
Lecture 2 196 Introduction of Lithium Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.03
Introduction of Lithium Batteries Chen Junsong School of Materials and Energy 2020.03 Lecture 2

Content /986 Important Terms of batteries Why lithium batteries? Necessity,and advantage Different types of lithium batteries Primary and secondary/rechargeable ·Working mechanism How they store charges 2
2 Content • Important Terms of batteries • Why lithium batteries? • Necessity, and advantage • Different types of lithium batteries • Primary and secondary/rechargeable • Working mechanism • How they store charges
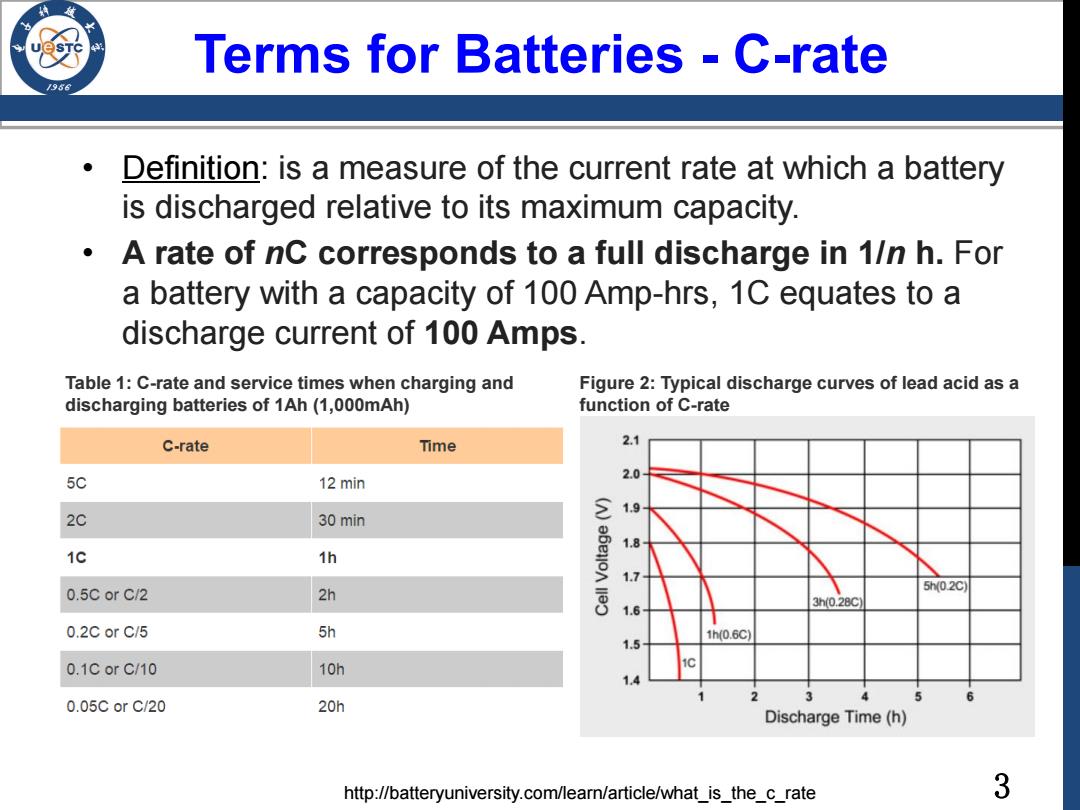
Terms for Batteries -C-rate Definition:is a measure of the current rate at which a battery is discharged relative to its maximum capacity. A rate of nC corresponds to a full discharge in 1/n h.For a battery with a capacity of 100 Amp-hrs,1C equates to a discharge current of 100 Amps. Table 1:C-rate and service times when charging and Figure 2:Typical discharge curves of lead acid as a discharging batteries of 1Ah(1,000mAh) function of C-rate C-rate Time 2.1 5C 2.0 12 min 1.9 2C 30 min 1.8 1c 1h 1.7 0.5C or C/2 2h 5h0.2c 3h0.28c 1.6 0.2C or C/5 5h 1h(0.6C) 1.5 0.1CorC/10 10h 1.4 0.05CorC/20 20h Discharge Time (h) http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/what_is_the_c_rate 3
3 Terms for Batteries - C-rate • Definition: is a measure of the current rate at which a battery is discharged relative to its maximum capacity. • A rate of nC corresponds to a full discharge in 1/n h. For a battery with a capacity of 100 Amp-hrs, 1C equates to a discharge current of 100 Amps. Table 1: C-rate and service times when charging and discharging batteries of 1Ah (1,000mAh) Figure 2: Typical discharge curves of lead acid as a function of C-rate http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/what_is_the_c_rate

