
实验二 细菌的芽孢染色 一 教学要求 了解芽孢方法的原理,掌握操作技术。 二 实验原理 A few genera of bacteria, such as Bacillus and Clostridium have the ability to produce resistant survival forms termed endospores. Unlike the reproductive spores of fungi and plants, these endospores are resistant to heat, drying, radiation, and various chemical disinfectants
实验二 细菌的芽孢染色 一 教学要求 了解芽孢方法的原理,掌握操作技术。 二 实验原理 A few genera of bacteria, such as Bacillus and Clostridium have the ability to produce resistant survival forms termed endospores. Unlike the reproductive spores of fungi and plants, these endospores are resistant to heat, drying, radiation, and various chemical disinfectants

Due to the resistant nature of the endospore coats, endospores are difficult to stain. Strong dyes and vigorous staining conditions such as heat are needed. Once stained, however, endospores are equally hard to decolorize. Since few bacterial genera produce endospores, the endospore stain is a good diagnostic test for species of Bacillus and Clostridium
Due to the resistant nature of the endospore coats, endospores are difficult to stain. Strong dyes and vigorous staining conditions such as heat are needed. Once stained, however, endospores are equally hard to decolorize. Since few bacterial genera produce endospores, the endospore stain is a good diagnostic test for species of Bacillus and Clostridium

三 材料与器材 ⚫ 菌种:蜡样芽孢杆菌约2 d 营养琼脂斜面培养 物,球形芽孢杆菌(B.sphaericus) 1-2 d 营养琼 脂斜面培养物。 ⚫ 染色剂:5% 孔雀绿水溶液, 10.5% 番红水 溶液。 ⚫ 小试管,滴管,烧杯,载玻片,显微镜等
三 材料与器材 ⚫ 菌种:蜡样芽孢杆菌约2 d 营养琼脂斜面培养 物,球形芽孢杆菌(B.sphaericus) 1-2 d 营养琼 脂斜面培养物。 ⚫ 染色剂:5% 孔雀绿水溶液, 10.5% 番红水 溶液。 ⚫ 小试管,滴管,烧杯,载玻片,显微镜等

1. Heat-fix a smear of Bacillus megaterium as follows: a. Using the dropper bottle of distilled water found in your staining rack, place a small drop of water on a clean slide by touching the dropper to the slide. b. Aseptically remove a small amount of the culture from the edge of the growth on the agar surface and generously mix it with the drop of water until the water turns cloudy. c. Burn the remaining bacteria off of the loop. d. Using the loop, spread the suspension over the entire slide to form a thin film. e. Allow this thin suspension to completely air dry. f. Pass the slide (film-side up) through the flame of the bunsen burner 3 or 4 times to heat-fix. 四 操作步骤
1. Heat-fix a smear of Bacillus megaterium as follows: a. Using the dropper bottle of distilled water found in your staining rack, place a small drop of water on a clean slide by touching the dropper to the slide. b. Aseptically remove a small amount of the culture from the edge of the growth on the agar surface and generously mix it with the drop of water until the water turns cloudy. c. Burn the remaining bacteria off of the loop. d. Using the loop, spread the suspension over the entire slide to form a thin film. e. Allow this thin suspension to completely air dry. f. Pass the slide (film-side up) through the flame of the bunsen burner 3 or 4 times to heat-fix. 四 操作步骤

2. Place a piece of blotting paper over the smear and saturate with malachite green. 3. Let the malachite green sit on the slide for one minute and proceed to the next step. 4. Holding the slide with forceps, carefully heat the slide in the flame of a bunsen burner until the stain just begins to steam. Remove the slide from the heat until steaming stops; then gently reheat. Continue steaming the smear in this manner for five minutes. As the malachite green evaporates, continually add more. Do not let the paper dry out
2. Place a piece of blotting paper over the smear and saturate with malachite green. 3. Let the malachite green sit on the slide for one minute and proceed to the next step. 4. Holding the slide with forceps, carefully heat the slide in the flame of a bunsen burner until the stain just begins to steam. Remove the slide from the heat until steaming stops; then gently reheat. Continue steaming the smear in this manner for five minutes. As the malachite green evaporates, continually add more. Do not let the paper dry out

