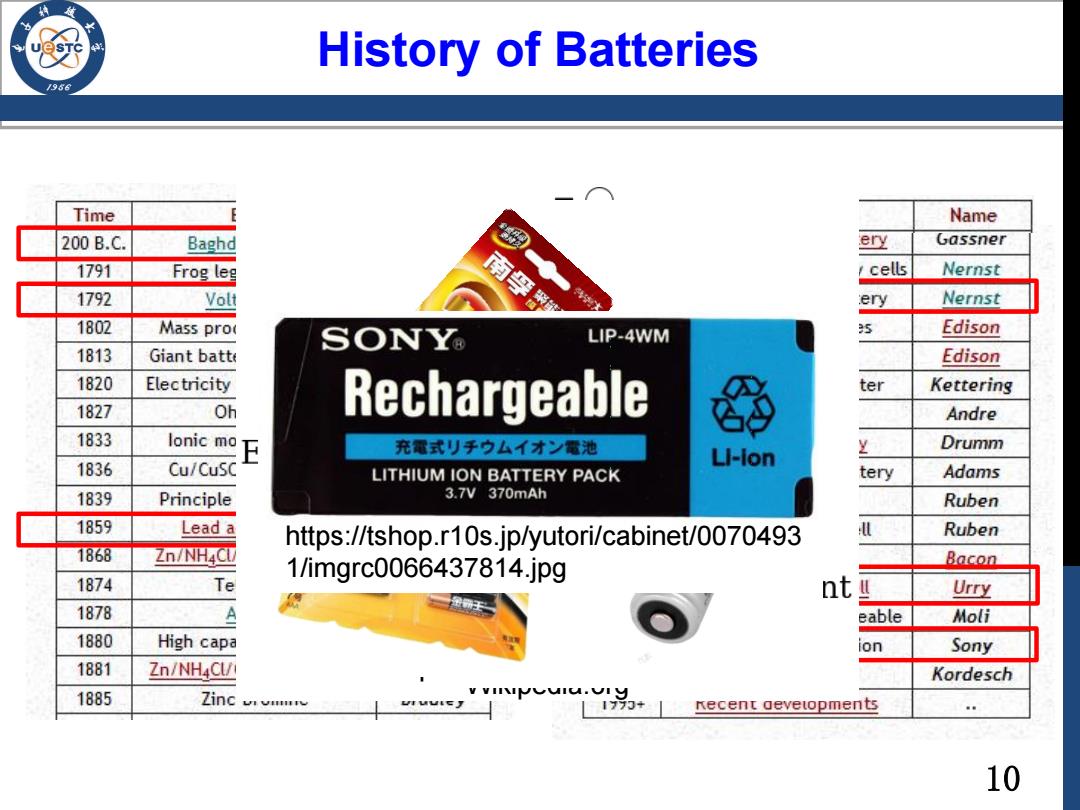
History of Batteries 196 Time Name 200B.C. Baghd ery Gassner 1791 Frog leg cells Nernst 1792 Volt 南孚 ery Nernst 1802 Mass pro SONY LIP-4WM 5 Edison 1813 Giant batte Edison 1820 Electricity ter Kettering 1827 Oh Rechargeable Andre 1833 lonic mo E 充霜式)子夕厶才量池 Drumm 1836 Cu/CuSC LI-ion LITHIUM ION BATTERY PACK tery Adams 1839 Principle 3.7V370mAh Ruben 1859 Lead a https://tshop.r10s.jp/yutori/cabinet/0070493 Ruben 1868 Zn/NH4CU 1/imgrc(0066437814.jpg Bacon 1874 Te nt Urry 1878 A eable Mol日 1880 High capa ion Sony 1881 Zn/NH4Cl/l Kordesch 1885 Zinc v.viy 1770+ Recent aevetopments 10
10 History of Batteries Wikipedia.org https://www.booksfact.com/ https://tshop.r10s.jp/yutori/cabinet/0070493 1/imgrc0066437814.jpg
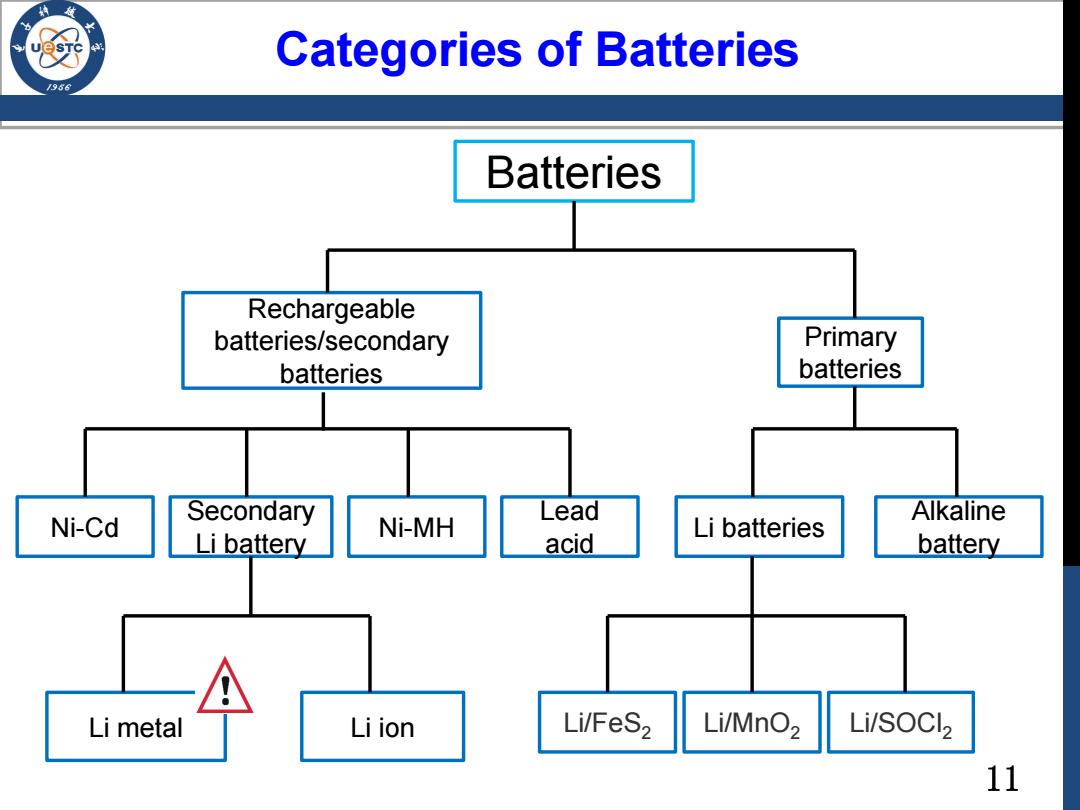
Categories of Batteries 196 Batteries Rechargeable batteries/secondary Primary batteries batteries Ni-Cd Secondary Lead Li battery Ni-MH Alkaline acid Li batteries battery Li metal Li ion Li/FeS2 Li/MnO2 Li/SOCl2 11