Terms for Batteries Over discharge: Definition:during discharge,if the battery continues to discharge even beyond the discharge voltage limit the reversibility of both electrode materials will be damaged,leading to a decreased battery capacity Overcharge: Definition:during charge,if the battery continues to charge even after the capacity is full,the battery would likely to suffer from deformation or electrolyte leakage with a significantly deteriorated performance. 4
4 Terms for Batteries • Over discharge: • Definition: during discharge, if the battery continues to discharge even beyond the discharge voltage limit, the reversibility of both electrode materials will be damaged, leading to a decreased battery capacity . • Overcharge: • Definition: during charge, if the battery continues to charge even after the capacity is full, the battery would likely to suffer from deformation or electrolyte leakage with a significantly deteriorated performance
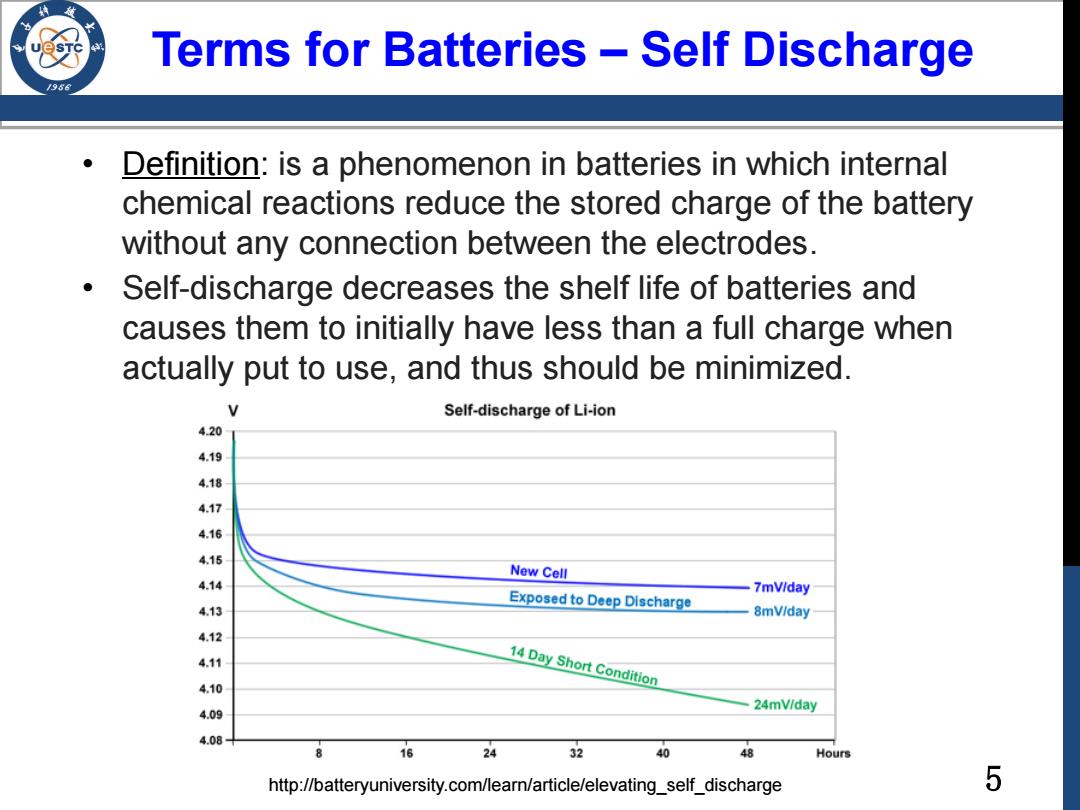
Terms for Batteries -Self Discharge /98 Definition:is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes. Self-discharge decreases the shelf life of batteries and causes them to initially have less than a full charge when actually put to use,and thus should be minimized. Self-discharge of Li-ion 4.20 New Cell Exposed to Deep Discharge 7mViday 8mV/day 410 14 Day Short Condition 409 24mV/day 4.08 8 16 24 32 40 48 Hours http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/elevating_self_discharge 5
5 Terms for Batteries – Self Discharge • Definition: is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes. • Self-discharge decreases the shelf life of batteries and causes them to initially have less than a full charge when actually put to use, and thus should be minimized. http://batteryuniversity.com/learn/article/elevating_self_discharge
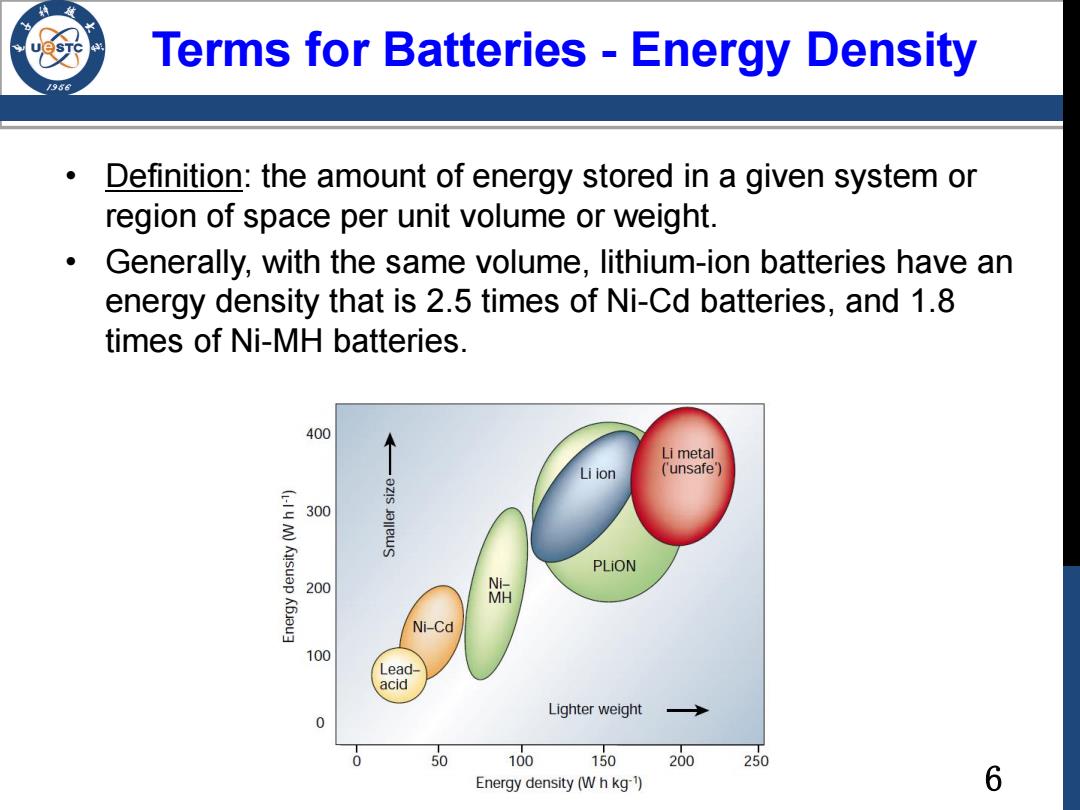
Terms for Batteries-Energy Density Definition:the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume or weight. Generally,with the same volume,lithium-ion batteries have an energy density that is 2.5 times of Ni-Cd batteries,and 1.8 times of Ni-MH batteries. 400 Li metal Li ion ('unsafe') 300 PLiON 200 洗 K6u3 Ni-Cd 100 Lead- acid Lighter weight 0 50 100 150 200 250 Energy density(W h kg) 6