5. After five minutes of steaming, wash the excess stain and blotting paper off the slide with water. Don't forget to wash of any dye that got onto the bottom of the slide. 6. Blot the slide dry. 7. Now flood the smear with safranin and stain for one minute. 8. Wash off the excess safranin with water, blot dry, and observe using oil immersion microscopy. With this endospore staining procedure, endospores will stain green while vegetative bacteria will stain red
5. After five minutes of steaming, wash the excess stain and blotting paper off the slide with water. Don't forget to wash of any dye that got onto the bottom of the slide. 6. Blot the slide dry. 7. Now flood the smear with safranin and stain for one minute. 8. Wash off the excess safranin with water, blot dry, and observe using oil immersion microscopy. With this endospore staining procedure, endospores will stain green while vegetative bacteria will stain red
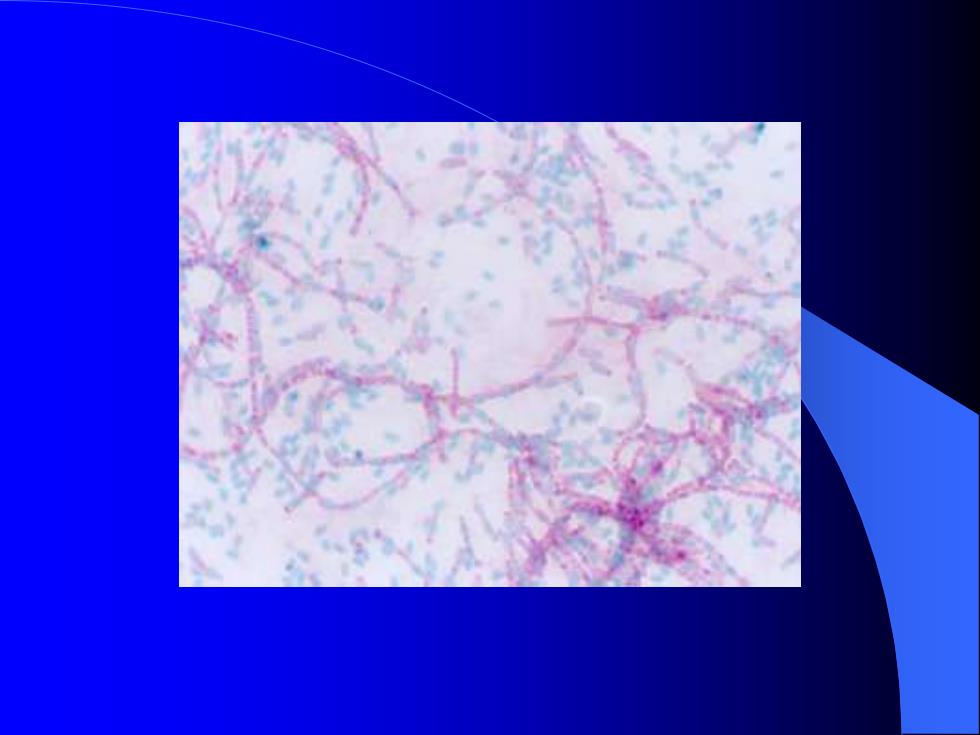

五 注意事项 ⚫ 注意掌握供试验菌种的培养时间。 ⚫ 染色加热过程要及时补充染液,切勿让涂片干 涸。 六 实验报告 绘出显微镜下观察到的结果。 七 思考题 ⚫ 用简单简单染色法是否能观察到细菌的芽孢? 为什么?
五 注意事项 ⚫ 注意掌握供试验菌种的培养时间。 ⚫ 染色加热过程要及时补充染液,切勿让涂片干 涸。 六 实验报告 绘出显微镜下观察到的结果。 七 思考题 ⚫ 用简单简单染色法是否能观察到细菌的芽孢? 为什么?