11 Categories of Batteries Batteries Rechargeable batteries/secondary batteries Primary batteries Li batteries Alkaline battery Lead acid Ni-MH Secondary Li battery Ni-Cd Li/FeS2 Li/MnO2 Li/SOCl Li metal Li ion 2

/986 Primary Battery Alkaline Batteries 12
12 Primary Battery Alkaline Batteries
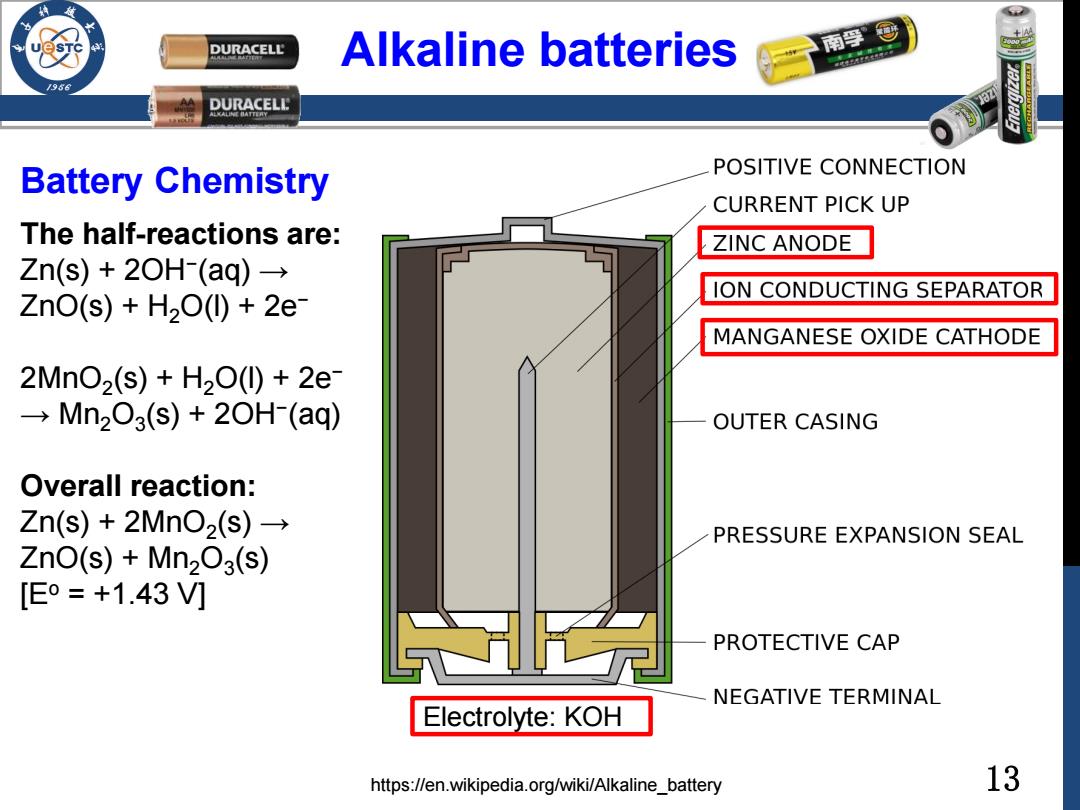
DURACELL Alkaline batteries 南停@ /98 DURACELL Battery Chemistry POSITIVE CONNECTION CURRENT PICK UP The half-reactions are: ZINC ANODE Zn(s)+2OH(aq)→ ION CONDUCTING SEPARATOR ZnO(s)+H200)+2e MANGANESE OXIDE CATHODE 2MnO2(s)+H200+2e →Mn203(s)+20H(aq) OUTER CASING Overall reaction: Zn(s)+2MnO2(s)→ PRESSURE EXPANSION SEAL ZnO(s)+Mn203(s) [Eo=+1.43V] PROTECTIVE CAP NEGATIVE TERMINAL Electrolyte:KOH https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkaline_battery 13