6 • Definition: the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume or weight. • Generally, with the same volume, lithium-ion batteries have an energy density that is 2.5 times of Ni-Cd batteries, and 1.8 times of Ni-MH batteries. Terms for Batteries - Energy Density

Terms for Batteries Cycle Life 9 Definition:the number of full charge-discharge cycles when the capacity of the batteries reaches 75%of the initial value. The cycle life is related to the testing conditions. For lithium-ion batteries,when tested at 1 C and 25 C,their cycle life is usually 300-500,maximally 800-1000. 900 SnO@Carbon B 0”3 SnO2 Theoretical Capecity of Graphite 600 300 0 20 40 60 80 100 Cycle Number Chem.Mater..2009,21,2868-2874 7
7 Terms for Batteries – Cycle Life • Definition: the number of full charge-discharge cycles when the capacity of the batteries reaches 75% of the initial value. • The cycle life is related to the testing conditions. • For lithium-ion batteries, when tested at 1 C and 25 oC, their cycle life is usually 300 – 500, maximally 800 – 1000. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2868–2874

Standard Electrode Potential(SEP) Definition:In electrochemistry,the standard electrode potential is the measure of the individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state,1 mol dm3 or 1 atm, with reference to a standard hydrogen electrode(SHE). The basis for an electrochemical cell,such as the galvanic cell,is always a redox reaction which can be broken down into two half-reactions:oxidation at anode (loss of electron) and reduction at cathode(gain of electron).Electricity is generated due to electric potential difference between two electrodes.This potential difference is created as a result of the difference between individual potentials of the two metal electrodes with respect to the electrolyte. 8
8 Standard Electrode Potential (SEP) Definition: In electrochemistry, the standard electrode potential is the measure of the individual potential of a reversible electrode at standard state, 1 mol dm-3 or 1 atm, with reference to a standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). The basis for an electrochemical cell, such as the galvanic cell, is always a redox reaction which can be broken down into two half-reactions: oxidation at anode (loss of electron) and reduction at cathode (gain of electron). Electricity is generated due to electric potential difference between two electrodes. This potential difference is created as a result of the difference between individual potentials of the two metal electrodes with respect to the electrolyte

Terms for Batteries Electromotive force (emf) Definition:is the electrical intensity or "pressure" developed by a source of electrical energy such as a battery or generator. A device that converts other forms of energy into electrical energy (a "battery")provides an emf as its output. ● In batteries,the emf is calculated by:the Standard Electrode Potential(SEP)of the cathode minus that of the anode. 9
9 Terms for Batteries • Electromotive force (emf) • Definition: is the electrical intensity or "pressure" developed by a source of electrical energy such as a battery or generator. • A device that converts other forms of energy into electrical energy (a “battery") provides an emf as its output. • In batteries, the emf is calculated by: the Standard Electrode Potential (SEP) of the cathode minus that of the anode

Why better batteries? 196 Type Advantage Disadvantage Alkaline High capacity primary Lead acid High surge current Large size Ni-Cd Rechargeable Memory effect NOKIA 能来电话 团 1990 ~2001 ~2010 Now 10
10 Why better batteries? Type Advantage Disadvantage Alkaline High capacity primary Lead acid High surge current Large size Ni-Cd Rechargeable Memory effect ~1990 ~2001 ~2010 Now