13 Alkaline batteries The half-reactions are: Zn(s) + 2OH− (aq) → ZnO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e− 2MnO2 (s) + H2O(l) + 2e− → Mn2O3 (s) + 2OH− (aq) Overall reaction: Zn(s) + 2MnO2 (s) → ZnO(s) + Mn2O3 (s) [Eo = +1.43 V] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkaline_battery Battery Chemistry Electrolyte: KOH

Alkaline batteries 196 AA AAA 4.5V +A2 9 510-0 AAA AA 9V D Capacity 1.250 2.890 0.625 8.350 20.500 (Ah) Voltage (V) 1.5 1.5 9 1.5 1.5 Energy 1.875 4.275 5.625 12.525 30.75 (Wh) 10.5× H:48.5 Size,g×h 14.0× L:26.5 26.2×50 34.2×61.5 (mm) 25.0 44.5 W:17.5 Increase in size,increase in capacity and energy 14
14 Alkaline batteries AAA AA 9 V C D Capacity (Ah) 1.250 2.890 0.625 8.350 20.500 Voltage (V) 1.5 1.5 9 1.5 1.5 Energy (Wh) 1.875 4.275 5.625 12.525 30.75 Size, ø × h (mm) 14.0 × 25.0 10.5 × 44.5 H: 48.5 L: 26.5 W: 17.5 26.2 × 50 34.2 × 61.5 AA AAA 9 V Increase in size, increase in capacity and energy